Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Clathrin-associated AP-1 controls termination of STING signalling
Clathrin-associated AP-1 controls termination of STING signalling
The adaptor protein AP-1 controls the shutdown of STING signalling through a mechanism in which AP-1 recognizes a dileucine motif in phosphorylated STING, which leads to targeted transport of STING to the endolysosomal system for degradation.
- Ying Liu
- , Pengbiao Xu
- & Andrea Ablasser
-
Article
| Open Access Organizing structural principles of the IL-17 ligand–receptor axis
Organizing structural principles of the IL-17 ligand–receptor axis
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of IL-25–IL-17RB–IL-17RA and IL-17A–IL-17RC–IL-17RA complexes show a tip-to-tip architecture, which is a key organizing principle of the IL-17 receptor family.
- Steven C. Wilson
- , Nathanael A. Caveney
- & K. Christopher Garcia
-
Article |
 CRISPR screens unveil signal hubs for nutrient licensing of T cell immunity
CRISPR screens unveil signal hubs for nutrient licensing of T cell immunity
CRISPR screening and protein–protein interaction networks identify components and mechanisms of nutrient-dependent mTORC1 signalling in regulatory T cells and reveal how mTORC1 integrates immunological cues and nutrient signals for adaptive immunity.
- Lingyun Long
- , Jun Wei
- & Hongbo Chi
-
Article |
 Lipid signalling enforces functional specialization of Treg cells in tumours
Lipid signalling enforces functional specialization of Treg cells in tumours
Identification of a metabolic checkpoint involving lipid signalling that is specific to regulatory T cells (Treg cells) in the tumour microenvironment raises the possibility of targeting this checkpoint for treatment of cancer.
- Seon Ah Lim
- , Jun Wei
- & Hongbo Chi
-
Article |
 IFITM3 functions as a PIP3 scaffold to amplify PI3K signalling in B cells
IFITM3 functions as a PIP3 scaffold to amplify PI3K signalling in B cells
IFITM3 shifts upon phosphorylation from acting as an antiviral effector to being a scaffold for PIP3 and thereby amplifies PI3K signalling, which can be co-opted for malignant transformation in B cell leukaemia and lymphoma.
- Jaewoong Lee
- , Mark E. Robinson
- & Markus Müschen
-
Article |
 Immune receptor inhibition through enforced phosphatase recruitment
Immune receptor inhibition through enforced phosphatase recruitment
A approach termed ‘receptor inhibition by phosphatase recruitment’ is described for attenuating both tonic and ligand-activated cell-surface receptor signalling.
- Ricardo A. Fernandes
- , Leon Su
- & K. Christopher Garcia
-
Article |
 Structural mechanism of cGAS inhibition by the nucleosome
Structural mechanism of cGAS inhibition by the nucleosome
Using cryo-electron microscopy, the authors determine the structure of cGAS bound to nucleosomes and present evidence for the mechanism by which nucleosome binding to cGAS prevents cGAS dimerization and its binding to free double-stranded DNA.
- Ganesh R. Pathare
- , Alexiane Decout
- & Andrea Ablasser
-
Article |
 TASL is the SLC15A4-associated adaptor for IRF5 activation by TLR7–9
TASL is the SLC15A4-associated adaptor for IRF5 activation by TLR7–9
The interaction between TASL and SLC15A4 links endolysosomal Toll-like receptors to the transcription factor IRF5, providing a mechanistic explanation for the involvement of the complex in systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Leonhard X. Heinz
- , JangEun Lee
- & Giulio Superti-Furga
-
Article |
 Activity of caspase-8 determines plasticity between cell death pathways
Activity of caspase-8 determines plasticity between cell death pathways
Alternative cell death pathways are revealed in the absence of caspase-8-dependent apoptosis and MLKL-dependent necroptosis.
- Kim Newton
- , Katherine E. Wickliffe
- & Vishva M. Dixit
-
Letter |
 SLC19A1 transports immunoreactive cyclic dinucleotides
SLC19A1 transports immunoreactive cyclic dinucleotides
A genome-wide CRISPR-interference screen is used to identify the reduced folate carrier SLC19A1 as the major transporter of cyclic dinucleotides in human cells, with potential roles in immunotherapeutic treatment of cancer, immune responses to pathogens and inflammatory diseases.
- Rutger D. Luteijn
- , Shivam A. Zaver
- & David H. Raulet
-
Article |
 Mechanosensation of cyclical force by PIEZO1 is essential for innate immunity
Mechanosensation of cyclical force by PIEZO1 is essential for innate immunity
PIEZO1 signalling mediates activation of a proinflammatory response to cyclical pressure fluctuations in immune cells.
- Angel G. Solis
- , Piotr Bielecki
- & Richard A. Flavell
-
Letter |
 FBXO38 mediates PD-1 ubiquitination and regulates anti-tumour immunity of T cells
FBXO38 mediates PD-1 ubiquitination and regulates anti-tumour immunity of T cells
PD-1 undergoes internalization, FBXO38-mediated ubiquitination and proteasome degradation in activated T cells, and inhibition of this pathway dampens anti-tumour immunity of T cells.
- Xiangbo Meng
- , Xiwei Liu
- & Chenqi Xu
-
Letter |
 Targeting STING with covalent small-molecule inhibitors
Targeting STING with covalent small-molecule inhibitors
The discovery and characterization of small-molecule antagonists that inhibit the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) protein may help to develop therapies for the treatment of autoinflammatory disease.
- Simone M. Haag
- , Muhammet F. Gulen
- & Andrea Ablasser
-
Letter |
 A multiprotein supercomplex controlling oncogenic signalling in lymphoma
A multiprotein supercomplex controlling oncogenic signalling in lymphoma
A pro-survival multiprotein signalling supercomplex consisting of the B cell receptor, MYD88, TLR9 and mTOR is discovered that coordinates NF-κB activation in diffuse large B cell lymphoma, and provides mechanistic insight into the efficacy of drug combinations.
- James D. Phelan
- , Ryan M. Young
- & Louis M. Staudt
-
Letter |
 Hippo/Mst signalling couples metabolic state and immune function of CD8α+ dendritic cells
Hippo/Mst signalling couples metabolic state and immune function of CD8α+ dendritic cells
A data-driven analysis helps to identify specific roles of the Hippo signalling kinases Mst1 and Mst2 in integrating metabolic activity and cytokine signalling in dendritic cells, and thereby orchestrating immune cell function.
- Xingrong Du
- , Jing Wen
- & Hongbo Chi
-
Letter |
 Homeostatic control of metabolic and functional fitness of Treg cells by LKB1 signalling
Homeostatic control of metabolic and functional fitness of Treg cells by LKB1 signalling
The tumour suppressor liver kinase B1 (LKB1) regulates the metabolic and functional fitness of regulatory T cells in the control of immune tolerance and homeostasis.
- Kai Yang
- , Daniel Bastardo Blanco
- & Hongbo Chi
-
Letter |
 m6A mRNA methylation controls T cell homeostasis by targeting the IL-7/STAT5/SOCS pathways
m6A mRNA methylation controls T cell homeostasis by targeting the IL-7/STAT5/SOCS pathways
The authors assess the role of N6-methyladenosine in T cell development and function, and show that RNA methylation controls T cell homeostasis by regulating IL-7-mediated STAT5 activation.
- Hua-Bing Li
- , Jiyu Tong
- & Richard A. Flavell
-
Letter |
 RIPK1 inhibits ZBP1-driven necroptosis during development
RIPK1 inhibits ZBP1-driven necroptosis during development
In the absence of RIPK1, ZBP1 engages RIPK3 in a RHIM-dependent manner and acts as a critical activator of RIPK3/MLKL-dependent necroptosis.
- Kim Newton
- , Katherine E. Wickliffe
- & Vishva M. Dixit
-
Letter |
 Ionic immune suppression within the tumour microenvironment limits T cell effector function
Ionic immune suppression within the tumour microenvironment limits T cell effector function
Potassium ions released by necrotic cells in tumours impair T cell function by increasing the intracellular potassium concentration in vitro and in vivo.
- Robert Eil
- , Suman K. Vodnala
- & Nicholas P. Restifo
-
Article |
 Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death
Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death
CRISPR-Cas9 genome-editing screens identify gasdermin D as a substrate for inflammatory caspases, and its N-terminal cleavage fragment, as well as the equivalent regions in other gasdermins, is shown to be capable of inducing pyroptosis.
- Jianjin Shi
- , Yue Zhao
- & Feng Shao
-
Letter |
 Cell intrinsic immunity spreads to bystander cells via the intercellular transfer of cGAMP
Cell intrinsic immunity spreads to bystander cells via the intercellular transfer of cGAMP
The cytoplasmic DNA receptor cGAS catalyses the synthesis of the second messenger cGAMP, which in turn activates type I interferon via STING; this study shows that cGAMP is transmitted to neighbouring cells via gap junction channels and activates STING, thus inducing an antiviral state in these bystander cells independent of paracrine interferon signalling.
- Andrea Ablasser
- , Jonathan L. Schmid-Burgk
- & Veit Hornung
-
Letter |
 An siRNA screen for NFAT activation identifies septins as coordinators of store-operated Ca2+ entry
An siRNA screen for NFAT activation identifies septins as coordinators of store-operated Ca2+ entry
A genome-wide RNA interference analysis identifies the septin family of cytoskeletal filaments as important regulators of store-operated Ca2+ entry into the cell; septins are shown to organize plasma membrane microdomains important in STIM1 and ORAI1 signalling, and may also be relevant in membrane microdomains underlying other signalling processes.
- Sonia Sharma
- , Ariel Quintana
- & Patrick G. Hogan
-
Letter |
 cGAS produces a 2′-5′-linked cyclic dinucleotide second messenger that activates STING
cGAS produces a 2′-5′-linked cyclic dinucleotide second messenger that activates STING
Cytosolic DNA induces type I interferon via activation of STING; the immediate STING activator is produced by the recently identified DNA sensor cGAS and is shown here to be an unorthodox cyclic dinucleotide harbouring a 2′-5′ linkage between guanosine and adenosine.
- Andrea Ablasser
- , Marion Goldeck
- & Veit Hornung
-
Letter |
 OTUD7B controls non-canonical NF-κB activation through deubiquitination of TRAF3
OTUD7B controls non-canonical NF-κB activation through deubiquitination of TRAF3
The deubiquitinase OTUD7B is shown to regulate the non-canonical NF-κB pathway by inhibiting TRAF3 proteolysis.
- Hongbo Hu
- , George C. Brittain
- & Shao-Cong Sun
-
Letter |
 Interleukin receptor activates a MYD88–ARNO–ARF6 cascade to disrupt vascular stability
Interleukin receptor activates a MYD88–ARNO–ARF6 cascade to disrupt vascular stability
Interleukin-1β-induced disruption to endothelial stability and vascular permeability in a human in vitro model is shown to be independent of downstream nuclear factor-κB activation, relying instead on a MYD88–ARNO–ARF6 signalling cascade; inhibiting proteins involved in this pathway is shown to improve outcomes in animal models of inflammatory disease.
- Weiquan Zhu
- , Nyall R. London
- & Dean Y. Li
-
Letter |
 Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia is driven by antigen-independent cell-autonomous signalling
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia is driven by antigen-independent cell-autonomous signalling
B-cell receptor (BCR) signalling in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) is found not to be dependent on exogenous antigens; instead, signalling may involve the binding of the BCR heavy-chain complementarity-determining region to self epitopes on the same receptor, a finding that may have important implications for understanding the pathogenesis of CLL and potential therapeutic approaches.
- Marcus Dühren-von Minden
- , Rudolf Übelhart
- & Hassan Jumaa
-
Letter |
 Phosphorylation of NLRC4 is critical for inflammasome activation
Phosphorylation of NLRC4 is critical for inflammasome activation
Phosphorylation of the NOD-like receptor NLRC4 is essential for activation of the NLRC4 inflammasome complex in response to bacterial stimuli.
- Yan Qu
- , Shahram Misaghi
- & Vishva M. Dixit
-
Research Highlights |
Pathway from breast to bone
-
Letter |
 NLRP6 negatively regulates innate immunity and host defence against bacterial pathogens
NLRP6 negatively regulates innate immunity and host defence against bacterial pathogens
The Nod-like receptor family member NLRP6 is characterized and shown to be a negative regulator of inflammatory signalling, dampening host responses against bacterial infections and impeding bacterial clearance.
- Paras K. Anand
- , R. K. Subbarao Malireddi
- & Thirumala-Devi Kanneganti
-
News & Views |
 Actin' dangerously
Actin' dangerously
Recognition of aberrant cell death is a crucial function of the immune system. It seems that one way in which immune cells identify damage is by sensing actin, an abundant intracellular protein.
- Gordon D. Brown
-
Article |
 Recognition of SUMO-modified PCNA requires tandem receptor motifs in Srs2
Recognition of SUMO-modified PCNA requires tandem receptor motifs in Srs2
Two carboxy-terminal motifs are necessary for Srs2 to recognize SUMO-conjugated PCNA, which is involved in DNA replication and repair; one motif is specific to SUMO, the other to PCNA.
- Anthony A. Armstrong
- , Firaz Mohideen
- & Christopher D. Lima
-
Letter |
 Cysteine methylation disrupts ubiquitin-chain sensing in NF-κB activation
Cysteine methylation disrupts ubiquitin-chain sensing in NF-κB activation
A conserved protein from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, NleE, inhibits innate immune defence against infection by disrupting the NF-κB signalling pathway through methylation of ubiquitin-chain sensing proteins.
- Li Zhang
- , Xiaojun Ding
- & Feng Shao
-
Research Highlights |
Two-faced cancer gene
-
Letter |
 Macrophage skewing by Phd2 haplodeficiency prevents ischaemia by inducing arteriogenesis
Macrophage skewing by Phd2 haplodeficiency prevents ischaemia by inducing arteriogenesis
- Yukiji Takeda
- , Sandra Costa
- & Massimiliano Mazzone
-
News & Views |
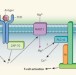 Magnesium in a signalling role
Magnesium in a signalling role
Magnesium binds to enzymes and nucleic acids and is essential for their activity. It emerges that this ion can also function as a signalling molecule with a crucial role in the immune system. See Article p.471
- Ning Wu
- & André Veillette
-
Letter |
 TLR signalling augments macrophage bactericidal activity through mitochondrial ROS
TLR signalling augments macrophage bactericidal activity through mitochondrial ROS
- A. Phillip West
- , Igor E. Brodsky
- & Sankar Ghosh
-
Letter |
 TRIM5 is an innate immune sensor for the retrovirus capsid lattice
TRIM5 is an innate immune sensor for the retrovirus capsid lattice
- Thomas Pertel
- , Stéphane Hausmann
- & Jeremy Luban
-
Letter |
 Dampening of death pathways by schnurri-2 is essential for T-cell development
Dampening of death pathways by schnurri-2 is essential for T-cell development
The zinc-finger-containing protein schnurri-2 is shown to regulate positive selection in T-cell development by dampening the mitochondrial death pathway.
- Tracy L. Staton
- , Vanja Lazarevic
- & Laurie H. Glimcher
-
Letter |
 SHARPIN is a component of the NF-κB-activating linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex
SHARPIN is a component of the NF-κB-activating linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex
The ubiquitin conjugation system regulates the canonical NF-κB-activation pathway, which mediates immune responses. Linear polyubiquitin chains—in which the C-terminal glycine of ubiquitin is conjugated to the α-amino group of the amino-terminal methionine of another ubiquitin—are generated by a unique ubiquitin ligase complex called linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC) composed of two RING domain proteins called HOIL-1 and HOIP. This is one of three complementary studies identifying a novel component of the LUBAC complex called SHARPIN, which is recruited to receptor signalling complexes (RSCs) that form after TNF and CD40L stimulation. The LUBAC complex containing SHARPIN stimulates the formation of linear ubiquitin chains in vitro and in vivo and is required for the activation of NF-κB signalling.
- Fuminori Tokunaga
- , Tomoko Nakagawa
- & Kazuhiro Iwai
-
Letter |
 SHARPIN forms a linear ubiquitin ligase complex regulating NF-κB activity and apoptosis
SHARPIN forms a linear ubiquitin ligase complex regulating NF-κB activity and apoptosis
The ubiquitin conjugation system regulates the canonical NF-κB activation pathway, which mediates immune responses. Linear polyubiquitin chains—in which the C terminal glycine of ubiquitin is conjugated to the α-amino group of the amino-terminal methionine of another ubiquitin—are generated by a unique ubiquitin ligase complex called linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC) composed of two RING domain proteins called HOIL-1 and HOIP. This is one of three complementary studies identifying a novel component of the LUBAC complex called SHARPIN, which is recruited to receptor signalling complexes (RSCs) that form after TNF and CD40L stimulation. The LUBAC complex containing SHARPIN stimulates the formation of linear ubiquitin chains in vitro and in vivo and is required for the activation of NF-κB signalling.
- Fumiyo Ikeda
- , Yonathan Lissanu Deribe
- & Ivan Dikic
-
Article |
 Linear ubiquitination prevents inflammation and regulates immune signalling
Linear ubiquitination prevents inflammation and regulates immune signalling
- Björn Gerlach
- , Stefanie M. Cordier
- & Henning Walczak
-
Letter |
 9p21 DNA variants associated with coronary artery disease impair interferon-γ signalling response
9p21 DNA variants associated with coronary artery disease impair interferon-γ signalling response
A non-coding region on chromosome 9p21 was previously shown to associate with coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes, and the region has been implicated in regulating neighbouring genes. Here, 33 distinct enhancers within this region are identified, showing that SNPs in one of the enhancers affect STAT1 binding. Furthermore, it is shown that in human vascular endothelial cells the enhancer interval physically interacts with a number of specific loci and that IFN-γ activation strongly affects the chromatin structure and transcriptional regulation of the 9p21 locus, including STAT1 binding, long-range enhancer interactions and expression of neighbouring genes.
- Olivier Harismendy
- , Dimple Notani
- & Kelly A. Frazer
-
Review Article |
 Autophagy in immunity and inflammation
Autophagy in immunity and inflammation
- Beth Levine
- , Noboru Mizushima
- & Herbert W. Virgin
-
Letter |
 Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma
Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma
This study finds frequent mutations in MYD88 in the activated B-cell-like subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and, with lower frequency, in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas. MYD88 mediates signalling by Toll-like receptors, and the mutations, most of which affect the same amino acid, are shown to activate the pathway and promote cancer cell survival.
- Vu N. Ngo
- , Ryan M. Young
- & Louis M. Staudt
-
Letter |
 Pannexin 1 channels mediate ‘find-me’ signal release and membrane permeability during apoptosis
Pannexin 1 channels mediate ‘find-me’ signal release and membrane permeability during apoptosis
Apoptotic cells discharge ATP and UTP, which act as 'find-me' signals for phagocytes that in turn engulf dying cells before potentially harmful cellular contents are released. These authors show that the release of ATP and UTP is exclusively by means of the plasma membrane channel pannexin 1, which is opened specifically by caspase activity.
- Faraaz B. Chekeni
- , Michael R. Elliott
- & Kodi S. Ravichandran
-
Letter |
 The structural basis for autonomous dimerization of the pre-T-cell antigen receptor
The structural basis for autonomous dimerization of the pre-T-cell antigen receptor
The pre-T-cell antigen receptor mediates early T-cell development and differentiation. These authors report its structure and explain how the head-to-tail dimeric arrangement allows the interaction of the pre-Tα domain with any variable β domain, and provides the basis for ligand-independent signalling.
- Siew Siew Pang
- , Richard Berry
- & Jamie Rossjohn
-
Letter |
 Single-cell NF-κB dynamics reveal digital activation and analogue information processing
Single-cell NF-κB dynamics reveal digital activation and analogue information processing
Multicellular organisms, particularly their immune systems, rely on complex cell-to-cell communication, mediated by signalling molecules that form spatiotemporal concentration gradients. Here, high-throughput microfluidic cell culture and fluorescence microscopy, together with quantitative gene expression analysis and mathematical modelling, have been used to investigate how mammalian cells respond to different levels of TNF-α and signal to NF-κB. Both digital and analogue responses are revealed.
- Savaş Tay
- , Jacob J. Hughey
- & Markus W. Covert
-
Letter |
 Sphingosine-1-phosphate is a missing cofactor for the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF2
Sphingosine-1-phosphate is a missing cofactor for the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF2
Engagement of the tumour-necrosis factor (TNF) receptor results in the assembly of multi-component signalling complexes by adaptor proteins that include TNF receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2). Genetic evidence indicates that TRAF2 is needed for the polyubiquitination of receptor interacting protein 1 (RIP1), but direct evidence has been lacking. Here it is shown that the lipid sphingosine-1-phosphate is a co-factor needed for this ubiquitination activity of TRAF2.
- Sergio E. Alvarez
- , Kuzhuvelil B. Harikumar
- & Sarah Spiegel
-
News & Views |
 Immunity takes a heavy Toll
Immunity takes a heavy Toll
Toll receptors trigger immune responses through adaptor proteins and kinase enzymes. Structural studies reveal that hierarchical assembly of these proteins into a helical tower initiates downstream signalling events.
- Steven A. Wasserman

 Formation of memory assemblies through the DNA-sensing TLR9 pathway
Formation of memory assemblies through the DNA-sensing TLR9 pathway