Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access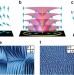 Morphogenesis of liquid crystal topological defects during the nematic-smectic A phase transition
Morphogenesis of liquid crystal topological defects during the nematic-smectic A phase transition
Defects in liquid crystals play a central role in determining their structural and dynamic properties, whilst it is challenging to characterize the defects at a molecule level. Here, Gimet al. trace the evolution pathway of defects during a phase transition from a nematic to a smectic state.
- Min-Jun Gim
- , Daniel A. Beller
- & Dong Ki Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access Deposition and drying dynamics of liquid crystal droplets
Deposition and drying dynamics of liquid crystal droplets
When particle-laden drops evaporate, coffee ring patterns form which can affect particle deposition. Here Davidsonet al. show that unlike previously investigated drops, the flows in drying drops of liquid crystals are driven by an increase in surface tension due to liquid crystal concentration.
- Zoey S. Davidson
- , Yongyang Huang
- & A. G. Yodh
-
Article
| Open Access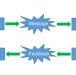 Interactive models of communication at the nanoscale using nanoparticles that talk to one another
Interactive models of communication at the nanoscale using nanoparticles that talk to one another
In the interactive model of communication, information is exchanged bidirectionally between a sender and receiver. Here, the authors realise interactive communication between two artificial nanoparticles, which relay information between each other in the form of chemical messengers and enzymatic reactions.
- Antoni Llopis-Lorente
- , Paula Díez
- & Ramón Martínez-Máñez
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrodynamic cavitation in Stokes flow of anisotropic fluids
Hydrodynamic cavitation in Stokes flow of anisotropic fluids
Cavitation is the formation of vapour bubbles within a liquid and is undesirable in many industrial applications. Here Stiegeret al. show how the anisotropic fluids influence this process in a nematic liquid crystal and find that orientational ordering of molecules can tune the onset of cavitation.
- Tillmann Stieger
- , Hakam Agha
- & Anupam Sengupta
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming the crystallization and designability issues in the ultrastable zirconium phosphonate framework system
Overcoming the crystallization and designability issues in the ultrastable zirconium phosphonate framework system
Zirconium phosphonate based metal-organic frameworks often exhibit superior chemical stabilities, but typically exist as poorly crystalline or amorphous materials. Here the authors exploit an ionothermal method to obtain highly porous and remarkably stable single crystalline zirconium phosphonate frameworks that can efficiently remove uranyl ions from aqueous solutions.
- Tao Zheng
- , Zaixing Yang
- & Shuao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid mass production of two-dimensional metal oxides and hydroxides via the molten salts method
Rapid mass production of two-dimensional metal oxides and hydroxides via the molten salts method
2D materials with exotic electronic properties are increasingly important for the development of low-dimensional electronic devices. Here, Huet al. have developed a fast and efficient method to synthesize 2D metal oxides and hydroxides, further enabling 2D electronics.
- Zhimi Hu
- , Xu Xiao
- & Jun Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access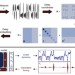 Chaos as an intermittently forced linear system
Chaos as an intermittently forced linear system
The huge amount of data generated in fields like neuroscience or finance calls for effective strategies that mine data to reveal underlying dynamics. Here Brunton et al.develop a data-driven technique to analyze chaotic systems and predict their dynamics in terms of a forced linear model.
- Steven L. Brunton
- , Bingni W. Brunton
- & J. Nathan Kutz
-
Article
| Open Access Amazonian forest-savanna bistability and human impact
Amazonian forest-savanna bistability and human impact
Deforestation and edge effects around cleared areas impact forest stability. Here, the authors examine human impacts on Amazonian forest-savanna bistability and show that tree cover bimodality is enhanced in regions close to human activities and is nearly absent in regions unaffected by human activities.
- Bert Wuyts
- , Alan R. Champneys
- & Joanna I. House
-
Article
| Open Access Conjugation of squalene to gemcitabine as unique approach exploiting endogenous lipoproteins for drug delivery
Conjugation of squalene to gemcitabine as unique approach exploiting endogenous lipoproteins for drug delivery
The interaction of nanoparticles with a range of biomolecules once they have been injected within the body can affect their performance. Here, the authors demonstrate that squalene nanomaterials conjugated with anticancer drugs can interact with lipoproteins and can be used to target cancer cells.
- Dunja Sobot
- , Simona Mura
- & Patrick Couvreur
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast coherence transfer in DNA-templated silver nanoclusters
Ultrafast coherence transfer in DNA-templated silver nanoclusters
DNA-templated silver nanoclusters possess desirable optical properties, but their excited state dynamics remain poorly understood. Here the authors show that intracluster relaxations in such clusters are strongly coupled to a vibrational mode, resulting in ultrafast concerted transfer of population and coherence between excited states.
- Erling Thyrhaug
- , Sidsel Ammitzbøll Bogh
- & Donatas Zigmantas
-
Article
| Open Access All pure bipartite entangled states can be self-tested
All pure bipartite entangled states can be self-tested
Device-independent self-testing is an approach that allows a complete certification of an unknown quantum state, simply by inspecting outcomes of measurements. Here, the authors demonstrate that any pure bipartite entangled state can be self-tested.
- Andrea Coladangelo
- , Koon Tong Goh
- & Valerio Scarani
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchically structured lithium titanate for ultrafast charging in long-life high capacity batteries
Hierarchically structured lithium titanate for ultrafast charging in long-life high capacity batteries
Both electronic and ionic transport must be optimized in Li4Ti5O12for its use in Li-ion batteries, most promisingly against high voltage cathodes. Here authors synthesize hierarchical porous micrometre-scale structures composed of primary nanoparticles to demonstrate an attractive combination of rate performance, capacity and cycling stability.
- Mateusz Odziomek
- , Frédéric Chaput
- & Stephane Parola
-
Article
| Open Access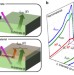 Virtual substrate method for nanomaterials characterization
Virtual substrate method for nanomaterials characterization
Quantitative characterization of supported nanomaterials is challenging, because the nanomaterial signals cannot easily be deconvoluted from those of the substrate. Here, the authors introduce an inventive approach to overcome this problem for electron-based surface analysis techniques.
- Bo Da
- , Jiangwei Liu
- & Zejun Ding
-
Article
| Open Access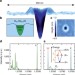 Highly indistinguishable and strongly entangled photons from symmetric GaAs quantum dots
Highly indistinguishable and strongly entangled photons from symmetric GaAs quantum dots
Scalable and integratable sources of entangled-photon pairs are an important building block for quantum photonic applications. Here, Huberet al. demonstrate that droplet-etched gallium arsenide quantum dots can emit highly indistinguishable photon pairs with a high degree of entanglement.
- Daniel Huber
- , Marcus Reindl
- & Rinaldo Trotta
-
Article
| Open Access Finding multiple reaction pathways via global optimization of action
Finding multiple reaction pathways via global optimization of action
Identifying pathways and transition states is critical to understanding chemical and biological reactions. Here, the authors introduce a capable computational approach using conformational space annealing to find multiple reaction pathways via global optimization of the Onsager-Machlup action.
- Juyong Lee
- , In-Ho Lee
- & Bernard R. Brooks
-
Article
| Open Access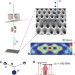 Scalable focused ion beam creation of nearly lifetime-limited single quantum emitters in diamond nanostructures
Scalable focused ion beam creation of nearly lifetime-limited single quantum emitters in diamond nanostructures
Interfacing spin quantum memories with photons requires the controlled creation of defect centre—nanocavity systems. Here the authors demonstrate direct, maskless creation of single silicon vacancy centres in diamond nanostructures, and report linewidths comparable to naturally occurring centres
- Tim Schröder
- , Matthew E. Trusheim
- & Dirk Englund
-
Article
| Open Access Solid-state ensemble of highly entangled photon sources at rubidium atomic transitions
Solid-state ensemble of highly entangled photon sources at rubidium atomic transitions
Scalable and integratable sources of entangled-photon pairs are an important building block for quantum photonic applications. Here, Keilet al. demonstrate that an ensemble of droplet-etched gallium arsenide quantum dots can emit polarization-entangled photons with almost 100% yield.
- Robert Keil
- , Michael Zopf
- & Oliver G. Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of coherent energy transfer in nonlinear micromechanical oscillators
Direct observation of coherent energy transfer in nonlinear micromechanical oscillators
Energy drain on micromechanical resonators is always compensated by energy gain from external sources during operation. Here, Chenet al. show a strategy that can sustain stable oscillations by redistributing mechanical energy between coupled vibrational modes when the external energy supply is off.
- Changyao Chen
- , Damián H. Zanette
- & Daniel López
-
Article
| Open Access Rationally designed mineralization for selective recovery of the rare earth elements
Rationally designed mineralization for selective recovery of the rare earth elements
Lanthanide elements are difficult to separate from aqueous solution with low energy input. Here, the authors design a peptide that recognizes and drives the precipitation of an insoluble lanthanide complex under physiological conditions, introducing a biomineralization-based approach for rare earth recovery.
- Takaaki Hatanaka
- , Akimasa Matsugami
- & Nobuhiro Ishida
-
Article
| Open Access The controlled disassembly of mesostructured perovskites as an avenue to fabricating high performance nanohybrid catalysts
The controlled disassembly of mesostructured perovskites as an avenue to fabricating high performance nanohybrid catalysts
Disassembly of three-dimensionally ordered materials generates nanoparticles with new structural and physicochemical properties. Here the authors show a fragmentation strategy applied to a perovskite material leading to nanostructures with improved catalytic activity in the methane combustion.
- Yuan Wang
- , Hamidreza Arandiyan
- & Rose Amal
-
Article
| Open Access A reaction mode of carbene-catalysed aryl aldehyde activation and induced phenol OH functionalization
A reaction mode of carbene-catalysed aryl aldehyde activation and induced phenol OH functionalization
Selective functionalization of aromatic compounds is important in synthetic chemistry. Here the authors report anN-heterocyclic carbene-catalysed approach for enantioselectively converting ortho-hydroxyaldehydes to cyclic products, via activation of both phenol and aldehyde groups.
- Xingkuan Chen
- , Hongling Wang
- & Yonggui Robin Chi
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of spiro quasi[1]catenanes and quasi[1]rotaxanes via a templated backfolding strategy
Synthesis of spiro quasi[1]catenanes and quasi[1]rotaxanes via a templated backfolding strategy
Spiro compounds contain two or more rings linked together through one common atom. Here the authors provide a method to backfold both rings, producing spiro quasi[1]catenanes, via a strategy of temporarily linking the linear intermediates with covalent bonds.
- Luuk Steemers
- , Martin J. Wanner
- & Jan H. van Maarseveen
-
Article
| Open Access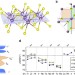 Negative Poisson’s ratio in 1T-type crystalline two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides
Negative Poisson’s ratio in 1T-type crystalline two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides
Auxetic materials—those that expand laterally when stretched—can possess enhanced mechanical properties, including shear modulus, indentation resistance, and fracture toughness. Here the authors show that 1T-type crystalline 2D transition metal dichalcogenides exhibit intrinsic in-plane negative Poisson’s ratios.
- Liping Yu
- , Qimin Yan
- & Adrienn Ruzsinszky
-
Article
| Open Access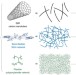 Nonlinear mechanics of hybrid polymer networks that mimic the complex mechanical environment of cells
Nonlinear mechanics of hybrid polymer networks that mimic the complex mechanical environment of cells
Mechanical properties of living organisms are determined by intra- and extra-cellular biopolymer networks. Here, the authors show how the mechanics of polyisocyanopeptide hydrogels, mimicking biopolymers, can be readily manipulated by introducing a second polymer network.
- Maarten Jaspers
- , Sarah L. Vaessen
- & Paul H. J. Kouwer
-
Article
| Open Access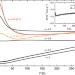 Gigantic negative magnetoresistance in the bulk of a disordered topological insulator
Gigantic negative magnetoresistance in the bulk of a disordered topological insulator
Large negative magnetoresistance is usually related to magnetism and the exceptions are rare. Here, Breuniget al. report a large negative magnetoresistance in a topological insulator, TlBi0.15Sb0.85Te2, which is likely due to the Zeeman effect on a barely percolating current path formed in the disordered bulk.
- Oliver Breunig
- , Zhiwei Wang
- & Yoichi Ando
-
Article
| Open Access High pressure synthesis of a hexagonal close-packed phase of the high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi
High pressure synthesis of a hexagonal close-packed phase of the high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi
High-entropy alloys represent a new strategy for the design of materials with properties superior to those of conventional alloys, but are largely limited to simple phases of cubic symmetry. By applying high pressures on CrMnFeCoNi, here authors demonstrate synthesis of a hexagonal close-packed phase.
- Cameron L. Tracy
- , Sulgiye Park
- & Wendy L. Mao
-
Article
| Open Access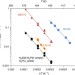 Tailoring nanoscopic confines to maximize catalytic activity of hydronium ions
Tailoring nanoscopic confines to maximize catalytic activity of hydronium ions
The rates of acid-catalysed reactions vary in constrained environments. Here the authors show that molecularly sized pores greatly promote aqueous phase alcohol dehydration by enhancing the association between substrate and hydronium ions, and even by lowering the free energy barrier.
- Hui Shi
- , Sebastian Eckstein
- & Johannes A. Lercher
-
Article
| Open Access Construction of hierarchically porous metal–organic frameworks through linker labilization
Construction of hierarchically porous metal–organic frameworks through linker labilization
Expanding pore sizes and volumes in metal-organic frameworks is challenging, but crucial for the encapsulation of larger guest molecules. Here, Zhou and colleagues report a linker labilization strategy to construct MOFs containing hierarchical pore architectures with dimensions ranging from 1.5 to 18 nm.
- Shuai Yuan
- , Lanfang Zou
- & Hong-Cai Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access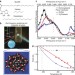 The interfacial structure of water droplets in a hydrophobic liquid
The interfacial structure of water droplets in a hydrophobic liquid
Nanoscopic water droplets in a hydrophobic liquid are abundant in the earth, our bodies and the sky. Here, it is shown that the surface of such a droplet has stronger hydrogen bonds than a planar interface of water and a hydrophobic liquid, equivalent to a 50 K reduction of the surface temperature.
- Nikolay Smolentsev
- , Wilbert J. Smit
- & Sylvie Roke
-
Article
| Open Access Non-Poissonian photon statistics from macroscopic photon cutting materials
Non-Poissonian photon statistics from macroscopic photon cutting materials
Photon-cutting materials provide a way around efficiency limits for energy conversion by absorbing high-energy photons and ‘cutting’ them into multiple low-energy excitations. Here, the authors show that photon-cutting material can be identified and characterised by studying their bunched emission statistics.
- Mathijs de Jong
- , Andries Meijerink
- & Freddy T. Rabouw
-
Review Article
| Open Access Exploring chemoselective S-to-N acyl transfer reactions in synthesis and chemical biology
Exploring chemoselective S-to-N acyl transfer reactions in synthesis and chemical biology
The conversion of thioesters to amides via acyl transfer has become one of the most important synthetic techniques for the chemical synthesis and modification of proteins. This review discusses this S-to-N acyl transfer process, and highlights some of the key applications across chemistry and biology.
- Helen M. Burke
- , Lauren McSweeney
- & Eoin M. Scanlan
-
Article
| Open Access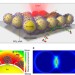 In situ dynamic tracking of heterogeneous nanocatalytic processes by shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
In situ dynamic tracking of heterogeneous nanocatalytic processes by shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Rational design of heterogeneous catalysts requires molecular understanding of catalytic processes. Here, the authors attach PtFe and Pd nanocatalysts to Raman signal-enhancing Au-silica nanoparticles, allowing them to spectroscopically observe the active species and bonds involved in CO oxidation in real time.
- Hua Zhang
- , Chen Wang
- & Zhong-Qun Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic-field induced multiple topological phases in pyrochlore iridates with Mott criticality
Magnetic-field induced multiple topological phases in pyrochlore iridates with Mott criticality
The interplay between multiple electronic interactions in solid promotes the emergence of exotic phases. Here, Uedaet al. report magnetotransport study on pyrochlore iridates R2Ir2O7near quantum metal-insulator transition reflecting the emergence of multiple Weyl semimetal states.
- Kentaro Ueda
- , Taekoo Oh
- & Yoshinori Tokura
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring the orbital angular momentum spectrum of an electron beam
Measuring the orbital angular momentum spectrum of an electron beam
Existing methods of characterizing electron beams carrying orbital angular momentum are inefficient as they allow measuring one OAM state at a time. Here the authors demonstrate an OAM spectrometer capable of analysing multiple OAM states and a potential tool for probing magnetic materials.
- Vincenzo Grillo
- , Amir H. Tavabi
- & Ebrahim Karimi
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent structural trapping through wave packet dispersion during photoinduced spin state switching
Coherent structural trapping through wave packet dispersion during photoinduced spin state switching
Ultrafast nonadiabatic chemical dynamics during molecular photo-transformations remain challenging to describe since electronic/nuclear configurations are coupled. Here the authors use time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy to probe the light-induced spin-state trapping dynamics of [Fe(bpy)3]2+beyond the Born-Oppenheimer approximation.
- Henrik T. Lemke
- , Kasper S. Kjær
- & Marco Cammarata
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-orbit torque-driven skyrmion dynamics revealed by time-resolved X-ray microscopy
Spin-orbit torque-driven skyrmion dynamics revealed by time-resolved X-ray microscopy
Magnetic skyrmions are potentially suitable for future spintronic devices, but their dynamical behaviour in real space remains elusive. Here, Wooet al. report nanosecond-dynamics of a 100nm-size magnetic skyrmion triggered by current-induced spin-orbit torques.
- Seonghoon Woo
- , Kyung Mee Song
- & Joonyeon Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Fibril polymorphism affects immobilized non-amyloid flanking domains of huntingtin exon1 rather than its polyglutamine core
Fibril polymorphism affects immobilized non-amyloid flanking domains of huntingtin exon1 rather than its polyglutamine core
Huntington's disease is caused by a polyglutamine stretch expansion in the first exon of huntingtin. Here, the authors use infrared spectroscopy and solid-state NMR and show that polymorphic huntingtin exon1 fibres differ in their flanking regions but not their core polyglutamine amyloid structures.
- Hsiang-Kai Lin
- , Jennifer C. Boatz
- & Patrick C. A. van der Wel
-
Article
| Open Access Visualization of lithium-ion transport and phase evolution within and between manganese oxide nanorods
Visualization of lithium-ion transport and phase evolution within and between manganese oxide nanorods
Hollandite structured materials are potentially useful for battery technologies. Here the authors report the unusual lateral transport of lithium ions between lithiated silver manages oxide nanorods where the reaction fronts and kinetics are maintained within the neighbouring nanorods.
- Feng Xu
- , Lijun Wu
- & Yimei Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying similarity of pore-geometry in nanoporous materials
Quantifying similarity of pore-geometry in nanoporous materials
Pore structure plays an important role in dictating gas storage performance for nanoporous materials. Here, Smit and colleagues develop a topological approach to quantify pore structure similarity, and exploit the resulting descriptor to screen for materials that possess structural similarities with top-performers.
- Yongjin Lee
- , Senja D. Barthel
- & Berend Smit
-
Article
| Open Access Thermoelectric quantum oscillations in ZrSiS
Thermoelectric quantum oscillations in ZrSiS
Studies of quantum oscillations provide a valuable probe into the electronic structure of topological semimetals. Matusiaket al. demonstrate that quantum features in ZrSiS can be probed with greater sensitivity using diffusive thermopower than magnetization and electrical resistivity approaches.
- Marcin Matusiak
- , J. R. Cooper
- & Dariusz Kaczorowski
-
Article
| Open Access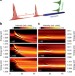 Long-term mutual phase locking of picosecond pulse pairs generated by a semiconductor nanowire laser
Long-term mutual phase locking of picosecond pulse pairs generated by a semiconductor nanowire laser
Although nanolasers have been an active field of research for over a decade, mode-locking on the nanoscale has not been achieved yet. Here, Mayeret al. show that semiconductor nanowire lasers can emit pairs of phase-locked picosecond pulses when the nanowires are incoherently pumped.
- B. Mayer
- , A. Regler
- & J. J. Finley
-
Article
| Open Access A light-driven artificial flytrap
A light-driven artificial flytrap
Stimuli-responsive materials are commonly used in autonomous systems, whilst it is challenging to power them in a programmable manner. Here, Waniet al. use an optical fibre to control the shape of light-responsive liquid-crystal elastomers, which allow the device to detect and trap targeted objects.
- Owies M. Wani
- , Hao Zeng
- & Arri Priimagi
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic evidence of temperature-induced Lifshitz transition and topological nature in ZrTe5
Electronic evidence of temperature-induced Lifshitz transition and topological nature in ZrTe5
To understand the anomalous electronic transport properties of ZrTe5 remains an elusive puzzle. Here, Zhang et al. report direct electronic evidence to the origin of the resistivity anomaly and temperature induced Lifshitz transition in ZrTe5, indicating it being a weak topological insulator.
- Yan Zhang
- , Chenlu Wang
- & X. J. Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Structural water engaged disordered vanadium oxide nanosheets for high capacity aqueous potassium-ion storage
Structural water engaged disordered vanadium oxide nanosheets for high capacity aqueous potassium-ion storage
The authors report that the interplay between structural water and highly disordered vanadium oxide can stabilize the layered metal oxides and enhanced their performance for aqueous potassium-ion storage based on neutron scattering measurements and electrochemical characterizations.
- Daniel Scott Charles
- , Mikhail Feygenson
- & Xiaowei Teng
-
Article
| Open Access Interface-driven formation of a two-dimensional dodecagonal fullerene quasicrystal
Interface-driven formation of a two-dimensional dodecagonal fullerene quasicrystal
Quasicrystals promise exciting technological advances in optical devices, but their formation mechanism is yet not fully understood. Here, the authors describe a two-dimensional dodecagonal fullerene quasicrystal, forming on a Pt3Ti(111)-surface due to the complex adsorption-energy landscape.
- M. Paßens
- , V. Caciuc
- & S. Karthäuser
-
Article
| Open Access Deterministic strain-induced arrays of quantum emitters in a two-dimensional semiconductor
Deterministic strain-induced arrays of quantum emitters in a two-dimensional semiconductor
The emergence of quantum emitters in 2D materials has led to the quest for methods and designs enabling their controllable spatial positioning. Here, the authors use strain engineering to fabricate a deterministic array of quantum emitters in WSe2with nanometre positioning accuracy.
- Artur Branny
- , Santosh Kumar
- & Brian D Gerardot
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale quantum-emitter arrays in atomically thin semiconductors
Large-scale quantum-emitter arrays in atomically thin semiconductors
Quantum emitters have been recently isolated in 2D materials, yet their spatial controllability remains an open challenge. Here, the authors devise a method to create arrays of quantum emitters in WSe2 and WS2, by taking advantage of the strain distribution induced by a nanopatterned silica substrate.
- Carmen Palacios-Berraquero
- , Dhiren M. Kara
- & Mete Atatüre
-
Article
| Open Access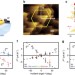 Spin injection and helicity control of surface spin photocurrent in a three dimensional topological insulator
Spin injection and helicity control of surface spin photocurrent in a three dimensional topological insulator
Surface spin current in a 3D topological insulator (TI) remains difficult to control and the out-of-plane spin texture is largely unexplored. Here, the authors identify subtle effect of the spin texture on surface photocurrent and demonstrate controlled spin injection from a semiconductor to a TI.
- Y. Q. Huang
- , Y. X. Song
- & W. M. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access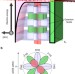 Artificial control of the bias-voltage dependence of tunnelling-anisotropic magnetoresistance using quantization in a single-crystal ferromagnet
Artificial control of the bias-voltage dependence of tunnelling-anisotropic magnetoresistance using quantization in a single-crystal ferromagnet
Reduction of power consumption for magnetization reversal in spintronic memory devices is of great importance. Here, Munetaet al. report the gate electric-field assisted control of the magnetic anisotropy of the density of states using quantum size effect in GaMnAs.
- Iriya Muneta
- , Toshiki Kanaki
- & Masaaki Tanaka

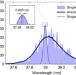 Attosecond interferometry with self-amplified spontaneous emission of a free-electron laser
Attosecond interferometry with self-amplified spontaneous emission of a free-electron laser