Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Multimaterial magnetically assisted 3D printing of composite materials
Multimaterial magnetically assisted 3D printing of composite materials
Endowing composite materials with spatially discrete mechanical behaviours is possible by varying the internal concentration and arrangement of particles. Here, the authors demonstrate a 3D magnetic printing technique which enables the fabrication of materials with intricate internal designs.
- Dimitri Kokkinis
- , Manuel Schaffner
- & André R. Studart
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation by oxygen over Pt/Al2O3 mediated by reactive platinum carbonates
Room-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation by oxygen over Pt/Al2O3 mediated by reactive platinum carbonates
There is economic impetus to achieve low-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation. Here, the authors use time-resolved diffuse reflectance infrared spectroscopy and mass spectrometry to show that platinum carbonates formed reversibly from platinum/aluminium oxide can oxidize carbon monoxide at room temperature.
- Mark A. Newton
- , Davide Ferri
- & Maarten Nachtegaal
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrahigh sensitivity and layer-dependent sensing performance of phosphorene-based gas sensors
Ultrahigh sensitivity and layer-dependent sensing performance of phosphorene-based gas sensors
Phosphorene is one of a growing number of 2D materials with high potential for device applications. Here, the authors report a sensor composed of phosphorene nanosheets, showing a high sensitivity to NO2in dry air and also demonstrate that the sensitivity depends on the nanosheet thickness.
- Shumao Cui
- , Haihui Pu
- & Junhong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Turning bubbles on and off during boiling using charged surfactants
Turning bubbles on and off during boiling using charged surfactants
Bubble generation during boiling is essential to power generation and heating/cooling systems, but it remains uncontrollable even with state-of-the-art surface engineering. Cho et al. electrostatically attract surfactants to the surface, on which bubble nucleation is manipulated in an on-demand manner.
- H. Jeremy Cho
- , Jordan P. Mizerak
- & Evelyn N. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying the density and utilization of active sites in non-precious metal oxygen electroreduction catalysts
Quantifying the density and utilization of active sites in non-precious metal oxygen electroreduction catalysts
Iron and nitrogen doped carbon materials are widely studied electrocatalysts, however measurement of features such as intrinsic turn-over frequency and active site utilization has proved difficult. Here, the authors use a combination of chemisorption and spectroscopy techniques to determine these properties.
- Nastaran Ranjbar Sahraie
- , Ulrike I. Kramm
- & Peter Strasser
-
Article
| Open Access Observing in space and time the ephemeral nucleation of liquid-to-crystal phase transitions
Observing in space and time the ephemeral nucleation of liquid-to-crystal phase transitions
The phenomenon of crystallization is common in nature, but surprisingly the nucleation pathways from liquid to solid are poorly understood due to the lack of effective experimental probes. Yoo et al. observe the existence of a nucleation precursor in titanium dioxide using single-pulse electron microscopy.
- Byung-Kuk Yoo
- , Oh-Hoon Kwon
- & Ahmed H. Zewail
-
Article
| Open Access Anisotropic in-plane thermal conductivity of black phosphorus nanoribbons at temperatures higher than 100 K
Anisotropic in-plane thermal conductivity of black phosphorus nanoribbons at temperatures higher than 100 K
Understanding the flow of heat in materials just one or a few atoms thick is vital for harnessing them in compact electronic devices. Here, the authors present the temperature-dependent thermal conductivity of black phosphorus ribbons and demonstrate an intrinsic orientation dependence.
- Sangwook Lee
- , Fan Yang
- & Junqiao Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Anisotropic in-plane thermal conductivity observed in few-layer black phosphorus
Anisotropic in-plane thermal conductivity observed in few-layer black phosphorus
The two-dimensional material black phosphorus could find uses in energy applications. Here, the authors study the difference in in-plane thermal conductivity along the armchair and zigzag directions in suspended few-layer black phosphorus, and show the dependence of this anisotropy on sample thickness.
- Zhe Luo
- , Jesse Maassen
- & Xianfan Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of correlated electronic decay in expanding clusters triggered by near-infrared fields
Observation of correlated electronic decay in expanding clusters triggered by near-infrared fields
In clusters, relaxation of excited atoms can lead to ionization of nearby atoms, a process known as interatomic Coulomb decay. Here, the authors report on a so far unobserved correlated electronic decay process following Rydberg atom generation in clusters ionized by intense near-infrared fields.
- B. Schütte
- , M. Arbeiter
- & A. Rouzée
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule spectroscopy exposes hidden states in an enzymatic electron relay
Single-molecule spectroscopy exposes hidden states in an enzymatic electron relay
A major challenge in following electron transfer through dithiol/disulfide exchange is the dearth of accompanying spectroscopic effects. Here, the authors use single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer experiments to illuminate disulfide bond rearrangements within the enzyme quiescin sulfhydryl oxidase.
- Iris Grossman
- , Haim Yuval Aviram
- & Deborah Fass
-
Article
| Open Access Cobalt-centred boron molecular drums with the highest coordination number in the CoB16− cluster
Cobalt-centred boron molecular drums with the highest coordination number in the CoB16− cluster
Boron is known to form a wide variety of molecular structures. Here, the authors observe the highly symmetric cobalt-centered boron drum-like structure of CoB16−, characterized by photoelectron spectroscopy and ab initio calculations, in which the cobalt atom is sixteen-coordinate.
- Ivan A. Popov
- , Tian Jian
- & Lai-Sheng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic dipolar interaction between correlated triplets created by singlet fission in tetracene crystals
Magnetic dipolar interaction between correlated triplets created by singlet fission in tetracene crystals
The exact mechanism of singlet fission remains unresolved. Here, Wang et al. report a quantitative measurement of the interaction between singlet-fission-induced correlated triplets in tetracene crystals with quantum beat spectroscopy, indicating the role played by exciton delocalization in singlet fission.
- Rui Wang
- , Chunfeng Zhang
- & Min Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access A biosynthetic model of cytochrome c oxidase as an electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction
A biosynthetic model of cytochrome c oxidase as an electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction
An artificial functional mimic of cytochrome coxidase is a long term research goal for the development of oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Here, the authors use site directed mutants of myoglobin to develop an electrocatalyst for reducing oxygen to water under ambient conditions.
- Sohini Mukherjee
- , Arnab Mukherjee
- & Abhishek Dey
-
Article
| Open Access Selective hydrogenation of 1,3-butadiene on platinum–copper alloys at the single-atom limit
Selective hydrogenation of 1,3-butadiene on platinum–copper alloys at the single-atom limit
Reducing the platinum content of industrial catalysts is an important research target. Here, the authors present a nanocatalyst containing less than 1% platinum, where the isolated platinum atoms contribute to both the catalyst activity and selectivity for butadiene hydrogenation.
- Felicia R. Lucci
- , Jilei Liu
- & E. Charles H. Sykes
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding catalysis in a multiphasic two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide
Understanding catalysis in a multiphasic two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide
Establishing structure–property relationships for catalytic materials is essential for optimization of performance. Here, the authors solve the structure of molybdenum disulfide monolayers, and probe the role of lithium intercalation and the subsequent effects on catalytic hydrogen activation.
- Stanley S. Chou
- , Na Sai
- & C. Jeffrey Brinker
-
Article
| Open Access Formation of oligopeptides in high yield under simple programmable conditions
Formation of oligopeptides in high yield under simple programmable conditions
Typically, in order to form large peptides, complex procedures or activating agents are required. Here, the authors show that simple aqueous conditions with dehydration-hydration cycles are sufficient for the oligomerization of amino acids into peptides (up to 20 amino acids long) in yields of up to 50%.
- Marc Rodriguez-Garcia
- , Andrew J. Surman
- & Leroy Cronin
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically activated switching of Si-based single-molecule junction as imaged with three-dimensional dynamic probe
Mechanically activated switching of Si-based single-molecule junction as imaged with three-dimensional dynamic probe
Mechanically induced conformational modulation can be used to control the conductance of single molecules junctions, but it is hard to be realized due to broken junctions. Here, the authors probe three-dimensional dynamics of Si/single-molecule/Si junctions, whose conductance shows a binary change.
- Miki Nakamura
- , Shoji Yoshida
- & Hidemi Shigekawa
-
Article
| Open Access Charge-transfer crystallites as molecular electrical dopants
Charge-transfer crystallites as molecular electrical dopants
The fundamental mechanisms of doping organic semiconductors are poorly understood compared with their inorganic counterparts. Here, the authors demonstrate that small conjugated molecules and conjugated polymers exhibit fundamentally different phenomena upon doping despite similar compositions.
- Henry Méndez
- , Georg Heimel
- & Ingo Salzmann
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring three-dimensional orbital imaging with energy-dependent photoemission tomography
Exploring three-dimensional orbital imaging with energy-dependent photoemission tomography
Experimental data from angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy can be utilized on molecular films to retrieve real-space images of molecular orbitals in two dimensions. Here, by scanning initial states as a function of photon energy, the authors can reconstruct three-dimensional orbital images.
- S. Weiß
- , D. Lüftner
- & P. Puschnig
-
Article
| Open Access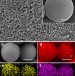 Ultrahigh volumetric capacitance and cyclic stability of fluorine and nitrogen co-doped carbon microspheres
Ultrahigh volumetric capacitance and cyclic stability of fluorine and nitrogen co-doped carbon microspheres
Carbon-based supercapacitors often suffer from poor volumetric capacitance due to the low packing density which arises from attempts to increase the electrode surface area. Here, in contrast, the authors fabricate N and F co-doped non-porous solid carbon spheres and achieve exceptional performances.
- Junshuang Zhou
- , Jie Lian
- & Faming Gao
-
Article
| Open Access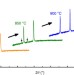 Entropy-stabilized oxides
Entropy-stabilized oxides
The composition of oxide compounds controls many of their properties and electronic phases. Here, the authors show that entropy and configurational disorder can stabilize new phases of oxides, potentially enabling a better engineering of their properties.
- Christina M. Rost
- , Edward Sachet
- & Jon-Paul Maria
-
Article
| Open Access The structural origin of the hard-sphere glass transition in granular packing
The structural origin of the hard-sphere glass transition in granular packing
Glass transition shows dramatic dynamic slowdown, but its origin remains unclear. Here, Xia et al. observe in granular systems the rapid growth of a geometrically frustrated polytetrahedral order with packing fraction, which is spatially correlated with the slow dynamics.
- Chengjie Xia
- , Jindong Li
- & Yujie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Sunlight-powered kHz rotation of a hemithioindigo-based molecular motor
Sunlight-powered kHz rotation of a hemithioindigo-based molecular motor
Although photodriven molecular motors—capable of converting light into unidirectional motion—hold promise for many applications, these typically require ultraviolet light. Here, the authors design and analyse a motor that can operate at high speeds (kHz) under visible light at ambient temperature.
- Manuel Guentner
- , Monika Schildhauer
- & Henry Dube
-
Article
| Open Access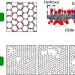 Atomistic understandings of reduced graphene oxide as an ultrathin-film nanoporous membrane for separations
Atomistic understandings of reduced graphene oxide as an ultrathin-film nanoporous membrane for separations
Ultrathin-film nanoporous membranes promise low-cost and high-performance separation for applications such as water desalination and the purification of natural gas. Here, the authors adopt a molecular dynamics approach to assess the potential of reduced grapheme oxide as such a material.
- Li-Chiang Lin
- & Jeffrey C. Grossman
-
Article
| Open Access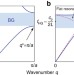 A new class of tunable hypersonic phononic crystals based on polymer-tethered colloids
A new class of tunable hypersonic phononic crystals based on polymer-tethered colloids
Hybridization-type band gaps are known to persist in phononic crystals, but their fabrication remains challenging for all-solid hypersonic composites. Here, the authors utilize the elastic anisotropy at the interface of polymer-tethered colloidal particles to control phonon propagation in GHz regime.
- E. Alonso-Redondo
- , M. Schmitt
- & G. Fytas
-
Article
| Open Access An insight into non-emissive excited states in conjugated polymers
An insight into non-emissive excited states in conjugated polymers
Conjugated polymers in thin films exhibit low fluorescence quantum yields, but the mechanism is still unclear. Here, Huet al. show the trade-off between charge transfer and emissive exciton states, whilst the former can be suppressed via dielectric-induced stabilization for large fluorescence quantum yields.
- Zhongjian Hu
- , Adam P. Willard
- & David A. Vanden Bout
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodynamic phase transitions in a frustrated magnetic metamaterial
Thermodynamic phase transitions in a frustrated magnetic metamaterial
Recently, periodic arrays of thermally active nanomagnets with bistable magnetization have been built which mimic the behaviour of frustrated magnets and model Ising systems. Here, the authors use muon spin relaxation to evidence thermodynamic phase transitions in an artificial kagome ice system.
- L. Anghinolfi
- , H. Luetkens
- & L. J. Heyderman
-
Article
| Open Access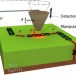 Probe-based measurement of lateral single-electron transfer between individual molecules
Probe-based measurement of lateral single-electron transfer between individual molecules
Detection and manipulation of single charges in molecules are fundamental cornerstones in molecular electronics. Here, Steurer et al. demonstrate a technique with the use of an atomic force microscope that is able to resolve charge states and single electron charge transfer between molecules.
- Wolfram Steurer
- , Shadi Fatayer
- & Gerhard Meyer
-
Article
| Open Access New insights into photoactivated volume generation boost surface morphing in liquid crystal coatings
New insights into photoactivated volume generation boost surface morphing in liquid crystal coatings
The photomechanical surface modulation of liquid crystal polymer networks can be amplified with a small amount of azobenzene, but its mechanism is not yet fully understood. Here, Liu and Broer propose that the continuously oscillating trans-to-cisisomerization of azobenzene plays the dominating role.
- Danqing Liu
- & Dirk J. Broer
-
Article
| Open Access Atomically resolved real-space imaging of hot electron dynamics
Atomically resolved real-space imaging of hot electron dynamics
Hot electrons—electrons with very high kinetic energies—are important in many processes but difficult to observe due to their short lifetimes. Here, the authors analyse STM based nonlocal manipulation of organic molecules on a surface, showing that the measurements probe hot electron dynamics in real space.
- D. Lock
- , K. R. Rusimova
- & P. A. Sloan
-
Article
| Open Access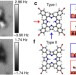 Measuring the mechanical properties of molecular conformers
Measuring the mechanical properties of molecular conformers
Manipulation of single molecules can be achieved using scanning probe microscopy but the influence of molecular conformation on this process has, until now, been unclear. Here, the authors probe two different types of porphyrin conformer on a surface and see strong differences in their mechanochemical response.
- S. P. Jarvis
- , S. Taylor
- & P. Moriarty
-
Article
| Open Access Strong frequency dependence of vibrational relaxation in bulk and surface water reveals sub-picosecond structural heterogeneity
Strong frequency dependence of vibrational relaxation in bulk and surface water reveals sub-picosecond structural heterogeneity
The structural heterogeneity in liquid water is commonly believed to disappear beyond 50 fs due to the strong intermolecular interaction. Here, the authors show frequency-dependent vibrational relaxation, which indicates the persistence of structural heterogeneity on a picosecond timescale.
- Sietse T. van der Post
- , Cho-Shuen Hsieh
- & Johannes Hunger
-
Article
| Open Access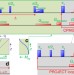 Ultrafast multidimensional Laplace NMR for a rapid and sensitive chemical analysis
Ultrafast multidimensional Laplace NMR for a rapid and sensitive chemical analysis
Laplace NMR provides complementary information to traditional NMR, such as details of molecular motion. Here, the authors report a correlation experiment capable of providing information on the physical environment of molecules while enhancing the chemical resolution and greatly reducing the experiment times.
- Susanna Ahola
- , Vladimir V Zhivonitko
- & Ville-Veikko Telkki
-
Article
| Open Access Covalency of hydrogen bonds in liquid water can be probed by proton nuclear magnetic resonance experiments
Covalency of hydrogen bonds in liquid water can be probed by proton nuclear magnetic resonance experiments
Covalency is a fundamental concept in chemical bonding, but experimentally it is not possible to measure the degree of covalency of a particular bond. Here, the authors report a model to link the covalency of hydrogen bonds in water with the anisotropy of the magnetic shielding tensor in the proton NMR.
- Hossam Elgabarty
- , Rustam Z. Khaliullin
- & Thomas D. Kühne
-
Article
| Open Access Unambiguous detection of nitrated explosive vapours by fluorescence quenching of dendrimer films
Unambiguous detection of nitrated explosive vapours by fluorescence quenching of dendrimer films
Selective standoff detection of explosives is challenging due to the presence of volatile interferents. Here, the authors report dendrimer thin films that display distinct fluorescence responses when exposed to explosives as opposed to common interferents, allowing selective detection of nitrated explosives.
- Yan Geng
- , Mohammad A. Ali
- & Paul E. Shaw
-
Article |
 Ultrafast isomerization initiated by X-ray core ionization
Ultrafast isomerization initiated by X-ray core ionization
Proton migration in the acetylene cation is commonly used as a model to study isomerisation dynamics. Here, the authors use X-ray pump-probe experiments to study this process, and show that isomerization occurs significantly faster than expected—within the first 12 femtoseconds following core ionization.
- Chelsea E. Liekhus-Schmaltz
- , Ian Tenney
- & Vladimir S. Petrovic
-
Article
| Open Access Combined operando X-ray diffraction–electrochemical impedance spectroscopy detecting solid solution reactions of LiFePO4 in batteries
Combined operando X-ray diffraction–electrochemical impedance spectroscopy detecting solid solution reactions of LiFePO4 in batteries
A clear understanding of the phase behaviour of lithium-ion electrode materials is essential for the development of the field. Here, the authors report a combined X-ray diffraction–electrochemical impedance spectroscopy method to detect solid solution reactions of LiFePO4.
- Michael Hess
- , Tsuyoshi Sasaki
- & Petr Novák
-
Article
| Open Access Borromean three-body FRET in frozen Rydberg gases
Borromean three-body FRET in frozen Rydberg gases
Rydberg atoms are promising platform for quantum simulations, due to their strong and controllable dipole–dipole interactions. Here, the authors predict few-body processes in Rydberg atoms which resemble fluorescence resonance energy transfer in biological setting, and observe them in cold caesium atoms.
- R. Faoro
- , B. Pelle
- & P. Pillet
-
Article
| Open Access Electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide and methane at an immobilized cobalt protoporphyrin
Electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide and methane at an immobilized cobalt protoporphyrin
The conversion of carbon dioxide to useful products is a major challenge in energy research. Here, the authors report a cobalt protoporphyrin immobilized on graphite that is capable of the selective and efficient electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide, primarily to carbon monoxide, in acidic media.
- Jing Shen
- , Ruud Kortlever
- & Marc T. M. Koper
-
Article
| Open Access Reversible adapting layer produces robust single-crystal electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution
Reversible adapting layer produces robust single-crystal electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution
There is extensive research into water-oxidation electrocatalysts which exhibit long-term stability. Here, the authors report a single-crystal cobalt oxide electrocatalyst displaying high activity and stability, and develop an in situX-ray diffraction method to probe the structure–activity relationship.
- Ching-Wei Tung
- , Ying-Ya Hsu
- & Hao Ming Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Efficiently photo-charging lithium-ion battery by perovskite solar cell
Efficiently photo-charging lithium-ion battery by perovskite solar cell
Photo-charged battery devices are an attractive technology but suffer from low photo-electric storage conversion efficiency and poor cycling stability. Here, the authors demonstrate the use of perovskite solar cells in conjunction with a lithium ion battery which displays excellent properties.
- Jiantie Xu
- , Yonghua Chen
- & Liming Dai
-
Review Article
| Open Access Wet-chemical synthesis and applications of non-layer structured two-dimensional nanomaterials
Wet-chemical synthesis and applications of non-layer structured two-dimensional nanomaterials
There is currently intensive research underway into the development of non-layer structured two dimensional nanomaterials. Here, Zhang et al.review the research progress on the most promising wet-chemical synthesis methods as well as a wide range of applications of this unique class of materials.
- Chaoliang Tan
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Electrical detection of ortho–para conversion in fullerene-encapsulated water
Electrical detection of ortho–para conversion in fullerene-encapsulated water
Water molecules can exist in one of two nuclear spin states—ortho or para. Here, the authors look at the bulk dielectric constant of water molecules enclosed in fullerenes (capable of rotating even at cryogenic temperatures) and show that it changes as the water molecules convert from ortho to para.
- Benno Meier
- , Salvatore Mamone
- & Malcolm H. Levitt
-
Article
| Open Access Accommodating lithium into 3D current collectors with a submicron skeleton towards long-life lithium metal anodes
Accommodating lithium into 3D current collectors with a submicron skeleton towards long-life lithium metal anodes
A major problem with the use of lithium metal as the battery anode is the undesired lithium dendrite formation during cycling. Here, the authors show that the problem can be mitigated with a carefully designed three-dimensional porous current collector.
- Chun-Peng Yang
- , Ya-Xia Yin
- & Yu-Guo Guo
-
Article |
 Catalysis on singly dispersed bimetallic sites
Catalysis on singly dispersed bimetallic sites
Singly dispersed bimetallic catalysts should exhibit different behaviour and activity to bulk bimetallic species. Here, the authors fabricate isolated Rh1Co3bimetallic catalytic sites and demonstrate their high activity and selectivity for nitric oxide reduction.
- Shiran Zhang
- , Luan Nguyen
- & Franklin Tao
-
Article
| Open Access Local atomic structure modulations activate metal oxide as electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution in acidic water
Local atomic structure modulations activate metal oxide as electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution in acidic water
Catalytic activity can be modulated by tuning local atomic structure. Here, the authors show that tungsten trioxide, which is usually inert, can be converted into an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution in acidic media, and claim that this could be due to the tailored electronic structure.
- Yu Hang Li
- , Peng Fei Liu
- & Hua Gui Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Flow-enhanced solution printing of all-polymer solar cells
Flow-enhanced solution printing of all-polymer solar cells
Solution printing is a desirable route for manufacturing organic solar cells, whilst the major challenge lies with morphology control. Here, Diao et al.use a microstructured blade to guide the solution flow during printing, which improves polymer crystallization and the resulting device performance.
- Ying Diao
- , Yan Zhou
- & Zhenan Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Ionization-induced annealing of pre-existing defects in silicon carbide
Ionization-induced annealing of pre-existing defects in silicon carbide
Silicon carbide possesses myriad properties which render it an ideal material for implementation in harsh radiation environments. Here, the authors show that damaged SiC can be repaired through ionization-induced healing, which has broader implications for the design of future radiation-tolerant materials.
- Yanwen Zhang
- , Ritesh Sachan
- & William J. Weber
-
Article
| Open Access Low surface recombination velocity in solution-grown CH3NH3PbBr3 perovskite single crystal
Low surface recombination velocity in solution-grown CH3NH3PbBr3 perovskite single crystal
Surface recombination velocity can have a major impact on solar cell performance. Here, Yanget al. measure surface recombination dynamics in perovskite single crystals using broadband transient reflectance spectroscopy. Grain size is crucial to avoid the effects of surface recombination on carrier lifetime.
- Ye Yang
- , Yong Yan
- & Matthew C. Beard

 Direct observation of ultrafast coherent exciton dynamics in helical π-stacks of self-assembled perylene bisimides
Direct observation of ultrafast coherent exciton dynamics in helical π-stacks of self-assembled perylene bisimides