Matters Arising
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Ice-nucleating proteins are activated by low temperatures to control the structure of interfacial water
Ice-nucleating proteins are activated by low temperatures to control the structure of interfacial water
Ice-nucleating proteins promote ice formation at high sub-zero temperatures, but the mechanism is still unclear. The authors investigate a model ice-nucleating protein at the air-water interface using vibrational sum frequency generation spectroscopy and simulations, revealing its reorientation at low temperatures, which increases contact with water molecules and promotes their ordering.
- Steven J. Roeters
- , Thaddeus W. Golbek
- & Tobias Weidner
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental evidence for the existence of a second partially-ordered phase of ice VI
Experimental evidence for the existence of a second partially-ordered phase of ice VI
Water ice exhibits several hydrogen-ordered and disordered phases and it’s unclear if a disordered phase can transform into only one ordered phase. Here, the authors identify a partially hydrogen-ordered phase at high pressure, ice XIX, as the second hydrogen-ordered phase of ice VI beside ice XV.
- Ryo Yamane
- , Kazuki Komatsu
- & Hiroyuki Kagi
-
Article
| Open Access Structural characterization of ice XIX as the second polymorph related to ice VI
Structural characterization of ice XIX as the second polymorph related to ice VI
Water ice exhibits several hydrogen-disordered phases that become ordered upon lowering the temperature, but ordering of ice VI, one of the main ice phases, is not well understood. Here the authors identify and structurally refine a partially hydrogen-ordered phase, ice XIX, obtained from ice VI, and observe its transition to its partially hydrogen-ordered sibling ice XV.
- Tobias M. Gasser
- , Alexander V. Thoeny
- & Thomas Loerting
-
Article
| Open Access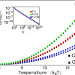 Thermodynamics of structure-forming systems
Thermodynamics of structure-forming systems
Structure-forming systems, such as chemical reaction networks, are usually described with the grand-canonical ensemble, but this may be inaccurate for small-sized systems. Here, the authors propose a canonical ensemble approach for closed structure-forming systems, showing its application to physical problems including the self-assembly of soft matter.
- Jan Korbel
- , Simon David Lindner
- & Stefan Thurner
-
Article
| Open Access Short-lived metal-centered excited state initiates iron-methionine photodissociation in ferrous cytochrome c
Short-lived metal-centered excited state initiates iron-methionine photodissociation in ferrous cytochrome c
The dissociation mechanism of the heme axial ligand in heme proteins is not yet fully understood. The authors investigate the photodissociation dynamics of the bond between heme Fe and methionine S in ferrous cytochrome c using femtosecond time-resolved X-ray solution scattering and X-ray emission spectroscopy, simultaneously tracking electronic and nuclear structure changes.
- Marco E. Reinhard
- , Michael W. Mara
- & Kelly J. Gaffney
-
Article
| Open Access Reentrant liquid condensate phase of proteins is stabilized by hydrophobic and non-ionic interactions
Reentrant liquid condensate phase of proteins is stabilized by hydrophobic and non-ionic interactions
Elucidating the molecular driving forces underlying liquid–liquid phase separation is a key objective for understanding biological function and malfunction. Here the authors show that a wide range of cellular proteins, including FUS, TDP-43, Brd4, Sox2, and Annexin A11, which form condensates at low salt concentrations, can reenter a phase-separated regime at high salt concentrations.
- Georg Krainer
- , Timothy J. Welsh
- & Tuomas P. J. Knowles
-
Article
| Open Access Bridging scales in disordered porous media by mapping molecular dynamics onto intermittent Brownian motion
Bridging scales in disordered porous media by mapping molecular dynamics onto intermittent Brownian motion
The diffusion of fluids in complex nanoporous geometries represents a challenge for modelling approaches. Here, the authors describe the macroscopic diffusivity of a simple fluid in disordered nanoporous materials by bridging microscopic and mesoscopic dynamics with parameters obtained from simple physical laws.
- Colin Bousige
- , Pierre Levitz
- & Benoit Coasne
-
Article
| Open Access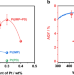 Sequential cocatalyst decoration on BaTaO2N towards highly-active Z-scheme water splitting
Sequential cocatalyst decoration on BaTaO2N towards highly-active Z-scheme water splitting
Activation of narrow-bandgap photocatalysts holds key to applicable solar-to-hydrogen energy conversion. Here, the authors demonstrate effective sequential cocatalyst decoration for such narrow-bandgap photocatalysts to realise highly-efficient hydrogen evolution and Z-scheme water splitting.
- Zheng Wang
- , Ying Luo
- & Kazunari Domen
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanism for rapid autoxidation in α-pinene ozonolysis
Molecular mechanism for rapid autoxidation in α-pinene ozonolysis
Oxidation of volatile organic compounds leads to aerosol formation in the atmosphere, but the mechanism of some fast reactions is still unclear. The authors, using quantum chemical modelling and experiments, reveal that in key monoterpenes the cyclobutyl ring that would hinder the reactivity is broken in the early exothermic steps of the reaction.
- Siddharth Iyer
- , Matti P. Rissanen
- & Theo Kurtén
-
Article
| Open Access Colloidal CdSe nanocrystals are inherently defective
Colloidal CdSe nanocrystals are inherently defective
Colloidal CdSe nanocrystals hold great promise in applications due to their tunable optical spectrum. Using hybrid time-dependent density functional theory, the authors show that colloidal CdSe nanocrystals are inherently defective with a low energy spectrum dominated by dark, surface-associated excitations.
- Tamar Goldzak
- , Alexandra R. McIsaac
- & Troy Van Voorhis
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidating intrinsic contribution of d-orbital states to oxygen evolution electrocatalysis in oxides
Elucidating intrinsic contribution of d-orbital states to oxygen evolution electrocatalysis in oxides
Despite many studies on the oxygen-evolution perovskite-type electrocatalysts thus far, significant constraints prevent precise evaluations of catalytic activity. Here authors examine over 50 heteroepitaxial LaNiO3 and LaCoO3 (001) thin films to assess the intrinsic catalytic behaviors.
- Tae Gyu Yun
- , Yoon Heo
- & Sung-Yoon Chung
-
Article
| Open Access Simulating the ghost: quantum dynamics of the solvated electron
Simulating the ghost: quantum dynamics of the solvated electron
The nature of the bulk hydrated electron has been a challenge for both experiment and theory. Here the authors use a machine-learning model trained on MP2 data to achieve an accurate determination of the structure, diffusion mechanisms, and vibrational spectroscopy of the solvated electron.
- Jinggang Lan
- , Venkat Kapil
- & Vladimir V. Rybkin
-
Article
| Open Access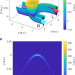 Electronic spin separation induced by nuclear motion near conical intersections
Electronic spin separation induced by nuclear motion near conical intersections
Spin polarization is at the basis of quantum information and underlies some natural processes, but many aspects still need to be explored. Here, the authors, by quantum mechanical computations, show that even a weak spin-orbit coupling near a conical intersection can induce large spin selection, with consequences for spin manipulation in photochemical or electrochemical reactions.
- Yanze Wu
- & Joseph E. Subotnik
-
Article
| Open Access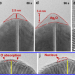 Defect-driven selective metal oxidation at atomic scale
Defect-driven selective metal oxidation at atomic scale
Crystal defects critically influence surface chemical reactions in nanomaterials, yet the basic mechanisms at play are still elusive. Here, the authors show the atomic-scale dynamics of surface oxidation at coherent planar defects in Ag and Pd, revealing how twins and stacking-faults selectively oxidize metallic nanocrystals.
- Qi Zhu
- , Zhiliang Pan
- & Jiangwei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Spin blockade and phonon bottleneck for hot electron relaxation observed in n-doped colloidal quantum dots
Spin blockade and phonon bottleneck for hot electron relaxation observed in n-doped colloidal quantum dots
Hot electrons in bulk semiconductors usually relax via electron-phonon scattering on a sub-picosecond timescale. Here, the authors observe hot electron lifetime as long as 320 picoseconds by performing a photochemical reduction reaction on colloidal quantum dots.
- Junhui Wang
- , Lifeng Wang
- & Kaifeng Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamical strengthening of covalent and non-covalent molecular interactions by nuclear quantum effects at finite temperature
Dynamical strengthening of covalent and non-covalent molecular interactions by nuclear quantum effects at finite temperature
The inclusion of nuclear quantum effects (NQE) in atomistic simulations of chemical systems is of key importance. Here the authors use machine learned force fields trained on coupled cluster reference data to show the dynamical strengthening of covalent and non-covalent molecular interactions induced by NQE.
- Huziel E. Sauceda
- , Valentin Vassilev-Galindo
- & Alexandre Tkatchenko
-
Article
| Open Access Preserving a robust CsPbI3 perovskite phase via pressure-directed octahedral tilt
Preserving a robust CsPbI3 perovskite phase via pressure-directed octahedral tilt
Inorganic lead halide perovskites are structurally unstable, which prevents their application in solar cells. Here the authors synthesize, using high pressure and temperature, a perovskite CsPbI3 phase that is metastably preserved to ambient conditions through a structural deformation induced at high pressure.
- Feng Ke
- , Chenxu Wang
- & Yu Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Crossover between the adiabatic and nonadiabatic electron transfer limits in the Landau-Zener model
Crossover between the adiabatic and nonadiabatic electron transfer limits in the Landau-Zener model
The Landau-Zener formula is a semiclassical model describing nonadiabatic transitions, but its range of validity in approaching the adiabatic regime had not been verified. The authors investigate electron transfer reactions in a series of mixed-valence complexes spanning the nonadiabatic throughout the adiabatic limit, and show that the model is valid in a broader range of conditions than previously expected.
- Guang Yuan Zhu
- , Yi Qin
- & Chun Y. Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Selective filling of n-hexane in a tight nanopore
Selective filling of n-hexane in a tight nanopore
Molecular sieving typically occurs when molecules with smaller kinetic diameter than a nanopore selectively enter the pore. Here the authors show, using photoluminescence imaging and ab initio molecular dynamics simulations, that single-walled carbon nanotubes can separate n-hexane from cyclohexane, despite both having larger kinetic diameter than the nanopore.
- Haoran Qu
- , Archith Rayabharam
- & YuHuang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring of a visible-light-absorbing biaxial ferroelectric towards broadband self-driven photodetection
Tailoring of a visible-light-absorbing biaxial ferroelectric towards broadband self-driven photodetection
2D lead-iodide ferroelectrics usually possess a wide bandgap along with the lacking of ferroelectric bulk photovoltaic effects due to the monolayered inorganic perovskite sheets. Here, the authors present a pathway to increase the thickness of inorganic sheets while retaining ferroelectricity.
- Shiguo Han
- , Maofan Li
- & Junhua Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Excited-state vibration-polariton transitions and dynamics in nitroprusside
Excited-state vibration-polariton transitions and dynamics in nitroprusside
Here the authors report spectroscopy and dynamics of cavity coupled NO band of sodium nitroprusside using 2D infrared and transient spectroscopy employing pump-probe technique. They find signatures of third-order nonlinearity, incoherent and strong coupling effects of vibrational polaritons.
- Andrea B. Grafton
- , Adam D. Dunkelberger
- & Jeffrey C. Owrutsky
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and dynamics of the drug-bound bacterial transporter EmrE in lipid bilayers
Structure and dynamics of the drug-bound bacterial transporter EmrE in lipid bilayers
The small proton-coupled transporter EmrE confers multidrug resistance in bacteria. The structure of drug-bound EmrE in phospholipid bilayers is now determined using solid-state NMR. The structure provides detailed insights into the molecular mechanism of substrate recognition by this transporter.
- Alexander A. Shcherbakov
- , Grant Hisao
- & Mei Hong
-
Article
| Open Access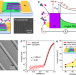 Controlling hot electron flux and catalytic selectivity with nanoscale metal-oxide interfaces
Controlling hot electron flux and catalytic selectivity with nanoscale metal-oxide interfaces
Chemical interaction between metal and oxide supports is an important molecular-level factor that influences the catalytic selectivity of a desirable reaction. Here, using Pt nanowires/TiO2 catalytic nanodiodes, the authors investigate an enhancement of both selectivity and hot electron generation on metal-oxide interfacial sites.
- Si Woo Lee
- , Jong Min Kim
- & Jeong Young Park
-
Article
| Open Access The corona of a surface bubble promotes electrochemical reactions
The corona of a surface bubble promotes electrochemical reactions
Gas bubbles forming on the surface of an electrode, a phenomenon common to several industrial electrolytic processes, are usually perceived as inert, passivating entities. Here, the authors show that that this general assumption does not hold for gas bubbles masking anodes operating in water.
- Yan B. Vogel
- , Cameron W. Evans
- & Simone Ciampi
-
Article
| Open Access Optical-field driven charge-transfer modulations near composite nanostructures
Optical-field driven charge-transfer modulations near composite nanostructures
Controlling and modulating charge transfer dynamics in composite nanostructures, though promising for optoelectronic applications, remains a challenge. Here, the authors report optical control of charge separation and recombination processes in organic semiconductor-based composite nanostructures.
- Kwang Jin Lee
- , Elke Beyreuther
- & Pascal André
-
Article
| Open Access Differential guest location by host dynamics enhances propylene/propane separation in a metal-organic framework
Differential guest location by host dynamics enhances propylene/propane separation in a metal-organic framework
Porous materials acting as molecular sieves for propylene/propane separation are important for the petrochemical industry. Here the authors show an example of how specific guest-host interactions can result in structural changes in the porous host and shut down diffusion of one of the two similar guest molecules.
- Dmytro Antypov
- , Aleksander Shkurenko
- & Matthew S. Dyer
-
Article
| Open Access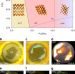 High pressure synthesis of phosphine from the elements and the discovery of the missing (PH3)2H2 tile
High pressure synthesis of phosphine from the elements and the discovery of the missing (PH3)2H2 tile
Chemical elements at high pressure may behave more consistently with their periodic properties than they do at ambient conditions. The authors report the synthesis of PH3 from black phosphorous and hydrogen, and the crystallization of the van der Waals compound (PH3)2H2 which fills a gap in the chemistry of adjacent elements in the periodic table.
- Matteo Ceppatelli
- , Demetrio Scelta
- & Maurizio Peruzzini
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy of bacteriochlorophyll a with synchronized dual mode-locked lasers
Two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy of bacteriochlorophyll a with synchronized dual mode-locked lasers
Multidimensional electronic spectroscopy techniques still have many limitations. Here, the authors introduce a 2D electronic spectroscopy technique that uses broadband, synchronized mode-locked lasers to study dynamics on a wide range of timescales.
- JunWoo Kim
- , Jonggu Jeon
- & Minhaeng Cho
-
Article
| Open Access The role of mixed vibronic Qy-Qx states in green light absorption of light-harvesting complex II
The role of mixed vibronic Qy-Qx states in green light absorption of light-harvesting complex II
The green component of the solar spectrum can efficiently drive natural photosynthesis, but the process has been little investigated due to the complexity of the excited states involved. Here the authors utilize polarization-dependent two-dimensional electronic-vibrational spectroscopy to define the origin and dynamics of these states in light-harvesting complex II.
- Eric A. Arsenault
- , Yusuke Yoneda
- & Graham R. Fleming
-
Article
| Open Access Vibrational couplings and energy transfer pathways of water’s bending mode
Vibrational couplings and energy transfer pathways of water’s bending mode
Vibrational energy transfer in water involves intermolecular coupling of O-H stretching modes, but much less is known about the role of the bending modes. Here the authors, combining static and femtosecond infrared, Raman, and hyper-Raman spectroscopy and ab initio molecular dynamics simulations, provide insight into the energy dynamics of the bend vibrations.
- Chun-Chieh Yu
- , Kuo-Yang Chiang
- & Yuki Nagata
-
Article
| Open Access Sensing the allosteric force
Sensing the allosteric force
Almost all allosteric systems are large multi-domain proteins which complicates the investigation of the mechanism in atomistic detail. Here authors designed a small allosteric protein system using the photocontrollable PDZ3 domain, that allows controlling allostery between the binding and allosteric site in both directions.
- Olga Bozovic
- , Brankica Jankovic
- & Peter Hamm
-
Article
| Open Access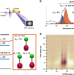 Attosecond spectroscopy reveals alignment dependent core-hole dynamics in the ICl molecule
Attosecond spectroscopy reveals alignment dependent core-hole dynamics in the ICl molecule
Here the authors report a study measuring lifetimes of core-hole states of ICl molecule using attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy. They find that lifetimes depend on the alignment of the orbital relative to the molecular axis.
- Hugo J. B. Marroux
- , Ashley P. Fidler
- & Daniel M. Neumark
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid water contains the building blocks of diverse ice phases
Liquid water contains the building blocks of diverse ice phases
Molecular understanding of water is challenging due to the structural complexity of liquid water and the large number of ice phases. Here the authors use a machine-learning potential trained on liquid water to demonstrate the structural similarity of liquid water and that of 54 real and hypothetical ice phases.
- Bartomeu Monserrat
- , Jan Gerit Brandenburg
- & Bingqing Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access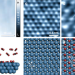 How Rh surface breaks CO2 molecules under ambient pressure
How Rh surface breaks CO2 molecules under ambient pressure
Direct observation of carbon dioxide dissociation provides an origin of catalytic conversion for industrial chemical reactions. Here, the authors reveal their molecular interactions on the rhodium catalyst at near-ambient pressure by interface science techniques and computational calculations.
- Jeongjin Kim
- , Hyunwoo Ha
- & Jeong Young Park
-
Article
| Open Access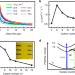 Conformational disorder of organic cations tunes the charge carrier mobility in two-dimensional organic-inorganic perovskites
Conformational disorder of organic cations tunes the charge carrier mobility in two-dimensional organic-inorganic perovskites
Understanding the correlation between molecular structure and properties of 2D hybrid perovskites is crucial for material design and device performance. Here, the authors reveal that conformation of organic cations in the inorganic cages has strong effects on charge mobility and broadband emission behaviour.
- Chuanzhao Li
- , Jin Yang
- & Shuji Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning in chemical reaction space
Machine learning in chemical reaction space
Application of machine-learning approaches to exploring chemical reaction networks is challenging due to need of including open-shell reaction intermediates. Here the authors introduce a density functional theory database of closed and open-shell molecules for machine-learning predictions of reaction energies.
- Sina Stocker
- , Gábor Csányi
- & Johannes T. Margraf
-
Article
| Open Access Infrared spectroscopic study of hydrogen bonding topologies in the smallest ice cube
Infrared spectroscopic study of hydrogen bonding topologies in the smallest ice cube
Spectroscopic studies of water clusters provide insight into the hydrogen bond structure of water and ice. The authors measure infrared spectra of neutral water octamers using a threshold photoionization technique based on a tunable vacuum-UV free electron laser, identifying two cubic isomers in addition to those previously observed.
- Gang Li
- , Yang-Yang Zhang
- & Ling Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of wet-dry cycling on the phase behavior and compartmentalization properties of complex coacervates
Impact of wet-dry cycling on the phase behavior and compartmentalization properties of complex coacervates
Wet-dry cycling is thought to have enabled the production of molecular building blocks of life. Here, the authors investigate the impact of dehydration/rehydration on RNA-containing complex coacervates, which are membraneless compartments formed by phase separation of polyelectrolyte solutions.
- Hadi M. Fares
- , Alexander E. Marras
- & Christine D. Keating
-
Article
| Open Access Reorientation-induced relaxation of free OH at the air/water interface revealed by ultrafast heterodyne-detected nonlinear spectroscopy
Reorientation-induced relaxation of free OH at the air/water interface revealed by ultrafast heterodyne-detected nonlinear spectroscopy
Water’s hydrogen-bond network is truncated at hydrophobic interfaces and the dynamics of the resulting free OH groups is not well understood. The authors experimentally show that the main vibrational relaxation mechanism for free OH at the air-water interface is a diffusive molecular reorientation, rather than intramolecular energy transfer.
- Ken-ichi Inoue
- , Mohammed Ahmed
- & Tahei Tahara
-
Article
| Open Access Sensitivity enhancement of homonuclear multidimensional NMR correlations for labile sites in proteins, polysaccharides, and nucleic acids
Sensitivity enhancement of homonuclear multidimensional NMR correlations for labile sites in proteins, polysaccharides, and nucleic acids
Here, the authors present an approach that enhances the sensitivity of basic 2D biomolecular NMR experiments like NOESY and TOCSY, when carried out in polysaccharides, proteins and nucleic acids. This method combines principles associated to quantum Anti-Zeno Effects and advanced data acquisition methods based on Hadamard multiplexing.
- Mihajlo Novakovic
- , Ēriks Kupče
- & Lucio Frydman
-
Article
| Open Access Electrification at water–hydrophobe interfaces
Electrification at water–hydrophobe interfaces
Electrification of water upon contact with hydrophobic surfaces is a ubiquitous but poorly understood phenomenon. Here, the authors pinpoint the factors responsible for the excess positive charge carried by water droplets dispensed from hydrophobic capillaries, thereby answering some outstanding questions and raising new ones.
- Jamilya Nauruzbayeva
- , Zhonghao Sun
- & Himanshu Mishra
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling the symmetry of inorganic ionic nanofilms with optical chirality
Controlling the symmetry of inorganic ionic nanofilms with optical chirality
The symmetry of metal ions in inorganic nanofilms can be manipulated by the transfer of optical spin from a chiral light beam. Here the authors present a route to functional manipulation that does not require the application of extreme conditions.
- Christopher Kelly
- , Donald A. MacLaren
- & Malcolm Kadodwala
-
Article
| Open Access Combinatorial entropy behaviour leads to range selective binding in ligand-receptor interactions
Combinatorial entropy behaviour leads to range selective binding in ligand-receptor interactions
Multivalent ligand-receptor interactions enhance binding selectivity in biological systems, and may be exploited to design synthetic systems. Here the authors demonstrate a multivalent behavior where the ability to bind the target occurs when the receptor density is within a specific range.
- Meng Liu
- , Azzurra Apriceno
- & Stefano Angioletti-Uberti
-
Article
| Open Access Design of highly efficient deep-blue organic afterglow through guest sensitization and matrices rigidification
Design of highly efficient deep-blue organic afterglow through guest sensitization and matrices rigidification
Though realizing organic materials with deep blue emission is attractive for next-generation display technologies, achieving this emission in afterglow molecules remains a challenge. Here, the authors report blue organic afterglow via a strategy involving guest sensitization and matrix rigidification.
- Shen Xu
- , Wu Wang
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access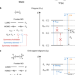 Optical gap and fundamental gap of oligoynes and carbyne
Optical gap and fundamental gap of oligoynes and carbyne
Carbyne, a linear sp-hybridized carbon allotrope, is synthetically inaccessible and its properties are extrapolated from those of defined oligomers. Here the authors analyze weak optical bands in two series of oligoynes and reassess the optical and fundamental gap of carbyne to lower values than previously suggested.
- Johannes Zirzlmeier
- , Stephen Schrettl
- & Holger Frauenrath
-
Article
| Open Access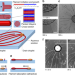 Autonomous mesoscale positioning emerging from myelin filament self-organization and Marangoni flows
Autonomous mesoscale positioning emerging from myelin filament self-organization and Marangoni flows
Buckling instabilities in amphiphile-based lamellar systems can lead to the formation of tubular fingers. Van der Weijden et al. show how to shepherd their growth and destination by using drain droplets that help establishing stable interconnected mesoscale droplet networks.
- Arno van der Weijden
- , Mitch Winkens
- & Peter A. Korevaar
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting heterogeneous ice nucleation with a data-driven approach
Predicting heterogeneous ice nucleation with a data-driven approach
Heterogenous ice nucleation is a ubiquitous phenomenon, but predicting the ice nucleation ability of a substrate is challenging. Here the authors develop a machine-learning data-driven approach to predict the ice nucleation ability of substrates, which is based on four descriptors related to physical properties of the interface.
- Martin Fitzner
- , Philipp Pedevilla
- & Angelos Michaelides
-
Perspective
| Open Access Designing and understanding light-harvesting devices with machine learning
Designing and understanding light-harvesting devices with machine learning
Photon-induced charge separation phenomena are at the heart of light-harvesting applications but challenging to be described by quantum mechanical models. Here the authors illustrate the potential of machine-learning approaches towards understanding the fundamental processes governing electronic excitations.
- Florian Häse
- , Loïc M. Roch
- & Alán Aspuru-Guzik
-
Article
| Open Access Probing the heterogeneous structure of eumelanin using ultrafast vibrational fingerprinting
Probing the heterogeneous structure of eumelanin using ultrafast vibrational fingerprinting
Eumelanin protects cells from sun damage and is promising for energy conversion applications, but its structure and excited state dynamics are elusive. Here the authors shed light on both aspects combining selective excitation of UV- and visible-absorbing chromophores with time-resolved infrared spectroscopy.
- Christopher Grieco
- , Forrest R. Kohl
- & Bern Kohler

 Reply to “A Thermodynamic assessment of the reported room-temperature chemical synthesis of C2”
Reply to “A Thermodynamic assessment of the reported room-temperature chemical synthesis of C2”