Featured
-
-
Article |
 A visual-language foundation model for computational pathology
A visual-language foundation model for computational pathology
Developed using diverse sources of histopathology images, biomedical text and over 1.17 million image–caption pairs, evaluated on a suite of 14 diverse benchmarks, a visual-language foundation model achieves state-of-the-art performance on a wide array of clinically relevant pathology tasks.
- Ming Y. Lu
- , Bowen Chen
- & Faisal Mahmood
-
Article |
 Towards a general-purpose foundation model for computational pathology
Towards a general-purpose foundation model for computational pathology
Pretrained using over 100,000 diagnostic histopathological slides across 20 major tissue types, a self-supervised model is shown to outperform existing baselines across various clinically relevant computational pathology tasks.
- Richard J. Chen
- , Tong Ding
- & Faisal Mahmood
-
News & Views |
 Harnessing medical twitter data for pathology AI
Harnessing medical twitter data for pathology AI
Using pathology data from Twitter, researchers have built a visual-language model for classifying and retrieving histopathology images — representing a milestone in the development of multifunctional foundational artificial intelligence models in computational pathology.
- Ming Y. Lu
- , Bowen Chen
- & Faisal Mahmood
-
Article |
 An automated histological classification system for precision diagnostics of kidney allografts
An automated histological classification system for precision diagnostics of kidney allografts
A decision-support system that automates the Banff classification system for diagnosis of kidney allograft rejection leads to reclassification and correction of pathologists’ diagnoses and improves risk stratification of allograft outcomes.
- Daniel Yoo
- , Valentin Goutaudier
- & Alexandre Loupy
-
Article |
 Multistain deep learning for prediction of prognosis and therapy response in colorectal cancer
Multistain deep learning for prediction of prognosis and therapy response in colorectal cancer
A deep learning model trained on multiple tumor immune cell stainings from patients with colorectal cancer outperforms currently used clinical and single tumor immune cell staining-based parameters in predicting prognosis. The model can also predict the response to neoadjuvant therapy.
- Sebastian Foersch
- , Christina Glasner
- & Moritz Jesinghaus
-
Article |
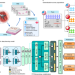 Deep learning-enabled assessment of cardiac allograft rejection from endomyocardial biopsies
Deep learning-enabled assessment of cardiac allograft rejection from endomyocardial biopsies
Deep learning applied to endomyocardial biopsy images, developed using datasets from three different countries, can detect rejection of transplanted hearts and determine the subtype and grade of rejection, with potential for reducing the interobserver variability inherent in manual interpretation of these biopsies.
- Jana Lipkova
- , Tiffany Y. Chen
- & Faisal Mahmood
-
Review Article |
 Deep learning in histopathology: the path to the clinic
Deep learning in histopathology: the path to the clinic
Recent advances in machine learning techniques have created opportunities to improve medical diagnostics, but implementing these advances in the clinic will not be without challenge.
- Jeroen van der Laak
- , Geert Litjens
- & Francesco Ciompi
-
Article |
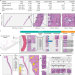 Clinical-grade computational pathology using weakly supervised deep learning on whole slide images
Clinical-grade computational pathology using weakly supervised deep learning on whole slide images
A deep learning model trained on real-world digital pathology data achieves clinical performance in cancer diagnosis.
- Gabriele Campanella
- , Matthew G. Hanna
- & Thomas J. Fuchs
-
News Feature |
 Tackling the brain: Clues emerge about the pathology of sports-related brain trauma
Tackling the brain: Clues emerge about the pathology of sports-related brain trauma
- Amanda B. Keener
-
-
Article |
 Inhibition of IL-12/IL-23 signaling reduces Alzheimer's disease–like pathology and cognitive decline
Inhibition of IL-12/IL-23 signaling reduces Alzheimer's disease–like pathology and cognitive decline
Proinflammatory cytokine expression increases as a result of amyloid deposition in Alzheimer's disease. Frank L. Heppner and colleagues show that genetic and pharmacological inhibition of IL-12 and IL-23 signaling reduces plaque load and improves cognitive deficits in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. As the concentration of p40 is also increased in the cerebrospinal fluid of individuals with Alzheimer's disease, this suggests that this pathway may be targeted therapeutically in patients.
- Johannes vom Berg
- , Stefan Prokop
- & Frank L Heppner
-
Resource |
 Tumor grafts derived from women with breast cancer authentically reflect tumor pathology, growth, metastasis and disease outcomes
Tumor grafts derived from women with breast cancer authentically reflect tumor pathology, growth, metastasis and disease outcomes
By implementing the conditions for orthotopic implantation of different types of human breast tumors, the authors have created a publicly available bank of new mouse models that more faithfully recreate individual tumor properties and provide individualized information about tumor behavior and prognosis.
- Yoko S DeRose
- , Guoying Wang
- & Alana L Welm
-
News & Views |
 A suPAR circulating factor causes kidney disease
A suPAR circulating factor causes kidney disease
For many years, investigators have been searching for an elusive circulating factor that could cause the common kidney disease focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). The finding that a circulating, soluble form of the urokinase receptor (suPAR) can activate podocyte β3 integrin, leading to FSGS pathology (pages 952–960), provides new insights into this disease and may have important clinical implications.
- Stuart J Shankland
- & Martin R Pollak
-
News & Views |
 A Nod toward understanding Crohn's pathology
A Nod toward understanding Crohn's pathology
Despite intensive study, the mechanisms of pathogenesis in inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) remain poorly understood. An innate T helper type 17 (TH17) response that requires nucleotide oligomerization domain (Nod)-like receptors and is primed by commensal bacteria is now shown to be crucial for controlling intestinal bacterial pathogens in a mouse model (pages 837–844). Thus, dysregulation of this protective immune response may be important in IBD development.
- Mathias Hornef
- & Christine Josenhans
-

 Demographic bias in misdiagnosis by computational pathology models
Demographic bias in misdiagnosis by computational pathology models Brain strains
Brain strains