Abstract
Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) is a peripheral T-cell neoplasm with a very poor outcome. However, several studies have shown a progress in the treatment. To evaluate the effect of the progress in the treatment of ATLL in a whole patient population, we used vital statistics data and estimated age-adjusted mortality and trends in the mortality from 1995 to 2009. Since allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) has been introduced as a modality with curative potential during study period, we also evaluated the association of the annual number of allo-HSCT and the trend of the mortality of ATLL. Endemic (Kyushu) and non-endemic areas (others) were evaluated separately. Significance in the trend of mortality was evaluated by joinpoint regression analysis. During the study period, a total of 14 932 patients died of ATLL in Japan, and mortality decreased significantly in both areas (annual percent change (95% confidence interval (CI)): Kyushu, −3.1% (−4.3, −1.9); others, −3.4% (−5.3, −1.5)). This decreasing trend in mortality seems to be associated with an increase in the number of allo-HSCTs (Kyushu, R-squared=0.70, P=0.003; and others, R-squared=0.55, P=0.058). This study reveals that the mortality of ATLL is now significantly decreasing in Japan and this decreasing trend might be associated with allo-HSCT.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) is a peripheral T-cell neoplasm that is associated with infection by the human T-cell leukemia virus type I.1, 2 Infection with human T-cell leukemia virus type I and cases of ATLL are endemic in several regions of the world, with the south-west area of Japan (Kyushu) being a well-known example. Although the total number of carriers in Japan has decreased by 10% over the past two decades,3 the incidence of this fatal disease has nevertheless significantly increased due to the aging of carriers.4
Recent advances in the treatment of ATLL include several combination chemotherapies and allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (allo-HSCT).5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 Allo-HSCT was deemed to show a successful outcome, in that around 30% of patients achieved long-term survival.6 Dose-intensified chemotherapy also showed a survival benefit, however, the usual outcome in patients with acute and lymphoma-type ATLL, for which allo-HSCT is not indicated, is markedly poor, with essentially no chance of prolonged remission.8 Another advance in the treatment of ATLL is an improvement in the infection control, which frequently strikes patients during the treatment. Despite these advances in treatment, however, the survival benefit in whole patient population had not been presented.
Here, to evaluate the progress in the treatment of ATLL, we estimated the age-standardized mortality and trends in the age-standardized mortality of ATLL. Since allo-HSCT has been introduced as a modality with curative potential during study period, we also evaluated the correlation of the annual number of allo-HSCT and the trend of the mortality of ATLL.
Patients and methods
We used the data of vital statics of Japan for 47 prefectures during 1995–2009,14 and estimated the ATLL-specific age-standardized mortality rate adjusted by world standard population. Since the incidence of ATLL differs significantly between endemic (Kyushu) and non-endemic areas in Japan (others), age-standardized mortality rates for these two areas were estimated separately. Data for the number of allo-HSCTs administered in Japan for ATLL were obtained from the Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation.
To assess the secular trend in the age-standardized mortality rate, we used joinpoint regression analysis, as described in detail elsewhere.15 The association between mortality rates of ATLL and annual numbers of allo-HSCT was evaluated by a regression framework.16 In this analysis, we explored zero-, one- or two-year time lags from the numbers of allo-HSCT to mortality rate to evaluate whether the number of transplants was associated with a later decrease in mortality. We examined R-squared to evaluate the strength of the association and interpreted the result such that for every increase in the annual number of allo-HSCTs, we expect a certain degree (coefficient) decrease in the mortality of ATLL.
All computations were performed with STATA version 11 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA), except for the joinpoint regression analysis, for which we used the Joinpoint Regression Program version 3.3 (US National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Results
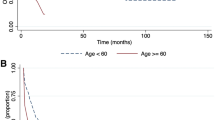
During the study period, a total of 14 932 patients died of ATLL in Japan. Estimated age-standardized mortalities of ATLL from 1995 to 2009 in Kyushu and others are shown as circles in Figure 1 and the exact rates with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) in both areas, which are the basis of Figure 1, are summarized in Supplementary Table 1. The solid line shows the age-standardized modeled mortality estimated by joinpoint regression analysis and the dotted line shows the annual numbers of allo-HSCT administered in each area. As depicted in Figure 1, the trend in age-standardized mortality changed significantly in 2000 in Kyushu and in 2003 in others (Table 1). Mortality decreased significantly after that period in both areas (annual percent change (95% CI); Kyushu: −3.1% (−4.3, −1.9), others: −3.4% (−5.3, −1.5)).
The mortality of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma and the number of allogeneic transplants administered in Kyushu and others. Circles indicate the observed age-standardized mortality rates and the solid line indicates the age-standardized mortality rates estimated by joinpoint regression analysis. The dashed line indicates the number of allogeneic transplants.
A total of 929 allo-HSCTs were performed in Japan during the study period. Median age at the allo-HSCT was 53 years old (range: 18–79). Table 2 summarizes the association between mortality and annual numbers of allo-HSCT. The increasing trend in allo-HSCT was negatively associated with the mortality of ATLL in Japan (Table 2). The association was strongest when no time lag was set in years from the number of transplants to mortality, indicating that the number of allo-HSCTs was directly associated with mortality in that year.
We also evaluated the association of the numbers of allo-HSCT with the decreasing trend of the mortality according to the age group. The increase in the numbers of allo-HSCT was associated with the decrease in the mortality in both patients aged younger than 55 years old and aged 55 years or older (<55 years old, R-squared=0.62, P=0.007; ⩾55 years old, R-squared=0.65, P=0.028).
Discussion
We previously reported that the incidence of ATLL is significantly increasing in Honshu (representative non-endemic area in Japan) but has shown no change in Kyushu.4 Although this increasing trend in Honshu might be due to an improvement in diagnostic accuracy, these findings show that the incidence of ATLL is at least not decreasing in the endemic areas of Japan where the disease is well known and would not be missed in the registry data. The significant decrease in the trend in mortality observed in the present study is therefore likely to have resulted from an improvement in treatment. The present findings show that the number of allo-HSCTs administered in Japan might be associated with this decreasing trend in mortality.
Utsunomiya et al.13 reported the first case series of patients with ATLL who received allo-HSCT in 2001. In their study, 5 of 10 patients showed long-term survival, which appeared to plateau after a median leukemia-free survival of 17.5 months. This aggressive but curative approach has now become the standard treatment for eligible patients, and the number of allo-HSCTs administered in Japan has increased rapidly, with >100 patients now receiving allo-HSCT annually. A nationwide retrospective analysis of patients who received allo-HSCT for ATLL in Japan reported a 3-year overall survival of 33%,6 which is the best treatment outcome in the eligible patients to this day. The rapid increase in the numbers of allo-HSCT reflects the introduction of the allo-HSCT to elderly patients with reduced-intensity conditioning regimen which has also been shown to be effective in ATLL.10, 17 In our analysis, allo-HSCT in patients aged 55 years or older showed an association with the decrease in the mortality suggesting that increasing the candidate of allo-HSCT in this population may improve the outcome of ATLL.
Recently, the new drug mogamulizumab, an anti-CCR4 antibody, has shown a clear benefit in the treatment for ATLL.18 Overall response rate to mogamulizumab on single agent use in a phase II study in relapsed patients was 50% (95% CI: 30–70%), which suggests the promising possibility of combined use with existing regimens as a new chemotherapy protocol. Patients who received allo-HSCT while in complete remission had a higher probability of survival than those who received when not in complete remission.6 Improvement in induction chemotherapy will increase the number of patients in remission, and thus the number of candidates for allo-HSCT beneficially impacting outcomes.
The association between decreased mortality and number of allo-HSCTs seems to be stronger in Kyushu than in other areas. This difference might be due to differences in indications for allo-HSCT, based on differences in the understanding of ATLL. Hematologists in Kyushu are well experienced with ATLL, and it is possible that their indications for allo-HSCT are well organized and they proceed to allo-HSCT with good patient’s condition during the treatment. In any case, this issue is difficult to analyze using registry data alone.
Although the potential for prolonged remission without allo-HSCT appears to be limited, other factors might have contributed to this decrease in mortality. The Japanese Clinical Oncology Group has conducted several clinical trials to improve survival with chemotherapy. Results have been shown to be effective on long-term follow-up and might have improved the survival of patients who were unable to proceed to transplantation. A dose-intensified multi-agent chemotherapy protocol named modified LSG15 improved 3-year overall survival of aggressive ATLL over bi-weekly CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone) to 24% from 13%.8 The more general improvement seen in the management of ATLL, such as with regard to infection control, might also have prolonged survival. Considering the dismal outcome by general treatments that have not progressed significantly during the study period, however, we speculate that the decreasing trends in the mortality would have been mostly achieved by allo-HSCT. Nevertheless, this study is conducted in two independent data sets that lack the information about the treatment of individual patient. We cannot evaluate the association between the decreasing in the mortality and other unmeasured variables which potentially could limit the clinical relevance of our results. We need to emphasize that it is difficult completely to rule out the possibility that our finding is not causal association. Further studies to assess the association of other factors with the decreased mortality are required.
In conclusion, this study showed that the mortality of ATLL in Japan is significantly decreasing, and this decreasing trend might be associated with the increasing number of allo-HSCTs. Nevertheless, allo-HSCT is associated with a significant toxicity, and further studies are needed to identify patients at high risk for treatment-related morbidity or mortality to improve the feasibility of allo-HSCT. Although ATLL remains a highly aggressive and still fatal disease, new drugs such as mogamulizumab and approaches such as reduced-intensity conditioning for elderly patients are promising treatment. A combined modality of improved induction chemotherapy followed by allo-HSCT may change the outcome of ATLL, and future studies may better focus on improving induction chemotherapy to allow an eventual increase in the number of candidates for allo-HSCT.
References
Swerdlow S, Campo E, Harris N, Jaffe E, Pileri S, Stein H et al Who Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): Lyon, France, 2008.
Shimoyama M . Diagnostic criteria and classification of clinical subtypes of adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma. a report from the Lymphoma Study Group (1984-87). Br J Haematol 1991; 79: 428–437.
Satake M, Yamaguchi K, Tadokoro K . Current prevalence of HTLV-1 in Japan as determined by screening of blood donors. J Med Virol 2012; 84: 327–335.
Chihara D, Ito H, Katanoda K, Shibata A, Matsuda T, Tajima K et al. Increase in Incidence of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma in non-endemic areas of Japan and the United States. Cancer Sci 2012; 103: 1857–1860.
Yamamoto K, Utsunomiya A, Tobinai K, Tsukasaki K, Uike N, Uozumi K et al. Phase I study of Kw-0761, a defucosylated humanized anti-Ccr4 antibody, in relapsed patients with adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 1591–1598.
Hishizawa M, Kanda J, Utsunomiya A, Taniguchi S, Eto T, Moriuchi Y et al. Transplantation of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cells for adult T-cell leukemia: a nationwide retrospective study. Blood 2010; 116: 1369–1376.
Tsukasaki K, Hermine O, Bazarbachi A, Ratner L, Ramos JC, Harrington W Jr et al. Definition, prognostic factors, treatment, and response criteria of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: a proposal from an International Consensus Meeting. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 453–459.
Tsukasaki K, Utsunomiya A, Fukuda H, Shibata T, Fukushima T, Takatsuka Y et al. VCAP-AMP-VECP compared with biweekly CHOP for adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study JCOG9801. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25 (34): 5458–5464.
Kato K, Kanda Y, Eto T, Muta T, Gondo H, Taniguchi S et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation from unrelated human T-cell leukemia virus-I-negative donors for adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: retrospective analysis of data from the Japan Marrow Donor Program. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 90–99.
Okamura J, Utsunomiya A, Tanosaki R, Uike N, Sonoda S, Kannagi M et al. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation with reduced conditioning intensity as a novel immunotherapy and antiviral therapy for adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood 2005; 105: 4143–4145.
Tsukasaki K, Tobinai K, Shimoyama M, Kozuru M, Uike N, Yamada Y et al. Deoxycoformycin-containing combination chemotherapy for adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study (JCOG9109). Int J Hematol 2003; 77: 164–170.
Yamada Y, Tomonaga M, Fukuda H, Hanada S, Utsunomiya A, Tara M et al. A new G-CSF-supported combination chemotherapy, LSG15, for adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study 9303. Br J Haematol 2001; 113: 375–382.
Utsunomiya A, Miyazaki Y, Takatsuka Y, Hanada S, Uozumi K, Yashiki S et al. Improved outcome of adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 27: 15–20.
Katanoda K, Matsuda T, Matsuda A, Shibata A, Nishino Y, Fujita M et al. An updated report of the trends in cancer incidence and mortality in Japan. Jpn J Clin Oncol 2013; 43: 492–507.
Kim HJ, Fay MP, Feuer EJ, Midthune DN . Permutation tests for joinpoint regression with applications to cancer rates. Stat Med 2000; 19: 335–351.
Shumway R, Stoffer D . Time Series Analysis and Its Applications: With R Examples 2nd edn. Springer: New York, 2006.
Ishida T, Hishizawa M, Kato K, Tanosaki R, Fukuda T, Taniguchi S et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma with special emphasis on preconditioning regimen: a nationwide retrospective study. Blood 2012; 120: 1734–1741.
Ishida T, Joh T, Uike N, Yamamoto K, Utsunomiya A, Yoshida S et al. Defucosylated Anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody (KW-0761) for relapsed adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: a multicenter phase II study. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 837–842.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the 3rd-term Comprehensive Ten-year Strategy for Cancer Control and by the Research Funding for Longevity Sciences (22-9) from the National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology (NCGG), Japan, and partly supported by a grant from Takeda Science Foundation. The authors thank all of the physicians and data managers at the centers that contributed valuable data on transplantation to the Japan Society for Haematopoietic Cell Transplantation and the Japan Marrow Donor Program. The authors also thank all of the members of the data management committees of the Japan Society for Haematopoietic Cell Transplantation and the Japan Marrow Donor Program for their management of data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Blood Cancer Journal website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Chihara, D., Ito, H., Matsuda, T. et al. Association between decreasing trend in the mortality of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants in Japan: analysis of Japanese vital statistics and Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (JSHCT). Blood Cancer Journal 3, e159 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/bcj.2013.57
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bcj.2013.57
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Increased incidence of adult T cell leukemia-lymphoma and peripheral T cell lymphoma—not otherwise specified with limited improvement in overall survival: a retrospective analysis using data from the population-based Osaka Cancer Registry
Annals of Hematology (2021)
-
Reversal of CYLD phosphorylation as a novel therapeutic approach for adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL)
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
Incidence of Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma in Nonendemic Areas
Current Treatment Options in Oncology (2015)