Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Mobile ion confinement for better thermoelectrics
Mobile ion confinement for better thermoelectrics
Restricting the directional segregation of mobile ions via strategic local ion confinement allows remarkable thermoelectric performance with better stability.
- Animesh Bhui
- & Kanishka Biswas
-
Article |
 Highly stabilized and efficient thermoelectric copper selenide
Highly stabilized and efficient thermoelectric copper selenide
Cu2Se is of interest for thermoelectrics as it is environmentally sustainable and has a high figure of merit ZT; however, copper ion migration impacts device stability. Here a co-doping strategy that combines steric and electrostatic effects is shown to improve device stability as well as improving ZT to 3.
- Haihua Hu
- , Yiwei Ju
- & Jing-Feng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Trapped O2 and the origin of voltage fade in layered Li-rich cathodes
Trapped O2 and the origin of voltage fade in layered Li-rich cathodes
Oxygen redox cathodes deliver higher energy densities than those based on transition metal redox but commonly exhibit voltage fade on extended cycling. The loss of O-redox capacity and voltage fade is shown to arise from a reduction in O2−/O2 redox process reversibility and O2 loss.
- John-Joseph Marie
- , Robert A. House
- & Peter G. Bruce
-
Article |
 Nanofeather ruthenium nitride electrodes for electrochemical capacitors
Nanofeather ruthenium nitride electrodes for electrochemical capacitors
Fast charging is driving extensive research on enhanced electrodes for high-performance electrochemical capacitors and micro-supercapacitors. Thick ruthenium nitride pseudocapacitive films are shown to exhibit enhanced capacitance with a time constant of less than 6 s.
- Huy Dinh Khac
- , Grace Whang
- & Christophe Lethien
-
Article |
 Nanosecond solvation dynamics in a polymer electrolyte for lithium batteries
Nanosecond solvation dynamics in a polymer electrolyte for lithium batteries
Solvation dynamics at picosecond timescales critically affect charge transport in aqueous systems, but conflicting values have been reported for organic electrolytes. Lifetimes on the order of 1 ns for mixtures of organic polymer and lithium salt exhibiting ultraslow dynamics of solvation shell break-up are now reported.
- Neel J. Shah
- , Chao Fang
- & Nitash P. Balsara
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid oxide coatings generate stable Cu catalysts for CO2 electroreduction
Hybrid oxide coatings generate stable Cu catalysts for CO2 electroreduction
Active and stable catalysts to accelerate the transition from fossil fuel to renewable feedstocks, reduce energy consumption and minimize environmental footprints are needed. Electrocatalysts based on copper nanocrystals encapsulated in hybrid alumina shells stable against structural reconstruction during CO2 electroreduction are reported.
- Petru P. Albertini
- , Mark A. Newton
- & Raffaella Buonsanti
-
Article |
 Photochemical tuning of dynamic defects for high-performance atomically dispersed catalysts
Photochemical tuning of dynamic defects for high-performance atomically dispersed catalysts
Developing active and stable atomically dispersed catalysts is challenging because of weak non-specific interactions between catalytically active metal atoms and supports. A general method for synthesizing these catalysts via photochemical defect tuning for controlling oxygen-vacancy dynamics is proposed.
- Chan Woo Lee
- , Byoung-Hoon Lee
- & Taeghwan Hyeon
-
Article
| Open Access Unlocking Li superionic conductivity in face-centred cubic oxides via face-sharing configurations
Unlocking Li superionic conductivity in face-centred cubic oxides via face-sharing configurations
Oxides with a face-centred cubic anion sublattice are generally not considered as solid-state electrolytes. Li superionic conductivity in face-centred cubic oxides with face-sharing Li configurations have now been created through cation over-stoichiometry in rocksalt-type lattices via excess Li.
- Yu Chen
- , Zhengyan Lun
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
Article
| Open Access Chemo-mechanical failure mechanisms of the silicon anode in solid-state batteries
Chemo-mechanical failure mechanisms of the silicon anode in solid-state batteries
Although silicon anodes are promising for solid-state batteries, they still suffer from poor electrochemical performance. Chemo-mechanical failure mechanisms of composite Si|Li6PS5Cl and solid-electrolyte-free silicon anodes are now revealed and should help in designing improved electrodes.
- Hanyu Huo
- , Ming Jiang
- & Jürgen Janek
-
Article |
 Fe–Ni-based alloys as highly active and low-cost oxygen evolution reaction catalyst in alkaline media
Fe–Ni-based alloys as highly active and low-cost oxygen evolution reaction catalyst in alkaline media
NiFe-based oxo-hydroxides are active for the oxygen evolution reaction but suffer from complex synthesis and durability when deposited. Easily processable Fe–Ni alloys with a highly active oxo-hydroxide surface are now shown to pave the way for oxygen-evolving electrodes for alkaline water electrolysers.
- Lucile Magnier
- , Garance Cossard
- & Marian Chatenet
-
Article
| Open Access Shallow defects and variable photoluminescence decay times up to 280 µs in triple-cation perovskites
Shallow defects and variable photoluminescence decay times up to 280 µs in triple-cation perovskites
Quantifying recombination in halide perovskites is crucial, but quantitative analysis remains rare. Here the authors observe a long-lived and continuously changing photoluminescence decay time due to the high density of shallow defects and substantial rates of charge carrier trapping.
- Ye Yuan
- , Genghua Yan
- & Thomas Kirchartz
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemical and chemical cycle for high-efficiency decoupled water splitting in a near-neutral electrolyte
Electrochemical and chemical cycle for high-efficiency decoupled water splitting in a near-neutral electrolyte
Hydrogen produced by water splitting using renewable electricity is key to achieve net-zero carbon emissions. Decoupling hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions during electrolysis is attractive but efficiency and operational challenges remain. A process producing hydrogen and oxygen in separate cells and supporting continuous operation in a membraneless system is now proposed.
- Ilya Slobodkin
- , Elena Davydova
- & Avner Rothschild
-
Article |
 Fast cycling of lithium metal in solid-state batteries by constriction-susceptible anode materials
Fast cycling of lithium metal in solid-state batteries by constriction-susceptible anode materials
Interfacial reactions between lithium and anodes are not well understood in an all-solid environment. For the silicon anode we now demonstrate that, rather than strong Li–Si alloying at the conventional solid–liquid interface, the lithiation reaction of micrometre-sized Si can be greatly constricted at the solid–solid interface.
- Luhan Ye
- , Yang Lu
- & Xin Li
-
Feature |
 Better standards are needed for membrane materials
Better standards are needed for membrane materials
Tae Hoon Lee and Zachary P. Smith argue that some of the most exciting materials that could be used for gas separations are metastable or crystalline, with properties that are altered by sample preparation and testing, but there are no widely accepted standards.
- Tae Hoon Lee
- & Zachary P. Smith
-
Feature |
 Thermoelectric measurements
Thermoelectric measurements
Joseph Heremans and Joshua Martin discuss the reproducibility of thermoelectric measurements and conclude that the uncertainty on the figure of merit zT is of the order of 15–20%.
- Joseph P. Heremans
- & Joshua Martin
-
Article
| Open Access Space charge governs the kinetics of metal exsolution
Space charge governs the kinetics of metal exsolution
The self-assembly of metallic nanoparticles on oxide supports via metal exsolution relies on dopant transport, but strong electrostatic gradients and space charges typically control the properties of surfaces. The surface–dopant interaction is shown to be the main determining factor for the exsolution kinetics of nickel in a perovskite system.
- Moritz L. Weber
- , Břetislav Šmíd
- & Christian Lenser
-
News & Views |
 Engineering porous crystals to do different things
Engineering porous crystals to do different things
An important but difficult separation, the removal of carbon monoxide from humid gas mixtures comprising oxygen, nitrogen and hydrocarbons, is addressed by exploiting Cu(I) coordination chemistry and framework flexibility.
- Michael J. Zaworotko
-
News & Views |
 Through the MOF looking glass
Through the MOF looking glass
Processible centimetre-scale porous glasses using zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF) materials are developed, while fine-tuning of the processing conditions allows control of pore size and molecular sieving properties.
- Georgia R. F. Orton
- & Neil R. Champness
-
Article
| Open Access Precise control over gas-transporting channels in zeolitic imidazolate framework glasses
Precise control over gas-transporting channels in zeolitic imidazolate framework glasses
Porosity of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks can be preserved beyond glass transition and melt processing. Here centimetre-scale porous glasses are demonstrated, whereas liquid processing enables fine-tuning of the size of the gas-transporting channels for molecular sieving.
- Oksana Smirnova
- , Seungtaik Hwang
- & Alexander Knebel
-
Research Briefing |
 Click-chemistry polymer membranes for hydrocarbon mixture fractionation
Click-chemistry polymer membranes for hydrocarbon mixture fractionation
Polymers made by click chemistry with spirocyclic building blocks form membranes that separate the components of crude oil based on molecular size and type, potentially using far less energy than distillation. Key enablers of this separation are moderate levels of polymer dynamic motion and frustrated chain packing.
-
Research Briefing |
 Machine-learning-accelerated selection of perovskite passivants
Machine-learning-accelerated selection of perovskite passivants
The discovery of passivating agents for perovskite photovoltaics can be an arduous and time-consuming process. Now, a machine-learning model is reported that accelerates the selection of bifunctional pseudo-halide passivators. The identified pseudo-halide passivators were experimentally shown to enhance the performance of perovskite solar cells.
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast vibrational control of organohalide perovskite optoelectronic devices using vibrationally promoted electronic resonance
Ultrafast vibrational control of organohalide perovskite optoelectronic devices using vibrationally promoted electronic resonance
Optically stimulated vibrational control for materials has the potential to improve the performance of optoelectronic devices. The vibrational control of FAPbBr3 perovskite solar cells has been demonstrated, where the fast dynamics of coupling between cations and inorganic sublattice may suppress non-radiative recombinations in perovskites, leading to reduced voltage losses.
- Nathaniel. P. Gallop
- , Dmitry R. Maslennikov
- & Artem A. Bakulin
-
Article |
 Quasi-open Cu(i) sites for efficient CO separation with high O2/H2O tolerance
Quasi-open Cu(i) sites for efficient CO separation with high O2/H2O tolerance
Chemical adsorption of CO on open metal sites enables separation from other gases but leads to selectivity and stability issues. Quasi-open metal sites in metal–organic frameworks are proposed here, which are accessible only by CO-induced structural transformation, enabling CO separation to 9N purity.
- Xue-Wen Zhang
- , Chao Wang
- & Jie-Peng Zhang
-
Article |
 Localized high-concentration electrolytes get more localized through micelle-like structures
Localized high-concentration electrolytes get more localized through micelle-like structures
Liquid electrolytes in batteries are considered to be macroscopically homogeneous ionic transport media despite having a complex chemical composition and atomistic solvation structures. A micelle-like structure in a localized high-concentration electrolyte for which the solvent acts as a surfactant is reported.
- Corey M. Efaw
- , Qisheng Wu
- & Bin Li
-
Article |
 Active learning guides discovery of a champion four-metal perovskite oxide for oxygen evolution electrocatalysis
Active learning guides discovery of a champion four-metal perovskite oxide for oxygen evolution electrocatalysis
Multi-metal and perovskite oxides are attractive as oxygen evolution electrocatalysts, and thus far the most promising candidates have emerged from experimental methodologies. Active-learning models supplemented by structural-characterization data and closed-loop experimentation can now identify a perovskite oxide with outstanding performance.
- Junseok Moon
- , Wiktor Beker
- & Bartosz A. Grzybowski
-
Article |
 Anion optimization for bifunctional surface passivation in perovskite solar cells
Anion optimization for bifunctional surface passivation in perovskite solar cells
Pseudo-halide anion engineering is an effective surface passivation strategy for perovskite-based optoelectronics but the large chemical space of molecules limits its potential. Here, the authors create a machine learning workflow to find optimized pseudo-halide anions, which are verified in devices with improved performances.
- Jian Xu
- , Hao Chen
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article |
 Sequencing polymers to enable solid-state lithium batteries
Sequencing polymers to enable solid-state lithium batteries
Solid polymer electrolytes are crucial for the development of lithium batteries, but their lower ionic conductivity compared with liquid/ceramics at room temperature limits their practical use. Precise positioning of designed repeating units in alternating polymer sequences now allows the Li+ conductivity to be tuned by up to three orders of magnitude.
- Shantao Han
- , Peng Wen
- & Mao Chen
-
Article |
 Solution-processable polytriazoles from spirocyclic monomers for membrane-based hydrocarbon separations
Solution-processable polytriazoles from spirocyclic monomers for membrane-based hydrocarbon separations
Thermal fractionation of petroleum consumes large amounts of energy. Here stable microporous polymers are synthesized using click chemistry, which have similar performance to commercial polyimides for the fractionation of light crude oils and successful application to heavy feeds under realistic conditions.
- Nicholas C. Bruno
- , Ronita Mathias
- & M. G. Finn
-
Article |
 Optimizing hierarchical membrane/catalyst systems for oxidative coupling of methane using additive manufacturing
Optimizing hierarchical membrane/catalyst systems for oxidative coupling of methane using additive manufacturing
Membrane/catalyst systems in the oxidative coupling of methane are promising for their high product selectivity but suffer from low volumetric chemical conversion rates, high capital cost and optimizing performance. A dual-layer additive manufacturing process, based on phase inversion, is now proposed to optimize a hollow-fibre membrane/catalyst system.
- James Wortman
- , Valentina Omoze Igenegbai
- & Suljo Linic
-
Article |
 Decoupling the roles of Ni and Co in anionic redox activity of Li-rich NMC cathodes
Decoupling the roles of Ni and Co in anionic redox activity of Li-rich NMC cathodes
Lithium-rich nickel manganese cobalt oxide cathodes are widely explored due to their high capacities related to their anionic redox chemistry. A compositional optimization pathway for these materials investigating the variation of using cobalt and nickel now provides valuable guidelines for future high-capacity cathode design.
- Biao Li
- , Zengqing Zhuo
- & Jean-Marie Tarascon
-
Article |
 Improving lithium-ion cells by replacing polyethylene terephthalate jellyroll tape
Improving lithium-ion cells by replacing polyethylene terephthalate jellyroll tape
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) tape is widely used for lithium-ion batteries but its chemical stability has been largely overlooked. Reversible self-discharge is now shown to be virtually eliminated in LiFePO4–graphite cells by replacing PET with polypropylene jellyroll tape.
- Anu Adamson
- , Kenneth Tuul
- & Michael Metzger
-
Perspective |
 Colloidal robotics
Colloidal robotics
This Perspective provides an overview on the emergent field of colloidal robotics, discussing recent developments on colloidal and micrometre-sized particles that can perform functions such as sensing, communication, computation and motion.
- Albert Tianxiang Liu
- , Marek Hempel
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Article |
 Precise molecular sieving of ethylene from ethane using triptycene-derived submicroporous carbon membranes
Precise molecular sieving of ethylene from ethane using triptycene-derived submicroporous carbon membranes
Ethylene separation from ethane is the most energy-intensive separation in the chemical process industry, but so far membranes have not exceeded an ethylene/ethane selectivity of >20 in mixed gases. Here a carbon molecular sieve with an ethylene selectivity of ~100 and long-term stability under high-pressure gas is reported.
- Khalid Hazazi
- , Yingge Wang
- & Ingo Pinnau
-
Article |
 Extreme lithium-metal cycling enabled by a mixed ion- and electron-conducting garnet three-dimensional architecture
Extreme lithium-metal cycling enabled by a mixed ion- and electron-conducting garnet three-dimensional architecture
The development of solid-state Li-metal batteries has been limited by Li plating and stripping rates and the formation of dendrites at relevant current densities. Single-phase mixed ion- and electron-conducting garnet with comparable Li-ion and electronic conductivities is now proposed to tackle these issues.
- George V. Alexander
- , Changmin Shi
- & Eric D. Wachsman
-
News & Views |
 A deeper look into argyrodite phonons
A deeper look into argyrodite phonons
By monitoring the lattice dynamics of single-crystal argyrodite Ag8SnSe6 through the superionic transition, low thermal conductivity and ionic transport are found to arise from extreme phonon anharmonicity.
- M. de Boissieu
-
Article |
 Amorphous nickel hydroxide shell tailors local chemical environment on platinum surface for alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction
Amorphous nickel hydroxide shell tailors local chemical environment on platinum surface for alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction
Elaborated catalysts design can substantially enhance performance under unfavourable reaction conditions. Amorphous nickel hydroxide proton sieve used to modify local chemical environment on a platinum surface results in unprecedented performance for alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction.
- Chengzhang Wan
- , Zisheng Zhang
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Perspective |
 Sustainability considerations for organic electronic products
Sustainability considerations for organic electronic products
It is imperative that sustainability issues are considered throughout the life cycle of modern organic electronic devices. Here McCulloch and colleagues evaluate the status of embedded carbon, options for more sustainable materials, and recycling solutions both during manufacturing and at the end of life in organic electronic products.
- Iain McCulloch
- , Michael Chabinyc
- & Scott Edward Watkins
-
Article |
 Extreme phonon anharmonicity underpins superionic diffusion and ultralow thermal conductivity in argyrodite Ag8SnSe6
Extreme phonon anharmonicity underpins superionic diffusion and ultralow thermal conductivity in argyrodite Ag8SnSe6
Superionic materials are of interest for solid-state batteries or thermoelectrics, yet a clear understanding of the atomistic mechanisms is lacking. Here it is shown that transverse acoustic phonons persist above the superionic transition in argyrodite Ag8SnSe6, and that the free-Se sublattice controls fast Ag cation diffusion.
- Qingyong Ren
- , Mayanak K. Gupta
- & Jie Ma
-
News & Views |
 Unlocked sieving potential
Unlocked sieving potential
A strategy of using a high ligand/metal ion concentration ratio eliminates lattice defects in polycrystalline zirconium metal–organic framework membranes, enhancing their molecular sieving performance.
- Jun Lu
- & Huanting Wang
-
News & Views |
 A catalyst for low-temperature CO2 activation
A catalyst for low-temperature CO2 activation
A low-valence carbon-doped ruthenium oxide-based catalytic material achieved a catalytic trinity of superior activity, selectivity and stability during the conversion of carbon dioxide into methane at low temperatures.
- Xin Zhang
- & Abhishek Dutta Chowdhury
-
Letter
| Open Access Probing lithium mobility at a solid electrolyte surface
Probing lithium mobility at a solid electrolyte surface
Understanding lithium dynamics in solid-state electrolytes used for Li-ion batteries can be challenging. Using nonlinear extreme-ultraviolet spectroscopies, a direct spectral signature of surface lithium ions showing a distinct blueshift relative to the bulk absorption spectra is observed in a prototypical solid-state electrolyte.
- Clarisse Woodahl
- , Sasawat Jamnuch
- & Michael Zuerch
-
Article |
 Imaging the strain evolution of a platinum nanoparticle under electrochemical control
Imaging the strain evolution of a platinum nanoparticle under electrochemical control
Surface strain can be used in gas phase catalysis and electrocatalysis to control the binding energies of adsorbates on active sites, but in situ or operando strain measurements can be challenging. Coherent diffraction now allows strain inside individual Pt nanoparticles to be mapped and quantified under electrochemical control.
- Clément Atlan
- , Corentin Chatelier
- & Marie-Ingrid Richard
-
Article |
 A soft co-crystalline solid electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries
A soft co-crystalline solid electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries
Alternative solid electrolytes with enhanced thermal and chemical stability are key for advancing lithium batteries. A soft solid electrolyte with improved stability and ionic conductivity, overcoming several limitations of conventional materials, is now reported.
- Prabhat Prakash
- , Birane Fall
- & Michael J. Zdilla
-
News & Views |
 Measuring the potential of zero charge
Measuring the potential of zero charge
A second-harmonic generation approach enables the direct measurement of the potential of zero charge at electrochemical interfaces.
- Jan Rossmeisl
-
Research Briefing |
 Revealing the origin of local atomic disorder in energy materials
Revealing the origin of local atomic disorder in energy materials
Spectroscopic and structural measurements often give conflicting results about the role of disorder in determining the properties of energy materials. A hybrid neutron scattering technique is used to measure atomic correlations in time and space for cubic GeTe, revealing that anisotropic elastic interactions mimic disorder but the time-averaged structure is crystalline.
-
Article |
 The role of the electrolyte in non-conjugated radical polymers for metal-free aqueous energy storage electrodes
The role of the electrolyte in non-conjugated radical polymers for metal-free aqueous energy storage electrodes
Redox-active non-conjugated radical polymers are promising candidates for metal-free aqueous batteries but their energy storage mechanism in an aqueous environment remains unclear. The role of the electrolyte in such polymers for designing metal-free aqueous energy storage electrodes is now elucidated.
- Ting Ma
- , Cheng-Han Li
- & Jodie L. Lutkenhaus
-
Article |
 A multiscale ion diffusion framework sheds light on the diffusion–stability–hysteresis nexus in metal halide perovskites
A multiscale ion diffusion framework sheds light on the diffusion–stability–hysteresis nexus in metal halide perovskites
This study identifies a fundamental link between slow-moving ions inside grains and fast-moving ions along grain boundaries in metal halide perovskites that governs their environmental stability and current–voltage responses.
- Masoud Ghasemi
- , Boyu Guo
- & Aram Amassian
-
Letter
| Open Access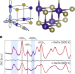 Dynamic crystallography reveals spontaneous anisotropy in cubic GeTe
Dynamic crystallography reveals spontaneous anisotropy in cubic GeTe
Cubic materials such as GeTe have low lattice thermal conductivity, thought to arise from a non-cubic local structural transition. Here, using a variable-shutter pair distribution function method, the average structure is shown to be crystalline but with anisotropic dynamics at higher temperatures.
- Simon A. J. Kimber
- , Jiayong Zhang
- & Simon J. L. Billinge
-
Article |
 Optical method for quantifying the potential of zero charge at the platinum–water electrochemical interface
Optical method for quantifying the potential of zero charge at the platinum–water electrochemical interface
The electric field created at an electrode–electrolyte interface can polarize the electrode’s surface and nearby molecules. Although its effect can be countered by an applied potential, quantifying the value of this potential is difficult. An optical method for determining the potential of zero charge at an electrochemical interface is now presented.
- Pengtao Xu
- , Alexander D. von Rueden
- & Jin Suntivich

 Effect of pre-intercalation on Li-ion diffusion mapped by topochemical single-crystal transformation and operando investigation
Effect of pre-intercalation on Li-ion diffusion mapped by topochemical single-crystal transformation and operando investigation