Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetotransport signatures of antiferromagnetism coexisting with charge order in the trilayer cuprate HgBa2Ca2Cu3O8+δ
Magnetotransport signatures of antiferromagnetism coexisting with charge order in the trilayer cuprate HgBa2Ca2Cu3O8+δ
The interplay between superconductivity and competing orders in multi-layered cuprates can shed light on the nature of the superconducting pairing. Here, the authors report on the coexistence of antiferromagnetic and charge orders in different CuO2 planes in a tri-layer cuprate, pointing to a magnetically-mediated mechanism.
- V. Oliviero
- , S. Benhabib
- & C. Proust
-
Article
| Open Access Topotactic fluorination of intermetallics as an efficient route towards quantum materials
Topotactic fluorination of intermetallics as an efficient route towards quantum materials
Insertion of light elements in intermetallics has been explored to synthesize functional materials. Here the authors report topotactic intercalation of fluorine atoms into intermetallics using a perfluorocarbon reactant with covalent C-F bonds to obtain quantum materials.
- Jean-Baptiste Vaney
- , Baptiste Vignolle
- & Sophie Tencé
-
Article
| Open Access Little-Parks like oscillations in lightly doped cuprate superconductors
Little-Parks like oscillations in lightly doped cuprate superconductors
Understanding the rich electronic orders in cuprate superconductors provide insights into the mechanism of high-temperature superconductivity. Here, the authors report a distinct charge order with Little-Parks like resistance oscillations at magnetic fields up to 10 T and around Tc in lightly doped Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x.
- Menghan Liao
- , Yuying Zhu
- & Qi-Kun Xue
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of the non-linear Meissner effect
Observation of the non-linear Meissner effect
The non-linear Meissner effect is a key manifestation of unconventional nodal superconductors but its experimental evidence has been elusive. Here, the authors observe the nonlinear Meissner effect in nodal superconductors CeCoIn5 and LaFePO.
- J. A. Wilcox
- , M. J. Grant
- & A. Carrington
-
Article
| Open Access Comparison of temperature and doping dependence of elastoresistivity near a putative nematic quantum critical point
Comparison of temperature and doping dependence of elastoresistivity near a putative nematic quantum critical point
Evidence for quantum criticality in Fe-based superconductors is still being accumulated. Here, the authors observe power-law behavior of the elastoresistivity as a function of composition in Ba(Fe1−xCox)2As2 near a putative nematic quantum critical point, consistent with expectations for quantum criticality, while the temperature dependence near the critical doping deviates from a power law.
- J. C. Palmstrom
- , P. Walmsley
- & I. R. Fisher
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of perfect diamagnetism and interfacial effect on the electronic structures in infinite layer Nd0.8Sr0.2NiO2 superconductors
Observation of perfect diamagnetism and interfacial effect on the electronic structures in infinite layer Nd0.8Sr0.2NiO2 superconductors
Nickelate superconductors attract enormous attention in the field of high-temperature superconductivity. Here the authors report observation of perfect diamagnetism and interfacial effect on the electronic structures in infinite layer Nd0.8Sr0.2NiO2 superconductors.
- S. W. Zeng
- , X. M. Yin
- & A. Ariando
-
Article
| Open Access Charge density waves and Fermi surface reconstruction in the clean overdoped cuprate superconductor Tl2Ba2CuO6+δ
Charge density waves and Fermi surface reconstruction in the clean overdoped cuprate superconductor Tl2Ba2CuO6+δ
The origin of the Fermi surface reconstruction that occurs in cuprate superconductors as hole doping increases remains unclear. Here, the authors observe long range charge density wave (CDW) order in the overdoped single-layer cuprate Tl2Ba2CuO6+δ, which then disappears above a hole concentration 0.265, suggesting a correlation between Fermi surface reconstruction and the emergence of the CDW.
- C. C. Tam
- , M. Zhu
- & S. M. Hayden
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic nature of charge density wave and electron-phonon coupling in kagome superconductor KV3Sb5
Electronic nature of charge density wave and electron-phonon coupling in kagome superconductor KV3Sb5
The impact of the charge density wave (CDW) state to the electronic structure in the Kagome superconductors AV3Sb5 remains unclear. Here, the authors observe CDW-induced Fermi surface reconstruction with a strongly anisotropic CDW gap and signatures of the electron-phonon coupling for all V-derived bands.
- Hailan Luo
- , Qiang Gao
- & X. J. Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Electron-momentum dependence of electron-phonon coupling underlies dramatic phonon renormalization in YNi2B2C
Electron-momentum dependence of electron-phonon coupling underlies dramatic phonon renormalization in YNi2B2C
Phonon anomalies are commonly attributed to Fermi-surface nesting or phonon anharmonicity, but these mechanisms do not apply in all cases. Here, the authors propose a new mechanism based on electron-momentum-dependent electron-phonon coupling in the case of YNi2B2C, that could also apply to other materials.
- Philipp Kurzhals
- , Geoffroy Kremer
- & Frank Weber
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging moiré deformation and dynamics in twisted bilayer graphene
Imaging moiré deformation and dynamics in twisted bilayer graphene
Local variations of twist angle and strain in twisted bilayer graphene (TBG) can produce relevant changes in the electronic properties of the system. Here, high-resolution low energy electron microscopy is used to characterize the spatial and temporal deformations of moiré patterns in TBG at high temperatures, showing the stability of these structures up to 600 ∘C.
- Tobias A. de Jong
- , Tjerk Benschop
- & Sense Jan van der Molen
-
Article
| Open Access High-temperature superconductivity on the verge of a structural instability in lanthanum superhydride
High-temperature superconductivity on the verge of a structural instability in lanthanum superhydride
The experimental studies to understand the superconductivity of superhydrides remain scarce. Here, the authors report pressure and magnetic field dependence of superconductivity in LaH10, and indicate lattice vibrations strongly affect superconducting coupling.
- Dan Sun
- , Vasily S. Minkov
- & Fedor F. Balakirev
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for anisotropic spin-triplet Andreev reflection at the 2D van der Waals ferromagnet/superconductor interface
Evidence for anisotropic spin-triplet Andreev reflection at the 2D van der Waals ferromagnet/superconductor interface
The interfaces between ferromagnets and superconductors receive many attentions due to emergent relativistic spin-orbit coupling. Here, the authors provide possible evidence for spin triplet Andreev reflection at the interface between a van der Waals ferromagnet Fe0.29TaS2 and a s-wave superconductor NbN.
- Ranran Cai
- , Yunyan Yao
- & Wei Han
-
Article
| Open Access Long range and highly tunable interaction between local spins coupled to a superconducting condensate
Long range and highly tunable interaction between local spins coupled to a superconducting condensate
The possibility of using superconductivity to control indirect interactions between magnetic moments remains largely unexplored. Here, the authors report tuning the interaction between local spins of Cr atoms coupled through a superconducting condensate in Nb.
- Felix Küster
- , Sascha Brinker
- & Paolo Sessi
-
Article
| Open Access Overactivated transport in the localized phase of the superconductor-insulator transition
Overactivated transport in the localized phase of the superconductor-insulator transition
Despite extensive work on the superconductor-insulator transition in two-dimensional materials, the nature of the insulator is still debated. The authors report measurements and simulations of NbxSi1–x films, showing that conduction in the insulating state occurs by single charges hopping between superconducting grains.
- V. Humbert
- , M. Ortuño
- & C. A. Marrache-Kikuchi
-
Article
| Open Access Twofold symmetry of c-axis resistivity in topological kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5 with in-plane rotating magnetic field
Twofold symmetry of c-axis resistivity in topological kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5 with in-plane rotating magnetic field
The recently discovered class of kagome metals AV3Sb5, where A stands for K, Rb, Cs, has been shown to host a variety of exotic phases. Here, the authors report the two-fold rotational symmetry of superconductivity and signatures of an in-plane nematic electronic state in CsV3Sb5 under in-plane magnetic field.
- Ying Xiang
- , Qing Li
- & Hai-Hu Wen
-
Article
| Open Access Van der Waals ferromagnetic Josephson junctions
Van der Waals ferromagnetic Josephson junctions
The superconductor-ferromagnet interface provides a unique opportunity to study the interplay between superconductivity and ferromagnetism. Here, the authors build a van der Waals ferromagnetic Josephson junction evidencing a strong 0 and π phase Josephson coupling.
- Linfeng Ai
- , Enze Zhang
- & Shaoming Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time observation of Cooper pair splitting showing strong non-local correlations
Real-time observation of Cooper pair splitting showing strong non-local correlations
The splitting of Cooper pairs in superconductors has been challenging to detect experimentally. Here, the authors observe the real-time splitting of individual Cooper pairs in a superconducting device.
- Antti Ranni
- , Fredrik Brange
- & Ville F. Maisi
-
Article
| Open Access Two distinct superconducting states controlled by orientations of local wrinkles in LiFeAs
Two distinct superconducting states controlled by orientations of local wrinkles in LiFeAs
The evolution of superconductivity in LiFeAs with respect to pressure or strain remains elusive. Here, the authors observe different response of superconducting states due to different orientations of local wrinkles on the surface of LiFeAs.
- Lu Cao
- , Wenyao Liu
- & Hong-Jun Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Scattering interference signature of a pair density wave state in the cuprate pseudogap phase
Scattering interference signature of a pair density wave state in the cuprate pseudogap phase
The pseudogap phase in cuprate superconductors is predicted to be a pair density wave state (PDW) but experimental evidence has been lacking. Here, the authors detect the temperature evolution of energy gap modulations and scattering interference signature suggesting the Bi2Sr2CaDyCu2O8 pseudogap phase contains a PDW.
- Shuqiu Wang
- , Peayush Choubey
- & J. C. Séamus Davis
-
Article
| Open Access Space-time crystalline order of a high-critical-temperature superconductor with intrinsic Josephson junctions
Space-time crystalline order of a high-critical-temperature superconductor with intrinsic Josephson junctions
A space-time crystal (STC) is a nonequilibrium phase of matter displaying long-range order in both space and time. Here, the authors propose that the high-Tc cuprate superconductor Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x is a candidate of a classical discrete STC, when a parametric modulation periodic in time and uniform in space is applied.
- Reinhold Kleiner
- , Xianjing Zhou
- & Dafei Jin
-
Article
| Open Access High temperature superconductivity at FeSe/LaFeO3 interface
High temperature superconductivity at FeSe/LaFeO3 interface
An enhanced superconducting pairing temperature (Tg) has only been observed in single-layer FeSe interfaced with TiOx system. Here, the authors construct a new interface composed of single-layer FeSe interfaced with LaFeO3 showing a highest Tg of 80 K among all-known interfacial superconductors.
- Yuanhe Song
- , Zheng Chen
- & Donglai Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Unveiling unconventional magnetism at the surface of Sr2RuO4
Unveiling unconventional magnetism at the surface of Sr2RuO4
Strontium Ruthenate, Sr2RuO4, displays a remarkable number of intriguing physical phenomena, from superconductivity, to strain-induced ferromagnetism. Here, using low-energy muon spectroscopy, Fittipaldi et al. demonstrate the existence of unconventional magnetism at the surface of Sr2RuO4 in its normal state and without any applied strain.
- R. Fittipaldi
- , R. Hartmann
- & A. Di Bernardo
-
Article
| Open Access Phonon-induced disorder in dynamics of optically pumped metals from nonlinear electron-phonon coupling
Phonon-induced disorder in dynamics of optically pumped metals from nonlinear electron-phonon coupling
Superconductivity reported in metals driven away from equilibrium via optical pumping has been proposed to arise from nonlinear coupling between electrons and optically excited phonons. The authors use an exact approach to show that here, disorder, which disfavors superconductivity, emerges even though the system is translationally invariant.
- John Sous
- , Benedikt Kloss
- & Andrew J. Millis
-
Article
| Open Access Strong correlation between electronic bonding network and critical temperature in hydrogen-based superconductors
Strong correlation between electronic bonding network and critical temperature in hydrogen-based superconductors
Several hydrides have been observed high-Tc superconductivity under pressure, but a physical-chemical understanding of the properties enhancing Tc is still lacking. Here, the authors propose a magnitude named as networking value, combined with hydrogen fraction and the contribution of hydrogen to the density of states at Fermi level, can predict Tc of all hydrogen-based compounds with an accuracy of about 60 K.
- Francesco Belli
- , Trinidad Novoa
- & Ion Errea
-
Article
| Open Access Pressure induced superconductivity in MnSe
Pressure induced superconductivity in MnSe
Superconductivity in FeSe attracted great interests to understand the mechanism of high temperature superconductivity. Here, the authors report a pressure induced superconductivity with a highest Tc of ~9 K in MnSe.
- T. L. Hung
- , C. H. Huang
- & T. K. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional supercurrent phase in Ising superconductor Josephson junction with atomically thin magnetic insulator
Unconventional supercurrent phase in Ising superconductor Josephson junction with atomically thin magnetic insulator
Van der Waals structures provide a new platform to explore novel physics of superconductor/ferromagnet interfaces. Here, NbSe2 Josephson junction with Cr2Ge2Te6 enables non-trivial Josephson phase by spin-dependent interaction, boosting the study of superconducting states with spin-orbit coupling and phase-controlled quantum electronic device.
- H. Idzuchi
- , F. Pientka
- & P. Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Coexistence of resistance oscillations and the anomalous metal phase in a lithium intercalated TiSe2 superconductor
Coexistence of resistance oscillations and the anomalous metal phase in a lithium intercalated TiSe2 superconductor
The interplay between superconductivity and charge density wave (CDW) gives rise to exotic quantum phenomena. Here, the authors observe magnetoresistance oscillations and an anomalous metal state due to the coexistence of superconductivity and CDW in lithium intercalated TiSe2.
- Menghan Liao
- , Heng Wang
- & Qi-Kun Xue
-
Article
| Open Access Preliminary demonstration of a persistent Josephson phase-slip memory cell with topological protection
Preliminary demonstration of a persistent Josephson phase-slip memory cell with topological protection
Superconducting computing promises enhanced computational power, but scalable and fast superconducting memories are still not implemented. Here, the authors demonstrate a superconducting memory cell based on hysteretic phase-slip transition, without degradation up to ~1 K over several days.
- Nadia Ligato
- , Elia Strambini
- & Francesco Giazotto
-
Article
| Open Access Superconductivity up to 243 K in the yttrium-hydrogen system under high pressure
Superconductivity up to 243 K in the yttrium-hydrogen system under high pressure
The discovery of high temperature superconductivity in hydrogen-rich compounds stimulates further extensive studies. Here, the authors report superconductivity in pressurized yttrium-hydrogen system with highest predicted Tc among binary compounds.
- Panpan Kong
- , Vasily S. Minkov
- & Mikhail I. Eremets
-
Article
| Open Access Emerging symmetric strain response and weakening nematic fluctuations in strongly hole-doped iron-based superconductors
Emerging symmetric strain response and weakening nematic fluctuations in strongly hole-doped iron-based superconductors
Whether the electronic nematicity is related to electronic pairing in strongly hole-doped iron-based superconductors remains controversial. Here, the authors perform transport measurements on AFe2As2 (A = K, Rb, Cs) superconductors under elastic strain, and find no indication of a nematic ordered state.
- P. Wiecki
- , M. Frachet
- & A. E. Böhmer
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent coupling between vortex bound states and magnetic impurities in 2D layered superconductors
Coherent coupling between vortex bound states and magnetic impurities in 2D layered superconductors
Bound states in superconducting vortices are expected to exhibit an electron-hole asymmetry, but it is usually tiny and can be easily washed out. Here, the authors show that the vortex bound states coupling to magnetic impurities provides an axial electron-hole asymmetry on a much longer scale, and that the direction of the asymmetry depends on the band character of the superconducting material.
- Sunghun Park
- , Víctor Barrena
- & Hermann Suderow
-
Article
| Open Access High-order replica bands in monolayer FeSe/SrTiO3 revealed by polarization-dependent photoemission spectroscopy
High-order replica bands in monolayer FeSe/SrTiO3 revealed by polarization-dependent photoemission spectroscopy
The origin of the photoemission replica bands in monolayer FeSe/SrTiO3 remains controversial. Here, the authors perform angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy with polarized photon on FeSe/SrTiO3 and observe high-order replica bands with high intensity from various Fe 3d bands, suggesting a mixed mechanism.
- Chong Liu
- , Ryan P. Day
- & Ke Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Superconductivity in an extreme strange metal
Superconductivity in an extreme strange metal
Understanding the strange metal behavior, characterized by linear-in-temperature resistivity, could shed light on the mechanism of unconventional superconductivity. Here, by using electrical resistivity measurements into the micro-Kelvin regime, the authors report evidence of unconventional superconductivity in the strange metal YbRh2Si2 and propose a possible pairing mechanism.
- D. H. Nguyen
- , A. Sidorenko
- & S. Paschen
-
Article
| Open Access Majorana zero modes in impurity-assisted vortex of LiFeAs superconductor
Majorana zero modes in impurity-assisted vortex of LiFeAs superconductor
Despite the discovery of Majorana zero modes (MZM) in iron-based superconductors, sample inhomogeneity may destroy MZMs during braiding. Here, authors observe MZM in impurity-assisted vortices due to tuning of the bulk Dirac fermions in a homogeneous superconductor LiFeAs.
- Lingyuan Kong
- , Lu Cao
- & Hong Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Unsplit superconducting and time reversal symmetry breaking transitions in Sr2RuO4 under hydrostatic pressure and disorder
Unsplit superconducting and time reversal symmetry breaking transitions in Sr2RuO4 under hydrostatic pressure and disorder
Two possible scenarios of the superconducting order parameter in Sr2RuO4 remain difficult to distinguish. Here, the authors observe that the onset temperature of time reversal symmetry breaking tracks the superconducting transition temperature in Sr2RuO4, supporting a dxz ± idyz order parameter.
- Vadim Grinenko
- , Debarchan Das
- & Rustem Khasanov
-
Article
| Open Access Atomically-resolved interlayer charge ordering and its interplay with superconductivity in YBa2Cu3O6.81
Atomically-resolved interlayer charge ordering and its interplay with superconductivity in YBa2Cu3O6.81
Charge ordering and superconductivity are known to compete in layered cuprates; however, precise real-space characterization of their interplay has been lacking. Here, the authors address this using atomically-resolved cross-sectional scanning tunnelling microscopy and spectroscopy on cryogenically cleaved YBa2Cu3O6.81.
- Chun-Chih Hsu
- , Bo-Chao Huang
- & Ya-Ping Chiu
-
Article
| Open Access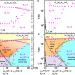 Magnetic field reveals vanishing Hall response in the normal state of stripe-ordered cuprates
Magnetic field reveals vanishing Hall response in the normal state of stripe-ordered cuprates
The Hall effect has been used as a probe of the normal state of cuprates, when superconductivity is supressed by a magnetic field. Here, the authors report the vanishing of the Hall coefficient at high magnetic field in cuprates with stripe order and interpret it as a signature of the stripe-ordered phase.
- Zhenzhong Shi
- , P. G. Baity
- & Dragana Popović
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for the Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov state in bulk NbS2
Evidence for the Fulde–Ferrell–Larkin–Ovchinnikov state in bulk NbS2
Superconductivity is often destroyed under magnetic field larger than a critical value called Pauli limit. Here, the authors report superconductivity beyond the Pauli limit in bulk single crystals of NbS2, suggesting the development of a Fulde-Ferrell-Larkin-Ovchinnikov state.
- Chang-woo Cho
- , Jian Lyu
- & Rolf Lortz
-
Article
| Open Access Unusual competition of superconductivity and charge-density-wave state in a compressed topological kagome metal
Unusual competition of superconductivity and charge-density-wave state in a compressed topological kagome metal
The recently discovered kagome metal AV3Sb5 is a new playground to study the interplay between superconductivity and charge-density-wave (CDW) state. Here, the authors report pressure-dependent evolution of CDW and superconductivity in CsV3Sb5, suggesting an unusual competition between the two phases.
- F. H. Yu
- , D. H. Ma
- & X. H. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Locally commensurate charge-density wave with three-unit-cell periodicity in YBa2Cu3Oy
Locally commensurate charge-density wave with three-unit-cell periodicity in YBa2Cu3Oy
Understanding cuprate superconductors requires better knowledge of the microscopic structure of their charge-density waves (CDW). Here, the authors report evidence that the long-range CDW order in YBa2Cu3Oy has a local commensurate period of three unit cells.
- Igor Vinograd
- , Rui Zhou
- & Marc-Henri Julien
-
Article
| Open Access Superconductivity emerging from a stripe charge order in IrTe2 nanoflakes
Superconductivity emerging from a stripe charge order in IrTe2 nanoflakes
Superconductivity often appears due to suppression of competing electronic orders. Here, the authors present a contrary example showing a superconducting dome inside the parent phase with a stripe charge order in IrTe2 nanoflakes and identify their unusual superconducting properties.
- Sungyu Park
- , So Young Kim
- & Jun Sung Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of spin excitations from bulk to monolayer FeSe
Evolution of spin excitations from bulk to monolayer FeSe
Here, Pelliciari et al. present resonant inelastic X-ray scattering on monolayer samples of unconventional superconductor FeSe, finding evidence for gapped and dispersionless spin excitations. These experiments are very difficult due to the extremely small scattering volume of the FeSe monolayer.
- Jonathan Pelliciari
- , Seher Karakuzu
- & Riccardo Comin
-
Article
| Open Access Superconductor-insulator transition in space charge doped one unit cell Bi2.1Sr1.9CaCu2O8+x
Superconductor-insulator transition in space charge doped one unit cell Bi2.1Sr1.9CaCu2O8+x
Previous work on critical scaling at the superconductor-to-insulator transition has shown variations across different materials. Here, the authors use a space charge doping technique to tune the transition in a single layer cuprate sample and present evidence of the universal scaling behaviour.
- Fang Wang
- , Johan Biscaras
- & Abhay Shukla
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of topological superconductivity in a stoichiometric transition metal dichalcogenide 2M-WS2
Observation of topological superconductivity in a stoichiometric transition metal dichalcogenide 2M-WS2
Topological superconductors are potentially important for future quantum computation, but they are very rare in nature. Here, the authors observe topological surface states acquiring a nodeless superconducting gap with similar magnitude as that of the bulk states in 2M-WS2, suggesting an intrinsic topological superconductor.
- Y. W. Li
- , H. J. Zheng
- & Y. L. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access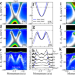 Spectroscopic evidence of superconductivity pairing at 83 K in single-layer FeSe/SrTiO3 films
Spectroscopic evidence of superconductivity pairing at 83 K in single-layer FeSe/SrTiO3 films
How high the superconducting transition temperature can reach in single layer FeSe/SrTiO3 films has been under debate. Here, the authors use Bogoliubov back-bending bands as a benchmark and demonstrate that superconductivity pairing can be realized up to 83 K in this system.
- Yu Xu
- , Hongtao Rong
- & X. J. Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Reducing the impact of radioactivity on quantum circuits in a deep-underground facility
Reducing the impact of radioactivity on quantum circuits in a deep-underground facility
Background radiation has been identified as a key factor limiting the coherence times of superconducting circuits. Here, the authors measure the impact of environmental and cosmic radiation on a superconducting resonator with varying degrees of shielding, including an underground facility.
- L. Cardani
- , F. Valenti
- & I. M. Pop
-
Article
| Open Access On the origin of the controversial electrostatic field effect in superconductors
On the origin of the controversial electrostatic field effect in superconductors
A recent report on electrostatic field effect in superconducting devices provides a high potential for advanced quantum technology, but it remains controversial. Here, the authors report that the suppression of critical current, which was attributed to the field effect, can instead be explained by quasiparticle excitations in the constriction of superconducting devices.
- I. Golokolenov
- , A. Guthrie
- & V. Tsepelin
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous normal fluid response in a chiral superconductor UTe2
Anomalous normal fluid response in a chiral superconductor UTe2
Chiral superconductors are predicted to realize Majorana normal fluid at its boundary, but remain elusive experimentally. Here, Bae et al. report anomalous surface normal fluid response in UTe2 single crystal which is further attributed to a chiral spin-triplet pairing state.
- Seokjin Bae
- , Hyunsoo Kim
- & Steven M. Anlage
-
Article
| Open Access Superconducting diode effect via conformal-mapped nanoholes
Superconducting diode effect via conformal-mapped nanoholes
A superconducting diode is dissipationless and desirable for electronic circuits with ultralow power consumption, yet it remains challenging to realize it. Here, the authors achieve a superconducting diode in a conventional superconducting film patterned with a conformal array of nanoscale holes.
- Yang-Yang Lyu
- , Ji Jiang
- & Wai-Kwong Kwok

 Giant second harmonic transport under time-reversal symmetry in a trigonal superconductor
Giant second harmonic transport under time-reversal symmetry in a trigonal superconductor