News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Visualizing excitations at buried heterojunctions in organic semiconductor blends
Visualizing excitations at buried heterojunctions in organic semiconductor blends
A pump–push–probe time-resolved technique is developed to characterize the dynamics of photoexcitations at buried, disordered interfaces. Applied to organic bulk heterojunctions, the method provides insight on charge separation in photovoltaic films.
- Andreas C. Jakowetz
- , Marcus L. Böhm
- & Richard H. Friend
-
News & Views |
 Slow recombination unveiled
Slow recombination unveiled
One of the most salient features of hybrid lead halide perovskites is the extended lifetime of their photogenerated charge carriers. This property has now been shown experimentally to originate from a slow, thermally activated recombination process.
- Jacques-E. Moser
-
Review Article |
 Energy conversion approaches and materials for high-efficiency photovoltaics
Energy conversion approaches and materials for high-efficiency photovoltaics
This Review describes the sunlight conversion strategies — and their technological implementations — that are currently being investigated to realize solar cells with efficiencies beyond the Shockley–Queisser limit.
- Martin A. Green
- & Stephen P. Bremner
-
Article |
 Solution-based electrical doping of semiconducting polymer films over a limited depth
Solution-based electrical doping of semiconducting polymer films over a limited depth
A solution process for the diffusion of dopants in organic semiconducting films over a limited depth has been developed. The method is applied to single polymers and donor–acceptor mixtures, and for the realization of single-layer solar cells.
- Vladimir A. Kolesov
- , Canek Fuentes-Hernandez
- & Bernard Kippelen
-
Article |
 Reducing the efficiency–stability–cost gap of organic photovoltaics with highly efficient and stable small molecule acceptor ternary solar cells
Reducing the efficiency–stability–cost gap of organic photovoltaics with highly efficient and stable small molecule acceptor ternary solar cells
Ternary organic blends using two non-fullerene acceptors are shown to improve the efficiency and stability of low-cost solar cells based on P3HT and of high-performance photovoltaic devices based on low-bandgap donor polymers.
- Derya Baran
- , Raja Shahid Ashraf
- & Iain McCulloch
-
Article |
 Hybrid organic–inorganic inks flatten the energy landscape in colloidal quantum dot solids
Hybrid organic–inorganic inks flatten the energy landscape in colloidal quantum dot solids
An improved ligand-exchange process allows the realization of solution-deposited films of quantum dots with reduced energetic disorder and, as a result, solar cells with improved open-circuit voltage, charge-carrier transport and stability.
- Mengxia Liu
- , Oleksandr Voznyy
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Letter |
 Graded bandgap perovskite solar cells
Graded bandgap perovskite solar cells
The use of monolayers of hexagonal boron nitride as the cationic diffusion barrier and graphene aerogel mixed with spiro-OMeTAD as the hole transport layer allows the fabrication of graded bandgap perovskite solar cells with high efficiency.
- Onur Ergen
- , S. Matt Gilbert
- & Alex Zettl
-
Article |
 Direct–indirect character of the bandgap in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite
Direct–indirect character of the bandgap in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite
Time-resolved photo-conductance and microwave conductance investigations reveal that methylammonium lead iodide perovskites have an indirect bandgap at temperatures relevant to photovoltaic applications.
- Eline M. Hutter
- , María C. Gélvez-Rueda
- & Tom J. Savenije
-
News & Views |
 Strong absorption in stiff polymers
Strong absorption in stiff polymers
Greater rigidity of conjugated polymer backbones increases their light-harvesting ability, making them better performers in solar-cell applications.
- John Grey
-
Commentary |
 Toxicity of organometal halide perovskite solar cells
Toxicity of organometal halide perovskite solar cells
In the last few years, the advent of metal halide perovskite solar cells has revolutionized the prospects of next-generation photovoltaics. As this technology is maturing at an exceptional rate, research on its environmental impact is becoming increasingly relevant.
- Aslihan Babayigit
- , Anitha Ethirajan
- & Bert Conings
-
-
-
Editorial |
 A checklist for photovoltaic research
A checklist for photovoltaic research
To aid the reproducibility of published results for photovoltaic devices, from now on we will ask authors of relevant manuscripts to complete a checklist of key technical information that must be reported.
-
Article |
 Design principles for maximizing photovoltage in metal-oxide-protected water-splitting photoanodes
Design principles for maximizing photovoltage in metal-oxide-protected water-splitting photoanodes
Although protecting photoanodes using metal oxides is attractive for solar fuel applications, the photoanodes typically suffer from poor photovoltage. Now, insulating oxide layers are shown to promote enhanced photovoltages and general design principles are suggested.
- Andrew G. Scheuermann
- , John P. Lawrence
- & Paul C. McIntyre
-
Article |
 An electrodeposited inhomogeneous metal–insulator–semiconductor junction for efficient photoelectrochemical water oxidation
An electrodeposited inhomogeneous metal–insulator–semiconductor junction for efficient photoelectrochemical water oxidation
Water splitting requires a semiconductor to absorb light and a catalyst to enhance the kinetics of electron transfer. An electrodeposition method to produce efficient photoanodes for the photoelectrochemical oxidation of water to oxygen is presented.
- James C. Hill
- , Alan T. Landers
- & Jay A. Switzer
-
News & Views |
 Hovering solar cells
Hovering solar cells
Ultrathin, flexible and lightweight perovskite solar cells with improved stability in air can now power model airplanes for several hours.
- Michele Sessolo
- & Henk J. Bolink
-
Article |
 Flexible high power-per-weight perovskite solar cells with chromium oxide–metal contacts for improved stability in air
Flexible high power-per-weight perovskite solar cells with chromium oxide–metal contacts for improved stability in air
The use of a chromium oxide interlayer separating the perovskite film from the metal contacts improves the stability of perovskite solar cells in air. Deposited on thin plastic foils, these ultralight devices power model airplanes and dirigibles.
- Martin Kaltenbrunner
- , Getachew Adam
- & Siegfried Bauer
-
-
News & Views |
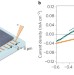 Perovskite cells charge forward
Perovskite cells charge forward
Now that certified energy conversion efficiencies for perovskite solar cells are above 20%, researchers are exploring other critical areas, such as understanding device hysteresis and film growth, as well as the replacement of lead and the development of tandem cell stacks. Cell stability remains a crucial issue.
- Martin A. Green
- & Thomas Bein
-
Article |
 Impact of mesoscale order on open-circuit voltage in organic solar cells
Impact of mesoscale order on open-circuit voltage in organic solar cells
The inclusion of long-range electrostatic effects in the modelling of donor–acceptor systems now leads to a more accurate estimation of the energy landscape and open-circuit voltage of organic solar cells.
- Carl Poelking
- , Max Tietze
- & Denis Andrienko
-
News & Views |
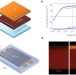 Switchable photovoltaics
Switchable photovoltaics
The migration of ions under the effect of an external electric field locally modifies the doping of organometal halide perovskite films. This is used to reversibly switch the photocurrent direction in very simple photovoltaic architectures.
- Nam-Gyu Park
-
Letter |
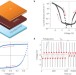 Giant switchable photovoltaic effect in organometal trihalide perovskite devices
Giant switchable photovoltaic effect in organometal trihalide perovskite devices
The direction of the current photogenerated in organic–inorganic perovskite films can be switched by poling the material with low electric fields that induce a reversible ion drift. Hybrid perovskites may thus find application as memristor devices.
- Zhengguo Xiao
- , Yongbo Yuan
- & Jinsong Huang
-
Article |
 Resonant energy transfer of triplet excitons from pentacene to PbSe nanocrystals
Resonant energy transfer of triplet excitons from pentacene to PbSe nanocrystals
Triplet excitons generated in a pentacene layer by singlet exciton fission are transferred to lead selenide colloidal nanocrystals with high efficiency when their energy matches the bandgap of the nanocrystals.
- Maxim Tabachnyk
- , Bruno Ehrler
- & Akshay Rao
-
Editorial |
 Perovskite fever
Perovskite fever
Staggering increases in the performance of organic–inorganic perovskite solar cells have renewed the interest in these materials. However, further developments and the support from academic and industrial partners will hinge on the reporting of accurate efficiency values.
-
News & Views |
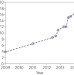 Continuing to soar
Continuing to soar
The dream of printing highly efficient solar cells is closer than ever to being realized. Solvent engineering has enabled the deposition of uniform perovskite semiconductor films that yield greater than 15% power-conversion efficiency.
- Michael D. McGehee
-
Commentary |
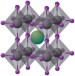 The light and shade of perovskite solar cells
The light and shade of perovskite solar cells
The rise of metal halide perovskites as light harvesters has stunned the photovoltaic community. As the efficiency race continues, questions on the control of the performance of perovskite solar cells and on its characterization are being addressed.
- Michael Grätzel
-
-
News & Views |
 The surface plays a core role
The surface plays a core role
Mastering the impact of surface chemistry on the electronic properties and stability of colloidal quantum dots enables the realization of architectures with enhanced photovoltaic performance and air stability.
- Delia J. Milliron
-
Article |
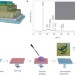 Solvent engineering for high-performance inorganic–organic hybrid perovskite solar cells
Solvent engineering for high-performance inorganic–organic hybrid perovskite solar cells
The performance of solar cells based on organic–inorganic perovskites strongly depends on the device architecture and processing conditions. It is now shown that solvent engineering enables the deposition of very dense perovskite layers on mesoporous titania, leading to photovoltaic devices with a high light-conversion efficiency and no hysteresis.
- Nam Joong Jeon
- , Jun Hong Noh
- & Sang Il Seok
-
-
Letter |
 Improved performance and stability in quantum dot solar cells through band alignment engineering
Improved performance and stability in quantum dot solar cells through band alignment engineering
Fabricating low-temperature solution-processed solar cells with good power-conversion efficiency and stability in ambient conditions has proved challenging. The use of ligands that protect colloidal quantum dots from degradation in air and tune their energy levels is now shown to be a viable approach for the realization of spin-coated solar cells with very high efficiency.
- Chia-Hao M. Chuang
- , Patrick R. Brown
- & Moungi G. Bawendi
-
-
Letter |
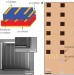 Printing-based assembly of quadruple-junction four-terminal microscale solar cells and their use in high-efficiency modules
Printing-based assembly of quadruple-junction four-terminal microscale solar cells and their use in high-efficiency modules
A strategy to overcome the maximum theoretical efficiency limit of single-junction solar cells is to realize stacked, multi-junction cells that are used under highly concentrated light. Now, a printing-based, scalable approach for the assembly of multi-junction solar cells in concentrator photovoltaic modules that reach a high power conversion efficiency is reported.
- Xing Sheng
- , Christopher A. Bower
- & John A. Rogers
-
-
News & Views |
 Efficient relaxation
Efficient relaxation
A study on carrier-collection efficiency in various organic photovoltaic systems now reveals that ultrafast relaxation of photoexcitations within the manifold of charge-transfer states does not impede mobile charge carrier generation.
- Daniel Moses
-
News & Views |
 Perovskites under the Sun
Perovskites under the Sun
Mixed-halide organic–inorganic hybrid perovskites are reported to display electron–hole diffusion lengths over 1 μm. This observation provides important insight into the charge-carrier dynamics of this class of semiconductors and increases the expectations for highly efficient and cheap solar cells.
- Maria Antonietta Loi
- & Jan C. Hummelen
-
Article |
 Efficient charge generation by relaxed charge-transfer states at organic interfaces
Efficient charge generation by relaxed charge-transfer states at organic interfaces
The efficiency of organic blends used for photovoltaic applications depends on their ability to convert photoexcited charges into free holes and electrons. It is now demonstrated that the lowermost energetic states formed at the donor/acceptor interface can reach conversion efficiencies close to 100%, and therefore do not behave as traps for charge carriers.
- Koen Vandewal
- , Steve Albrecht
- & Alberto Salleo
-
Letter |
 Potassium-induced surface modification of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin films for high-efficiency solar cells
Potassium-induced surface modification of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin films for high-efficiency solar cells
Compared with their rigid counterparts, thin-film solar cells grown on flexible substrates usually display lower power-conversion efficiencies. Now, the application of a post-deposition alkaline treatment that modifies the chemical composition of the surfaces of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin films reduces optical losses in these flexible photovoltaic architectures. Furthermore, efficiencies comparable to solar cells based on polycrystalline silicon are achieved.
- Adrian Chirilă
- , Patrick Reinhard
- & Ayodhya N. Tiwari
-
-
News & Views |
 Solar spin devices see the light
Solar spin devices see the light
Semiconductor devices that convert light of arbitrary polarization into a flow of electron spin have now been demonstrated using an approach that is applicable to any semiconductor material.
- Ron Jansen
-
Correspondence |
 Measuring internal quantum efficiency to demonstrate hot exciton dissociation
Measuring internal quantum efficiency to demonstrate hot exciton dissociation
- Markus Scharber
-
Correspondence |
 Measuring internal quantum efficiency to demonstrate hot exciton dissociation
Measuring internal quantum efficiency to demonstrate hot exciton dissociation
- Ardalan Armin
- , Yuliang Zhang
- & Almantas Pivrikas
-
Correspondence |
 Reply to 'Measuring internal quantum efficiency to demonstrate hot exciton dissociation'
Reply to 'Measuring internal quantum efficiency to demonstrate hot exciton dissociation'
- G. Grancini
- , M. Binda
- & G. Lanzani
-
Article |
 H2 evolution at Si-based metal–insulator–semiconductor photoelectrodes enhanced by inversion channel charge collection and H spillover
H2 evolution at Si-based metal–insulator–semiconductor photoelectrodes enhanced by inversion channel charge collection and H spillover
Photoelectrochemical water-splitting is a promising route for the renewable production of hydrogen, but trade-offs between photoelectrode stability and efficiency remain problematic. A metal–oxide–semiconductor photoelectrode architecture demonstrates stable and efficient water splitting using narrow-bandgap semiconductors. Substantial improvement in the performance of Si-based photocathodes is achieved by combining a high-quality SiO2 layer and bilayer metal catalysts.
- Daniel V. Esposito
- , Igor Levin
- & A. Alec Talin
-
-
News & Views |
 Some like it hot
Some like it hot
Excitation of organic donor–acceptor systems with high-energy light can produce hot charge-transfer states that are delocalized across the heterojunction and readily dissociate. Two studies now reveal the dynamics of this process and pave the way towards unravelling the details of the molecular landscape that favours fast photocarrier generation.
- Carlos Silva
-
Letter |
 Hot exciton dissociation in polymer solar cells
Hot exciton dissociation in polymer solar cells
The standard picture of organic photovoltaics predicts that excitons, which are created under light irradiation, thermalize before dissociation into free electrons and holes. Experimental results and calculations on a low-bandgap polymer–fullerene blend now illustrate the dynamics of hot charge-transfer states and their contribution to charge generation in bulk heterojunctions.
- G. Grancini
- , M. Maiuri
- & G. Lanzani
-
Article |
 Hot charge-transfer excitons set the time limit for charge separation at donor/acceptor interfaces in organic photovoltaics
Hot charge-transfer excitons set the time limit for charge separation at donor/acceptor interfaces in organic photovoltaics
Photocurrent generation in organic solar cells relies on the dissociation of excitons into free electrons and holes at donor/acceptor heterointerfaces. Femtosecond spectroscopy and non-adiabatic simulations on the phthalocyanine–fullerene model system now reveal the relaxation dynamics of hot charge-transfer excitons in this process.
- Askat E. Jailaubekov
- , Adam P. Willard
- & X-Y. Zhu
-

 Pushing the knowledge of interfaces
Pushing the knowledge of interfaces Cationic vibrations
Cationic vibrations The importance of coherence
The importance of coherence Perovskite photovoltaics
Perovskite photovoltaics