Featured
-
-
Article |
 Observing the emergence of a quantum phase transition shell by shell
Observing the emergence of a quantum phase transition shell by shell
An atomic simulator formed of a few ultracold fermionic atoms trapped in a two-dimensional harmonic potential exhibits precursors of a quantum phase transition, revealing the onset of collective quantum many-body phenomena in a few-body system.
- Luca Bayha
- , Marvin Holten
- & Selim Jochim
-
Article |
 Correlated insulating states at fractional fillings of moiré superlattices
Correlated insulating states at fractional fillings of moiré superlattices
An optical sensing technique reveals an abundance of correlated insulating states at fractional fillings of moiré superlattices that are proposed to arise from a series of charge-ordered states.
- Yang Xu
- , Song Liu
- & Jie Shan
-
Article |
 Evidence for supercritical behaviour of high-pressure liquid hydrogen
Evidence for supercritical behaviour of high-pressure liquid hydrogen
Simulations using machine-learning-based interatomic potentials in dense hydrogen overcome system size and timescale limitations, providing evidence of a supercritical behaviour of high-pressure liquid hydrogen and reconciling theoretical and experimental discrepancies.
- Bingqing Cheng
- , Guglielmo Mazzola
- & Michele Ceriotti
-
Article |
 Liquid–liquid transition and critical point in sulfur
Liquid–liquid transition and critical point in sulfur
Under high pressure, elemental sulfur shows a sharp density discontinuity that evolves with pressure and temperature and terminates at a critical point, indicating a first-order liquid–liquid phase transition.
- Laura Henry
- , Mohamed Mezouar
- & Frédéric Datchi
-
Article |
 Electronic phase separation in multilayer rhombohedral graphite
Electronic phase separation in multilayer rhombohedral graphite
High-quality rhombohedral graphite films are found to offer an alternative to twisted bilayer graphene as a platform for studying correlated physics in carbon materials.
- Yanmeng Shi
- , Shuigang Xu
- & Artem Mishchenko
-
Article |
 Coherent control of a surface structural phase transition
Coherent control of a surface structural phase transition
A structural phase transition from metal to insulator on a solid surface is controlled by an ultrafast sequence of optical pulses.
- Jan Gerrit Horstmann
- , Hannes Böckmann
- & Claus Ropers
-
Article |
 Untying the insulating and superconducting orders in magic-angle graphene
Untying the insulating and superconducting orders in magic-angle graphene
Tuning the electronic interactions by changing the dielectric environment of twisted bilayer graphene reveals the disappearance of the insulating states and their replacement by superconducting phases, suggesting a competition between the two phases.
- Petr Stepanov
- , Ipsita Das
- & Dmitri K. Efetov
-
Article |
 Tunable correlated states and spin-polarized phases in twisted bilayer–bilayer graphene
Tunable correlated states and spin-polarized phases in twisted bilayer–bilayer graphene
Small-angle twisted bilayer–bilayer graphene is tunable by the twist angle and electric and magnetic fields, and can be used to gain further insights into correlated states in two-dimensional superlattices.
- Yuan Cao
- , Daniel Rodan-Legrain
- & Pablo Jarillo-Herrero
-
Article |
 Composition-dependent thermodynamics of intracellular phase separation
Composition-dependent thermodynamics of intracellular phase separation
Heterotypic multicomponent interactions are shown to dominate the liquid–liquid phase separation that enables the formation of intracellular condensates.
- Joshua A. Riback
- , Lian Zhu
- & Clifford P. Brangwynne
-
Article |
 A mechanism of ferritin crystallization revealed by cryo-STEM tomography
A mechanism of ferritin crystallization revealed by cryo-STEM tomography
Cryo-STEM tomography of ferritin crystallization is used to reveal nonclassical evolution of crystalline order, indicating that it may be desolvation that drives the continuous evolution of order in crystallization.
- Lothar Houben
- , Haim Weissman
- & Boris Rybtchinski
-
Article |
 Simulation of Hubbard model physics in WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattices
Simulation of Hubbard model physics in WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattices
Study of WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattices reveals the phase diagram of the triangular-lattice Hubbard model, including a Mott insulating state at half-filling and a possible magnetic quantum phase transition near 0.6 filling.
- Yanhao Tang
- , Lizhong Li
- & Kin Fai Mak
-
Article |
 Strange-metal behaviour in a pure ferromagnetic Kondo lattice
Strange-metal behaviour in a pure ferromagnetic Kondo lattice
The ferromagnet CeRh6Ge4 is found to exhibit strange-metal behaviour at a quantum critical point, suggesting that changes in the pattern of quantum entanglement, not antiferromagnetism, underlie the development of strange metals.
- Bin Shen
- , Yongjun Zhang
- & Huiqiu Yuan
-
Article |
 Synchrotron infrared spectroscopic evidence of the probable transition to metal hydrogen
Synchrotron infrared spectroscopic evidence of the probable transition to metal hydrogen
The probable transition of hydrogen to its metal state near 425 GPa is observed, with the required high pressures created using a toroidal diamond anvil cell.
- Paul Loubeyre
- , Florent Occelli
- & Paul Dumas
-
Article |
 Signatures of self-organized criticality in an ultracold atomic gas
Signatures of self-organized criticality in an ultracold atomic gas
A driven–dissipative gas of ultracold potassium atoms is used to demonstrate three key signatures of self-organized criticality, and provides a system in which the phenomenon can be experimentally tested.
- S. Helmrich
- , A. Arias
- & S. Whitlock
-
Article |
 Inverse transition of labyrinthine domain patterns in ferroelectric thin films
Inverse transition of labyrinthine domain patterns in ferroelectric thin films
The labyrinthine domain patterns formed in ultrathin films of ferroelectric oxides by subcritical quenching undergo an inverse phase transition to the less-symmetric parallel-stripe domain structure upon increasing temperature.
- Y. Nahas
- , S. Prokhorenko
- & L. Bellaiche
-
Article |
 Cooperative elastic fluctuations provide tuning of the metal–insulator transition
Cooperative elastic fluctuations provide tuning of the metal–insulator transition
Theoretical modelling shows that elastic fluctuations can enable the tuning of metal-to-insulator transitions, potentially also explaining the dependence of the transition temperature on cation radius in perovskite transition-metal oxides.
- G. G. Guzmán-Verri
- , R. T. Brierley
- & P. B. Littlewood
-
Article |
 Interlayer exciton laser of extended spatial coherence in atomically thin heterostructures
Interlayer exciton laser of extended spatial coherence in atomically thin heterostructures
Efficient lasing from two transition-metal dichalcogenide layers is engineered by exploiting the excitonic states that emerge when the layers are placed together to form a heterostructure.
- Eunice Y. Paik
- , Long Zhang
- & Hui Deng
-
Article |
 Quantifying the dynamics of failure across science, startups and security
Quantifying the dynamics of failure across science, startups and security
A model demonstrates that people who eventually succeed and those who do not may initially appear similar, but are characterized by fundamentally distinct failure dynamics in terms of the efficiency and quality of each subsequent attempt to succeed.
- Yian Yin
- , Yang Wang
- & Dashun Wang
-
Letter |
 Ultrahigh-pressure isostructural electronic transitions in hydrogen
Ultrahigh-pressure isostructural electronic transitions in hydrogen
X-ray diffraction measurements of solid hydrogen provide crystallographic information for high-pressure phases of hydrogen and transitions between them, suggesting a series of isostructural transitions under compression before band closure and metallization.
- Cheng Ji
- , Bing Li
- & Ho-Kwang Mao
-
Letter |
 Constraints on the superconducting order parameter in Sr2RuO4 from oxygen-17 nuclear magnetic resonance
Constraints on the superconducting order parameter in Sr2RuO4 from oxygen-17 nuclear magnetic resonance
17O nuclear magnetic resonance measurements on Sr2RuO4 reveal a drop of the Knight shift in the superconducting state, contradicting previous work and imposing tight constraints on the order parameter symmetry of the system.
- A. Pustogow
- , Yongkang Luo
- & S. E. Brown
-
Letter |
 Quantum critical behaviour at the many-body localization transition
Quantum critical behaviour at the many-body localization transition
Quantum critical behaviour at the many-body localization transition in a disordered Bose–Hubbard system of bosonic rubidium atoms in an optical lattice is observed, connecting the macroscopic phenomenology of the transition to the system’s microscopic quantum correlations.
- Matthew Rispoli
- , Alexander Lukin
- & Markus Greiner
-
Letter |
 Observing crystal nucleation in four dimensions using atomic electron tomography
Observing crystal nucleation in four dimensions using atomic electron tomography
Atomic electron tomography captures crystal nucleation in four dimensions in FePt nanoparticles, with the observed early-stage nucleation not consistent with classical nucleation theory.
- Jihan Zhou
- , Yongsoo Yang
- & Jianwei Miao
-
Letter |
 Nanosecond X-ray diffraction of shock-compressed superionic water ice
Nanosecond X-ray diffraction of shock-compressed superionic water ice
The atomic structure of H2O is documented at several million atmospheres of pressure and temperatures of several thousand degrees, revealing shockwave-induced ultrafast crystallization and a novel water ice phase, ice XVIII, with exotic superionic properties.
- Marius Millot
- , Federica Coppari
- & Jon H. Eggert
-
Letter |
 Three-dimensional quantum Hall effect and metal–insulator transition in ZrTe5
Three-dimensional quantum Hall effect and metal–insulator transition in ZrTe5
Evidence of the three-dimensional quantum Hall effect and a magnetic-field-driven quantum phase transition are observed in zirconium pentatelluride crystals.
- Fangdong Tang
- , Yafei Ren
- & Liyuan Zhang
-
Letter |
 Subthreshold firing in Mott nanodevices
Subthreshold firing in Mott nanodevices
Mott materials feature scale-less relaxation dynamics after the insulator-to-metal transition that make its electric triggering dependent on recent switching events.
- Javier del Valle
- , Pavel Salev
- & Ivan K. Schuller
-
Letter |
 Quantum Kibble–Zurek mechanism and critical dynamics on a programmable Rydberg simulator
Quantum Kibble–Zurek mechanism and critical dynamics on a programmable Rydberg simulator
A Rydberg atom quantum simulator with programmable interactions is used to experimentally verify the quantum Kibble–Zurek mechanism through the growth of spatial correlations during quantum phase transitions.
- Alexander Keesling
- , Ahmed Omran
- & Mikhail D. Lukin
-
Letter |
 Colossal barocaloric effects in plastic crystals
Colossal barocaloric effects in plastic crystals
Colossal barocaloric effects are observed in the plastic crystal neopentylglycol and found to originate from the extensive molecular orientational disorder, giant compressibility and highly anharmonic lattice dynamics of the material.
- Bing Li
- , Yukinobu Kawakita
- & Zhidong Zhang
-
Letter |
 Large teams develop and small teams disrupt science and technology
Large teams develop and small teams disrupt science and technology
Analyses of the output produced by large versus small teams of researchers and innovators demonstrate that their work differs systematically in the extent to which it disrupts or develops existing science and technology.
- Lingfei Wu
- , Dashun Wang
- & James A. Evans
-
Letter |
 Thermodynamic signatures of quantum criticality in cuprate superconductors
Thermodynamic signatures of quantum criticality in cuprate superconductors
Measurements of the specific heat of two cuprate materials at low temperature in magnetic fields large enough to suppress superconductivity and over a wide doping range reveal that the pseudogap phase of cuprates ends at a quantum critical point.
- B. Michon
- , C. Girod
- & T. Klein
-
Letter |
 Electrical resistivity across a nematic quantum critical point
Electrical resistivity across a nematic quantum critical point
The pattern of electrical resistivity in an unconventional superconductor at high magnetic fields and low temperatures across the nematic quantum critical point reveals two classic signatures of quantum criticality.
- S. Licciardello
- , J. Buhot
- & N. E. Hussey
-
Letter |
 Ferroelectric polymers exhibiting behaviour reminiscent of a morphotropic phase boundary
Ferroelectric polymers exhibiting behaviour reminiscent of a morphotropic phase boundary
An organic copolymer with compositionally tailored tacticity exhibits behaviour reminiscent of a morphotropic phase boundary, with an intramolecular order-to-disorder transition in the crystalline phase and a very large piezoelectric coefficient.
- Yang Liu
- , Haibibu Aziguli
- & Qing Wang
-
Letter |
 A Brownian quasi-crystal of pre-assembled colloidal Penrose tiles
A Brownian quasi-crystal of pre-assembled colloidal Penrose tiles
A lithographic patterning and release method is used to create a dense, fluctuating, Brownian system of mobile colloidal kite- and dart-shaped Penrose tiles over large areas that retains quasi-crystalline order.
- Po-Yuan Wang
- & Thomas G. Mason
-
Letter |
 Observation of topological phenomena in a programmable lattice of 1,800 qubits
Observation of topological phenomena in a programmable lattice of 1,800 qubits
A large-scale programmable quantum simulation is described, using a D-Wave quantum processor to simulate a two-dimensional magnetic lattice in the vicinity of a topological phase transition.
- Andrew D. King
- , Juan Carrasquilla
- & Mohammad H. Amin
-
Letter |
 Molecular nucleation mechanisms and control strategies for crystal polymorph selection
Molecular nucleation mechanisms and control strategies for crystal polymorph selection
Cryo-transmission electron microscopy reveals the initiation of glucose isomerase crystals and their growth into different crystalline or gel polymorphs, and shows that mutating specific amino acids controls which polymorph grows.
- Alexander E. S. Van Driessche
- , Nani Van Gerven
- & Mike Sleutel
-
Letter |
 Correlated insulator behaviour at half-filling in magic-angle graphene superlattices
Correlated insulator behaviour at half-filling in magic-angle graphene superlattices
When the two graphene sheets in a van der Waals heterostructure are twisted relative to each other by a specific amount, Mott-like insulating phases are observed at half-filling.
- Yuan Cao
- , Valla Fatemi
- & Pablo Jarillo-Herrero
-
Article |
 Unconventional superconductivity in magic-angle graphene superlattices
Unconventional superconductivity in magic-angle graphene superlattices
A superlattice consisting of two graphene sheets twisted relative to each other by a specific amount exhibits superconductivity when doped electrostatically, with a relatively high critical temperature.
- Yuan Cao
- , Valla Fatemi
- & Pablo Jarillo-Herrero
-
Letter |
 Freezing on a sphere
Freezing on a sphere
Freezing on a spherical surface is shown to proceed by the sequestration of defects into 12 icosahedrally coordinated ‘seas’ that enable the formation of a crystalline ‘continent’ with long-range orientational order.
- Rodrigo E. Guerra
- , Colm P. Kelleher
- & Paul M. Chaikin
-
Letter |
 Global patterns of tropical forest fragmentation
Global patterns of tropical forest fragmentation
Satellite data and modelling reveal that tropical forest fragments have similar size distributions across continents, and that forest fragmentation is close to a critical point, beyond which fragment numbers will strongly increase.
- Franziska Taubert
- , Rico Fischer
- & Andreas Huth
-
Letter |
 Experimental observation of Bethe strings
Experimental observation of Bethe strings
Many-body two- and three-string states are realized experimentally in the antiferromagnetic Heisenberg–Ising chain SrCo2V2O8 in strong longitudinal magnetic fields.
- Zhe Wang
- , Jianda Wu
- & Alois Loidl
-
Letter |
 Role of stacking disorder in ice nucleation
Role of stacking disorder in ice nucleation
Stacking-disordered ice crystallites are shown to have an ice nucleation rate much higher than predicted by classical nucleation theory, which needs to be taken into account in cloud modelling.
- Laura Lupi
- , Arpa Hudait
- & Valeria Molinero
-
Letter |
 In situ X-ray diffraction measurement of shock-wave-driven twinning and lattice dynamics
In situ X-ray diffraction measurement of shock-wave-driven twinning and lattice dynamics
In situ femtosecond X-ray diffraction measurements reveal that the dominant mechanism of shock-wave-driven deformation in tantalum changes from twinning to dislocation slip as pressure increases.
- C. E. Wehrenberg
- , D. McGonegle
- & J. S. Wark
-
Letter |
 Structural phase transition in monolayer MoTe2 driven by electrostatic doping
Structural phase transition in monolayer MoTe2 driven by electrostatic doping
A structural phase transition in a monolayer of molybdenum ditelluride has been shown experimentally to be driven forwards and backwards by electrostatic doping.
- Ying Wang
- , Jun Xiao
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Letter |
 Electronic in-plane symmetry breaking at field-tuned quantum criticality in CeRhIn5
Electronic in-plane symmetry breaking at field-tuned quantum criticality in CeRhIn5
Electronic nematicity is observed in a heavy-fermion superconductor, CeRhIn5, suggesting a close link between unconventional superconductivity and the appearance of nematicity.
- F. Ronning
- , T. Helm
- & P. J. W. Moll
-
Letter |
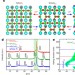 Electric-field control of tri-state phase transformation with a selective dual-ion switch
Electric-field control of tri-state phase transformation with a selective dual-ion switch
Materials are described here that can change their crystalline phase in response to the electrically controlled insertion or extraction of oxygen and hydrogen ions, giving rise to three distinct phases with different optical, electrical and magnetic properties.
- Nianpeng Lu
- , Pengfei Zhang
- & Pu Yu
-
Letter |
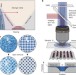 A cold-atom Fermi–Hubbard antiferromagnet
A cold-atom Fermi–Hubbard antiferromagnet
An antiferromagnet with a correlation length that encompasses the whole system is created with the aid of quantum gas microscopy of cold atoms in an optical lattice.
- Anton Mazurenko
- , Christie S. Chiu
- & Markus Greiner
-
Letter |
 Optically excited structural transition in atomic wires on surfaces at the quantum limit
Optically excited structural transition in atomic wires on surfaces at the quantum limit
A structural transition in an atomic indium wire on a silicon substrate proceeds as fast as the indium atom vibrations and is facilitated by strong In–Si interface bonds.
- T. Frigge
- , B. Hafke
- & W. G. Schmidt
-
Letter |
 Observation of a discrete time crystal
Observation of a discrete time crystal
A time crystal is a state of matter that shows robust oscillations in time, and although forbidden in equilibrium, a discrete time crystal has now been observed in a periodically driven quantum system.
- J. Zhang
- , P. W. Hess
- & C. Monroe
-
Letter |
 Observation of discrete time-crystalline order in a disordered dipolar many-body system
Observation of discrete time-crystalline order in a disordered dipolar many-body system
Discrete time-crystalline order is observed in a driven, disordered ensemble of about one million dipolar spin impurities in diamond at room temperature, and is shown to be very stable to perturbations.
- Soonwon Choi
- , Joonhee Choi
- & Mikhail D. Lukin
-
Letter |
 Strongly correlated perovskite fuel cells
Strongly correlated perovskite fuel cells
A fundamentally different approach to designing solid oxide electrolytes is presented, using a phase transition to suppress electronic conduction in a correlated perovskite nickelate; this yields ionic conductivity comparable to the best-performing solid electrolytes in the same temperature range.
- You Zhou
- , Xiaofei Guan
- & Shriram Ramanathan

 Origins of structural and electronic transitions in disordered silicon
Origins of structural and electronic transitions in disordered silicon