Featured
-
-
Technology Feature |
 Single-cell analysis enters the multiomics age
Single-cell analysis enters the multiomics age
A rapidly growing collection of software tools is helping researchers to analyse multiple huge ‘-omics’ data sets.
- Jeffrey M. Perkel
-
Article |
 Dysregulation of brain and choroid plexus cell types in severe COVID-19
Dysregulation of brain and choroid plexus cell types in severe COVID-19
Single-nucleus transcriptomes of frontal cortex and choroid plexus samples from patients with COVID-19 reveal pathological cell states that are similar to those associated with human neurodegenerative diseases and chronic brain disorders.
- Andrew C. Yang
- , Fabian Kern
- & Tony Wyss-Coray
-
Research Summary |
 Protein architecture of the yeast genome
Protein architecture of the yeast genome
Use of chromatin immunoprecipitation with exonuclease treatment (ChIP–exo) determines the positional organization of hundreds of chromosomal proteins throughout the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. The resulting ultra-high-resolution map provides insight into the regulation of genes, enhancers, replication origins, centromeres, subtelomeres and transposons.
- B. Franklin Pugh
-
Article |
 A molecular cell atlas of the human lung from single-cell RNA sequencing
A molecular cell atlas of the human lung from single-cell RNA sequencing
Expression profiling on 75,000 single cells creates a comprehensive cell atlas of the human lung that includes 41 out of 45 previously known cell types and 14 new ones.
- Kyle J. Travaglini
- , Ahmad N. Nabhan
- & Mark A. Krasnow
-
Article |
 Persistent transcriptional programmes are associated with remote memory
Persistent transcriptional programmes are associated with remote memory
The authors identify long-lasting transcriptional programmes in neurons and glia that are associated with the storage of a remote memory.
- Michelle B. Chen
- , Xian Jiang
- & Thomas C. Südhof
-
Article |
 Innovations present in the primate interneuron repertoire
Innovations present in the primate interneuron repertoire
Single-nucleus RNA-sequencing analyses of brain from humans, macaques, marmosets, mice and ferrets reveal diverse ways that interneuron populations have changed during evolution.
- Fenna M. Krienen
- , Melissa Goldman
- & Steven A. McCarroll
-
Outlook |
 The RNA and protein landscape that could bring precision medicine to more people
The RNA and protein landscape that could bring precision medicine to more people
The limitations of genomic data have led to a deeper exploration of transcriptomic and proteomic data in cancer.
- Simon Makin
-
Article |
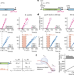 Functionally uncoupled transcription–translation in Bacillus subtilis
Functionally uncoupled transcription–translation in Bacillus subtilis
In Bacillus subtilis, unlike in Escherichia coli, transcription and translation of genes are not tightly coupled, and pioneering ribosomes lag substantially behind RNA polymerases.
- Grace E. Johnson
- , Jean-Benoît Lalanne
- & Gene-Wei Li
-
Article |
 A single-cell transcriptome atlas of marsupial embryogenesis and X inactivation
A single-cell transcriptome atlas of marsupial embryogenesis and X inactivation
Single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis of embryogenesis and X chromosome inactivation in the opossum (Monodelphis domestica) resolves the developmental trajectory of a marsupial, and sheds light on the evolution of embryogenesis in mammals.
- Shantha K. Mahadevaiah
- , Mahesh N. Sangrithi
- & James M. A. Turner
-
News & Views |
 Expanded ENCODE delivers invaluable genomic encyclopedia
Expanded ENCODE delivers invaluable genomic encyclopedia
The third phase of the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) project has generated the most comprehensive catalogue yet of the functional elements that regulate our genes.
- Chung-Chau Hon
- & Piero Carninci
-
Perspective |
 Perspectives on ENCODE
Perspectives on ENCODE
The authors summarize the history of the ENCODE Project, the achievements of ENCODE 1 and ENCODE 2, and how the new data generated and analysed in ENCODE 3 complement the previous phases.
- Federico Abascal
- , Reyes Acosta
- & Richard M. Myers
-
Article
| Open Access A large-scale binding and functional map of human RNA-binding proteins
A large-scale binding and functional map of human RNA-binding proteins
A combination of five assays is used to produce a catalogue of RNA elements to which RNA-binding proteins bind in human cells.
- Eric L. Van Nostrand
- , Peter Freese
- & Gene W. Yeo
-
Article
| Open Access Occupancy maps of 208 chromatin-associated proteins in one human cell type
Occupancy maps of 208 chromatin-associated proteins in one human cell type
ChIP–seq and CETCh–seq data are used to analyse binding maps for 208 transcription factors and other chromatin-associated proteins in a single human cell type, providing a comprehensive catalogue of the transcription factor landscape and gene regulatory networks in these cells.
- E. Christopher Partridge
- , Surya B. Chhetri
- & Eric M. Mendenhall
-
Article
| Open Access The changing mouse embryo transcriptome at whole tissue and single-cell resolution
The changing mouse embryo transcriptome at whole tissue and single-cell resolution
RNA expression is quantified at a tissue level in seventeen mouse tissues across embryonic development, and at the single-cell level in the developing limb.
- Peng He
- , Brian A. Williams
- & Barbara J. Wold
-
Article |
 Ageing hallmarks exhibit organ-specific temporal signatures
Ageing hallmarks exhibit organ-specific temporal signatures
Bulk RNA sequencing of organs and plasma proteomics at different ages across the mouse lifespan is integrated with data from the Tabula Muris Senis, a transcriptomic atlas of ageing mouse tissues, to describe organ-specific changes in gene expression during ageing.
- Nicholas Schaum
- , Benoit Lehallier
- & Tony Wyss-Coray
-
Article
| Open Access Lineage dynamics of the endosymbiotic cell type in the soft coral Xenia
Lineage dynamics of the endosymbiotic cell type in the soft coral Xenia
Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies the pattern of gene expression during lineage progression in endosymbiotic cells of the fast-growing soft coral Xenia, revealing principles that underlie uptake and maintenance of endosymbionts by this coral.
- Minjie Hu
- , Xiaobin Zheng
- & Yixian Zheng
-
Technology Feature |
 Alexa, do science! Voice-activated assistants hit the lab bench
Alexa, do science! Voice-activated assistants hit the lab bench
Research-optimized tools can take notes, dictate instructions and answer questions, allowing researchers to work hands-free.
- Jeffrey M. Perkel
-
Article
| Open Access Transcript expression-aware annotation improves rare variant interpretation
Transcript expression-aware annotation improves rare variant interpretation
A novel variant annotation metric that quantifies the level of expression of genetic variants across tissues is validated in the Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD) and is shown to improve rare variant interpretation.
- Beryl B. Cummings
- , Konrad J. Karczewski
- & Daniel G. MacArthur
-
Article |
 Construction of a human cell landscape at single-cell level
Construction of a human cell landscape at single-cell level
Single-cell RNA sequencing is used to generate a dataset covering all major human organs in both adult and fetal stages, enabling comparison with similar datasets for mouse tissues.
- Xiaoping Han
- , Ziming Zhou
- & Guoji Guo
-
News & Views |
 Techniques converge to map the developing human heart at single-cell level
Techniques converge to map the developing human heart at single-cell level
Three methods for gene-expression profiling have now been combined to produce spatially defined single-cell maps of developing human organs from limited sample material, overcoming a major hurdle in studying human development.
- Ragini Phansalkar
- & Kristy Red-Horse
-
News & Views |
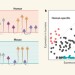 A recipe book for cell types in the human brain
A recipe book for cell types in the human brain
Whether cell types in the brain have been conserved during evolution is not clear. A comparison of the molecular recipes that define brain cell types in humans and mice reveals similarities and differences between species.
- Matthew G. Keefe
- & Tomasz J. Nowakowski
-
Technology Feature |
 Starfish enterprise: finding RNA patterns in single cells
Starfish enterprise: finding RNA patterns in single cells
Combining the data-analysis tool Starfish with technologies to pinpoint RNA’s cellular locations can add spatial detail to in situ transcriptomics.
- Jeffrey M. Perkel
-
Letter |
 Single-cell analysis of cardiogenesis reveals basis for organ-level developmental defects
Single-cell analysis of cardiogenesis reveals basis for organ-level developmental defects
Single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis reveals functions of lineage-specifying transcription factors underlying congenital defects in heart development.
- T. Yvanka de Soysa
- , Sanjeev S. Ranade
- & Deepak Srivastava
-
Letter |
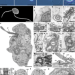 Non-photosynthetic predators are sister to red algae
Non-photosynthetic predators are sister to red algae
Species of the eukaryotic phylum Rhodelphidia are non-photosynthetic, flagellate predators with gene-rich genomes, in contrast to their closely related sister lineage—the red algae—which are immotile, typically photoautotrophic and have relatively small intron-poor genomes and reduced metabolism.
- Ryan M. R. Gawryluk
- , Denis V. Tikhonenkov
- & Patrick J. Keeling
-
News & Views |
 A deep dive into the development of sea squirts
A deep dive into the development of sea squirts
An analysis of gene expression in sea-squirt embryos at different stages of development deepens our understanding of how the body plans of vertebrates might have evolved from those of less complex animals.
- Noriyuki Satoh
-
Article |
 Comprehensive single-cell transcriptome lineages of a proto-vertebrate
Comprehensive single-cell transcriptome lineages of a proto-vertebrate
Comprehensive single-cell transcriptomes in the proto-vertebrate Ciona intestinalis identified provisional gene networks for 41 different neural subtypes, providing insights into the swimming circuit of tadpoles and the evolution of the vertebrate telencephalon.
- Chen Cao
- , Laurence A. Lemaire
- & Kai Chen
-
Letter |
 scSLAM-seq reveals core features of transcription dynamics in single cells
scSLAM-seq reveals core features of transcription dynamics in single cells
A technique known as scSLAM-seq that combines single-cell RNA sequencing with metabolic RNA labelling and nucleoside conversion is used to study the onset of cytomegalovirus infection in single mouse fibroblasts.
- Florian Erhard
- , Marisa A. P. Baptista
- & Lars Dölken
-
News & Views |
 How mutations express themselves in blood-cell production
How mutations express themselves in blood-cell production
A method for detecting mutations and measuring gene-expression levels in the same cell has enabled an investigation into the effects of mutations in a specific gene on the emergence of a form of blood cancer.
- Siddharth Raju
- & Chun Jimmie Ye
-
Article |
 Developmental dynamics of lncRNAs across mammalian organs and species
Developmental dynamics of lncRNAs across mammalian organs and species
A transcriptome dataset from seven organs and seven mammalian species throughout development is used to analyse the expression of long noncoding RNAs in tissues within and between species, and at different stages of organ development.
- Ioannis Sarropoulos
- , Ray Marin
- & Henrik Kaessmann
-
News & Views |
 Pinpointing a spatial address for RNA profiles in tissues
Pinpointing a spatial address for RNA profiles in tissues
Knowing the gene-expression pattern of individual cells can unlock their identity. A refined method for generating cellular RNA profiles offers a way to obtain such data at a high level of spatial resolution in intact tissues.
- Samantha A. Morris
-
Letter |
 Transcriptome-wide off-target RNA editing induced by CRISPR-guided DNA base editors
Transcriptome-wide off-target RNA editing induced by CRISPR-guided DNA base editors
CRISPR DNA base editors induce transcriptome-wide off-target RNA editing, which can be reduced by using engineered variants that retain on-target DNA editing activities.
- Julian Grünewald
- , Ronghao Zhou
- & J. Keith Joung
-
Article |
 A single-cell molecular map of mouse gastrulation and early organogenesis
A single-cell molecular map of mouse gastrulation and early organogenesis
Single-cell profiling is used to create a molecular-level atlas of cell differentiation trajectories during gastrulation and early organogenesis in the mouse.
- Blanca Pijuan-Sala
- , Jonathan A. Griffiths
- & Berthold Göttgens
-
Article |
 The single-cell transcriptional landscape of mammalian organogenesis
The single-cell transcriptional landscape of mammalian organogenesis
Data from single-cell combinatorial-indexing RNA-sequencing analysis of 2 million cells from mouse embryos between embryonic days 9.5 and 13.5 are compiled in a cell atlas of mouse organogenesis, which provides a global view of developmental processes occurring during this critical period.
- Junyue Cao
- , Malte Spielmann
- & Jay Shendure
-
Article |
 Excised linear introns regulate growth in yeast
Excised linear introns regulate growth in yeast
A set of 34 excised introns in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, characterized by having a short distance between the lariat branch point and the 3′ splice site, have a biological function within the TOR growth-signalling network.
- Jeffrey T. Morgan
- , Gerald R. Fink
- & David P. Bartel
-
Letter |
 Subcellular transcriptomes and proteomes of developing axon projections in the cerebral cortex
Subcellular transcriptomes and proteomes of developing axon projections in the cerebral cortex
A subcellular sorting approach enables quantitative analysis of subtypes of growth cones in the brain, and reveals subcellular relationships between local mRNA and local proteomes in developing projection neurons.
- Alexandros Poulopoulos
- , Alexander J. Murphy
- & Jeffrey D. Macklis
-
Letter |
 Genomic encoding of transcriptional burst kinetics
Genomic encoding of transcriptional burst kinetics
Allele-specific single-cell RNA sequencing provides insights into transcription kinetics, with data indicating that core promoter sequences affect burst size, whereas enhancers mainly affect burst frequency.
- Anton J. M. Larsson
- , Per Johnsson
- & Rickard Sandberg
-
Letter |
 Helios is a key transcriptional regulator of outer hair cell maturation
Helios is a key transcriptional regulator of outer hair cell maturation
Ikzf2, which encodes the transcription factor Helios, is identified as a crucial regulator of gene expression in maturing cochlear outer hair cells, and overexpression of Ikzf2 in inner hair cells induces prestin expression and electromotility.
- Lauren Chessum
- , Maggie S. Matern
- & Ronna Hertzano
-
News & Views |
 Cell atlas reveals the landscape of early pregnancy
Cell atlas reveals the landscape of early pregnancy
RNA sequencing of thousands of single cells located at the interface between mother and fetus in early pregnancy reveals remarkable complexity in the cell types and regulatory networks that support reproduction.
- Sumati Rajagopalan
- & Eric O. Long
-
News & Views |
 Single-cell sequencing paints diverse pictures of the brain
Single-cell sequencing paints diverse pictures of the brain
A single-cell sequencing study reveals how different types of neuron are distributed in the brain. An analysis then demonstrates how these data can improve our understanding of neuronal functions.
- Aparna Bhaduri
- & Tomasz J. Nowakowski
-
Article |
 Shared and distinct transcriptomic cell types across neocortical areas
Shared and distinct transcriptomic cell types across neocortical areas
Single-cell transcriptomics of more than 20,000 cells from two functionally distinct areas of the mouse neocortex identifies 133 transcriptomic types, and provides a foundation for understanding the diversity of cortical cell types.
- Bosiljka Tasic
- , Zizhen Yao
- & Hongkui Zeng
-
Letter |
 Widespread intronic polyadenylation inactivates tumour suppressor genes in leukaemia
Widespread intronic polyadenylation inactivates tumour suppressor genes in leukaemia
The inactivation of tumour suppressor genes at the level of mRNA occurs by the generation of truncated proteins in leukaemia.
- Shih-Han Lee
- , Irtisha Singh
- & Christine Mayr
-
News & Views |
 Technique to measure the expression dynamics of each gene in a single cell
Technique to measure the expression dynamics of each gene in a single cell
A method has been developed to infer whether the expression of each gene in a single cell is increasing or decreasing, and at what rate, using RNA-sequencing data. This tool has many potential applications.
- Allon M. Klein
-
News & Views |
 Profile of an unknown airway cell
Profile of an unknown airway cell
RNA sequencing of single cells in the mammalian trachea reveals a previously unknown airway cell that expresses genes involved in fluid and solute balance, and that might play a part in cystic fibrosis.
- Kyle J. Travaglini
- & Mark A. Krasnow
-
Article |
 A revised airway epithelial hierarchy includes CFTR-expressing ionocytes
A revised airway epithelial hierarchy includes CFTR-expressing ionocytes
Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis identifies cell types and lineages in airway epithelium, including the pulmonary ionocyte, a new cell type predominantly expressing the cystic fibrosis gene CFTR.
- Daniel T. Montoro
- , Adam L. Haber
- & Jayaraj Rajagopal
-
Letter |
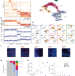 Single-cell mapping of the thymic stroma identifies IL-25-producing tuft epithelial cells
Single-cell mapping of the thymic stroma identifies IL-25-producing tuft epithelial cells
A comprehensive characterization of the thymic stroma identifies a tuft-cell-like thymic epithelial cell population that is critical for shaping the immune niche in the thymus.
- Chamutal Bornstein
- , Shir Nevo
- & Ido Amit
-
Technology Feature |
 Single-cell approaches to immune profiling
Single-cell approaches to immune profiling
Protein- and sequencing-based technologies are helping researchers to profile immune cells ever more deeply.
- Esther Landhuis
-
News & Views |
 An inflammatory transcriptional switch
An inflammatory transcriptional switch
The mouse pancreas adopts a pre-inflammatory state in response to a chemical injury or the loss of one copy of the gene Nr5a2. This state might predispose mice, and possibly humans, to pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer.
- L. Charles Murtaugh
- & Raymond J. MacDonald
-
Letter |
 Sequences enriched in Alu repeats drive nuclear localization of long RNAs in human cells
Sequences enriched in Alu repeats drive nuclear localization of long RNAs in human cells
A sequence that is frequently found in Alu elements drives the localization of some long RNAs to the nucleus in human cells.
- Yoav Lubelsky
- & Igor Ulitsky
-
Toolbox |
 A test drive of a DNA-analysis toolkit in the cloud
A test drive of a DNA-analysis toolkit in the cloud
The Bioconductor project gathers genomics tools and data into a handy package that can run in the cloud.
- W. Wayt Gibbs

 Molecular architecture of the developing mouse brain
Molecular architecture of the developing mouse brain