Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Geminiviruses employ host DNA glycosylases to subvert DNA methylation-mediated defense
Geminiviruses employ host DNA glycosylases to subvert DNA methylation-mediated defense
Plants tightly regulate DNA methylation to regulate gene expression. Here, the authors show that the tomato yellow leaf curl China virus βC1 protein interacts with plant DNA glycosylases to promote demethylation of viral DNA and promote virulence.
- Xiaojian Gui
- , Chang Liu
- & Xueping Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Phloem iron remodels root development in response to ammonium as the major nitrogen source
Phloem iron remodels root development in response to ammonium as the major nitrogen source
Ammonium affects plant root development through different mechanisms than nitrate. Here, the authors show that the Arabidopsis cell wall-localized ferroxidase LPR2 is required to attenuate root growth in response to ammonium.
- Xing Xing Liu
- , Hai Hua Zhang
- & Chong Wei Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Carbohydrate-aromatic interface and molecular architecture of lignocellulose
Carbohydrate-aromatic interface and molecular architecture of lignocellulose
The plant biomass is a composite formed by a variety of polysaccharides and an aromatic polymer named lignin. Here, the authors use solid-state NMR spectroscopy to unveil the carbohydrate-aromatic interface that leads to the variable architecture of lignocellulose biomaterials.
- Alex Kirui
- , Wancheng Zhao
- & Tuo Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Citrus Huanglongbing is a pathogen-triggered immune disease that can be mitigated with antioxidants and gibberellin
Citrus Huanglongbing is a pathogen-triggered immune disease that can be mitigated with antioxidants and gibberellin
Huanglongbing is a devastating disease of citrus, caused by phloem-colonizing bacteria. Here, the authors present evidence that the disease is the result of an exacerbated immune response to the infection, including production of reactive oxygen species, and that antioxidants and a growth-promoting hormone can mitigate disease symptoms.
- Wenxiu Ma
- , Zhiqian Pang
- & Nian Wang
-
Article
| Open Access The pollen virome of wild plants and its association with variation in floral traits and land use
The pollen virome of wild plants and its association with variation in floral traits and land use
Pollen can be a vehicle for viral spread among plants. Here, Fetters et al. apply viral metagenomics to characterize the pollen virome of a diverse set of wild plants, find known and previously un-known viruses and show that wild plant species harbor more viruses when surrounded by less natural vegetation and when they have traits that promote increased plant-pollinator vector interactions.
- Andrea M. Fetters
- , Paul G. Cantalupo
- & Tia-Lynn Ashman
-
Article
| Open Access PHOSPHATE STARVATION RESPONSE transcription factors enable arbuscular mycorrhiza symbiosis
PHOSPHATE STARVATION RESPONSE transcription factors enable arbuscular mycorrhiza symbiosis
Arbuscular mycorrhiza support plant phosphate uptake. Here Das et al. show that PHR transcription factors permit arbuscular mycorrhiza symbiosis by promoting gene expression related to symbiosis development and maintenance.
- Debatosh Das
- , Michael Paries
- & Caroline Gutjahr
-
Article
| Open Access Nitrogen nutrition contributes to plant fertility by affecting meiosis initiation
Nitrogen nutrition contributes to plant fertility by affecting meiosis initiation
Nitrogen deficiency can cause floral abortion during reproductive development of rice. Here the authors show that when nitrogen is limited, rice plants require the ETFβ protein, which is involved in branched chain amino acid catabolism, to promote nitrogen reutilization and support the initiation of meiosis.
- Han Yang
- , Yafei Li
- & Zhukuan Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Activation of the plant mevalonate pathway by extracellular ATP
Activation of the plant mevalonate pathway by extracellular ATP
Products of the mevalonate pathway support plant development. Here the authors show that the extracellular ATP receptor P2K1 phosphorylates mevalonate kinase and this affects the mevalonate pathway.
- Sung-Hwan Cho
- , Katalin Tóth
- & Gary Stacey
-
Article
| Open Access Shared features and reciprocal complementation of the Chlamydomonas and Arabidopsis microbiota
Shared features and reciprocal complementation of the Chlamydomonas and Arabidopsis microbiota
Plants and algae associate with microbial communities that affect their growth and development. Here, the authors characterize the microbiota associated with a unicellular alga in soil, revealing extensive taxonomic and functional overlap with the root microbiota of land plants.
- Paloma Durán
- , José Flores-Uribe
- & Ruben Garrido-Oter
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of a diarylpentanoid-producing polyketide synthase revealing an unusual biosynthetic pathway of 2-(2-phenylethyl)chromones in agarwood
Identification of a diarylpentanoid-producing polyketide synthase revealing an unusual biosynthetic pathway of 2-(2-phenylethyl)chromones in agarwood
2-(2-Phenylethyl)chromones (PECs) contribute to the distinctive fragrance of agarwood. Here the authors identify a diarylpentanoid-producing polyketide synthase from Aquilaria sinensis and show how it catalyzes PEC formation.
- Xiao-Hui Wang
- , Bo-Wen Gao
- & She-Po Shi
-
Article
| Open Access NuA4 and H2A.Z control environmental responses and autotrophic growth in Arabidopsis
NuA4 and H2A.Z control environmental responses and autotrophic growth in Arabidopsis
Function of nucleosomal acetyltransferase of H4 (NuA4), one major complex of HAT, remains unclear in plants. Here, the authors generate mutants targeting two components of the putative NuA4 complex in Arabidopsis (EAF1 and EPL1) and show their roles in photosynthesis genes regulation through H4K5ac and H2A.Z acetylation.
- Tomasz Bieluszewski
- , Weronika Sura
- & Piotr A. Ziolkowski
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct mechanisms orchestrate the contra-polarity of IRK and KOIN, two LRR-receptor-kinases controlling root cell division
Distinct mechanisms orchestrate the contra-polarity of IRK and KOIN, two LRR-receptor-kinases controlling root cell division
Protein polarization coordinates many plant developmental processes. Here the authors show that IRK and KOIN, two LRR-receptor-kinases polarized to opposite sides of cells in the root meristem, rely on distinct mechanisms to achieve polarity.
- Cecilia Rodriguez-Furlan
- , Roya Campos
- & Jaimie M. Van Norman
-
Article
| Open Access Signatures of selection in recently domesticated macadamia
Signatures of selection in recently domesticated macadamia
Macadamia is a recently domesticated nut crop. Here, the authors report the genome assembly of Hawaiian cultivar ‘Kau’ and conduct population genomic analyses to reveal the origin of Hawaiian cultivars and the genomic basis for one-step operation for the clonal crop domestication.
- Jishan Lin
- , Wenping Zhang
- & Ray Ming
-
Article
| Open Access The CLASSY family controls tissue-specific DNA methylation patterns in Arabidopsis
The CLASSY family controls tissue-specific DNA methylation patterns in Arabidopsis
CLASSY (CLSY) proteins regulate DNA methylation at specific loci in the Arabidopsis genome. Here the authors show that the CLSYs also control tissue-specific DNA methylation, including at siren loci in ovules, and that the lack of an individual CLSYs can shift the epigenetic landscape between tissues.
- Ming Zhou
- , Ceyda Coruh
- & Julie A. Law
-
Article
| Open Access SYP72 interacts with the mechanosensitive channel MSL8 to protect pollen from hypoosmotic shock during hydration
SYP72 interacts with the mechanosensitive channel MSL8 to protect pollen from hypoosmotic shock during hydration
Pollen grains undergo desiccation and rehydration prior to germination and must survive osmotic shock. Here the authors show that the Qc-SNARE protein SYP72 is required for the localization of the mechanosensitive channel MSL8 at the plasma membrane and to maintain viability during rehydration.
- Xuemei Zhou
- , Yifan Zheng
- & Peng Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Connected function of PRAF/RLD and GNOM in membrane trafficking controls intrinsic cell polarity in plants
Connected function of PRAF/RLD and GNOM in membrane trafficking controls intrinsic cell polarity in plants
The polarly localized BASL protein controls asymmetric cell division during stomatal lineage development in Arabidopsis. Here, the authors show that BASL polarization depends on PRAF/RLD proteins that interact with GNOM and suggest a role for endosomal trafficking in establishing polarity.
- Lu Wang
- , Dongmeng Li
- & Juan Dong
-
Article
| Open Access The 2018 European heatwave led to stem dehydration but not to consistent growth reductions in forests
The 2018 European heatwave led to stem dehydration but not to consistent growth reductions in forests
Forest dynamics are monitored at large scales with remote sensing, but individual tree data are necessary for ground-truthing and mechanistic insights. This study on high temporal resolution dendrometer data across Europe reveals that the 2018 heatwave affected tree physiology and growth in unexpected way.
- Roberto L. Salomón
- , Richard L. Peters
- & Kathy Steppe
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics and mechanism of dimer dissociation of photoreceptor UVR8
Dynamics and mechanism of dimer dissociation of photoreceptor UVR8
UVR8 is a plant photoreceptor that dissociates into monomers after sensing UV. Here, via ultrafast spectroscopy and computational calculations, the authors describe the dynamics of charge separation and charge neutralization in UVR8 and describe how these unzip interactions at the dimer interface.
- Xiankun Li
- , Zheyun Liu
- & Dongping Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access The genomes of 204 Vitis vinifera accessions reveal the origin of European wine grapes
The genomes of 204 Vitis vinifera accessions reveal the origin of European wine grapes
Reports on the origin of European wine grapes are controversial. Here, the authors perform population genetics analyses on a large set of representative wine-making varieties and reveal a single domestication event at the origin of the entire germplasm followed by repeated introgression from wild populations.
- Gabriele Magris
- , Irena Jurman
- & Michele Morgante
-
Article
| Open Access Oxicam-type non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit NPR1-mediated salicylic acid pathway
Oxicam-type non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit NPR1-mediated salicylic acid pathway
The plant defense hormone salicylic acid has structural similarity to oxicam-type non-steroidal antiinflammatories. Here the authors show oxicams, as well as endogenous salicylic acid, can alter cellular redox state and immune signaling without affecting the redox status of cysteines in NPR1.
- Nobuaki Ishihama
- , Seung-won Choi
- & Ken Shirasu
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic analyses provide insights into spinach domestication and the genetic basis of agronomic traits
Genomic analyses provide insights into spinach domestication and the genetic basis of agronomic traits
Spinach is a nutritious leafy vegetable growing worldwide. Here, the authors report a high-quality chromosome-scale reference genome assembly of spinach and genome resequencing of 305 accessions, and provide insights into spinach domestication and the genetic basis of agronomic traits.
- Xiaofeng Cai
- , Xuepeng Sun
- & Quanhua Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Interdependent iron and phosphorus availability controls photosynthesis through retrograde signaling
Interdependent iron and phosphorus availability controls photosynthesis through retrograde signaling
Iron deficiency induces chlorosis in plants but only when phosphate supply is sufficient. Here, the authors show that phosphate-dependency is governed by a ROS-mediated retrograde signaling pathway involving the PHT4;4 chloroplast ascorbate transporter and the bZIP58 nuclear transcription factor.
- Hye-In Nam
- , Zaigham Shahzad
- & Hatem Rouached
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic determinants of endophytism in the Arabidopsis root mycobiome
Genetic determinants of endophytism in the Arabidopsis root mycobiome
Plant roots host diverse fungal communities that affect plant health. Here, Mesny et al. use comparative genomics and transcriptomics of fungal isolates from the Arabidopsis thaliana root mycobiota, together with root colonization assays, to identify genetic determinants of endophytism.
- Fantin Mesny
- , Shingo Miyauchi
- & Stéphane Hacquard
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainable intensification for a larger global rice bowl
Sustainable intensification for a larger global rice bowl
Increasing rice yield while improving resource use efficiency is of great importance. This study examines cropping systems globally to highlight areas where rice production can be improved by prioritizing R&D strategies.
- Shen Yuan
- , Bruce A. Linquist
- & Patricio Grassini
-
Article
| Open Access A different perspective for nonphotochemical quenching in plant antenna complexes
A different perspective for nonphotochemical quenching in plant antenna complexes
Nonphotochemical quenching (NPQ) protects photosynthetic complexes from damage due to excess light. Here the authors explore different conformations of the plant CP29 light harvesting complex, showing how protein tuning of carotenoid excitation energies and carotenoid-chlorophyll interactions account for NPQ.
- Edoardo Cignoni
- , Margherita Lapillo
- & Benedetta Mennucci
-
Article
| Open Access A plant virus satellite RNA directly accelerates wing formation in its insect vector for spread
A plant virus satellite RNA directly accelerates wing formation in its insect vector for spread
The cucumber mosaic virus is accompanied by short RNA molecules, satellite RNAs. This study shows that leaves infected with Y-satellite RNA preferentially attract aphids and manipulate aphid physiology to promote their spread to neighbouring plants.
- Wikum H. Jayasinghe
- , Hangil Kim
- & Chikara Masuta
-
Article
| Open Access Widespread homogenization of plant communities in the Anthropocene
Widespread homogenization of plant communities in the Anthropocene
Human-driven movements and extinctions of species have made plant communities across biomes more homogenous. Here the authors quantify plant vascular species and phylogenetic homogenization across the globe, finding that non-native species naturalisations have been a major driver.
- Barnabas H. Daru
- , T. Jonathan Davies
- & Charles C. Davis
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of phosphate sensing and signaling revealed by rice SPX1-PHR2 complex structure
Mechanism of phosphate sensing and signaling revealed by rice SPX1-PHR2 complex structure
SPX proteins sense phosphate levels in plant cells by binding to inositol polyphosphates (InsP) and suppressing the activity of PHR transcription factors. Here the authors show that when bound to InsP6, the rice SPX1 protein inhibits the activity of PHR2 by attenuating both its dimerization and DNA binding activity.
- Jia Zhou
- , Qinli Hu
- & Weiman Xing
-
Article
| Open Access VviPLATZ1 is a major factor that controls female flower morphology determination in grapevine
VviPLATZ1 is a major factor that controls female flower morphology determination in grapevine
Unlike wild Vitis species, which produce either female or male flowers, modern grapevine cultivars form hermaphrodite flowers for self-pollination. Here, the authors report that the VviPLATZ1 (plant AT-rich sequence-and zinc-binding protein1) transcription factor functions in controlling female flower morphology determination.
- Pat Iocco-Corena
- , Jamila Chaïb
- & Harley M. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Heterochromatin is a quantitative trait associated with spontaneous epiallele formation
Heterochromatin is a quantitative trait associated with spontaneous epiallele formation
The molecular origins of epialleles remain unknown. Here, the authors show that a positive feedback loop between H3K9me2 and CMT2/3 is a major contributing factor to the origins of spontaneous epialleles and that heterochromatin is a quantitative trait associated with spontaneous epiallele formation.
- Yinwen Zhang
- , Hosung Jang
- & Robert J. Schmitz
-
Article
| Open Access The Chloranthus sessilifolius genome provides insight into early diversification of angiosperms
The Chloranthus sessilifolius genome provides insight into early diversification of angiosperms
Chloranthales remain the last lineage of core angiosperms that lacks a nuclear genome assembly. Here, the authors report the genome assembly of Chloranthus sesilifolius and show that both hybridization and incomplete lineage sorting may have contributed to the phylogenetic incongruities in the literature.
- Jianxiang Ma
- , Pengchuan Sun
- & Yongzhi Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Coalescence and directed anisotropic growth of starch granule initials in subdomains of Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplasts
Coalescence and directed anisotropic growth of starch granule initials in subdomains of Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplasts
Starch is the major form of energy storage in plant cells and forms discrete, semi-crystalline granules within plastids. Here the authors use electron tomography and nanoSIMS to show that Arabidopsis starch granules initiate in stromal pockets between thylakoid membranes that coalesce before growing anisotropically.
- Léo Bürgy
- , Simona Eicke
- & Samuel C. Zeeman
-
Article
| Open Access Chloranthus genome provides insights into the early diversification of angiosperms
Chloranthus genome provides insights into the early diversification of angiosperms
Chloranthales remain the last lineage of core angiosperms that lacks a nuclear genome assembly. Here, the authors report the genome assembly of Chloranthus spicatus and show its contribution to deepen our understanding on diversification, phylogeny, and genome evolution in angiosperms.
- Xing Guo
- , Dongming Fang
- & Huan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access The barley immune receptor Mla recognizes multiple pathogens and contributes to host range dynamics
The barley immune receptor Mla recognizes multiple pathogens and contributes to host range dynamics
The genes underlying stripe rust host specificity between wheat and barley remain unknown. Here, the authors report that Rps6, Rps7 and Rps8 determine host species specificity in barley at different stages of the pathogen lifecycle and the barley powdery mildew immune receptor Mla8 and Rps7 are the same gene.
- Jan Bettgenhaeuser
- , Inmaculada Hernández-Pinzón
- & Matthew J. Moscou
-
Article
| Open Access Initiation of cytosolic plant purine nucleotide catabolism involves a monospecific xanthosine monophosphate phosphatase
Initiation of cytosolic plant purine nucleotide catabolism involves a monospecific xanthosine monophosphate phosphatase
Dephosphorylation of xanthosine monophosphate (XMP) initiates purine nucleotide catabolism in plant cells. Here the authors identify an XMP phosphatase from Arabidopsis that channels XMP towards catabolism in vivo and demonstrate the structural basis for its XMP specificity.
- Katharina J. Heinemann
- , Sun-Young Yang
- & Claus-Peter Witte
-
Article
| Open Access Interaction of two MADS-box genes leads to growth phenotype divergence of all-flesh type of tomatoes
Interaction of two MADS-box genes leads to growth phenotype divergence of all-flesh type of tomatoes
The all-flesh type of tomato fruits is caused by mutation of the MBP3 gene, however, knocking down MBP3 in certain genotypes also affect plant and fruit development. Here, the authors show that a natural mutation of AGL11, a close homolog of MBP3, is responsible for the phenotypic divergence.
- Baowen Huang
- , Guojian Hu
- & Mondher Bouzayen
-
Article
| Open Access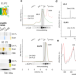 Plant LHC-like proteins show robust folding and static non-photochemical quenching
Plant LHC-like proteins show robust folding and static non-photochemical quenching
Plant light harvesting complex (LHC)‐like proteins protect the photosynthetic machinery from excess light. Here the authors show that plant LHC‐like dimers are stabilized by associated pigments and can quench chlorophyll fluorescence via direct energy transfer from chlorophyll to zeaxanthin.
- Petra Skotnicová
- , Hristina Staleva-Musto
- & Roman Sobotka
-
Article
| Open Access The main oxidative inactivation pathway of the plant hormone auxin
The main oxidative inactivation pathway of the plant hormone auxin
Auxin inactivation plays important roles in plant development. Here the authors show that the main route of IAA inactivation in Arabidopsis is via conjugation by GH3 IAA-amidosynthetases followed by DAO1 dioxygenase-mediated oxidation of the conjugated forms and hydrolysis by ILR1 to release inactive oxIAA.
- Ken-ichiro Hayashi
- , Kazushi Arai
- & Kosuke Fukui
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanistic and genetic basis of single-strand templated repair at Cas12a-induced DNA breaks in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Mechanistic and genetic basis of single-strand templated repair at Cas12a-induced DNA breaks in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Single-stranded oligodeoxynucleotides are often used as templates for DNA repair during genome editing. Here the authors show that, unlike in animals, single-strand templated DNA repair in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii relies on the alternative end-joining enzyme polymerase θ.
- Aron Ferenczi
- , Yen Peng Chew
- & Attila Molnar
-
Comment
| Open Access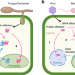 Homecoming: rewinding the reductive evolution of the chloroplast genome for increasing crop yields
Homecoming: rewinding the reductive evolution of the chloroplast genome for increasing crop yields
Developing more productive and sustainable crops will be essential to achieving food security in coming decades. A core process in plant evolution has been the transfer of chloroplast-encoded genes to the nuclear genome. We propose reverting this process as a new approach to improve plant disease resistance and photosynthesis in future crops.
- Briardo Llorente
- , María Eugenia Segretin
- & Nicolás E. Blanco
-
Article
| Open Access Nitrate restricts nodule organogenesis through inhibition of cytokinin biosynthesis in Lotus japonicus
Nitrate restricts nodule organogenesis through inhibition of cytokinin biosynthesis in Lotus japonicus
Nodule development in legumes is a cytokinin dependent process. Here the authors show that high nitrate supply, which limits nodulation, suppresses cytokinin biosynthesis in Lotus japonicus which contrasts with the positive effect of nitrate on cytokinin biosynthesis in non-legumes
- Jieshun Lin
- , Yuda Purwana Roswanjaya
- & Dugald Reid
-
Article
| Open Access The parent-of-origin lncRNA MISSEN regulates rice endosperm development
The parent-of-origin lncRNA MISSEN regulates rice endosperm development
The cereal endosperm is a major determinant of seed size and shape. Here the authors show that a lncRNA, MISSEN, is expressed from the maternally derived allele in rice seeds and regulates a helicase family protein to support efficient nuclear division, distribution and cellularization in the endosperm.
- Yan-Fei Zhou
- , Yu-Chan Zhang
- & Yue-Qin Chen
-
Article
| Open Access MPK3- and MPK6-mediated VLN3 phosphorylation regulates actin dynamics during stomatal immunity in Arabidopsis
MPK3- and MPK6-mediated VLN3 phosphorylation regulates actin dynamics during stomatal immunity in Arabidopsis
Plants can rapidly close stomata to restrict pathogen entry into leaves. Here the authors show that phosphorylation of villin3 by mitogen-activated protein kinases modulates actin remodeling to activate stomatal defense in Arabidopsis.
- Minxia Zou
- , Mengmeng Guo
- & Jiejie Li
-
Article
| Open Access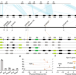 A giant NLR gene confers broad-spectrum resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean
A giant NLR gene confers broad-spectrum resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean
While multiple resistance-to-Phytophthora sojae loci/alleles have been mapped in soybean, many of them have become ineffective to newly evolved isolates. Here, the authors show that a 27.7-kb nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat gene confers broad-spectrum resistance to P. sojae in soybean.
- Weidong Wang
- , Liyang Chen
- & Jianxin Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Arabidopsis P4 ATPase-mediated cell detoxification confers resistance to Fusarium graminearum and Verticillium dahliae
Arabidopsis P4 ATPase-mediated cell detoxification confers resistance to Fusarium graminearum and Verticillium dahliae
Toxic metabolites produced by phytopathogens can subvert host immunity. Here the authors show that the Arabidopsis P4-ATPases, AtALA1 and AtALA7 mediate mycotoxin detoxification by promoting vesicle transport and their subsequent sequestration and degradation in vacuoles.
- Fanlong Wang
- , Xianbi Li
- & Yan Pei
-
Article
| Open Access CLAVATA3 mediated simultaneous control of transcriptional and post-translational processes provides robustness to the WUSCHEL gradient
CLAVATA3 mediated simultaneous control of transcriptional and post-translational processes provides robustness to the WUSCHEL gradient
WUSCHEL is a critical regulator of stem cell homeostasis at shoot apical meristems. Here the authors show that CLV3 regulates WUSCHEL by not only repressing WUSCHEL transcription but also by controlling nuclear export of WUSCHEL and therefore its diffusion between adjacent cells.
- Alexander Plong
- , Kevin Rodriguez
- & G. Venugopala Reddy
-
Article
| Open Access Underwater CAM photosynthesis elucidated by Isoetes genome
Underwater CAM photosynthesis elucidated by Isoetes genome
Despite extensive characterization of crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) in terrestrial angiosperms, little attention has been given to aquatics and early diverging land plants. Here, the authors assemble the genome of Isoetes taiwanensis and investigate the genetic factors driving CAM in this aquatic lycophyte.
- David Wickell
- , Li-Yaung Kuo
- & Fay-Wei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for high selectivity of a rice silicon channel Lsi1
Structural basis for high selectivity of a rice silicon channel Lsi1
The rice Lsi1 aquaporin mediates uptake of silicic acid via the roots. Here the authors show the crystal structure of rice Lsi1 and characterize a unique five residue hydrophilic selectivity filter providing a structural basis for the highly selective activity of Lsi1 in Si uptake.
- Yasunori Saitoh
- , Namiki Mitani-Ueno
- & Michihiro Suga
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of plant phototropic growth by NPH3/RPT2-like substrate phosphorylation and 14-3-3 binding
Regulation of plant phototropic growth by NPH3/RPT2-like substrate phosphorylation and 14-3-3 binding
The plasma membrane-localized NPH3 protein is required for phototropic growth in Arabidopsis. Here the authors show that phototropin 1 phosphorylates NPH3 at a conserved C-terminal sequence motif triggering binding of 14-3-3 proteins to NPH3 that is necessary for the phototropic response.
- Stuart Sullivan
- , Thomas Waksman
- & John M. Christie
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Biofuels
- Light responses
- Natural variation in plants
- Photosynthesis
- Plant biotechnology
- Plant breeding
- Plant cell biology
- Plant development
- Plant domestication
- Plant ecology
- Plant evolution
- Plant genetics
- Plant hormones
- Plant immunity
- Plant molecular biology
- Plant physiology
- Plant reproduction
- Plant signalling
- Plant stress responses
- Plant symbiosis
- Secondary metabolism
- Stomata
- Tropism

 Buxus and Tetracentron genomes help resolve eudicot genome history
Buxus and Tetracentron genomes help resolve eudicot genome history