Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding trends in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction rates
Understanding trends in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction rates
Identifying trends in electrocatalytic activity for carbon dioxide reduction can help with catalyst design, but are difficult to define. Here, the authors develop an electrochemical kinetic model of the process, identifying scaling relations relating transition state energies to CO adsorption energy on metal surfaces.
- Xinyan Liu
- , Jianping Xiao
- & Jens K. Nørskov
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule detection of dihydroazulene photo-thermal reaction using break junction technique
Single-molecule detection of dihydroazulene photo-thermal reaction using break junction technique
The conductance across single-molecule junctions is highly dependent on the electronic properties of the molecule in question. Here the authors use this fact to monitor a photo-thermal reaction by analysing break junction data, and observe significant differences compared to solution state behaviour.
- Cancan Huang
- , Martyn Jevric
- & Wenjing Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Tomographic active optical trapping of arbitrarily shaped objects by exploiting 3D refractive index maps
Tomographic active optical trapping of arbitrarily shaped objects by exploiting 3D refractive index maps
Controlling the three-dimensional behaviour of arbitrarily shaped and oriented particles with optical tweezers is a challenging task. Here, Kim and Park use tomographic active trapping to manipulate non-spherical particles and particle ensembles as well as biological cells.
- Kyoohyun Kim
- & YongKeun Park
-
Article
| Open Access Long-range ferrimagnetic order in a two-dimensional supramolecular Kondo lattice
Long-range ferrimagnetic order in a two-dimensional supramolecular Kondo lattice
Long-range magnetic order hardly ever emerges in a two-dimensional system due to the competition of fundamental magnetic interactions. Here, Girovskyet al. directly observe a long-range ferrimagnetic order emerging in a two-dimensional supramolecular Kondo lattice.
- Jan Girovsky
- , Jan Nowakowski
- & Nirmalya Ballav
-
Article
| Open Access Antiferromagnetic CuMnAs multi-level memory cell with microelectronic compatibility
Antiferromagnetic CuMnAs multi-level memory cell with microelectronic compatibility
Devices based on antiferromagnetic materials have advantages of robustness to external magnetic fields and the potential for ultrafast operation. Here the authors present a multilevel antiferromagnetic memory cell that can be operated using standard electronic interfaces.
- K. Olejník
- , V. Schuler
- & T. Jungwirth
-
Article
| Open Access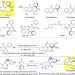 Brønsted acid-catalysed enantioselective construction of axially chiral arylquinazolinones
Brønsted acid-catalysed enantioselective construction of axially chiral arylquinazolinones
Axially chiral arylquinazolinones are structural motifs in several natural products and can also act as chiral ligands. Here, the authors show a chiral phosphoric acid-catalysed strategy to access enantiomerically pure arylquinazolinones by efficient transfer of central chirality into axial chirality.
- Yong-Bin Wang
- , Sheng-Cai Zheng
- & Bin Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic computing of spatial differentiation
Plasmonic computing of spatial differentiation
For specific problems, analog optical computing can be faster and more computationally efficient than digital methods. Here, Zhuet al. simplify the often metamaterial-based approach to a single thin metal film, with which they demonstrate spatial differentiation.
- Tengfeng Zhu
- , Yihan Zhou
- & Shanhui Fan
-
Article
| Open Access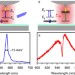 Sub-nanometre control of the coherent interaction between a single molecule and a plasmonic nanocavity
Sub-nanometre control of the coherent interaction between a single molecule and a plasmonic nanocavity
Assessing the coupling between a plasmonic nanocavity and a single quantum emitter is challenging due to the lack of spatial control at the atomic scale. Here Zhanget al. achieve control with sub-nanometre precision and demonstrate the Fano resonance and Lamb shift at the single-molecule level.
- Yao Zhang
- , Qiu-Shi Meng
- & J G Hou
-
Article
| Open Access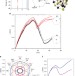 Emptying Dirac valleys in bismuth using high magnetic fields
Emptying Dirac valleys in bismuth using high magnetic fields
Materials in large magnetic fields can be driven into the quantum limit, where electrons occupy only the lowest Landau level and the response is determined by interactions. Here the authors go beyond this limit by emptying one or two of bismuth’s electronic valleys, depending on the field direction.
- Zengwei Zhu
- , Jinhua Wang
- & Kamran Behnia
-
Article
| Open Access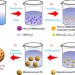 Mesoporous metallic rhodium nanoparticles
Mesoporous metallic rhodium nanoparticles
Mesoporous noble metal nanostructures offer great promise in catalytic applications. Here, Yamauchi and co-workers synthesize mesoporous rhodium nanoparticles using polymeric micelle templates, and report appreciable activities for methanol oxidation and NO remediation.
- Bo Jiang
- , Cuiling Li
- & Yusuke Yamauchi
-
Article
| Open Access Out-of-plane chiral domain wall spin-structures in ultrathin in-plane magnets
Out-of-plane chiral domain wall spin-structures in ultrathin in-plane magnets
Chiral domain walls in magnetic films can be electrically controlled, which makes them attractive for applications, but domain walls in ultrathin films are normally non-chiral. Here, the authors observe chiral domain walls in ultrathin Fe/Ni bilayers that are stabilized by the magnetic anisotropy.
- Gong Chen
- , Sang Pyo Kang
- & Andreas K. Schmid
-
Article
| Open Access Dual-stimuli responsive and reversibly activatable theranostic nanoprobe for precision tumor-targeting and fluorescence-guided photothermal therapy
Dual-stimuli responsive and reversibly activatable theranostic nanoprobe for precision tumor-targeting and fluorescence-guided photothermal therapy
A number of nanomaterials for dual diagnostic and therapeutic application have a number of limitations including poor signal-to-noise ratio. Here, the authors developed dual stimuli-responsive and reversibly activatable nanoprobes for tumour targeting and fluorescence-guided photothermal therapy.
- Xu Zhao
- , Cheng-Xiong Yang
- & Xiu-Ping Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Energy landscape-driven non-equilibrium evolution of inherent structure in disordered material
Energy landscape-driven non-equilibrium evolution of inherent structure in disordered material
Fundamental understanding of glass dynamics is challenging owing to their complex non-equilibrium nature and thus the multi-dimensional potential energy landscape. Here, Fanet al. present a model to explore the glass energy landscape driven by thermal activation and relaxation, which are temporally decoupled.
- Yue Fan
- , Takuya Iwashita
- & Takeshi Egami
-
Article
| Open Access An in vivo strategy to counteract post-administration anticoagulant activity of azido-Warfarin
An in vivo strategy to counteract post-administration anticoagulant activity of azido-Warfarin
The interaction of long circulating drugs with biological molecules might trigger harmful side effects. Here, the authors design an anticoagulant compound that can be deactivatedin vivo using click chemistry, paving the way to the design of drugs with tunable in vivoproperties.
- Sylvain Ursuegui
- , Marion Recher
- & Alain Wagner
-
Article
| Open Access Divergent prebiotic synthesis of pyrimidine and 8-oxo-purine ribonucleotides
Divergent prebiotic synthesis of pyrimidine and 8-oxo-purine ribonucleotides
While mechanisms have been proposed for the prebiotic nucleotide synthesis, these require separate (and potentially incompatible) routes for pyrimidines and purines. Here the authors show that both of these classes of molecules can be formed by a divergent synthesis from a common prebiotic precursor.
- Shaun Stairs
- , Arif Nikmal
- & Matthew W. Powner
-
Article
| Open Access A high quantum yield molecule-protein complex fluorophore for near-infrared II imaging
A high quantum yield molecule-protein complex fluorophore for near-infrared II imaging
Near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence imaging >1,000 nm allows deep tissue imaging, but available organic dyes display poor brightness and temporal resolution. Here, the authors synthesize a NIR dye that, upon binding serum proteins, exhibits a 110-fold increase in intensity, giving an 11% quantum yield.
- Alexander L. Antaris
- , Hao Chen
- & Zhen Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly of a supramolecular hexagram and a supramolecular pentagram
Self-assembly of a supramolecular hexagram and a supramolecular pentagram
Star motifs are ubiquitous throughout nature and in man-made architectures, but their molecular level design remains challenging. Here the authors present a stepwise approach to self-assemble pentagonal and hexagonal star-shaped metallo-architectures through the careful design of metallo-organic ligands.
- Zhilong Jiang
- , Yiming Li
- & Pingshan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Surface chemistry governs cellular tropism of nanoparticles in the brain
Surface chemistry governs cellular tropism of nanoparticles in the brain
There have been numerous attempts to develop nanomaterials to reach cells of the central nervous system for drug delivery. Here, the authors investigate the cellular fate of polymer-based nanoparticles with varying surface chemistries after administration directly into the brain.
- Eric Song
- , Alice Gaudin
- & W. Mark Saltzman
-
Article
| Open Access Nanometric holograms based on a topological insulator material
Nanometric holograms based on a topological insulator material
Holograms generally need to be as thick as a wavelength of light to introduce the necessary optical phase shifts that create true three-dimensional images. Here, Yueet al. use a high-index topological insulator material to create a resonant optical cavity and thin holograms to the nanometre scale.
- Zengji Yue
- , Gaolei Xue
- & Min Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial local magnetic field inhomogeneity enhances T2 relaxivity
Artificial local magnetic field inhomogeneity enhances T2 relaxivity
The signal detected in magnetic resonance imaging comes from the relaxation of proton nuclear magnetization. Here, Zhouet al. introduce magnetic field inhomogeneity as a parameter to design iron oxide nanoparticle clusters to enhance the relaxation rate of nearby protons, thereby increasing image contrast.
- Zijian Zhou
- , Rui Tian
- & Xiaoyuan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Heat guiding and focusing using ballistic phonon transport in phononic nanostructures
Heat guiding and focusing using ballistic phonon transport in phononic nanostructures
Heat conduction at the nanoscale is unlike macroscopic diffusion and phonons can travel in straight lines without dissipation. Here Anufrievet al. show that heat conduction can be spatially directed in nanostructured silicon and exploit this effect to concentrate heat into a focal point.
- Roman Anufriev
- , Aymeric Ramiere
- & Masahiro Nomura
-
Article
| Open Access Self-folding origami at any energy scale
Self-folding origami at any energy scale
Origami is widely practiced in the design of foldable structures for smart applications and usually consists of stiff sheets that only deform along prescribed creases. Pinsonet al. take a statistical physics approach to design and characterize arbitrary patterns as a function of folding energy.
- Matthew B. Pinson
- , Menachem Stern
- & Arvind Murugan
-
Article
| Open Access Electrostatic melting in a single-molecule field-effect transistor with applications in genomic identification
Electrostatic melting in a single-molecule field-effect transistor with applications in genomic identification
DNA hybridization of two single-strands to form a double-stranded helix is widely used for genomic identification applications. Here, Vernicket al. record duplex formation of 20-mer oligonucleotide using a single-molecule field-effect transistor, where DNA kinetics is affected by electrostatic bias.
- Sefi Vernick
- , Scott M. Trocchia
- & Kenneth L. Shepard
-
Article
| Open Access Equilibrium oxygen storage capacity of ultrathin CeO2-δ depends non-monotonically on large biaxial strain
Equilibrium oxygen storage capacity of ultrathin CeO2-δ depends non-monotonically on large biaxial strain
The surface oxygen storage capacity is an important metric of catalytic activity, but its dependence on strain is not well characterized. Here, the authors show the surface oxygen nonstoichiometry in coherently strained CeO2-δ films increases non-monotonically with biaxial strain.
- Chirranjeevi Balaji Gopal
- , Max García-Melchor
- & William C. Chueh
-
Article
| Open Access Unified model for singlet fission within a non-conjugated covalent pentacene dimer
Unified model for singlet fission within a non-conjugated covalent pentacene dimer
Singlet fission is an important process occurring in solar cells, however the mechanism is not well understood. Here the authors reveal intermediates during singlet fission of a non-conjugated pentacene dimer, developing a single kinetic model to describe the data over seven temporal orders of magnitude at room and cryogenic temperatures.
- Bettina S. Basel
- , Johannes Zirzlmeier
- & Dirk M. Guldi
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral correlations in a random distributed feedback fibre laser
Spectral correlations in a random distributed feedback fibre laser
The feedback mechanism in random fibre lasers has been insofar deemed incoherent. To reveal the dynamic evolution of the random fibre laser spectra, Sugavanamet al. use a real-time spectral measurement technique and observe long-lived narrowband components in the random fibre laser’s spectrum.
- Srikanth Sugavanam
- , Mariia Sorokina
- & Dmitry V. Churkin
-
Article
| Open Access High conductance values in π-folded molecular junctions
High conductance values in π-folded molecular junctions
Foldamers are synthetic oligomers that adopt folded conformations through non-covalent intramolecular interactions. Here, Cariniet al. describe a family of foldamers with a large number of anthracene units that are able to transport charge efficiently at the single-molecule level.
- Marco Carini
- , Marta P. Ruiz
- & Aurelio Mateo-Alonso
-
Article
| Open Access Solid frustrated-Lewis-pair catalysts constructed by regulations on surface defects of porous nanorods of CeO2
Solid frustrated-Lewis-pair catalysts constructed by regulations on surface defects of porous nanorods of CeO2
Surface engineering of catalysts allows the tailoring of active sites. Here the authors produce a heterogeneous nanoceria catalyst with engineered defects producing active solid frustrated Lewis pair sites, and use these materials for the hydrogenation of alkynes and alkenes.
- Sai Zhang
- , Zheng-Qing Huang
- & Yongquan Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Histone deacetylase 10 structure and molecular function as a polyamine deacetylase
Histone deacetylase 10 structure and molecular function as a polyamine deacetylase
Polyamines bind to nucleic acids and their function is regulated by reversible acetylation. Here, the authors show that histone deacetylase 10 is a polyamine deacetylase and present its crystal structure with a bound polyamine transition state analogue inhibitor.
- Yang Hai
- , Stephen A. Shinsky
- & David W. Christianson
-
Article
| Open Access An optimized strategy to measure protein stability highlights differences between cold and hot unfolded states
An optimized strategy to measure protein stability highlights differences between cold and hot unfolded states
Crowding effects—important when considering cellular environments—greatly influence protein stability. Here the authors study the impact of macromolecular crowders on high and low temperature protein unfolding, and show that volume exclusion effects are larger when the protein and crowder volumes are similar.
- Caterina Alfano
- , Domenico Sanfelice
- & Piero Andrea Temussi
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced heterogeneous ice nucleation by special surface geometry
Enhanced heterogeneous ice nucleation by special surface geometry
Understanding ice nucleation is important for the development of accurate cloud models. Here Biet al. show that sharp wedges can enhance ice nucleation both when the wedge geometry matches the ice lattice and when such matching is absent, in which case nucleation is promoted by topological defects.
- Yuanfei Bi
- , Boxiao Cao
- & Tianshu Li
-
Article
| Open Access Inertial displacement of a domain wall excited by ultra-short circularly polarized laser pulses
Inertial displacement of a domain wall excited by ultra-short circularly polarized laser pulses
Domain wall motion driven by ultra-short laser pulses has potential for storage of information in magnetoelectronic devices. Here the authors demonstrate the conversion of a circularly polarized femtosecond laser light into inertial displacement of a domain wall in a ferromagnetic semiconductor.
- T. Janda
- , P. E. Roy
- & J. Wunderlich
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient hydrogen production on MoNi4 electrocatalysts with fast water dissociation kinetics
Efficient hydrogen production on MoNi4 electrocatalysts with fast water dissociation kinetics
In water-alkali electrolyzers, sluggish water dissociation kinetics on platinum-free electrocatalysts result in poor hydrogen-production activities. Here the authors report a MoNi4electrocatalyst which reduces the kinetic energy barrier of water dissociation, leading to improved hydrogen-production performance.
- Jian Zhang
- , Tao Wang
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Optical determination of crystal phase in semiconductor nanocrystals
Optical determination of crystal phase in semiconductor nanocrystals
Identifying crystallographic phases in solution is not possible with standard diffraction methods. Here, Limet al. demonstrate the in situidentification of cubic and hexagonal phases of cadmium selenide nanocrystals using optical methods based on first-principles electronic theory.
- Sung Jun Lim
- , André Schleife
- & Andrew M. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring spin defects in diamond by lattice charging
Tailoring spin defects in diamond by lattice charging
Ion implantation is used to introduce spin defects in solids, but it inflicts residual lattice damage, degrading performances. Here the authors demonstrate that the charge state of induced defects influences such damage, and that charging vacancies leads to improved coherence times and yield of centres.
- Felipe Fávaro de Oliveira
- , Denis Antonov
- & Jörg Wrachtrup
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental quantum compressed sensing for a seven-qubit system
Experimental quantum compressed sensing for a seven-qubit system
Quantum compressed sensing can provide a scalable way to characterize quantum states and devices, but has been so far limited to states with quickly decaying eigenvalues. Here the authors show that it can be appropriate even in the general case, demonstrating reconstruction the state of a seven-qubit system.
- C. A. Riofrío
- , D. Gross
- & J. Eisert
-
Article
| Open Access Neuromorphic device architectures with global connectivity through electrolyte gating
Neuromorphic device architectures with global connectivity through electrolyte gating
Global regulation of synaptic strengths in neural systems is known as homeoplasticity. Here, Gkoupideniset al. use an electrolyte to connect and control an array of organic electrochemical devices, in order to demonstrate behaviour that resembles homeoplasticity phenomena in the brain.
- Paschalis Gkoupidenis
- , Dimitrios A. Koutsouras
- & George G. Malliaras
-
Article
| Open Access Giant tunnelling electroresistance in metal/ferroelectric/semiconductor tunnel junctions by engineering the Schottky barrier
Giant tunnelling electroresistance in metal/ferroelectric/semiconductor tunnel junctions by engineering the Schottky barrier
Alternative non-volatile memory designs are needed as the scaling of flash-based memories reaches its physical limits. By careful engineering, Xiet al. achieve ON/OFF ratios as great as 6.0 × 106in ferroelectric tunnel junction devices making them comparable to commercial flash memories.
- Zhongnan Xi
- , Jieji Ruan
- & Di Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Vacuum ultraviolet spectroscopy of the lowest-lying electronic state in subcritical and supercritical water
Vacuum ultraviolet spectroscopy of the lowest-lying electronic state in subcritical and supercritical water
The link between hydrogen bonding and the optical properties of water has been debated for many years, but not fully understood. Here, the authors report vacuum ultraviolet absorption spectra for subcritical and supercritical water, providing insight into the electronic structure of water and its relation to hydrogen bonding.
- Timothy W. Marin
- , Ireneusz Janik
- & Daniel M. Chipman
-
Article
| Open Access Thermophoretic migration of vesicles depends on mean temperature and head group chemistry
Thermophoretic migration of vesicles depends on mean temperature and head group chemistry
Thermal gradients are shown to provide a robust and chemically specific driving force to liposomes. Here the authors show controlled direction of migration of unilamellar lipid vesicles by varying the temperature in the suspension and the exposed polar lipid head groups.
- Emma L. Talbot
- , Jurij Kotar
- & Pietro Cicuta
-
Article
| Open Access Electricity from methane by reversing methanogenesis
Electricity from methane by reversing methanogenesis
Microbial fuel cells generate electricity from a variety of sources, however from methane only negligible electrical power has been reported so far. Here the authors convert methane into electricity using a synthetic consortium consisting of an engineered archaeal strain, microorganisms from methane-acclimated sludge, andGeobacter sulfurreducens.
- Michael J. McAnulty
- , Venkata G. Poosarla
- & Thomas K. Wood
-
Article
| Open Access Tetrahelical structural family adopted by AGCGA-rich regulatory DNA regions
Tetrahelical structural family adopted by AGCGA-rich regulatory DNA regions
DNA tetrahelical structures such as G-quadruplexes are known to play important roles in DNA replication and repair. Here the authors present the structure of 5′-AGCGA-3′-quadruplexes enriched in genetic regulatory regions.
- Vojč Kocman
- & Janez Plavec
-
Article
| Open Access Power generator driven by Maxwell’s demon
Power generator driven by Maxwell’s demon
The study of Maxwell's demon provides a link between information thermodynamics and modern electronics. Using integrated nanometer-scale transistors in a single electron box configuration, Chidaet al., demonstrate the extraction of electrical power by Maxwell’s demon.
- Kensaku Chida
- , Samarth Desai
- & Akira Fujiwara
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning colloidal quantum dot band edge positions through solution-phase surface chemistry modification
Tuning colloidal quantum dot band edge positions through solution-phase surface chemistry modification
The band edge positions of semiconductors decide their optoelectronic properties. Here, the authors establish a simple ligand exchange strategy to tune the band edge positions of colloidal PbS semiconductor quantum dots, revealing clear relationships between surface chemistry and band edge position.
- Daniel M. Kroupa
- , Márton Vörös
- & Matthew C. Beard
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling photophysical properties of ultrasmall conjugated polymer nanoparticles through polymer chain packing
Controlling photophysical properties of ultrasmall conjugated polymer nanoparticles through polymer chain packing
Synthesis of small conjugated polymer nanoparticles (Pdots) with bright and stable fluorescence is an active challenge. Here, the authors introduce a strategy to fabricate ultrasmall Pdots with high fluorescence intensity by using twisted, rather than planar, conjugated polymers, lending new insight into the molecular design of Pdots.
- Hubert Piwoński
- , Tsuyoshi Michinobu
- & Satoshi Habuchi
-
Article
| Open Access Injection and controlled motion of conducting domain walls in improper ferroelectric Cu-Cl boracite
Injection and controlled motion of conducting domain walls in improper ferroelectric Cu-Cl boracite
Conducting ferroelectric domain walls constitute a new class of functional material, but to achieve site-specific injection and annihilation of such walls is challenging. Here, McQuaidet al. report site-specific injection of such walls in Cu3B7O13Cl created by local point-stress and controlled by electric field.
- Raymond G.P. McQuaid
- , Michael P. Campbell
- & J. Marty Gregg
-
Article
| Open Access Inferring personal economic status from social network location
Inferring personal economic status from social network location
It is believed that patterns of social ties are related to individuals’ financial status. Here the authors substantiate this concept by quantitatively demonstrating that a measure of an individual’s location and influence within their social network can be used to infer their economic wellness.
- Shaojun Luo
- , Flaviano Morone
- & Hernán A. Makse
-
Article
| Open Access Voltage-controlled interlayer coupling in perpendicularly magnetized magnetic tunnel junctions
Voltage-controlled interlayer coupling in perpendicularly magnetized magnetic tunnel junctions
Exploring electric field controlled magnetism enables high efficiency and low energy consumption spintronic devices. Here, by manipulating oxygen vacancies and magnetic moment, the authors achieve voltage control of magnetic interlayer coupling in GdOxbased magnetic tunnel junctions.
- T. Newhouse-Illige
- , Yaohua Liu
- & W. G. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Onset of meso-scale turbulence in active nematics
Onset of meso-scale turbulence in active nematics
Bacteria continuously inject energy into their surroundings and thus induce chaotic like flows, namely meso-scale turbulence. Here, the authors show that transition to meso-scale turbulence and inertial turbulence observed in pipes share the same scaling behavior that belongs to the directed percolation universality class.
- Amin Doostmohammadi
- , Tyler N. Shendruk
- & Julia M. Yeomans

 Artificial control of the bias-voltage dependence of tunnelling-anisotropic magnetoresistance using quantization in a single-crystal ferromagnet
Artificial control of the bias-voltage dependence of tunnelling-anisotropic magnetoresistance using quantization in a single-crystal ferromagnet