Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access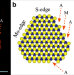 Site-dependent reactivity of MoS2 nanoparticles in hydrodesulfurization of thiophene
Site-dependent reactivity of MoS2 nanoparticles in hydrodesulfurization of thiophene
MoS2 nanoparticles catalyze the extraction of heteroatom S in hydrocarbons by adsorption onto S vacancies. Here, the authors show that S vacancy properties are highly site sensitive and that adsorption of thiophene leads to self-generation of a more open double vacancy site.
- Norberto Salazar
- , Srinivas Rangarajan
- & Jeppe V. Lauritsen
-
Article
| Open Access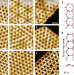 Tuning the activities of cuprous oxide nanostructures via the oxide-metal interaction
Tuning the activities of cuprous oxide nanostructures via the oxide-metal interaction
The design of oxide-metal interface for heterogeneous catalysis has been hampered by the limited fundamental understanding. Here, the authors demonstrate that the activities of cuprous oxide nanostructures for CO oxidation can be tuned via the oxide-metal (Cu2O/M, M = Pt, Ag, Au) interaction.
- Wugen Huang
- , Qingfei Liu
- & Fan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access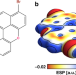 Combining high-resolution scanning tunnelling microscopy and first-principles simulations to identify halogen bonding
Combining high-resolution scanning tunnelling microscopy and first-principles simulations to identify halogen bonding
Scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) is commonly used to study 2D molecular self-assembly but is not always enough to fully solve a supramolecular structure. Here, the authors combine a high-resolution version of STM with first-principles simulations to precisely identify halogen bonding in polycyclic aromatic molecules.
- James Lawrence
- , Gabriele C. Sosso
- & Giovanni Costantini
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogen migration at restructuring palladium–silver oxide boundaries dramatically enhances reduction rate of silver oxide
Hydrogen migration at restructuring palladium–silver oxide boundaries dramatically enhances reduction rate of silver oxide
Species migration across interfacial boundaries can affect the function of bimetallic catalysts. Here the authors report that palladium oxide drives the reduction of silver oxide by facilitating molecular hydrogen dissociation and migration of hydrogen atoms across the Pd–Ag interface with concurrent surface restructuring.
- Christopher R. O’Connor
- , Matthijs A. van Spronsen
- & Cynthia M. Friend
-
Article
| Open Access Template-controlled on-surface synthesis of a lanthanide supernaphthalocyanine and its open-chain polycyanine counterpart
Template-controlled on-surface synthesis of a lanthanide supernaphthalocyanine and its open-chain polycyanine counterpart
Extending the π‐conjugation of phthalocyanine dyes, while synthetically challenging, has the potential to produce desirable new molecular materials. Here, the authors use a templated on‐surface approach to synthesize several extended phthalocyanine derivatives from the same building block, including a lanthanide superphthalocyanine and an open‐chain polycyanine.
- Qitang Fan
- , Jan-Niclas Luy
- & J. Michael Gottfried
-
Article
| Open Access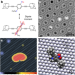 How to control single-molecule rotation
How to control single-molecule rotation
The orientation of a molecule on a surface affects many processes, so the ability to control single-molecule rotation could be powerful. Here, the authors use the electric field from a scanning tunneling microscope tip to precisely induce unidirectional rotation of a polar molecule, allowing visualization of the molecule’s internal dipole moment.
- Grant J. Simpson
- , Víctor García-López
- & Leonhard Grill
-
Article
| Open Access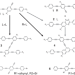 Reaction selectivity of homochiral versus heterochiral intermolecular reactions of prochiral terminal alkynes on surfaces
Reaction selectivity of homochiral versus heterochiral intermolecular reactions of prochiral terminal alkynes on surfaces
Controlling selectivity between homochiral and heterochiral reaction pathways on surfaces is intriguing but challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate strategies in steering the reactions of prochiral terminal alkynes between the homochiral and heterochiral pathways by tuning the precursor substituents and the kinetic parameters.
- Tao Wang
- , Haifeng Lv
- & Junfa Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access A chiral molecular propeller designed for unidirectional rotations on a surface
A chiral molecular propeller designed for unidirectional rotations on a surface
Controlling the rotation direction of individual molecular machines requires precise design and manipulation. Here, the authors describe a surface-adsorbed molecular propeller that, upon excitation with a scanning tunneling microscope tip, can rotate clockwise or anticlockwise depending on its chirality, and directly visualize its stepwise rotation with STM images.
- Yuan Zhang
- , Jan Patrick Calupitan
- & Saw Wai Hla
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable giant magnetoresistance in a single-molecule junction
Tunable giant magnetoresistance in a single-molecule junction
Molecular electronics or spintronics relies on manipulating the electronic transport through microscopic molecule structures. Here the authors demonstrate the selective electron pathway in single-molecule device by magnetic field which enables a tunable anisotropic magnetoresistance up to 93%.
- Kai Yang
- , Hui Chen
- & Hong-Jun Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Ab initio nonrigid X-ray nanotomography
Ab initio nonrigid X-ray nanotomography
Radiation induced sample deformation can be a limiting factor for X-ray imaging resolution at the nanoscale. The authors report a tomographic model that estimates and accounts for morphological changes during data acquisition and enables reconstruction of a high-resolution image ab initio.
- Michal Odstrcil
- , Mirko Holler
- & Manuel Guizar-Sicairos
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic transport in planar atomic-scale structures measured by two-probe scanning tunneling spectroscopy
Electronic transport in planar atomic-scale structures measured by two-probe scanning tunneling spectroscopy
Measuring electronic transport at the atomic scale requires atom precise contacts. Here, the authors demonstrate quasi-one-dimensional electronic transport along a single dimer row on a germanium surface using a two probe scanning tunneling microscopy protocol.
- Marek Kolmer
- , Pedro Brandimarte
- & Marek Szymonski
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface light-induced generation of higher acenes and elucidation of their open-shell character
On-surface light-induced generation of higher acenes and elucidation of their open-shell character
The synthesis of large acenes via traditional solution-chemistry routes is hindered by their poor solubility and high reactivity under ambient conditions. Here, the authors demonstrate the on-surface formation of large acenes, via visible-light-induced photo-dissociation of α-bisdiketone molecular precursors on an Au(111) substrate.
- José I. Urgel
- , Shantanu Mishra
- & Roman Fasel
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring atomic layer growth at the liquid-metal interface
Tailoring atomic layer growth at the liquid-metal interface
Ultrathin metallic films are most often fabricated by atomic or molecular beam epitaxy under ultrahigh vacuum conditions, where it is difficult to control deposition and growth. Here, the authors describe a wet deposition method, using solution-borne gold nanocluster precursors, to regulate growth of atomically flat gold nanoislands on a surface.
- Hai Cao
- , Deepali Waghray
- & Steven De Feyter
-
Article
| Open Access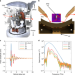 Imaging the nanoscale phase separation in vanadium dioxide thin films at terahertz frequencies
Imaging the nanoscale phase separation in vanadium dioxide thin films at terahertz frequencies
The insulator-to-metal transition in vanadium dioxide still has many unexplored properties. Here the authors use multi-modal THz and mid-IR nano-imaging to examine the phase transition in VO2 thin films, and discuss the unexpectedly smooth transition at THz frequencies in the context of a dimer Hubbard model.
- H. T. Stinson
- , A. Sternbach
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular overlayer with the Fibonacci square grid structure
A molecular overlayer with the Fibonacci square grid structure
Quasicrystals possess long range order but no translational symmetry, and rotational symmetries that are forbidden in periodic crystals. Here, a fullerene overlayer deposited on a surface of an icosahedral intermetallic quasicrystal achieves a Fibonacci square grid structure, by selective adsorption at specific sites.
- Sam Coates
- , Joseph A. Smerdon
- & Hem Raj Sharma
-
Article
| Open Access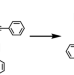 Self-assembly directed one-step synthesis of [4]radialene on Cu(100) surfaces
Self-assembly directed one-step synthesis of [4]radialene on Cu(100) surfaces
Radialenes have distinct structural, electronic and chemical properties from other hydrocarbons, but their synthesis remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a copper catalyzed one-step synthetic protocol of [4]radialene via the cyclotetramerization of phenylacetylene molecules upon thermal activation.
- Qing Li
- , Jianzhi Gao
- & Minghu Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Real-space imaging with pattern recognition of a ligand-protected Ag374 nanocluster at sub-molecular resolution
Real-space imaging with pattern recognition of a ligand-protected Ag374 nanocluster at sub-molecular resolution
Translating high-resolution imaging methods to the curved organic surface of a nanoparticle has been challenging. Here, the authors are able to spatially resolve the sub-molecular surface details of a silver nanocluster by comparing scanning tunneling microscopy images and simulated topography data through a pattern recognition algorithm.
- Qin Zhou
- , Sami Kaappa
- & Lansun Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access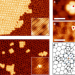 Non-covalent control of spin-state in metal-organic complex by positioning on N-doped graphene
Non-covalent control of spin-state in metal-organic complex by positioning on N-doped graphene
Molecules can change their electronic properties when they are adsorbed on substrates, which can be useful for sensing and catalysis. Here, the authors use atomic force microscopy to show that the spin state of an iron complex can be changed upon displacing the molecule to different sites of a nitrogen-doped graphene
- Bruno de la Torre
- , Martin Švec
- & Pavel Jelínek
-
Article
| Open Access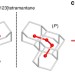 Assigning the absolute configuration of single aliphatic molecules by visual inspection
Assigning the absolute configuration of single aliphatic molecules by visual inspection
Deciphering absolute configuration of individual molecules directly by visual inspection remains a highly attractive goal. Here, the authors determine the absolute configuration and orientation of a single [123]tetramantane molecule adsorbed on Cu(111) using low temperature atomic force microscopy with a CO-functionalized tip.
- Daniel Ebeling
- , Marina Šekutor
- & Peter R. Schreiner
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing hydrogen-induced reshaping and edge activation in MoS2 and Co-promoted MoS2 catalyst clusters
Visualizing hydrogen-induced reshaping and edge activation in MoS2 and Co-promoted MoS2 catalyst clusters
Rational design of a hydrodesulfurization catalyst relies on a fundamental understanding of its working principles. Here, the authors use scanning tunneling microscopy to directly visualize and quantify hydrogen-induced reshaping and edge activation in MoS2 and Co-promoted MoS2 catalyst clusters.
- Signe S. Grønborg
- , Norberto Salazar
- & Jeppe V. Lauritsen
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal step edges can trap electrons on the surfaces of n-type organic semiconductors
Crystal step edges can trap electrons on the surfaces of n-type organic semiconductors
The microstructure of organic semiconductors affects their transport properties, but directly probing this relationship is challenging. He et al. show that step edges act as electron traps on the surfaces of n-type single crystals, resulting in a field effect transistor mobility that depends on step density.
- Tao He
- , Yanfei Wu
- & C. Daniel Frisbie
-
Article
| Open Access Transient modes of zeolite surface growth from 3D gel-like islands to 2D single layers
Transient modes of zeolite surface growth from 3D gel-like islands to 2D single layers
While zeolites are industrially relevant as molecular sieves and catalysts, their growth mechanisms remain widely debated. Here, Rimer and colleagues probe the crystallization pathway of zeolite LTA with spatiotemporal resolution, identifying a distinctive nonclassical pathway, and demonstrating that growth is highly dependent on synthetic conditions.
- Manjesh Kumar
- , Madhuresh K. Choudhary
- & Jeffrey D. Rimer
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis of a nitrogen-embedded buckybowl with inverse Stone–Thrower–Wales topology
On-surface synthesis of a nitrogen-embedded buckybowl with inverse Stone–Thrower–Wales topology
Heteroatom doping of buckybowls is a viable route to tune their intrinsic physico-chemical properties, but their synthesis remains challenging. Here, the authors report on a combined in-solution and on-surface synthetic strategy towards the fabrication of a buckybowl containing two fused nitrogen-doped pentagonal rings.
- Shantanu Mishra
- , Maciej Krzeszewski
- & Daniel T. Gryko
-
Article
| Open Access Studying an antiaromatic polycyclic hydrocarbon adsorbed on different surfaces
Studying an antiaromatic polycyclic hydrocarbon adsorbed on different surfaces
Indeno[1,2-b]fluorene (IF) is an extremely reactive polycyclic conjugated hydrocarbon with antiaromatic character, thus it has not been detected to date. Here, the authors present the successful generation and characterisation of IF both on-surface and in-solution.
- Zsolt Majzik
- , Niko Pavliček
- & Leo Gross
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast current imaging by Bayesian inversion
Ultrafast current imaging by Bayesian inversion
Scanning probe microscopy is widely used to characterize material properties with atomic resolution, yet electronic property mapping is normally constrained by slow data acquisition. Somnath et al. show a current–voltage method, which enables fast electronic spectroscopy mapping over micrometer-sized areas.
- S. Somnath
- , K. J. H. Law
- & R. K. Vasudevan
-
Article
| Open Access Weakly perturbative imaging of interfacial water with submolecular resolution by atomic force microscopy
Weakly perturbative imaging of interfacial water with submolecular resolution by atomic force microscopy
Scanning probe microscopy has been extensively applied to probe interfacial water but the probes tend to disturb the structure of water easily. Here, the authors report submolecular-resolution imaging of water clusters within the nearly non-invasive region by qPlus noncontact atomic force microscopy.
- Jinbo Peng
- , Jing Guo
- & Ying Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-resolution three-dimensional hydration structures on a heterogeneously charged surface
Atomic-resolution three-dimensional hydration structures on a heterogeneously charged surface
Local hydration structures at solid-liquid interfaces are important in catalytic, electrochemical, and biological processes. Here, the authors demonstrate atomic-scale 3D hydration structures around the boundary on a heterogeneous mineral surface using atomic force microscopy experiments and molecular dynamics simulations.
- Kenichi Umeda
- , Lidija Zivanovic
- & Hirofumi Yamada
-
Article
| Open Access Broad modulus range nanomechanical mapping by magnetic-drive soft probes
Broad modulus range nanomechanical mapping by magnetic-drive soft probes
Force-distance curve-based atomic force microscopy can measure material nanomechanics, but only if the probe and material stiffness match, which limits the measurement range. Here, the authors broaden the dynamic range of the probe by up to four orders of magnitude using magnetic drive peak force modulation.
- Xianghe Meng
- , Hao Zhang
- & Hui Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping microscale wetting variations on biological and synthetic water-repellent surfaces
Mapping microscale wetting variations on biological and synthetic water-repellent surfaces
Real-world surfaces exhibit spatially varying wettability, which affects water repellency and droplet behaviour on such surfaces. Here, the authors use scanning droplet adhesion microscopy to create wetting maps that visualize variations in wettability with a spatial resolution down to 10 μm.
- Ville Liimatainen
- , Maja Vuckovac
- & Robin H. A. Ras
-
Article
| Open Access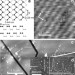 Supramolecular networks stabilise and functionalise black phosphorus
Supramolecular networks stabilise and functionalise black phosphorus
Few-layered black phosphorus has been exploited in transistors and other devices, but its poor stability under ambient conditions remains problematic. Here, a UK-Swiss collaboration show that a monolayer-thick supramolecular hydrogen-bonded network can protect a black phosphorus surface for over a month.
- Vladimir V. Korolkov
- , Ivan G. Timokhin
- & Peter H. Beton
-
Article
| Open Access Piezo-generated charge mapping revealed through direct piezoelectric force microscopy
Piezo-generated charge mapping revealed through direct piezoelectric force microscopy
Piezoelectrics and ferroelectrics are important for everyday applications, but methods to characterize these materials at the nanoscale are lacking. Here the authors present direct piezoelectric force microscopy, an AFM mode that can measure charges generated by the direct piezoelectric effect with nanoscale resolution.
- A. Gomez
- , M. Gich
- & X. Obradors
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time tracking of metal nucleation via local perturbation of hydration layers
Real-time tracking of metal nucleation via local perturbation of hydration layers
Electrochemical deposition is important for industrial processes however, tracking the early stages of metallic phase nucleation is challenging. Here, the authors visualize the birth and growth of metal nuclei at electrode surfaces in real time via high-speed non-contact lateral molecular force microscopy.
- Robert L. Harniman
- , Daniela Plana
- & David J. Fermín
-
Article
| Open Access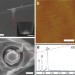 Direction-specific interaction forces underlying zinc oxide crystal growth by oriented attachment
Direction-specific interaction forces underlying zinc oxide crystal growth by oriented attachment
Crystal growth is a fundamental process, important in a wide range of fields, but the interparticle forces responsible for molecule alignment are not well understood. Here, the authors measure the alignment forces in ZnO using dynamic force spectroscopy, highlighting the role of intervening water molecules.
- X. Zhang
- , Z. Shen
- & K. M. Rosso
-
Article
| Open Access Observing the oxidation of platinum
Observing the oxidation of platinum
Improving platinum as an oxidation catalyst requires understanding its structure under catalytic conditions. Here, the authors discover that catalytically important surface oxides form only when Pt is exposed to high pressure and temperature, highlighting the need to study catalysts in realistic environments.
- Matthijs A. van Spronsen
- , Joost W. M. Frenken
- & Irene M. N. Groot
-
Article
| Open Access Strain-induced skeletal rearrangement of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon on a copper surface
Strain-induced skeletal rearrangement of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon on a copper surface
Mechanical strains can induce chemical transformations otherwise inaccessible by conventional stimuli. Here, the authors show the unusual strain-induced transformation of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon on a metal surface by means of atomic force microscopy.
- Akitoshi Shiotari
- , Takahiro Nakae
- & Yoshiaki Sugimoto
-
Article
| Open Access Highly-conducting molecular circuits based on antiaromaticity
Highly-conducting molecular circuits based on antiaromaticity
Antiaromatic molecules are predicted to have unusual charge transport properties, but are notoriously unstable and reactive. Here, the authors successfully fabricate an antiaromatic molecular circuit, based on a macrocyclic complex, displaying much higher conductance than its aromatic counterpart.
- Shintaro Fujii
- , Santiago Marqués-González
- & Manabu Kiguchi
-
Article
| Open Access Correlated rotational switching in two-dimensional self-assembled molecular rotor arrays
Correlated rotational switching in two-dimensional self-assembled molecular rotor arrays
Single molecular machines are capable of a variety of functions, but methods to couple motion between them are still lacking. Here, Wasioet al. report the emergent behaviour of spontaneously formed two-dimensional crystals, which display correlated switching of their sub-molecular rotor units.
- Natalie A. Wasio
- , Diana P. Slough
- & E. Charles H. Sykes
-
Article
| Open Access Highly selective covalent organic functionalization of epitaxial graphene
Highly selective covalent organic functionalization of epitaxial graphene
Organic functionalization is key to the development of graphene-based functional composites, yet selective covalent functionalization is hindered by graphene chemical inertness. Here, the authors demonstrate a versatile route to graphene covalent bonding with amino-terminated organic molecules.
- Rebeca A. Bueno
- , José I. Martínez
- & José A. Martín-Gago
-
Article
| Open Access Electronegativity determination of individual surface atoms by atomic force microscopy
Electronegativity determination of individual surface atoms by atomic force microscopy
Electronegativity is a fundamental concept in chemistry; however it is an elusive quantity to evaluate experimentally. Here, the authors estimate the Pauling electronegativity of individual atoms on a surface via atomic force microscopy using a variety of chemically reactive tips.
- Jo Onoda
- , Martin Ondráček
- & Yoshiaki Sugimoto
-
Article
| Open Access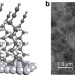 Single-molecule electrical contacts on silicon electrodes under ambient conditions
Single-molecule electrical contacts on silicon electrodes under ambient conditions
The next level of miniaturization of electronic circuits calls for a connection between current single-molecule and traditional semiconductor processing technologies. Here, the authors show a method to prepare metal/molecule/silicon diodes that present high current rectification ratios exceeding 4,000.
- Albert C. Aragonès
- , Nadim Darwish
- & Ismael Díez-Pérez
-
Article
| Open Access Templated bilayer self-assembly of fully conjugated π-expanded macrocyclic oligothiophenes complexed with fullerenes
Templated bilayer self-assembly of fully conjugated π-expanded macrocyclic oligothiophenes complexed with fullerenes
Controlling the self-assembly of oligothiophene complexes that are used in multi-functional thin films can be challenging. Here the authors show a hierarchy of non-covalent interactions for robust self-assembly that orders Saturn-like complexes of fullerenes with oligothiophene macrocycles.
- José D. Cojal González
- , Masahiko Iyoda
- & Jürgen P. Rabe
-
Article
| Open Access Edge reactivity and water-assisted dissociation on cobalt oxide nanoislands
Edge reactivity and water-assisted dissociation on cobalt oxide nanoislands
Earth abundant transition metal oxides show great promise as catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. Here, the authors reveal a self-assisted water dissociation mechanism and favourable theoretical adsorption energetics for water oxidation at the edge sites of cobalt oxide nano-islands.
- J. Fester
- , M. García-Melchor
- & J. V. Lauritsen
-
Article
| Open Access Bond selectivity in electron-induced reaction due to directed recoil on an anisotropic substrate
Bond selectivity in electron-induced reaction due to directed recoil on an anisotropic substrate
The ability to selectively break a chemical bond in a molecule is indispensable to chemical synthesis. Here, the authors show that a hundred-fold bond selectivity can be obtained in electron-induced surface reaction due simply to different bond alignments at the surface.
- Kelvin Anggara
- , Kai Huang
- & John C. Polanyi
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale assembly of superconducting vortices with scanning tunnelling microscope tip
Nanoscale assembly of superconducting vortices with scanning tunnelling microscope tip
Scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is a powerful tool but local control of superconductivity with the STM tip is still lacking. Here, Geet al. show the use of an STM tip to control the local pinning in a superconductor through the heating effect, allowing to manipulate single superconducting vortex at nanoscale.
- Jun-Yi Ge
- , Vladimir N. Gladilin
- & Victor V. Moshchalkov
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid mapping of polarization switching through complete information acquisition
Rapid mapping of polarization switching through complete information acquisition
Resolution of classical piezoresponse force microscopy is limited in data acquisition rates and energy scales. Here, Somnath et al. report an approach for rapid probing of ferroelectric switching using direct strain detection of material response to probe bias, enabling spectroscopic imaging at a rate of 3,504 times faster the current state of the art.
- Suhas Somnath
- , Alex Belianinov
- & Stephen Jesse
-
Article
| Open Access Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with low-repetition-rate pulsed light source through phase-domain sampling
Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with low-repetition-rate pulsed light source through phase-domain sampling
Low repetition rate lasers are suitable for studying nonlinear optical phenomena, while near-field microscopy allows high spatial resolution for nanomaterial characterisation. Here, Wang et al. enable scattering-type near-field microscopy with low repetition rate lasers through phase-domain sampling.
- Haomin Wang
- , Le Wang
- & Xiaoji G. Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Initiating and imaging the coherent surface dynamics of charge carriers in real space
Initiating and imaging the coherent surface dynamics of charge carriers in real space
The charge injected from the tip of a scanning tunnelling microscope quickly spreads across the surface and can manipulate distant adsorbates. Here, the authors use this nonlocal manipulation to probe the ultrafast ballistic dynamics and coherent evolution of the injected charge carrier.
- K. R. Rusimova
- , N. Bannister
- & P. A. Sloan
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscopic imaging of thick heterogeneous soft-matter structures in aqueous solution
Nanoscopic imaging of thick heterogeneous soft-matter structures in aqueous solution
Integration time limits the capacity of super-resolution microscopy to study dynamics. Here, Bartsch et al. use the 3D scanning of a nanoparticle held in an optical trap, and its thermal noise motion within the trap, to image the local dynamics of soft-matter structures with a 50 kHz bandwidth.
- Tobias F. Bartsch
- , Martin D. Kochanczyk
- & Ernst-Ludwig Florin
-
Article
| Open Access Non-destructive imaging of buried electronic interfaces using a decelerated scanning electron beam
Non-destructive imaging of buried electronic interfaces using a decelerated scanning electron beam
Imaging buried interfaces is necessary to assess the quality of electronic devices and their degradation mechanisms. Here, Hirohata et al. use energy-filtered scanning electron microscopy to image buried defects in an inorganic lateral spin-valve device, at the nanometre scale and non-destructively.
- Atsufumi Hirohata
- , Yasuaki Yamamoto
- & Andrew J. Vick

 Tailoring π-conjugation and vibrational modes to steer on-surface synthesis of pentalene-bridged ladder polymers
Tailoring π-conjugation and vibrational modes to steer on-surface synthesis of pentalene-bridged ladder polymers