Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Slow on, fast off
Slow on, fast off
The slow turn-on speed in accumulation-mode organic electrochemical transistors is explained by asymmetric ion transport in switching kinetics.
- Hang Yu
- & Jenny Nelson
-
Article |
 Understanding asymmetric switching times in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors
Understanding asymmetric switching times in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors
The turn-off time is generally faster than the turn-on time in accumulation mode organic electrochemical transistors (OECTs), but the mechanism is less understood. Here the authors find different transient behaviours of turn-on and turn-off in accumulation mode OECTs, and ion transport is the limiting factor of device kinetics.
- Jiajie Guo
- , Shinya E. Chen
- & David S. Ginger
-
News & Views |
 A soft crystalline packing with no metallic analogue
A soft crystalline packing with no metallic analogue
Pentagonal polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS)-based giant atoms self-assemble into Frank–Kasper phases that have not been previously observed in soft-matter systems.
- Pengyu Chen
- & Kevin D. Dorfman
-
Research Briefing |
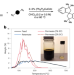 Click-chemistry polymer membranes for hydrocarbon mixture fractionation
Click-chemistry polymer membranes for hydrocarbon mixture fractionation
Polymers made by click chemistry with spirocyclic building blocks form membranes that separate the components of crude oil based on molecular size and type, potentially using far less energy than distillation. Key enablers of this separation are moderate levels of polymer dynamic motion and frustrated chain packing.
-
Article |
 Nanoconfined polymerization limits crack propagation in hysteresis-free gels
Nanoconfined polymerization limits crack propagation in hysteresis-free gels
Simultaneously highly elastic and deformable gels that maintain their mechanical properties have remained elusive. Here, using in situ polymerization confined within nanochannels, the authors prepare hysteresis-free gels insensitive to crack propagation.
- Weizheng Li
- , Xiaoliang Wang
- & Feng Yan
-
Article |
 Sequencing polymers to enable solid-state lithium batteries
Sequencing polymers to enable solid-state lithium batteries
Solid polymer electrolytes are crucial for the development of lithium batteries, but their lower ionic conductivity compared with liquid/ceramics at room temperature limits their practical use. Precise positioning of designed repeating units in alternating polymer sequences now allows the Li+ conductivity to be tuned by up to three orders of magnitude.
- Shantao Han
- , Peng Wen
- & Mao Chen
-
Article |
 Solution-processable polytriazoles from spirocyclic monomers for membrane-based hydrocarbon separations
Solution-processable polytriazoles from spirocyclic monomers for membrane-based hydrocarbon separations
Thermal fractionation of petroleum consumes large amounts of energy. Here stable microporous polymers are synthesized using click chemistry, which have similar performance to commercial polyimides for the fractionation of light crude oils and successful application to heavy feeds under realistic conditions.
- Nicholas C. Bruno
- , Ronita Mathias
- & M. G. Finn
-
News & Views |
 Electrons lighter than ever
Electrons lighter than ever
A two-dimensional conjugated polymer is synthesized that demonstrates low electron effective masses and high mobility. These properties show that this material could act as a viable alternative to silicon-based semiconductors.
- Shu Seki
- & Zhuowei Li
-
Article |
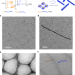 High-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of block copolymer nanofibres with a crystalline core
High-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of block copolymer nanofibres with a crystalline core
Detailed structures of both solvated corona chains and sub-nanometre crystalline core lattice of polymer-based nanofibres in solution are obtained using high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy.
- Jia Tian
- , Song-Hai Xie
- & Ian Manners
-
Article |
 Operando NMR electrochemical gating studies of ion dynamics in PEDOT:PSS
Operando NMR electrochemical gating studies of ion dynamics in PEDOT:PSS
Understanding charge-compensating interactions and ionic dynamics in organic mixed conductors can be challenging. Operando NMR spectroscopy is now used to quantify cation and water movement during doping/dedoping in mixed conductor films.
- Dongxun Lyu
- , Yanting Jin
- & Clare P. Grey
-
Editorial |
 Simple connections take the prize
Simple connections take the prize
Click chemistry and bioorthogonal chemistry have finally been recognized with the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
-
-
Article |
 Hierarchically engineered nanostructures from compositionally anisotropic molecular building blocks
Hierarchically engineered nanostructures from compositionally anisotropic molecular building blocks
Independently tailored nano- and mesoscale features are obtained in hierarchically assembled mixed graft block copolymers with precisely defined side-chain sequences.
- Ruiqi Liang
- , Yazhen Xue
- & Mingjiang Zhong
-
Article |
 Highly stretchable organic electrochemical transistors with strain-resistant performance
Highly stretchable organic electrochemical transistors with strain-resistant performance
Highly stretchable organic electrochemical transistors with stable charge transport under severe tensional strains are demonstrated using a honeycomb semiconducting polymer morphology, thereby enabling controllable signal output for diverse stretchable bioelectronic applications.
- Jianhua Chen
- , Wei Huang
- & Antonio Facchetti
-
Perspective |
 Molecular weaving
Molecular weaving
Molecular weaving is the entanglement of one-dimensional flexible molecules into higher-dimensional networks. This Perspective provides an overview of the progress so far, and discusses the future challenges and potentials of this field.
- Zhi-Hui Zhang
- , Björn J. Andreassen
- & Liang Zhang
-
Article |
 Highly compressible glass-like supramolecular polymer networks
Highly compressible glass-like supramolecular polymer networks
Glass-like supramolecular polymer networks with high compressibility and fast self-recovery are fabricated using host–guest crosslinkers with slow dissociation kinetics.
- Zehuan Huang
- , Xiaoyi Chen
- & Oren A. Scherman
-
Article |
 Computational prediction of the molecular configuration of three-dimensional network polymers
Computational prediction of the molecular configuration of three-dimensional network polymers
A computational platform describing the spatial and temporal interactions of monomers during the formation of network polymers provides structure–property relationships that are used to synthesize 3D network polymers with tailored functionalities.
- Lies De Keer
- , Karsu I. Kilic
- & Dagmar R. D’hooge
-
Article |
 n-type charge transport in heavily p-doped polymers
n-type charge transport in heavily p-doped polymers
A broad range of characterization techniques is used to understand the dominant electron conduction in various p-type doped π-conjugated polymers, which show p-type and n-type thermoelectric power factors depending on the dopant concentration.
- Zhiming Liang
- , Hyun Ho Choi
- & Kenneth R. Graham
-
News & Views |
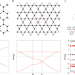 Making 2D topological polymers a reality
Making 2D topological polymers a reality
First-principles calculations predicted electronic topological properties for 2D honeycomb–kagome polymers, which have been now confirmed experimentally thanks to improvements in on-surface synthesis.
- Yu Jing
- & Thomas Heine
-
Article |
 Ground-state electron transfer in all-polymer donor–acceptor heterojunctions
Ground-state electron transfer in all-polymer donor–acceptor heterojunctions
Doping through spontaneous electron transfer between donor and acceptor polymers is obtained by selecting organic semiconductors with suitable electron affinity and ionization energy, achieving high conductivity in blends and bilayer configuration.
- Kai Xu
- , Hengda Sun
- & Simone Fabiano
-
Article |
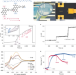 Biofuel powered glucose detection in bodily fluids with an n-type conjugated polymer
Biofuel powered glucose detection in bodily fluids with an n-type conjugated polymer
An n-type semiconducting polymer is used to realize an organic electrochemical transistor working as a glucose sensor and an all-polymer enzymatic biofuel cell able to power the sensor itself.
- David Ohayon
- , Georgios Nikiforidis
- & Sahika Inal
-
News & Views |
 Beware the nanovoids
Beware the nanovoids
Nanovoids in organic semiconductors can serve as hosts for water inclusions that lead to trapping of electrons and holes.
- David J. Yaron
- & Tomasz Kowalewski
-
Article |
 Double doping of conjugated polymers with monomer molecular dopants
Double doping of conjugated polymers with monomer molecular dopants
A monomer molecular dopant with high electron affinity is shown to accept up to two electrons from conjugated polymers with low ionization efficiency and then generate free charge carriers with an efficiency of up to 170%.
- David Kiefer
- , Renee Kroon
- & Christian Müller
-
News & Views |
 Ultrapermeable membranes
Ultrapermeable membranes
Microporous membranes were designed from the loose packing of two-dimensional polymer chains — a breakthrough giving both ultrahigh permeability and good selectivity for gas separations.
- Yan Yin
- & Michael D. Guiver
-
Article |
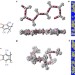 Polymer ultrapermeability from the inefficient packing of 2D chains
Polymer ultrapermeability from the inefficient packing of 2D chains
Polymer membranes were formed from the inefficient packing of 2D polymer chains in a 3D amorphous solid, forming small and large micropores that enable high gas selectivity and permeability. This strategy may be applied to other polymers.
- Ian Rose
- , C. Grazia Bezzu
- & Neil B. McKeown
-
News & Views |
 Probing the solid–liquid interface
Probing the solid–liquid interface
Exploring the minute mechanical deformations induced by electrical bias at the interface with electrolytes allows the identification of local crystallinity and distinguishing adsorption and intercalation of ions in electroactive polymers.
- Xavier Crispin
- & Sergei V. Kalinin
-
Article |
 Reducing the efficiency–stability–cost gap of organic photovoltaics with highly efficient and stable small molecule acceptor ternary solar cells
Reducing the efficiency–stability–cost gap of organic photovoltaics with highly efficient and stable small molecule acceptor ternary solar cells
Ternary organic blends using two non-fullerene acceptors are shown to improve the efficiency and stability of low-cost solar cells based on P3HT and of high-performance photovoltaic devices based on low-bandgap donor polymers.
- Derya Baran
- , Raja Shahid Ashraf
- & Iain McCulloch
-
Article |
 Charge-transport model for conducting polymers
Charge-transport model for conducting polymers
A generalized charge-transport model is reported that is able to describe the thermopower–conductivity relation at various temperatures in several semiconducting polymers, suggesting a rethinking of conduction mechanisms in these materials.
- Stephen Dongmin Kang
- & G. Jeffrey Snyder
-
Article |
 Polymer nanofilms with enhanced microporosity by interfacial polymerization
Polymer nanofilms with enhanced microporosity by interfacial polymerization
Here it is shown how ultrathin and microporous polymer membranes, fabricated using sterically contorted monomers, can achieve enhanced performance for solvent-based separations.
- Maria F. Jimenez-Solomon
- , Qilei Song
- & Andrew G. Livingston
-
Letter |
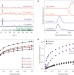 Enhanced ethylene separation and plasticization resistance in polymer membranes incorporating metal–organic framework nanocrystals
Enhanced ethylene separation and plasticization resistance in polymer membranes incorporating metal–organic framework nanocrystals
The dispersion of metal–organic framework nanocrystals within a polyimide yields membranes for selective chemical separations with strong resistance to plasticization.
- Jonathan E. Bachman
- , Zachary P. Smith
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Letter |
 Proton conduction in crystalline and porous covalent organic frameworks
Proton conduction in crystalline and porous covalent organic frameworks
The design of large-pore proton conductors with well-defined high-order structures is challenging. Proton conduction in a crystalline covalent organic framework 2–4 orders of magnitude higher than microporous polymers is now demonstrated.
- Hong Xu
- , Shanshan Tao
- & Donglin Jiang
-
News & Views |
 Hand-twisting light
Hand-twisting light
Macroscopic deformation can induce chirality in initially achiral nanoparticle composites, and reversibly modulate their chiroptical properties.
- Daeyeon Lee
- & Sang Eon Han
-
Letter |
 Solvent-free, supersoft and superelastic bottlebrush melts and networks
Solvent-free, supersoft and superelastic bottlebrush melts and networks
Solvent-free, supersoft and superelastic polymer melts and networks made from bottlebrush macromolecules can display low modulus, high strain at break, and extraordinary elasticity.
- William F. M. Daniel
- , Joanna Burdyńska
- & Sergei S. Sheiko
-
Review Article |
 Programmable and adaptive mechanics with liquid crystal polymer networks and elastomers
Programmable and adaptive mechanics with liquid crystal polymer networks and elastomers
This Review discusses stimuli-responsive liquid crystalline polymer networks and elastomers as materials with programmable mechanics for use in functional devices.
- Timothy J. White
- & Dirk J. Broer
-
News & Views |
 Straining to expand entanglements
Straining to expand entanglements
Porous solids comprising a self-entangled coiled polymer fibre or metal wire reversibly increase their volume when either stretched or compressed in an axial direction, possibly providing a new type of mechanical behaviour for tuning functional properties.
- Ray H. Baughman
- & Alexandre F. Fonseca
-
News & Views |
 Longer and safer gastric residence
Longer and safer gastric residence
A supramolecular polymer that is stable in the acidic environment of the stomach but dissolves in the neutral-pH environment of the intestines prolongs the safe retention of gastric devices.
- Vitaliy V. Khutoryanskiy
-
News & Views |
 Framing upconversion materials
Framing upconversion materials
Solid-state organic materials that convert low-power visible light into higher-energy radiation have been synthesized using metal–organic frameworks. This approach could be used to make polymers that increase the efficiency of photovoltaic devices.
- Yoan C. Simon
- & Christoph Weder
-
Article |
 A pH-responsive supramolecular polymer gel as an enteric elastomer for use in gastric devices
A pH-responsive supramolecular polymer gel as an enteric elastomer for use in gastric devices
A supramolecular elastic polymer that is stable in the acidic environment of the stomach but dissolves in the neutral-pH environment of the intestines is shown to function as a safe gastric-retentive device in pigs.
- Shiyi Zhang
- , Andrew M. Bellinger
- & Giovanni Traverso
-
Letter |
 Dynamic polymer systems with self-regulated secretion for the control of surface properties and material healing
Dynamic polymer systems with self-regulated secretion for the control of surface properties and material healing
Dynamic liquid exchanges in a supramolecular polymer-gel matrix with liquid-storage compartments and a thin liquid layer on top lead to self-healing properties and controllable secretion kinetics.
- Jiaxi Cui
- , Daniel Daniel
- & Joanna Aizenberg
-
Article |
 A design strategy for intramolecular singlet fission mediated by charge-transfer states in donor–acceptor organic materials
A design strategy for intramolecular singlet fission mediated by charge-transfer states in donor–acceptor organic materials
Design rules for the synthesis of donor–acceptor systems with efficient intramolecular singlet fission are now proposed. These guidelines have been applied to both small molecules and polymeric chains.
- Erik Busby
- , Jianlong Xia
- & Matthew Y. Sfeir
-
News & Views |
 Sticky when wet
Sticky when wet
Inspired by the chemistry of adhesive proteins in mussels, hydrogels can now be made to self-heal in water without the aid of metal chelates.
- Jonathan J. Wilker
-
-
Article |
 Bacteria-instructed synthesis of polymers for self-selective microbial binding and labelling
Bacteria-instructed synthesis of polymers for self-selective microbial binding and labelling
Enzymes involved in copper metabolism and residing within bacterial outer layers are used to polymerize monomers bound to the bacterial cell surface. The composition of the polymers is affected by templating processes and hence the polymers are specific binding agents for the bacteria on which they are grown.
- E. Peter Magennis
- , Francisco Fernandez-Trillo
- & Cameron Alexander
-
-
News & Views |
 Behind organics' thermopower
Behind organics' thermopower
Conjugated polymers with high electrical conductivity and high thermopower are now demonstrated. The electronic structure of these materials is that of a semi-metal, a previously unreported state for organic conductors.
- Michael Chabinyc
-
News & Views |
 Long and winding polymeric roads
Long and winding polymeric roads
Poorly ordered films of conjugated polymers that show high charge mobility recently challenged the idea that disorder is detrimental for electrical conduction. Systematic studies now reveal that long polymeric chains can bridge small crystalline domains thus supporting charge transport on length scales relevant for device operation.
- Vitaly Podzorov
-
Article |
 A general relationship between disorder, aggregation and charge transport in conjugated polymers
A general relationship between disorder, aggregation and charge transport in conjugated polymers
The recent demonstration that highly disordered polymer films can transport charges as effectively as polycrystalline semiconductors has called into question the relationship between structural order and mobility in organic materials. It is now shown that, in high-molecular-weight polymers, efficient charge transport is allowed due to a network of interconnected aggregates that are characterized by short-range order.
- Rodrigo Noriega
- , Jonathan Rivnay
- & Alberto Salleo
-
-
News & Views |
 Some like it hot
Some like it hot
Excitation of organic donor–acceptor systems with high-energy light can produce hot charge-transfer states that are delocalized across the heterojunction and readily dissociate. Two studies now reveal the dynamics of this process and pave the way towards unravelling the details of the molecular landscape that favours fast photocarrier generation.
- Carlos Silva

 Organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors progress at pace
Organic mixed ionic–electronic conductors progress at pace Composites from photo-stereochemical patterning
Composites from photo-stereochemical patterning Stains of authenticity
Stains of authenticity Polymer toroids
Polymer toroids