Abstract
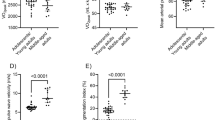
We hypothesised that differences in cardiac baroreflex sensitivity (BRS) would be independently associated with aortic stiffness and augmentation index (AI), clinical biomarkers of cardiovascular disease risk, among young sedentary and middle-aged/older sedentary and endurance-trained adults. A total of 36 healthy middle-aged/older (age 55–76 years, n=22 sedentary and n=14 endurance-trained) and 5 young sedentary (age 18–31 years) adults were included in a cross-sectional study. A subset of the middle-aged/older sedentary adults (n=12) completed an 8-week-aerobic exercise intervention. Invasive brachial artery blood pressure waveforms were used to compute spontaneous cardiac BRS (via sequence technique), estimated aortic pulse wave velocity (PWV) and AI (AI, via brachial–aortic transfer function and wave separation analysis). In the cross-sectional study, cardiac BRS was 71% lower in older compared with young sedentary adults (P<0.05), but only 40% lower in older adults who performed habitual endurance exercise (P=0.03). In a regression model that included age, sex, resting heart rate, mean arterial pressure (MAP), body mass index and maximal exercise oxygen uptake, estimated aortic PWV (β±s.e.=−5.76±2.01, P=0.01) was the strongest predictor of BRS (model R2=0.59, P<0.001). The 8-week-exercise intervention improved BRS by 38% (P=0.04) and this change in BRS was associated with improved aortic PWV (r=−0.65, P=0.044, adjusted for changes in MAP). Age- and endurance-exercise-related differences in cardiac BRS are independently associated with corresponding alterations in aortic PWV among healthy adults, consistent with a mechanistic link between variations in the sensitivity of the baroreflex and aortic stiffness with age and exercise.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Monahan KD, Dinenno FA, Tanaka H, Clevenger CM, DeSouza CA, Seals DR . Regular aerobic exercise modulates age-associated declines in cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity in healthy men. J Physiol 2000; 529 (Pt 1): 263–271.
Monahan KD, Dinenno FA, Seals DR, Clevenger CM, Desouza CA, Tanaka H . Age-associated changes in cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity are related to central arterial compliance. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2001; 281: H284–H289.
Monahan KD, Tanaka H, Dinenno FA, Seals DR . Central arterial compliance is associated with age- and habitual exercise-related differences in cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity. Circulation 2001; 104: 1627–1632.
Gribbin B, Pickering TG, Sleight P, Peto R . Effect of age and high blood pressure on baroreflex sensitivity in man. Circ Res 1971; 29: 424–431.
Billman GE, Schwartz PJ, Stone HL . Baroreceptor reflex control of heart rate: a predictor of sudden cardiac death. Circulation 1982; 66: 874–880.
La Rovere MT, Bigger JT Jr, Marcus FI, Mortara A, Schwartz PJ . Baroreflex sensitivity and heart-rate variability in prediction of total cardiac mortality after myocardial infarction. ATRAMI (Autonomic Tone and Reflexes After Myocardial Infarction) Investigators. Lancet 1998; 351: 478–484.
Deley G, Picard G, Taylor JA . Arterial baroreflex control of cardiac vagal outflow in older individuals can be enhanced by aerobic exercise training. Hypertension 2009; 53: 826–832.
Michas F, Manios E, Stamatelopoulos K, Koroboki E, Toumanidis S, Panerai RB et al. Baroreceptor reflex sensitivity is associated with arterial stiffness in a population of normotensive and hypertensive patients. Blood Press Monit 2012; 17: 155–159.
Mattace-Raso FU, van den Meiracker AH, Bos WJ, van der Cammen TJ, Westerhof BE, Elias-Smale S et al. Arterial stiffness, cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity and postural blood pressure changes in older adults: the Rotterdam Study. J Hypertens 2007; 25: 1421–1426.
Mitchell GF, Wang N, Palmisano JN, Larson MG, Hamburg NM, Vita JA et al. Hemodynamic correlates of blood pressure across the adult age spectrum: noninvasive evaluation in the framingham heart study. Circulation 2010; 122: 1379–1386.
McEniery CM, Yasmin, Hall IR, Qasem A, Wilkinson IB, Cockcroft JR . Normal vascular aging: differential effects on wave reflection and aortic pulse wave velocity: the Anglo-Cardiff Collaborative Trial (ACCT). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005; 46: 1753–1760.
Tanaka H, Dinenno F, Monahan K, Clevenger C, DeSouza C, Seals D . Aging habitual exercise, and dynamic arterial compliance. Circulation 2000; 102: 1270–1275.
Tanaka H, DeSouza CA, Seals DR . Absence of age-related increase in central arterial stiffness in physically active women. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1998; 18: 127–132.
Pierce GL, Casey DP, Fiedorowicz JG, Seals DR, Curry TB, Barnes JN et al. Aortic pulse wave velocity and reflecting distance estimation from peripheral waveforms in humans: detection of age- and exercise training-related differences. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2013; 305: H135–H142.
Vaitkevicius PV, Fleg JL, Engel JH, O'Connor FC, Wright JG, Lakatta LE et al. Effects of age and aerobic capacity on arterial stiffness in healthy adults. Circulation 1993; 88: 1456–1462.
Ben-Shlomo Y, Spears M, Boustred C, May M, Anderson SG, Benjamin EJ et al. Aortic pulse wave velocity improves cardiovascular event prediction: an individual participant meta-analysis of prospective observational data from 17 635 subjects. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014; 63: 636–646.
Gates PE, Tanaka H, Graves J, Seals DR . Left ventricular structure and diastolic function with human ageing. Relation to habitual exercise and arterial stiffness. Eur Heart J 2003; 24: 2213–2220.
Madden KM, Lockhart C, Cuff D, Potter TF, Meneilly GS . Short-term aerobic exercise reduces arterial stiffness in older adults with type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia. Diabetes Care 2009; 32: 1531–1535.
Vogel T, Lepretre PM, Brechat PH, Lonsdorfer-Wolf E, Kaltenbach G, Lonsdorfer J et al. Effect of a short-term intermittent exercise-training programme on the pulse wave velocity and arterial pressure: a prospective study among 71 healthy older subjects. Int J Clin Pract 2013; 67: 420–426.
Oudegeest-Sander MH, Olde Rikkert MG, Smits P, Thijssen DH, van Dijk AP, Levine BD et al. The effect of an advanced glycation end-product crosslink breaker and exercise training on vascular function in older individuals: a randomized factorial design trial. Exp Gerontol 2013; 48: 1509–1517.
Ferrier KE, Waddell TK, Gatzka CD, Cameron JD, Dart AM, Kingwell BA . Aerobic exercise training does not modify large-artery compliance in isolated systolic hypertension. Hypertension 2001; 38: 222–226.
Seals DR, Tanaka H, Clevenger CM, Monahan KD, Reiling MJ, Hiatt WR et al. Blood pressure reductions with exercise and sodium restriction in postmenopausal women with elevated systolic pressure: role of arterial stiffness. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001; 38: 506–513.
Weber T, Auer J, O'Rourke MF, Kvas E, Lassnig E, Lamm G et al. Increased arterial wave reflections predict severe cardiovascular events in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions. Eur Heart J 2005; 26: 2657–2663.
Chirinos JA, Zambrano JP, Chakko S, Veerani A, Schob A, Willens HJ et al. Aortic pressure augmentation predicts adverse cardiovascular events in patients with established coronary artery disease. Hypertension 2005; 45: 980–985.
Pierce GL, Eskurza I, Walker AE, Fay TN, Seals DR . Sex specific effects of habitual aerobic exercise on brachial artery flow-mediated dilation in middle-aged and older adults. Clin Sci (Lond) 2011; 120: 13–23.
Davy KP, DeSouza CA, Jones PP, Seals DR . Elevated heart rate variability in physically active young and older adult women. Clin Sci (Lond) 1998; 94: 579–584.
Davy KP, Miniclier NL, Taylor JA, Stevenson ET, Seals DR . Elevated heart rate variability in physically active postmenopausal women: a cardioprotective effect? Am J Physiol 1996; 271: H455–H460.
Monahan KD, Eskurza I, Seals DR . Ascorbic acid increases cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity in healthy older men. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2004; 286: H2113–H2117.
Tomiyama H, Matsumoto C, Kimura K, Odaira M, Shiina K, Yamashina A . Pathophysiological contribution of vascular function to baroreflex regulation in hypertension. Circ J 2014; 78: 1414–1419.
Gupta A, Jain G, Kaur M, Jaryal AK, Deepak KK, Bhowmik D et al. Association of impaired baroreflex sensitivity and increased arterial stiffness in peritoneal dialysis patients. Clin Exp Nephrol (e-pub ahead of print 5 September 2015).
Tarumi T, de Jong DL, Zhu DC, Tseng BY, Liu J, Hill C et al. Central artery stiffness, baroreflex sensitivity, and brain white matter neuronal fiber integrity in older adults. Neuroimage 2015; 110: 162–170.
Hunt BE, Farquhar WB, Taylor JA . Does reduced vascular stiffening fully explain preserved cardiovagal baroreflex function in older, physically active men? Circulation 2001; 103: 2424–2427.
Davy KP, Willis WL, Seals DR . Influence of exercise training on heart rate variability in post-menopausal women with elevated arterial blood pressure. Clin Physiol 1997; 17: 31–40.
Matsubara T, Miyaki A, Akazawa N, Choi Y, Ra SG, Tanahashi K et al. Aerobic exercise training increases plasma Klotho levels and reduces arterial stiffness in postmenopausal women. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2014; 306: H348–H355.
Parlow J, Viale JP, Annat G, Hughson R, Quintin L . Spontaneous cardiac baroreflex in humans. Comparison with drug-induced responses. Hypertension 1995; 25: 1058–1068.
Okada Y, Galbreath MM, Shibata S, Jarvis SS, VanGundy TB, Meier RL et al. Relationship between sympathetic baroreflex sensitivity and arterial stiffness in elderly men and women. Hypertension 2012; 59: 98–104.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Institutes of Health awards AG-000279, AG-043722, HL-014388, AG-013038 and UL1 RR-024979, and American Heart Association award SDG143400012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Journal of Human Hypertension website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pierce, G., Harris, S., Seals, D. et al. Estimated aortic stiffness is independently associated with cardiac baroreflex sensitivity in humans: role of ageing and habitual endurance exercise. J Hum Hypertens 30, 513–520 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2016.3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2016.3
This article is cited by
-
Self-recorded heart rate variability profiles are associated with health and lifestyle markers in young adults
Clinical Autonomic Research (2022)
-
Aortic haemodynamics: the effects of habitual endurance exercise, age and muscle sympathetic vasomotor outflow in healthy men
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2022)
-
Ageing affects the balance between central and peripheral mechanisms of cerebrovascular regulation with increasing influence of systolic blood pressure levels
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2019)
-
Glycemic variability in continuous glucose monitoring is inversely associated with baroreflex sensitivity in type 2 diabetes: a preliminary report
Cardiovascular Diabetology (2018)
-
Aortic Stiffness in Aging and Hypertension: Prevention and Treatment with Habitual Aerobic Exercise
Current Hypertension Reports (2017)