Abstract
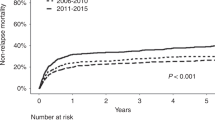
We present the first detailed study analysing OS in BMT for paediatric ALL following the introduction of high-resolution (HR) HLA matching. A total of 356 consecutive paediatric ALL stem cell transplants performed between 1988 and 2007 were reviewed; 80 of them were performed following the introduction of HR HLA class I and class II matching to the transplant programme in 2002. Comparisons of matched unrelated donor (MUD) transplant outcomes before and after this period were made. Matching at the HR level for HLA-A, -B, -C, -DRB1 and -DQB1 (HR-MUD) correlated with a greater than 25% improvement in 2- and 5-year OS in paediatric ALL patients transplanted with MUDs (P=0.009, P=0.005, respectively). Two-year OS for contemporaneous HLA-matched sibling transplants (80.8%) and HR-MUD transplants (78.8%) was equivalent. At 6%, non-relapse mortality (NRM) in MUD transplants since 2002 was significantly reduced compared with previous epochs. Changes in treatment and epoch-dependent improvements in outcome were reviewed for possible confounders to the influence of HR typing using univariate and multivariate analysis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flomenberg N, Baxter-Lowe LA, Confer D, Fernandez-Vina M, Filipovich A, Horowitz M et al. Impact of HLA class I and class II high-resolution matching on outcomes of unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation: HLA-C mismatching is associated with a strong adverse effect on transplantation outcome. Blood 2004; 104: 1923–1930.
Lee SJ, Klein J, Haagenson M, Baxter-Lowe LA, Confer DL, Eapen M et al. High-resolution donor-recipient HLA matching contributes to the success of unrelated donor marrow transplantation. Blood 2007; 110: 4576–4583.
Petersdorf EW, Gooley T, Malkki M, Horowitz M . Clinical significance of donor-recipient HLA matching on survival after myeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation from unrelated donors. Tissue Antigens 2007; 69(Suppl 1): 25–30.
Petersdorf EW . HLA matching in allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Curr Opin Hematol 2004; 11: 386–391.
Crocchiolo R, Ciceri F, Fleischhauer K, Oneto R, Bruno B, Pollichieni S et al. HLA matching affects clinical outcome of adult patients undergoing haematopoietic SCT from unrelated donors: a study from the Gruppo Italiano Trapianto di Midollo Osseo and Italian Bone Marrow Donor Registry. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 44: 571–577.
Macmillan ML, Davies SM, Nelson GO, Chitphakdithai P, Confer DL, King RJ et al. Twenty years of unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for pediatric acute leukemia facilitated by the National Marrow Donor Program. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14 (Suppl 9): 16–22.
Shaw PJ, Kan F, Ahn KW, Spellman SR, Aljurf M, Ayas M et al. Outcomes of pediatric bone marrow transplantation for leukemia and myelodysplasia using matched sibling, mismatched related or matched unrelated donors. Blood 2010; 116: 4007–4015.
Kurtzberg J, Prasad VK, Carter SL, Wagner JE, Baxter-Lowe LA, Wall D et al. Results of the Cord Blood Transplantation Study (COBLT): clinical outcomes of unrelated donor umbilical cord blood transplantation in pediatric patients with hematologic malignancies. Blood 2008; 112: 4318–4327.
Klingebiel T, Bader P . HSCT for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in children. In: Apperley J, Carreras E, Gluckman E, Gratwohl A, Masszi T (eds). The ESH-EBMT Handbook. Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation, 5th Edition forum service editore, Genoa, 2008, pp 506–514.
Oakhill A, Pamphilon DH, Potter MN, Steward CG, Goodman S, Green A et al. Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for children with relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in second complete remission. Br J Haematol 1996; 94: 574–578.
Marks DI, Khattry N, Cummins M, Goulden N, Green A, Harvey J et al. Haploidentical stem cell transplantation for children with acute leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2006; 134: 196–201.
Bradburn MJ, Clark TG, Love SB, Altman DG . Survival analysis part II: multivariate data analysis–an introduction to concepts and methods. Br J Cancer 2003; 89: 431–436.
Bradburn MJ, Clark TG, Love SB, Altman DG . Survival analysis Part III: multivariate data analysis—choosing a model and assessing its adequacy and fit. Br J Cancer 2003; 89: 605–611.
Green A, Clarke E, Hunt L, Canterbury A, Lankester A, Hale G et al. Children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who receive T-cell-depleted HLA mismatched marrow allografts from unrelated donors have an increased incidence of primary graft failure but a similar overall transplant outcome. Blood 1999; 94: 2236–2246.
Bray RA, Hurley CK, Kamani NR, Woolfrey A, Müller C, Spellman S et al. National marrow donor program HLA matching guidelines for unrelated adult donor hematopoietic cell transplants. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14 (Suppl 9): 45–53.
Einsiedel HG, von Stackelberg A, Hartmann R, Fengler R, Schrappe M, Janka-Schaub G et al. Long-term outcome in children with relapsed ALL by risk-stratified salvage therapy: results of trial acute lymphoblastic leukemia-relapse study of the Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster Group 87. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 7942–7950.
Parker C, Waters R, Leighton C, Hancock J, Sutton R, Moorman AV et al. Effect of mitoxantrone on outcome of children with first relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL R3): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet 2010; 376: 2009–2017.
Harvey J, Green A . Survey of human leukocyte antigen matching criteria used in donor selection for haematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the United Kingdom and Ireland (Abstract). Hum Immunol 2009; 70 (Suppl 1): 97.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the staff of the Histocompatibility and Immunogenetics Department, NHS Blood and Transplant, Bristol and the medical, nursing and support staff at the stem cell transplant unit of the Bristol Royal Hospital for Children without whose dedication this study would not have been possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harvey, J., Green, A., Cornish, J. et al. Improved survival in matched unrelated donor transplant for childhood ALL since the introduction of high-resolution matching at HLA class I and II. Bone Marrow Transplant 47, 1294–1300 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.8
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and the Role of MRD: A Single Centre Experience from India
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion (2018)
-
Correlation between microsatellite discrepancy scores and transplant outcome after haemopoietic SCT for pediatric ALL
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2015)
-
Beating the odds: factors implicated in the speed and availability of unrelated haematopoietic cell donor provision
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2013)