Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Orphan high field superconductivity in non-superconducting uranium ditelluride
Orphan high field superconductivity in non-superconducting uranium ditelluride
In addition to its low-field superconducting state, UTe2 features a re-entrant superconducting state when high magnetic fields are applied at a particular range of angles. Here, the authors demonstrate that the high-field re-entrant superconducting state survives even when the low-field superconducting state is destroyed by disorder.
- Corey E. Frank
- , Sylvia K. Lewin
- & Nicholas P. Butch
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic inhomogeneity and phase fluctuation in one-unit-cell FeSe films
Electronic inhomogeneity and phase fluctuation in one-unit-cell FeSe films
The authors study monolayer FeSe via scanning tunneling microscopy and simultaneous micron-scale-probe-based transport. They observe distinct superconducting phases in domains and on boundaries between domains, with different superconducting gaps and pairing temperatures.
- Dapeng Zhao
- , Wenqiang Cui
- & Qi-Kun Xue
-
Article
| Open Access Using strain to uncover the interplay between two- and three-dimensional charge density waves in high-temperature superconducting YBa2Cu3Oy
Using strain to uncover the interplay between two- and three-dimensional charge density waves in high-temperature superconducting YBa2Cu3Oy
Strain is a valuable tuning knob for studying the electronic properties of quantum materials. Here, the authors use strain to modulate and study the competition between 2D and 3D charge orders in a high-temperature superconductor.
- I. Vinograd
- , S. M. Souliou
- & M. Le Tacon
-
Article
| Open Access Violation of emergent rotational symmetry in the hexagonal Kagome superconductor CsV
Violation of emergent rotational symmetry in the hexagonal Kagome superconductor CsV3 Sb5 Superconductors with hexagonal symmetry are expected to be isotropic particularly near the critical temperature Tc, a property called emergent rotational symmetry (ERS). Here, the authors use calorimetry to study the hexagonal kagome superconductor CsV3Sb5 and find a violation of the expected ERS, hinting at realization of exotic superconductivity.
- Kazumi Fukushima
- , Keito Obata
- & Shingo Yonezawa
-
Article
| Open Access Structural phase transition, s±-wave pairing, and magnetic stripe order in bilayered superconductor La3Ni2O7 under pressure
Structural phase transition, s±-wave pairing, and magnetic stripe order in bilayered superconductor La3Ni2O7 under pressure
Recently superconductivity with Tc of about 80 K was discovered in a bilayer nickelate La3Ni2O7 under high pressure. Here the authors report a density functional theory and random phase approximation study of structural and electronic properties as a function of pressure and discuss the pairing mechanism.
- Yang Zhang
- , Ling-Fang Lin
- & Elbio Dagotto
-
Article
| Open Access Broadened quantum critical ground state in a disordered superconducting thin film
Broadened quantum critical ground state in a disordered superconducting thin film
The authors present Nernst measurements on a 2D film of amorphous MoxGe1−x, which shows a magnetic-field-induced superconductor-metal-insulator transition. The intermediate metal phase is known as the “anomalous metal” (AM) state. The authors conclude that the AM state originates from broadening of the superconductor-insulator transition.
- Koichiro Ienaga
- , Yutaka Tamoto
- & Satoshi Okuma
-
Article
| Open Access Dislocation Majorana bound states in iron-based superconductors
Dislocation Majorana bound states in iron-based superconductors
The authors propose that screw or edge dislocations can trap Majorana zero modes in the absence of an external magnetic field. They predict that the Majoranas will appear as second-order topological modes on the four corners of an embedded 2D subsystem defined by the cutting plane of the dislocation.
- Lun-Hui Hu
- & Rui-Xing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Theory of resonantly enhanced photo-induced superconductivity
Theory of resonantly enhanced photo-induced superconductivity
The authors theoretically propose a simple microscopic mechanism for light-induced superconductivity based on a boson coupled to an electronic interband transition. The electron-electron attraction needed for the superconductivity can be resonantly amplified when the boson’s frequency is close to the energy difference between the two electronic bands. The model can be engineered using a 2D heterostructure.
- Christian J. Eckhardt
- , Sambuddha Chattopadhyay
- & Marios H. Michael
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning of the flat band and its impact on superconductivity in Mo5Si3−xPx
Tuning of the flat band and its impact on superconductivity in Mo5Si3−xPx
R. Khasanov et al. report thermodynamic and muon-spin-rotation measurements on the Mo5Si3−xPx superconducting family. They find that a flat band reaches the Fermi level at x ≃ 1.3, leading to enhancement of electronic correlations and an abrupt change of the superconducting properties.
- Rustem Khasanov
- , Bin-Bin Ruan
- & Zurab Guguchia
-
Article
| Open Access Superconductivity in a van der Waals layered quasicrystal
Superconductivity in a van der Waals layered quasicrystal
Recent theoretical work has shown that quasicrystal (QC) superconductors should exhibit unconventional behaviors, such as vortex pinning without impurities and FFLO-like states. Here, Y. Tokumoto et al. report experimental observation of bulk superconductivity in Ta1.6Te, a van-der-Waals-layered QC with Tc = 1 K.
- Yuki Tokumoto
- , Kotaro Hamano
- & Keiichi Edagawa
-
Article
| Open Access Anharmonic strong-coupling effects at the origin of the charge density wave in CsV3Sb5
Anharmonic strong-coupling effects at the origin of the charge density wave in CsV3Sb5
The origin of the charge density wave in vanadium antimonides has been widely debated. Here, the authors report the cooperation of electron-phonon and phonon-phonon coupling for the formation of the charge density wave in CsV3Sb5.
- Ge He
- , Leander Peis
- & Rudi Hackl
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis and superconductivity in yttrium-cerium hydrides at high pressures
Synthesis and superconductivity in yttrium-cerium hydrides at high pressures
The field of hydride superconductivity is currently attempting to increase the critical temperature Tc, while also lowering the required stabilization pressure. Here, L.C. Chen et al. study (Y,Ce)H9 alloys and find maximum Tc ~ 140 K at 130 GPa pressure.
- Liu-Cheng Chen
- , Tao Luo
- & Xiao-Jia Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Light-induced switching between singlet and triplet superconducting states
Light-induced switching between singlet and triplet superconducting states
S. Gassner et al. propose using light pulses to drive a centrosymmetric s-wave superconductor with strong spin-orbit coupling into a metastable triplet p-wave superconductor with non-trivial topology. The two superconducting orders must be closely competing in equilibrium and the light pulse must break a generalized, dynamic form of inversion symmetry.
- Steven Gassner
- , Clara S. Weber
- & Martin Claassen
-
Article
| Open Access Finite-momentum Cooper pairing in proximitized altermagnets
Finite-momentum Cooper pairing in proximitized altermagnets
An altermagnet has highly anisotropic spin splitting but zero net magnetization. Here, S.-B. Zhang et al. theoretically study the behavior of s-wave superconductor/altermagnet hybrid structures, finding that Cooper pairs in the proximitized altermagnet have an anisotropic non-zero momentum.
- Song-Bo Zhang
- , Lun-Hui Hu
- & Titus Neupert
-
Article
| Open Access Vestigial singlet pairing in a fluctuating magnetic triplet superconductor and its implications for graphene superlattices
Vestigial singlet pairing in a fluctuating magnetic triplet superconductor and its implications for graphene superlattices
P. Poduval et al. theoretically study the nonzero-temperature vestigial phases of a 2D model exhibiting both triplet superconductivity and magnetism. They show that this model allows for a unique superconducting state in which the condensate consists of entities with three electrons and one hole, with properties similar to those seen in experiments on moiré systems.
- Prathyush P. Poduval
- & Mathias S. Scheurer
-
Article
| Open Access Intrinsic supercurrent non-reciprocity coupled to the crystal structure of a van der Waals Josephson barrier
Intrinsic supercurrent non-reciprocity coupled to the crystal structure of a van der Waals Josephson barrier
J.-K. Kim et al. study vertical Josephson junctions where the weak link is Td-WTe2 and the superconductor is NbSe2. The use of an inversion-symmetry-breaking Td-WTe2 weak link allows the authors to demonstrate the intrinsic origin of the observed Josephson non-reciprocity in these devices.
- Jae-Keun Kim
- , Kun-Rok Jeon
- & Stuart S. P. Parkin
-
Article
| Open Access Two-component nematic superconductivity in 4Hb-TaS2
Two-component nematic superconductivity in 4Hb-TaS2
I. Silber et al. discover a two-fold symmetry of the superconducting upper critical field in hexagonal 4Hb-TaS2 just below Tc, a clear signature of nematic, two-component superconductivity. They further suggest a theoretical model that reconciles the nematic superconductivity with the previously-observed time-reversal-symmetry-breaking in this material.
- I. Silber
- , S. Mathimalar
- & Y. Dagan
-
Article
| Open Access Microwave quantum diode
Microwave quantum diode
Quantum devices exhibiting non-reciprocal behaviour have been attracting attention for fundamental studies and applications. Here the authors report a microwave quantum diode based on a superconducting flux qubit coupled to two resonators, which has the advantage of compactness and scalability.
- Rishabh Upadhyay
- , Dmitry S. Golubev
- & Jukka P. Pekola
-
Article
| Open Access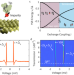 Tracking a spin-polarized superconducting bound state across a quantum phase transition
Tracking a spin-polarized superconducting bound state across a quantum phase transition
The Yu-Shiba-Rusinov state, arising from exchange coupling between a magnetic impurity and a superconductor, undergoes a quantum phase transition at a critical coupling. In a scanning tunnelling microscopy experiment, Karan et al. reveal distinct tunnelling spectra on each side of the transition in a magnetic field, which allows them to distinguish the free spin regime from the screened spin regime.
- Sujoy Karan
- , Haonan Huang
- & Christian R. Ast
-
Article
| Open Access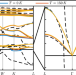 Temperature and quantum anharmonic lattice effects on stability and superconductivity in lutetium trihydride
Temperature and quantum anharmonic lattice effects on stability and superconductivity in lutetium trihydride
Superconductivity was recently reported experimentally in nitrogen-doped lutetium hydride with Tc = 294 K at 1 GPa. Here, via theoretical calculations taking into account temperature and quantum anharmonic lattice effects, the authors find that room-temperature superconductivity in the suggested parent phase of LuH3 cannot be explained by a conventional electron-phonon mediated pairing mechanism.
- Roman Lucrezi
- , Pedro P. Ferreira
- & Christoph Heil
-
Article
| Open Access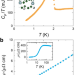 Quasi-2D Fermi surface in the anomalous superconductor UTe2
Quasi-2D Fermi surface in the anomalous superconductor UTe2
A. G. Eaton et al. directly probe the Fermi surface of the candidate triplet superconductor UTe2 by measuring magnetic quantum oscillations in ultra-pure crystals. By comparison with model calculations, the data are found to be consistent with a Fermi surface that consists of two cylindrical sections of electron and hole-type respectively.
- A. G. Eaton
- , T. I. Weinberger
- & M. Vališka
-
Article
| Open Access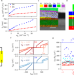 Parity-conserving Cooper-pair transport and ideal superconducting diode in planar germanium
Parity-conserving Cooper-pair transport and ideal superconducting diode in planar germanium
M. Valentini et al. study superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs) where the weak link of the Josephson junctions is a germanium 2D hole gas. They report signatures of the tunneling of pairs of Cooper pairs. For a particular microwave drive power, they observe a 100% efficient superconducting diode effect.
- Marco Valentini
- , Oliver Sagi
- & Georgios Katsaros
-
Article
| Open Access Field-induced compensation of magnetic exchange as the possible origin of reentrant superconductivity in UTe2
Field-induced compensation of magnetic exchange as the possible origin of reentrant superconductivity in UTe2
The superconductor UTe2 exhibits a reentrant superconducting phase at magnetic fields above 40 T for particular field angles. Here, from high-field Hall-effect measurements, T. Helm et al. find evidence for a partial compensation between the applied field and an exchange field, pointing to the Jaccarino-Peter effect as a possible mechanism for the reentrant superconductivity.
- Toni Helm
- , Motoi Kimata
- & Jean-Pascal Brison
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-dependent Andreev molecules and superconducting gap closing in coherently-coupled Josephson junctions
Phase-dependent Andreev molecules and superconducting gap closing in coherently-coupled Josephson junctions
S. Matsuo et al. report tunneling spectroscopy measurements on a device consisting of two Josephson junctions (JJ) sharing a single superconducting electrode. In isolation, each JJ would host an Andreev bound state (ABS). In their coherently-coupled JJs, the authors report the formation of an Andreev molecule due to hybridization of the two ABSs.
- Sadashige Matsuo
- , Takaya Imoto
- & Seigo Tarucha
-
Article
| Open Access Dichotomy of heavy and light pairs of holes in the t−J model
Dichotomy of heavy and light pairs of holes in the t−J model
The microscopic mechanism of superconducting pairing in hole-doped cuprates is still debated. Here, using state-of-the-art numerical techniques, the authors examine the properties of pairs of holes in a model relevant to cuprates revealing two types of bound states involving light and heavy hole pairs.
- A. Bohrdt
- , E. Demler
- & F. Grusdt
-
Article
| Open Access Charge-4e superconductivity and chiral metal in 45°-twisted bilayer cuprates and related bilayers
Charge-4e superconductivity and chiral metal in 45°-twisted bilayer cuprates and related bilayers
Liu et al. theoretically study maximally-twisted homo-bilayers, such as 45∘-twisted bilayer cuprates and 30∘-twisted bilayer graphene. Through renormalization group and Monte-Carlo calculations, the authors reveal the presence of charge-4e superconductivity and chiral-metal phases in the phase diagram.
- Yu-Bo Liu
- , Jing Zhou
- & Fan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Phase biasing of a Josephson junction using Rashba–Edelstein effect
Phase biasing of a Josephson junction using Rashba–Edelstein effect
The authors study transport in Nb-(Pt/Cu)-Nb Josephson junctions (JJ), where Pt/Cu is a Rashba interface. Due to the Rashba–Edelstein effect, a charge current leads to a non-equilibrium spin moment at the Pt/Cu interface, which can be measured from a shift of the Fraunhofer pattern of the JJ.
- Tapas Senapati
- , Ashwin Kumar Karnad
- & Kartik Senapati
-
Article
| Open Access Microscopic theory of colour in lutetium hydride
Microscopic theory of colour in lutetium hydride
Nitrogen-doped lutetium hydride, recently proposed as a superconductor at near-ambient conditions, features distinct color changes from blue to pink to red as a function of pressure. Using theoretical calculations, the authors identify the pink phase as hydrogen-deficient LuH2 and find that this phase is not a phonon-mediated superconductor near room temperature. Further, the color is controlled by the concentration of hydrogen vacancies.
- Sun-Woo Kim
- , Lewis J. Conway
- & Bartomeu Monserrat
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence for charge delocalization crossover in the quantum critical superconductor CeRhIn5
Evidence for charge delocalization crossover in the quantum critical superconductor CeRhIn5
Heavy-fermion superconductors feature a magnetic quantum critical point linked to the Kondo effect breakdown. Wang et al. use pressure-dependent Hall measurements to identify a crossover energy scale, confirming this in pure CeRhIn5, while revealing a shift to spin density wave criticality with Sn-doping.
- Honghong Wang
- , Tae Beom Park
- & Tuson Park
-
Article
| Open Access Precursor region with full phonon softening above the charge-density-wave phase transition in 2H-TaSe2
Precursor region with full phonon softening above the charge-density-wave phase transition in 2H-TaSe2
The authors study the charge-density-wave (CDW) compound 2H-TaSe2 by inelastic x-ray scattering combined with photoemission spectroscopy. They find evidence for a precursor region above the CDW transition temperature, which is characterized by an overdamped phonon mode and is not detectable by photoemission.
- Xingchen Shen
- , Rolf Heid
- & Frank Weber
-
Article
| Open Access Reentrance of interface superconductivity in a high-Tc cuprate heterostructure
Reentrance of interface superconductivity in a high-Tc cuprate heterostructure
The authors study interface superconductivity in over-doped La2-xSrxCuO4/La2CuO4 heterostructures. As x increases, the superconductivity is killed at x = 0.8 but fully recovers at x = 1.0, a “re-entrant” superconductivity.
- J. Y. Shen
- , C. Y. Shi
- & J. Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Superconducting nonlinear transport in optically driven high-temperature K3C60
Superconducting nonlinear transport in optically driven high-temperature K3C60
The authors report ultrafast transport measurements on the photo-excited superconducting state in K3C60. They observe characteristic superconducting nonlinear current-voltage responses.
- E. Wang
- , J. D. Adelinia
- & A. Cavalleri
-
Article
| Open Access Local control of superconductivity in a NbSe2/CrSBr van der Waals heterostructure
Local control of superconductivity in a NbSe2/CrSBr van der Waals heterostructure
Two-dimensional magnets and superconductors are emerging as tunable building blocks for quantum computing and superconducting spintronic devices. Here, Jo et al. demonstrate NbSe2/CrSBr van der Waals superconducting spin valves that exhibit infinite magnetoresistance and nonreciprocal charge transport, arising from a unique metamagnetic transition in CrSBr.
- Junhyeon Jo
- , Yuan Peisen
- & Luis E. Hueso
-
Article
| Open Access Signature of quantum criticality in cuprates by charge density fluctuations
Signature of quantum criticality in cuprates by charge density fluctuations
It has been suggested that the strange metal phase in cuprates stems from a quantum critical point slightly above optimal doping. By resonant x-ray scattering in two cuprate families in a wide doping range, Arpaia et al. show that charge density fluctuations could be associated with this quantum critical point.
- Riccardo Arpaia
- , Leonardo Martinelli
- & Giacomo Ghiringhelli
-
Article
| Open Access Rotational symmetry breaking in superconducting nickelate Nd0.8Sr0.2NiO2 films
Rotational symmetry breaking in superconducting nickelate Nd0.8Sr0.2NiO2 films
The authors study transport in the superconducting state of infinite-layer nickelate Nd0.8Sr0.2NiO2 films using a Corbino-disk configuration, finding that the magnetoresistance changes from isotropic to four-fold anisotropic with increasing magnetic field. At even higher field, an additional two-fold component emerges, which coincides with an anomalous upturn of the critical field.
- Haoran Ji
- , Yi Liu
- & Jian Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Dirac-fermion-assisted interfacial superconductivity in epitaxial topological-insulator/iron-chalcogenide heterostructures
Dirac-fermion-assisted interfacial superconductivity in epitaxial topological-insulator/iron-chalcogenide heterostructures
The authors study (Bi,Sb)2Te3/FeTe bilayers, which feature emergent superconductivity at the interface with Tc ~ 12 K. Through angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy and electrical transport measurements, they argue that the Dirac-fermion-mediated Ruderman-Kittel-Kasuya-Yosida-type interaction weakens antiferromagnetic order in FeTe layer, allowing for superconductivity.
- Hemian Yi
- , Lun-Hui Hu
- & Cui-Zu Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Nodal band-off-diagonal superconductivity in twisted graphene superlattices
Nodal band-off-diagonal superconductivity in twisted graphene superlattices
The authors theoretically study superconductivity in twisted-bilayer and twisted-trilayer graphene, finding that flavor polarization allows for Cooper pairing in which the pairs consist of electrons in different bands. Both intervalley phonons and fluctuations of a time-reversal-symmetric intervalley coherent order can favor such pairing.
- Maine Christos
- , Subir Sachdev
- & Mathias S. Scheurer
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative assessment of the universal thermopower in the Hubbard model
Quantitative assessment of the universal thermopower in the Hubbard model
High-temperature behaviour of thermopower is special in cuprates, allowing for theory-experiment comparisons. Wang et al. use quantum Monte Carlo to compute high temperature thermopower in the Hubbard model, demonstrating qualitative and quantitative agreement with experiments across multiple cuprate families.
- Wen O. Wang
- , Jixun K. Ding
- & Thomas P. Devereaux
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct spin and orbital dynamics in Sr2RuO4
Distinct spin and orbital dynamics in Sr2RuO4
The authors present resonant inelastic x-ray scattering measurements of Sr2RuO4 in the normal Fermi-liquid state. They find that spin excitations are confined below 200 meV, while orbital fluctuations appear only at higher energies. This separation of energy scales is a hallmark of Hund’s-rule-induced electron correlations.
- H. Suzuki
- , L. Wang
- & B. Keimer
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent superconductivity in topological-kagome-magnet/metal heterostructures
Emergent superconductivity in topological-kagome-magnet/metal heterostructures
The authors deposit non-superconducting metallic thin films on surfaces of the kagome Chern magnet TbMn6Sn6 and observe emergent superconductivity even though neither component is a superconductor. Furthermore, the superconducting state is quasi-two-dimensional and coexists with ferromagnetism, consistent with possible spin-triplet pairing and topological superconductivity.
- He Wang
- , Yanzhao Liu
- & Jian Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Intrinsic surface p-wave superconductivity in layered AuSn4
Intrinsic surface p-wave superconductivity in layered AuSn4
The authors study the layered superconductor AuSn4 (Tc = 2.4 K) and reveal a two-fold symmetric angular dependence, consistent with unconventional pairing. They argue that the two-fold symmetry results from the Rashba-driven mixture of p-wave surface and s-wave bulk contributions.
- Wenliang Zhu
- , Rui Song
- & Qi-Kun Xue
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-filtered measurements of Andreev bound states in semiconductor-superconductor nanowire devices
Spin-filtered measurements of Andreev bound states in semiconductor-superconductor nanowire devices
Andreev bound states can form in hybrid semiconducting-superconducting devices and can mirror the experimental signatures of the much sought topologically non-trivial Majorana bound states. Here, van Driel, Wang and coauthors present a method of directly measuring the spin-polarized excitation spectrum of Andreev bound states.
- David van Driel
- , Guanzhong Wang
- & Tom Dvir
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of unconventional superconductivity on the surface of the nodal semimetal CaAg1−xPdxP
Evidence of unconventional superconductivity on the surface of the nodal semimetal CaAg1−xPdxP
CaAg1−xPdxP is a nodal-line Dirac semimetal. Here, using ionic-liquid gated transport and soft point-contact spectroscopy, the authors show that this material realizes surface-confined unconventional superconductivity.
- Rikizo Yano
- , Shota Nagasaka
- & Satoshi Kashiwaya
-
Article
| Open Access Microwave-induced conductance replicas in hybrid Josephson junctions without Floquet—Andreev states
Microwave-induced conductance replicas in hybrid Josephson junctions without Floquet—Andreev states
The authors study conductance replicas emerging under microwave irradiation in the tunnelling spectrum of Josephson junctions in InAs/Al heterostructures, focusing on distinguishing the signatures of Floquet-Andreev states (FASs) from those of photon-assisted tunneling (PAT). They establish that PAT largely dominates the response to microwave radiation in their device.
- Daniel Z. Haxell
- , Marco Coraiola
- & Fabrizio Nichele
-
Article
| Open Access Microwave excitation of atomic scale superconducting bound states
Microwave excitation of atomic scale superconducting bound states
Magnetic impurities on superconductors lead to bound states within the superconducting gap, so called Yu-Shiba-Rusinov (YSR) states. Here, the authors study tunneling from a vanadium STM tip to a V(100) surface and show that YSR states can be excited at very low temperature by applying a microwave signal.
- Janis Siebrecht
- , Haonan Huang
- & Christian R. Ast
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-engineering the Andreev band structure of a three-terminal Josephson junction
Phase-engineering the Andreev band structure of a three-terminal Josephson junction
The authors study Andreev bound states (ABSs) in 3-terminal InAs/Al Josephson-junction devices. They find signatures of hybridization between two ABSs, with band structure tunable by electric currents that generate magnetic fluxes threading superconducting loops in the device.
- Marco Coraiola
- , Daniel Z. Haxell
- & Fabrizio Nichele
-
Article
| Open Access Calorimetric evidence for two phase transitions in Ba1−xKxFe2As2 with fermion pairing and quadrupling states
Calorimetric evidence for two phase transitions in Ba1−xKxFe2As2 with fermion pairing and quadrupling states
The authors report two anomalies in the specific heat of (Ba,K)Fe2As2, providing thermodynamic confirmation of the separation of superconducting Tc and the onset of time-reversal symmetry breaking (TRSB). Further, they argue that the TRSB is associated with a four-fermion condensate induced by phase fluctuations.
- Ilya Shipulin
- , Nadia Stegani
- & Vadim Grinenko
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent ferromagnetism with superconductivity in Fe(Te,Se) van der Waals Josephson junctions
Emergent ferromagnetism with superconductivity in Fe(Te,Se) van der Waals Josephson junctions
The authors study Josephson junctions where the superconductors are Fe(Te,Se) flakes and the weak link is just a 0.36 nm van-der-Waals gap between the two stacked flakes. They report global device-level transport signatures of interfacial ferromagnetism.
- Gang Qiu
- , Hung-Yu Yang
- & Kang L. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access High anisotropy in electrical and thermal conductivity through the design of aerogel-like superlattice (NaOH)0.5NbSe2
High anisotropy in electrical and thermal conductivity through the design of aerogel-like superlattice (NaOH)0.5NbSe2
Interlayer decoupling plays an essential role in realizing unprecedented properties. Here, authors construct a superlattice consisting of alternating layers of NbSe2 and highly porous hydroxide, realizing interlayer decoupling and thus realizing exotic monolayer behaviors in bulk materials.
- Ruijin Sun
- , Jun Deng
- & Xiaolong Chen

 Atomic-scale observation of localized phonons at FeSe/SrTiO3 interface
Atomic-scale observation of localized phonons at FeSe/SrTiO3 interface