Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access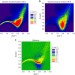 Observation of dynamic atom-atom correlation in liquid helium in real space
Observation of dynamic atom-atom correlation in liquid helium in real space
Liquid helium can be treated as an ideal gas or a condensed liquid and displays intriguing features like Bose–Einstein condensation. Here the authors show that roton excitation reveals information on real space dynamic atom-atom correlations in superfluid helium, which could be used to benchmark models.
- W. Dmowski
- , S. O. Diallo
- & T. Egami
-
Article
| Open Access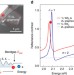 Coulomb engineering of the bandgap and excitons in two-dimensional materials
Coulomb engineering of the bandgap and excitons in two-dimensional materials
Electronic bandgap tuning in semiconductors enables key functionalities in solid-state devices. Here, the authors present a strategy to control the bandgap of atomically thin WS2 and WSe2semiconductors via manipulation of the surrounding dielectric environment rather than by modifications of the materials themselves.
- Archana Raja
- , Andrey Chaves
- & Alexey Chernikov
-
Article
| Open Access Organocatalytic atroposelective synthesis of axially chiral styrenes
Organocatalytic atroposelective synthesis of axially chiral styrenes
Many methods exist for the atroposelective synthesis of axially chiral biaryls, but axially chiral styrenes are much less explored. Here the authors report an organocatalytic procedure for the synthesis of configurationally stable, axially chiral styrenes with high enantio- and diastereoselectivities.
- Sheng-Cai Zheng
- , San Wu
- & Bin Tan
-
Article
| Open Access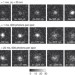 Pointwise error estimates in localization microscopy
Pointwise error estimates in localization microscopy
Super-resolution localization microscopy produces biophysical information in the form of estimated positions of single molecules. Here, Lindénet al. estimate the uncertainty of single localizations, and show that this additional information can improve data analysis and localization precision.
- Martin Lindén
- , Vladimir Ćurić
- & Johan Elf
-
Article
| Open Access Membraneless water filtration using CO2
Membraneless water filtration using CO2
Water treatment processes mostly rely on the use of membranes and filters, which have high pumping costs and require periodic replacement. Here, the authors describe an efficient membraneless method that induces directed motion of suspended colloidal particles by exposing the suspension to CO2.
- Sangwoo Shin
- , Orest Shardt
- & Howard A. Stone
-
Article
| Open Access Directly converting CO2 into a gasoline fuel
Directly converting CO2 into a gasoline fuel
Direct hydrogenation of CO2 into liquid fuels can mitigate CO2 emissions and reduce the rapid depletion of fossil fuels. Here, the authors show an iron-based multifunctional catalyst that converts CO2to gasoline with high selectivity due to synergistic cooperation of multiple catalytic active sites.
- Jian Wei
- , Qingjie Ge
- & Jian Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Facile access to potent antiviral quinazoline heterocycles with fluorescence properties via merging metal-free domino reactions
Facile access to potent antiviral quinazoline heterocycles with fluorescence properties via merging metal-free domino reactions
Heterocycles are ubiquitous in bioactive compounds and routes to different substitution patterns are important to access the full substrate space. Here the authors report a route to 4,5,7,8-substituted antiviral fluorescent quinazolines, to allow cellular uptake visualization without external marker.
- Felix E. Held
- , Anton A. Guryev
- & Svetlana B. Tsogoeva
-
Article
| Open Access Ion-specific ice recrystallization provides a facile approach for the fabrication of porous materials
Ion-specific ice recrystallization provides a facile approach for the fabrication of porous materials
Ice recrystallization is important for a range of research fields, both applied and fundamental, however the effect of ions on this process is not well known. Here the authors discover an ion-specific Hofmeister type effect on ice recrystallization, using this phenomenon to prepare porous materials with tuneable pore sizes.
- Shuwang Wu
- , Chongqin Zhu
- & Jianjun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Homogeneously catalysed conversion of aqueous formaldehyde to H2 and carbonate
Homogeneously catalysed conversion of aqueous formaldehyde to H2 and carbonate
Aqueous formaldehyde is an attractive hydrogen storage system due to the high weight percentage of hydrogen present. Here the authors report a highly active homogeneous ruthenium catalyst system, allowing hydrogen production from formaldehyde-water under mild conditions.
- M. Trincado
- , Vivek Sinha
- & Hansjörg Grützmacher
-
Article
| Open Access Solid-state synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbon catalysts via a mechanochemical assembly through coordination cross-linking
Solid-state synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbon catalysts via a mechanochemical assembly through coordination cross-linking
Ordered mesoporous carbons have shown promise in a range of applications, but sustainable methods to achieve their large scale production are lacking. Here, Dai and coworkers produce OMCs via the mechanochemical assembly of non-toxic polyphenol-metal complexes and triblock copolymers, followed by pyrolysis.
- Pengfei Zhang
- , Li Wang
- & Sheng Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Segregation of liquid crystal mixtures in topological defects
Segregation of liquid crystal mixtures in topological defects
Liquid crystal mixtures are used in commercial applications and their composition affects their properties. Here Rahimiet al. use atomistic simulations to show that defects influence the molecular arrangement of the mixture components leading to a deviation of the local order from that of the bulk.
- Mohammad Rahimi
- , Hadi Ramezani-Dakhel
- & Juan J. de Pablo
-
Article
| Open Access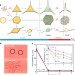 Efficient self-emulsification via cooling-heating cycles
Efficient self-emulsification via cooling-heating cycles
Emulsions are mixtures of liquids which have applications to pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food components. Here Tcholakovaet al. have developed a low-energy emulsification method which requires a low amount of surfactant, works for temperature-sensitive compounds and has potential for scale-up.
- Slavka Tcholakova
- , Zhulieta Valkova
- & Stoyan K. Smoukov
-
Article
| Open Access High-order harmonics measured by the photon statistics of the infrared driving-field exiting the atomic medium
High-order harmonics measured by the photon statistics of the infrared driving-field exiting the atomic medium
Describing the properties of high harmonic photons is challenging due to the complexity of XUV spectroscopy. Here the authors use the photon statistics of the transmitted infrared laser photons to characterize the XUV photon flux without the need of XUV spectrometers.
- N. Tsatrafyllis
- , I. K. Kominis
- & P. Tzallas
-
Article
| Open Access Creation of energetic biothermite inks using ferritin liquid protein
Creation of energetic biothermite inks using ferritin liquid protein
Energetic liquids often suffer from low energy density. Here, the authors create a highly energetic liquid by stabilizing aluminium nanoparticles in ferritin liquid protein, and use this ink to print energetic 3D structures.
- Joseph M. Slocik
- , Ruel McKenzie
- & Rajesh R. Naik
-
Article
| Open Access Wearable smart sensor systems integrated on soft contact lenses for wireless ocular diagnostics
Wearable smart sensor systems integrated on soft contact lenses for wireless ocular diagnostics
Wearable electronics have been utilized for a number of applications including for ocular use, although their use has been limited to a single function. Here, the authors developed a multifunctional contact lens with wireless electronics for measurement of glucose and intraocular pressure.
- Joohee Kim
- , Minji Kim
- & Jang-Ung Park
-
Article
| Open Access Multifunctionality of silver closo-boranes
Multifunctionality of silver closo-boranes
Silver compounds have long been known to possess exceptional solid-state conductivity. Here the authors present silvercloso-boranes in which facile Ag+migration occurs, leading to exceptionally high ion conductivities and potential utility in silver nanowire production and photocatalysis due to their semiconductivity.
- Mark Paskevicius
- , Bjarne R. S. Hansen
- & Torben R. Jensen
-
Article
| Open Access Electronegativity determination of individual surface atoms by atomic force microscopy
Electronegativity determination of individual surface atoms by atomic force microscopy
Electronegativity is a fundamental concept in chemistry; however it is an elusive quantity to evaluate experimentally. Here, the authors estimate the Pauling electronegativity of individual atoms on a surface via atomic force microscopy using a variety of chemically reactive tips.
- Jo Onoda
- , Martin Ondráček
- & Yoshiaki Sugimoto
-
Article
| Open Access Fundamental limits of repeaterless quantum communications
Fundamental limits of repeaterless quantum communications
Quantum communications will be used to transmit entanglement and secure keys, but it is important to estimate their optimal transfer rates. Here the authors compute the fundamental limit of repeaterless quantum communications for the most relevant practical scenario.
- Stefano Pirandola
- , Riccardo Laurenza
- & Leonardo Banchi
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic behaviour of interphases and its implication on high-energy-density cathode materials in lithium-ion batteries
Dynamic behaviour of interphases and its implication on high-energy-density cathode materials in lithium-ion batteries
In lithium-ion batteries the interactions between the electrode and electrolyte represent a complex but critical process. Here the authors reveal the dynamic behaviour of interphases driven by conductive carbon through chemical and imaging analyses of a model transition-metal oxide cathode material.
- Wangda Li
- , Andrei Dolocan
- & Arumugam Manthiram
-
Article
| Open Access Rich complex behaviour of self-assembled nanoparticles far from equilibrium
Rich complex behaviour of self-assembled nanoparticles far from equilibrium
Unravelling the fundamental mechanisms of emergence of complex behaviour is key to understanding living systems. Here, the authors provide a simple experimental platform to investigate and control a rich set of complex phenomena, akin to those seen in living organisms, from a nonliving system of colloidal nanoparticles.
- Serim Ilday
- , Ghaith Makey
- & F. Ömer Ilday
-
Article
| Open Access Holey two-dimensional transition metal oxide nanosheets for efficient energy storage
Holey two-dimensional transition metal oxide nanosheets for efficient energy storage
As alkali-ion battery anodes, metal oxide nanomaterials suffer from severe structural degradation after charging/discharging cycling. Here the authors develop two-dimensional holey nanosheet anodes which display minimal structural changes during electrochemical operation.
- Lele Peng
- , Pan Xiong
- & Guihua Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Nanodiamond-enhanced MRI via in situ hyperpolarization
Nanodiamond-enhanced MRI via in situ hyperpolarization
Hyperpolarized magnetic resonance imaging can enhance imaging contrast by orders of magnitude, but applications are limited by the thermal relaxation of hyperpolarized states. Here, Waddingtonet al. demonstrate the on-demand hyperpolarization of hydrogen spins through the Overhauser effect with nanodiamonds.
- David E. J. Waddington
- , Mathieu Sarracanie
- & Matthew S. Rosen
-
Article
| Open Access Active matter logic for autonomous microfluidics
Active matter logic for autonomous microfluidics
Active fluids consist of self-driven particles that can drive spontaneous flow without the intervention of external forces. Here Woodhouseet al. show how to design logic circuits using this phenomenon in active fluid networks, which could be further exploited for autonomous microfluidic computing.
- Francis G. Woodhouse
- & Jörn Dunkel
-
Article
| Open Access Visible light guided manipulation of liquid wettability on photoresponsive surfaces
Visible light guided manipulation of liquid wettability on photoresponsive surfaces
Controlling surface wettability using visible light is highly attractive for a range of liquid separation technologies. Here, Varanasi, McKinley and colleagues fabricate dye-sensitized photocatalytic TiO2surfaces on which liquid droplet motion can be externally manipulated by visible light illumination.
- Gibum Kwon
- , Divya Panchanathan
- & Kripa K. Varanasi
-
Article
| Open Access A reversible dendrite-free high-areal-capacity lithium metal electrode
A reversible dendrite-free high-areal-capacity lithium metal electrode
Despite recent technological advances, it remains challenging to realize reversible high-areal-capacity lithium metal anodes. Here, the authors demonstrate such an anode by tailoring the top solid electrolyte interphase layer.
- Hui Wang
- , Masaki Matsui
- & Nobuyuki Imanishi
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of extended polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by oxidative tandem spirocyclization and 1,2-aryl migration
Synthesis of extended polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by oxidative tandem spirocyclization and 1,2-aryl migration
Simple synthetic routes to polyaromatic hydrocarbons are important due to their applications in organic electronics. Here the authors report a straightforward synthesis of a diverse range of polyaromatic hydrocarbons, via a one-pot oxidative cyclisation and subsequent 1,2-aryl migration.
- Xuan Zhang
- , Zhanqiang Xu
- & Tienan Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional Mo1.33C MXene with divacancy ordering prepared from parent 3D laminate with in-plane chemical ordering
Two-dimensional Mo1.33C MXene with divacancy ordering prepared from parent 3D laminate with in-plane chemical ordering
Vacancies in 2D materials can influence their properties, however controlling their formation remains a challenge. Here the authors show that selective etching of a 3D laminate with in-plane chemical ordering results in formation of MXenes with ordered divacancies, as well as elevated conductance and supercapacitance.
- Quanzheng Tao
- , Martin Dahlqvist
- & Johanna Rosen
-
Article
| Open Access Ruthenium-cobalt nanoalloys encapsulated in nitrogen-doped graphene as active electrocatalysts for producing hydrogen in alkaline media
Ruthenium-cobalt nanoalloys encapsulated in nitrogen-doped graphene as active electrocatalysts for producing hydrogen in alkaline media
Ruthenium is the cheapest platinum-group metal, yet active hydrogen evolution catalysts with low amounts of ruthenium have yet to be designed. Here, the authors report the preparation of a ruthenium–cobalt nanoalloy and demonstrate its potential as an effective hydrogen evolution catalyst in basic media.
- Jianwei Su
- , Yang Yang
- & Qianwang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access An extra-uterine system to physiologically support the extreme premature lamb
An extra-uterine system to physiologically support the extreme premature lamb
The ability to support the development of a premature fetus in the form of an extracorporeal system has had limited success. Here, the authors show that an extra-uterine device that mimics the intra-uterine environment can provide physiologic support for the extreme premature lamb fetus for four weeks.
- Emily A. Partridge
- , Marcus G. Davey
- & Alan W. Flake
-
Article
| Open Access Gold nanoclusters-assisted delivery of NGF siRNA for effective treatment of pancreatic cancer
Gold nanoclusters-assisted delivery of NGF siRNA for effective treatment of pancreatic cancer
Nerve growth factor (NGF) contributes to the sustained growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells. Here, the authors develop a gold nanocluster-coupled siRNA against NGF that efficiently silences theNGFgene and inhibits tumour growth of pancreatic cancer in mice.
- Yifeng Lei
- , Lixue Tang
- & Xingyu Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Time-reversal symmetry breaking hidden order in Sr2(Ir,Rh)O4
Time-reversal symmetry breaking hidden order in Sr2(Ir,Rh)O4
Exploring ordered states in similarly structured oxides aids the understanding of structure-property correlations. Here the authors discover an unconventional magnetic order in Sr2(Ir,Rh)O4, which is analogous to a loop-current phase in cuprate superconductors with the same lattice structure.
- Jaehong Jeong
- , Yvan Sidis
- & Philippe Bourges
-
Article
| Open Access Photostriction of strontium ruthenate
Photostriction of strontium ruthenate
Light-induced deformation known as photostriction could be used for green energy devices but in most materials the effect is too small to be of practical use. Here, Weiet al. study the photostriction of strontium ruthenate and find photon-induced strain efficiencies of more than one percent.
- Tzu-Chiao Wei
- , Hsin-Ping Wang
- & Jr-Hau He
-
Article
| Open Access A metallic molybdenum dioxide with high stability for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy
A metallic molybdenum dioxide with high stability for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Semiconducting materials are potential SERS substrates as alternatives to noble metals, but often suffer from poor stabilities and sensitivities. Here, the authors use molybdenum dioxide as a SERS material, showing high enhancement factors and stability to oxidation even at high temperatures.
- Qiqi Zhang
- , Xinshi Li
- & Guangcheng Xi
-
Article
| Open Access Volumetric chemical imaging by stimulated Raman projection microscopy and tomography
Volumetric chemical imaging by stimulated Raman projection microscopy and tomography
Recent advances have enabled high-speed three-dimensional optical imaging through the use of fluorescent markers. Here, Chenet al. integrate stimulated Raman imaging into those methods, enabling the label-free and chemically specific volumetric imaging of complex samples.
- Xueli Chen
- , Chi Zhang
- & Ji-Xin Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Band structure engineered layered metals for low-loss plasmonics
Band structure engineered layered metals for low-loss plasmonics
Here the authors show that Ohmic losses are reduced in certain layered metals, such as the transition metal dichalcogenide, due to a small density of states for scattering in the near-IR originating from the electronic band structure, thus leading to improved performance for low-loss plasmonic applications.
- Morten N. Gjerding
- , Mohnish Pandey
- & Kristian S. Thygesen
-
Article
| Open Access Energy scaling of targeted optimal control of complex networks
Energy scaling of targeted optimal control of complex networks
The energy required to control a dynamical complex network can be prohibitively large when there are only a few control inputs. Here the authors demonstrate that if only a subset of the network is targeted the energy requirements decrease exponentially.
- Isaac Klickstein
- , Afroza Shirin
- & Francesco Sorrentino
-
Article
| Open Access Platinum-nickel alloy excavated nano-multipods with hexagonal close-packed structure and superior activity towards hydrogen evolution reaction
Platinum-nickel alloy excavated nano-multipods with hexagonal close-packed structure and superior activity towards hydrogen evolution reaction
While crystal phase modification may endow materials with altered functionality, the fabrication of allomorphic noble metal nanomaterials is challenging. Here, the authors synthesize an unusual hexagonal close-packed platinum-nickel alloy and demonstrate its enhanced hydrogen evolution catalytic activity.
- Zhenming Cao
- , Qiaoli Chen
- & Lansun Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemical generation of sulfur vacancies in the basal plane of MoS2 for hydrogen evolution
Electrochemical generation of sulfur vacancies in the basal plane of MoS2 for hydrogen evolution
In order to fully utilize sulfur vacancies in MoS2 catalysts for industrial applications, a facile and general route for making sulfur vacancies in MoS2 is needed. Here, the authors introduce a scalable route towards generating sulfur vacancies on the MoS2basal plane using electrochemical desulfurization.
- Charlie Tsai
- , Hong Li
- & Frank Abild-Pedersen
-
Article
| Open Access Single-photon test of hyper-complex quantum theories using a metamaterial
Single-photon test of hyper-complex quantum theories using a metamaterial
Hyper-complex quantum theories are generalizations of quantum mechanics where amplitudes are generalized complex numbers. Here the authors study phase commutation in a photonic experiment, reporting consistency with standard quantum mechanics and placing precise bounds on hyper-complex theories.
- Lorenzo M. Procopio
- , Lee A. Rozema
- & Philip Walther
-
Article
| Open Access Fine structure of the topological defect cores studied for disclinations in lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals
Fine structure of the topological defect cores studied for disclinations in lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals
Topological defects play important roles in determining material properties, whilst their core regions remain unexplored due to strongly distorted structures. Zhouet al. take advantage of extended core regions in a chromonic liquid crystal and show both a radial and azimuthal dependent director and scalar order parameter.
- Shuang Zhou
- , Sergij V. Shiyanovskii
- & Oleg D. Lavrentovich
-
Article
| Open Access Bi1Te1 is a dual topological insulator
Bi1Te1 is a dual topological insulator
Coexistence of a topological insulator phase and a topological crystalline insulator phase helps to maintain topological properties under a controlled symmetry breaking perturbation. Here, Eschbacket al. report a superlattice of Bi and Bi2Te3to be such a dual topological insulator.
- Markus Eschbach
- , Martin Lanius
- & Claus M. Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Global distribution of particle phase state in atmospheric secondary organic aerosols
Global distribution of particle phase state in atmospheric secondary organic aerosols
Secondary organic aerosols (SOA) are important for climate and aerosol quality, but the phase state is unclear. Here, the authors show that SOA is liquid in tropical and polar air, semi-solid in the mid-latitudes, solid over dry lands and in a glassy solid phase state in the middle and upper troposphere.
- Manabu Shiraiwa
- , Ying Li
- & Ulrich Pöschl
-
Article
| Open Access Role of chiral quantum Hall edge states in nuclear spin polarization
Role of chiral quantum Hall edge states in nuclear spin polarization
Quantum Hall phases in two-dimensional systems have chiral edges, along which electrons propagate in one direction without backscattering. Here, the authors use nuclear magnetic resonance to demonstrate how chiral modes establish dynamical nuclear polarization in a quantum Hall ferromagnet.
- Kaifeng Yang
- , Katsumi Nagase
- & Hongwu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structures of the NO sensor NsrR reveal how its iron-sulfur cluster modulates DNA binding
Crystal structures of the NO sensor NsrR reveal how its iron-sulfur cluster modulates DNA binding
NsrR is a bacterial transcriptional regulator that acts as a nitric oxide (NO) sensor. Here, the authors present the crystal structure of NsrR, which reveals an unusual Fe-S cluster coordination and explains how NO exposure leads to the degradation of the cluster.
- Anne Volbeda
- , Erin L. Dodd
- & Juan C. Fontecilla-Camps
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced superconductivity accompanying a Lifshitz transition in electron-doped FeSe monolayer
Enhanced superconductivity accompanying a Lifshitz transition in electron-doped FeSe monolayer
The origin of superconductivity enhancement in FeSe monolayer grown on SrTiO3 compared to bulk FeSe is still a debated issue. Here, Shi et al. report a further 15 K jump of Tc accompanying a second Lifshitz transition triggered by electron doping in FeSe/SrTiO3monolayer films.
- X. Shi
- , Z-Q Han
- & H. Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient electrical control of thin-film black phosphorus bandgap
Efficient electrical control of thin-film black phosphorus bandgap
Layered black phosphorous has gained significant attention in the 2D materials community, and dynamical control of its bandgap is key to enable novel applications. Here, the authors demonstrate continuous electrical bandgap tuning using moderate displacement fields.
- Bingchen Deng
- , Vy Tran
- & Fengnian Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Electron transport and visible light absorption in a plasmonic photocatalyst based on strontium niobate
Electron transport and visible light absorption in a plasmonic photocatalyst based on strontium niobate
Metallic oxide SrNbO3has been identified as an efficient hydrogen evolution photocatalyst. Here, Venkatesan and co-workers show that its visible light absorption stems from plasmon resonance, thanks to its large carrier density (despite a large 4.1 eV bandgap), as opposed to from an interband transition.
- D. Y. Wan
- , Y. L. Zhao
- & T Venkatesan
-
Article
| Open Access Optical-helicity-driven magnetization dynamics in metallic ferromagnets
Optical-helicity-driven magnetization dynamics in metallic ferromagnets
Optical switching of ferromagnets has attracted interest for use in ultrafast spintronics but the physical origin of the effect remains unclear. Here the authors determine the contributions of two proposed mechanisms, the inverse Faraday effect and optical spin-transfer torque.
- Gyung-Min Choi
- , André Schleife
- & David G. Cahill
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale interface confinement of ultrafast spin transfer torque driving non-uniform spin dynamics
Nanoscale interface confinement of ultrafast spin transfer torque driving non-uniform spin dynamics
Fundamental understanding of ultrafast spin dynamics is crucial for spintronics applications. Here the authors demonstrate an ultrafast technique to explore the inhomogeneous THz spin dynamics in Fe/Au/Fe multilayers triggered by spin transfer torque.
- Ilya Razdolski
- , Alexandr Alekhin
- & Alexey Melnikov

 Fabrication of MoSe2 nanoribbons via an unusual morphological phase transition
Fabrication of MoSe2 nanoribbons via an unusual morphological phase transition