Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Mode attraction, rejection and control in nonlinear multimode optics
Mode attraction, rejection and control in nonlinear multimode optics
The authors introduce and demonstrate experimentally a novel fundamental property of nonlinear multimode optical systems, named mode rejection. This paves the way towards a more general idea of all-optical mode control and its related applications.
- Kunhao Ji
- , Ian Davidson
- & Massimiliano Guasoni
-
Article
| Open Access Phonon-enhanced nonlinearities in hexagonal boron nitride
Phonon-enhanced nonlinearities in hexagonal boron nitride
Nonlinear optical processes like higher-order harmonic generation in solids depend on several factors. Here the authors explore the optical nonlinearity of hexagonal boron nitride and find that enhanced nonlinearity is due to electron-phonon and phonon-polariton couplings.
- Jared S. Ginsberg
- , M. Mehdi Jadidi
- & Alexander L. Gaeta
-
Article
| Open Access All electromagnetic scattering bodies are matrix-valued oscillators
All electromagnetic scattering bodies are matrix-valued oscillators
The usual treatment of wave scattering theory relies on a formalism that does not easily allow for probing optimal spectral response. Here, the authors show how an alternative formalism, encoding fundamental principles of causality and passivity, can be used to make sense of complex scattered fields’ structures.
- Lang Zhang
- , Francesco Monticone
- & Owen D. Miller
-
Article
| Open Access Synchronous micromechanically resonant programmable photonic circuits
Synchronous micromechanically resonant programmable photonic circuits
MEMS-based photonic integrated circuits (PICs) are often limited in speed by mechanical resonances. Here the authors report a programmable architecture for PICs which uses mechanical eigenmodes for synchronized, resonantly enhanced optical modulation.
- Mark Dong
- , Julia M. Boyle
- & Dirk Englund
-
Article
| Open Access Autonomous nanorobots with powerful thrust under dry solid-contact conditions by photothermal shock
Autonomous nanorobots with powerful thrust under dry solid-contact conditions by photothermal shock
Optically trapping objects, marked by Nobel Prizes in 1997 and 2018 for applications in vacuum and liquids, remains challenging on solid surfaces. Here, the authors demonstrate a breakthrough by using photothermal-shock tweezers and explore nano-conventional robot applications
- Zhaoqi Gu
- , Runlin Zhu
- & Fuxing Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasmall and tunable TeraHertz surface plasmon cavities at the ultimate plasmonic limit
Ultrasmall and tunable TeraHertz surface plasmon cavities at the ultimate plasmonic limit
In this work, the authors use a surface plasmonic mechanism to efficiently confine TeraHertz photons inside ultrasmall cavities. These plasmonic-based TeraHertz cavities are shown to operate until the ultimate limit that is allowed fundamentally and at which plasmons start to behave in a nonlocal fashion.
- Ian Aupiais
- , Romain Grasset
- & Yannis Laplace
-
Article
| Open Access Optomechanical ring resonator for efficient microwave-optical frequency conversion
Optomechanical ring resonator for efficient microwave-optical frequency conversion
The authors showed a high-efficiency microwave-optical conversion using optomechanical rings where co-resonant traveling photons and phonons induce enhanced interconversion, which enables transduction application in quantum and classical domains.
- I-Tung Chen
- , Bingzhao Li
- & Mo Li
-
Article
| Open Access 3.5 × 3.5 μm2 GaN blue micro-light-emitting diodes with negligible sidewall surface nonradiative recombination
3.5 × 3.5 μm2 GaN blue micro-light-emitting diodes with negligible sidewall surface nonradiative recombination
Here Wang et al. demonstrate the fabrication of GaN micro-light emitting diodes with a low rate of efficiency decrease in low current density regions, these features are strongly desired for augmented-reality glass applications.
- Xuelun Wang
- , Xixi Zhao
- & Seiji Samukawa
-
Article
| Open Access Woven organic crystals
Woven organic crystals
The entanglement of fibrous elements produces flexible structures with enhanced strength and resilience to abrasion. Here, the authors report the weaving of organic crystals into flexible and robust patches with plain, twill, and satin topologies of arbitrary porosity, expanding one-dimensional crystals into flexible, two-dimensional planar structures with potential for future applications in flexible electronics.
- Linfeng Lan
- , Liang Li
- & Hongyu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated microwave photonic notch filter using a heterogeneously integrated Brillouin and active-silicon photonic circuit
Integrated microwave photonic notch filter using a heterogeneously integrated Brillouin and active-silicon photonic circuit
Microwave photonic technologies are poised to revolutionise electronic systems. Here the authors integrate necessary but until now elusive, MHz-level resolution photonic processing with on-chip electro-optic components in a compact microwave photonic notch filter.
- Matthew Garrett
- , Yang Liu
- & Benjamin J. Eggleton
-
Article
| Open Access Bidirectional light-emitting diode as a visible light source driven by alternating current
Bidirectional light-emitting diode as a visible light source driven by alternating current
The bidirectional light-emitting diode emits visible light regardless of the direction of current flow, leading to AC applications. This is made possible by the use of two oppositely oriented tunnel junctions that surround the active region.
- Mikołaj Żak
- , Grzegorz Muziol
- & Czesław Skierbiszewski
-
Article
| Open Access Strong transient magnetic fields induced by THz-driven plasmons in graphene disks
Strong transient magnetic fields induced by THz-driven plasmons in graphene disks
The authors provide an experimental demonstration of magnetic field generation in graphene disks via the inverse Faraday effect. When the disks are illuminated with circularly polarized radiation in resonance with the graphene plasmon frequency, the corresponding rotational motion of the charge carriers gives rise to a unipolar magnetic field.
- Jeong Woo Han
- , Pavlo Sai
- & Martin Mittendorff
-
Article
| Open Access Critical role of electrons in the short lifetime of blue OLEDs
Critical role of electrons in the short lifetime of blue OLEDs
Designing robust blue organic light-emitting diodes is a long-standing challenge in the display industry. Here, the authors show that electron-induced degradation reactions play a more critical role in the short lifetime of devices with iridium-based emitters under real operational conditions.
- Jaewook Kim
- , Joonghyuk Kim
- & Woo Youn Kim
-
Article
| Open Access On-chip silicon electro-optical modulator with ultra-high extinction ratio for fiber-optic distributed acoustic sensing
On-chip silicon electro-optical modulator with ultra-high extinction ratio for fiber-optic distributed acoustic sensing
On-chip optoelectronic devices are promising to build compact and efficient distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) systems. Here, the authors demonstrate an ultra-high extinction ratio electro-optical modulator on silicon and its application for DAS.
- Zhuo Cheng
- , Xiaoqian Shu
- & Yunjiang Rao
-
Article
| Open Access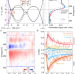 Enhanced optical conductivity and many-body effects in strongly-driven photo-excited semi-metallic graphite
Enhanced optical conductivity and many-body effects in strongly-driven photo-excited semi-metallic graphite
Strong optical excitation near band extrema can drive novel correlated states. Here the authors report a non-equilibrium many-body state in graphite driven by a strong excitation near van Hove singularity, yielding a tenfold increase in optical conductivity attributed to carrier excitations in the flat bands.
- T. P. H. Sidiropoulos
- , N. Di Palo
- & J. Biegert
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering chirality at wafer scale with ordered carbon nanotube architectures
Engineering chirality at wafer scale with ordered carbon nanotube architectures
Methods for generating macroscopic chiral matter struggle with limited scalability. Here, the authors show two vacuum filtration methods - twist stacking and mechanical rotation - to align carbon nanotubes into chiral structures at wafer scale with tunable circular dichroism.
- Jacques Doumani
- , Minhan Lou
- & Weilu Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Bulk-local-density-of-state correspondence in topological insulators
Bulk-local-density-of-state correspondence in topological insulators
Current approaches to distinguish topological phases from topologically-trivial phases have limited general applicability. Here, in a photonic-crystal context, the authors demonstrate that in trivial structures the bulk local density of states (LDOS) extends all the way to the edges and corners, while in topological structures the bulk LDOS actually avoids the edges and corners.
- Biye Xie
- , Renwen Huang
- & Shuang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Mitigating stimulated Brillouin scattering in multimode fibers with focused output via wavefront shaping
Mitigating stimulated Brillouin scattering in multimode fibers with focused output via wavefront shaping
The authors demonstrate a high-power delivery through a highly multimode optical fiber by shaping the incident wavefront of a laser beam to strongly suppress the stimulated Brillouin scattering in the fiber and simultaneously control the output beam profile.
- Chun-Wei Chen
- , Linh V. Nguyen
- & Hui Cao
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic construction of refractive index-dependent vibrations using surface plasmon-phonon polaritons
Dynamic construction of refractive index-dependent vibrations using surface plasmon-phonon polaritons
Molecular vibrations serve as valuable signatures for the constituent elements and bonding in compounds. Here, using Surface-Enhanced Infrared Absorption spectroscopy, the authors study refractive index dependent vibrations of surface phonon polaritons and surface plasmon platform, targeting dynamic biomonitoring.
- Hong Zhou
- , Zhihao Ren
- & Chengkuo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing ultrafast photothermal dynamics with decoupled optical force nanoscopy
Visualizing ultrafast photothermal dynamics with decoupled optical force nanoscopy
Diving deep into material insights, the authors introduce the ‘Decoupled Optical Force Nanoscopy’. This innovation uncovers the physical origins of light induced forces and captures dynamic thermal details with unparalleled nanometer precision.
- Hanwei Wang
- , Sean M. Meyer
- & Yang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Time-domain observation of interlayer exciton formation and thermalization in a MoSe2/WSe2 heterostructure
Time-domain observation of interlayer exciton formation and thermalization in a MoSe2/WSe2 heterostructure
Here, the authors use ultrafast transient absorption spectroscopy with a broadband white-light probe to simultaneously resolve interlayer charge transfer and interlayer exciton formation dynamics in a MoSe2/WSe2 heterostructure.
- Veronica R. Policht
- , Henry Mittenzwey
- & Stefano Dal Conte
-
Article
| Open Access Metafiber transforming arbitrarily structured light
Metafiber transforming arbitrarily structured light
Structured light has proven useful for numerous photonic applications. However, its current use in optical fibers is severely limited. The authors report a highly integrated metafiber platform based on 3D laser nanoprinting, capable of creating arbitrarily structured light.
- Chenhao Li
- , Torsten Wieduwilt
- & Haoran Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Superconducting nonlinear transport in optically driven high-temperature K3C60
Superconducting nonlinear transport in optically driven high-temperature K3C60
The authors report ultrafast transport measurements on the photo-excited superconducting state in K3C60. They observe characteristic superconducting nonlinear current-voltage responses.
- E. Wang
- , J. D. Adelinia
- & A. Cavalleri
-
Article
| Open Access Large area inkjet-printed OLED fabrication with solution-processed TADF ink
Large area inkjet-printed OLED fabrication with solution-processed TADF ink
Low-cost manufacturing of large-scale thermally activated delayed fluorescence organic light-emitting diodes has been restricted due to their incompatibility with solution processing techniques. Here, authors develop inkjet printing ink formulation to fabricate patterns without use of lithography.
- Chandra Kant
- , Atul Shukla
- & Monica Katiyar
-
Article
| Open Access Prediction on X-ray output of free electron laser based on artificial neural networks
Prediction on X-ray output of free electron laser based on artificial neural networks
Methods to characterize the free-electron laser pulses are evolving and their performances are also improving. Here the authors demonstrate a method based on the artificial neural networks to predict the output pulses of the X-ray free-electron laser by considering the electron beam parameters as input.
- Kenan Li
- , Guanqun Zhou
- & Anne Sakdinawat
-
Article
| Open Access Accessible hotspots for single-protein SERS in DNA-origami assembled gold nanorod dimers with tip-to-tip alignment
Accessible hotspots for single-protein SERS in DNA-origami assembled gold nanorod dimers with tip-to-tip alignment
The identification of individual proteins is highly desirable in diagnostics. Here, the authors report on DNA-origami assembled dimers of gold nanorod with accessible hotspots to capture and identify single proteins from solution by SERS.
- Francis Schuknecht
- , Karol Kołątaj
- & Theobald Lohmueller
-
Article
| Open Access Multipole engineering by displacement resonance: a new degree of freedom of Mie resonance
Multipole engineering by displacement resonance: a new degree of freedom of Mie resonance
Mie resonances are typically manipulated through varying nanostructure shape/size. Here, authors found that Gaussian beam displacement excites higher-order multipolar modes, not accessible by plane wave, featuring maximal linear and nonlinear scattering efficiency when the focus is misaligned.
- Yu-Lung Tang
- , Te-Hsin Yen
- & Shi-Wei Chu
-
Article
| Open Access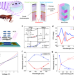 Circular polarization-resolved ultraviolet photonic artificial synapse based on chiral perovskite
Circular polarization-resolved ultraviolet photonic artificial synapse based on chiral perovskite
Circularly polarized light adds a unique dimension to optical information processing and communication. Here, the authors present a development of a photonic artificial synapse device using chiral perovskite hybrid materials and carbon nanotubes. The heterostructure exhibits efficient synaptic and neuromorphic behaviors, enabling accurate recognition of circularly polarized images.
- Qi Liu
- , Qi Wei
- & Mingjie Li
-
Article
| Open Access Disordered metasurface enabled single-shot full-Stokes polarization imaging leveraging weak dichroism
Disordered metasurface enabled single-shot full-Stokes polarization imaging leveraging weak dichroism
Polarization imaging can capture information from the scene that cannot directly be recorded by traditional intensity cameras. Here, authors demonstrate a single-shot full Stokes polarization camera incorporating a disordered metasurface array with weak dichroism.
- Qingbin Fan
- , Weizhu Xu
- & Ting Xu
-
Article
| Open Access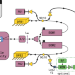 Frequency stable and low phase noise THz synthesis for precision spectroscopy
Frequency stable and low phase noise THz synthesis for precision spectroscopy
The authors demonstrate a very stable yet broadly tunable photonic THz source, characterized from 2 GHz to 1.4 THz. A very narrow Lamb dip feature is observed in a water absorption line, showcasing its potential for sub-kHz resolution spectroscopy.
- Léo Djevahirdjian
- , Loïc Lechevallier
- & Samir Kassi
-
Article
| Open Access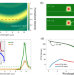 Highly efficient octave-spanning long-wavelength infrared generation with a 74% quantum efficiency in a χ(2) waveguide
Highly efficient octave-spanning long-wavelength infrared generation with a 74% quantum efficiency in a χ(2) waveguide
A χ(2) nonlinear micro-waveguide platform is demonstrated based on the birefringence phase matching for simple and efficient long-wavelength infrared generation, which could trigger new frontiers of MIR integrated nonlinear photonics.
- Bo Hu
- , Xuemei Yang
- & Houkun Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable Tamm plasmon cavity as a scalable biosensing platform for surface enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy
Tunable Tamm plasmon cavity as a scalable biosensing platform for surface enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy
The researchers present a scalable Tamm plasmon cavity using phase change material with large resonance tunability and demonstrated tunable SERS by matching the plasmonic resonance with the molecule absorption for sensitivity enhanced biosensing.
- Kandammathe Valiyaveedu Sreekanth
- , Jayakumar Perumal
- & Jinghua Teng
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum noise and its evasion in feedback oscillators
Quantum noise and its evasion in feedback oscillators
Feedback oscillators are a fundamental tool in science and engineering. Here, Loughlin and Sudhir provide a generalized Schawlow-Townes-like formula for quantum-limited feedback oscillators, thus giving a general model to study the fundamental output noise of these devices and techniques to reduce their noise further.
- Hudson A. Loughlin
- & Vivishek Sudhir
-
Article
| Open Access Training large-scale optoelectronic neural networks with dual-neuron optical-artificial learning
Training large-scale optoelectronic neural networks with dual-neuron optical-artificial learning
Optoelectronic neural networks are a promising avenue in AI computing for parallelization, power efficiency, and speed. Here, the authors present a dual-neuron optical-artificial learning approach for training large-scale diffractive neural networks, achieving VGG-level performance on ImageNet in simulation with a network that is 10 times larger than existing ones.
- Xiaoyun Yuan
- , Yong Wang
- & Lu Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Double boron–oxygen-fused polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: skeletal editing and applications as organic optoelectronic materials
Double boron–oxygen-fused polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: skeletal editing and applications as organic optoelectronic materials
The development of chemically diverse boron-oxygen-fused polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons has been limited by their synthetic complexity. Here, authors report a one-pot strategy for their facile synthesis and demonstrate their potential as ultralong afterglow and host materials for deep-blue OLEDs.
- Guijie Li
- , Kewei Xu
- & Yuan-Bin She
-
Article
| Open Access Dispersion engineered metasurfaces for broadband, high-NA, high-efficiency, dual-polarization analog image processing
Dispersion engineered metasurfaces for broadband, high-NA, high-efficiency, dual-polarization analog image processing
Here the authors demonstrate a path to design metasurfaces that perform broadband, high-NA, high-efficiency and dual-polarization edge detection without using bulky 4 f systems. This work introduces new approaches towards passive, ultra-compact optical computing and image processing.
- Michele Cotrufo
- , Akshaj Arora
- & Andrea Alù
-
Article
| Open Access Negative capacitors and inductors enabling wideband waveguide metatronics
Negative capacitors and inductors enabling wideband waveguide metatronics
The authors showcase a method to design negative lumped elements by engineering the effective permittivity within the waveguide, which enables realizations of wideband waveguide metatronics and promises performance enhancement in various fields.
- Xu Qin
- , Pengyu Fu
- & Yue Li
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient optical plasmonic tweezer-controlled single-molecule SERS characterization of pH-dependent amylin species in aqueous milieus
Efficient optical plasmonic tweezer-controlled single-molecule SERS characterization of pH-dependent amylin species in aqueous milieus
Studying rare species in mixtures is challenging. Here, authors utilize on-and-off optical plasmonic trapping to control SERS-active nanocavity to analyse pH-dependent amylin species at single-molecule level, unveiling amyloid aggregation mechanisms.
- Wenhao Fu
- , Huanyu Chi
- & Jinqing Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Metasurface-empowered snapshot hyperspectral imaging with convex/deep (CODE) small-data learning theory
Metasurface-empowered snapshot hyperspectral imaging with convex/deep (CODE) small-data learning theory
Hyperspectral imagers play a vital role in material identification, but traditionally, they have been bulky. Here, the authors introduce a compact hyperspectral imaging system that combines metasurface optics with small-data deep learning.
- Chia-Hsiang Lin
- , Shih-Hsiu Huang
- & Pin Chieh Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Wafer-scale organic-on-III-V monolithic heterogeneous integration for active-matrix micro-LED displays
Wafer-scale organic-on-III-V monolithic heterogeneous integration for active-matrix micro-LED displays
The electrical properties of solution deposited organic semiconductor channels are sensitive to substrate surface and processing conditions. Here, authors develop organic-last-integration technology to fabricate multilayer organic thin film transistor material stack onto micro light-emitting diode.
- Lei Han
- , Simon Ogier
- & Xiaojun Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene/silicon heterojunction for reconfigurable phase-relevant activation function in coherent optical neural networks
Graphene/silicon heterojunction for reconfigurable phase-relevant activation function in coherent optical neural networks
Designing an efficient activation function for optical neural networks remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a modulator-detector-in-one graphene/silicon heterojunction ring resonators enabling on-chip reconfigurable activation function devices with phase activation capability for optical neural networks.
- Chuyu Zhong
- , Kun Liao
- & Hongtao Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Organic photodiodes with bias-switchable photomultiplication and photovoltaic modes
Organic photodiodes with bias-switchable photomultiplication and photovoltaic modes
Preparation of photodiodes with photomultiplication/photovoltaic two operating modes is promising but challenging. Here, the authors report a bias-switchable dual-mode organic photodiode by adopting traps and blocking layer, achieving detectivity of 1012 Jones and fast response speed in both modes.
- Qingxia Liu
- , Lingfeng Li
- & Yadong Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Tracing multiple scattering trajectories for deep optical imaging in scattering media
Tracing multiple scattering trajectories for deep optical imaging in scattering media
Deep imaging in complex scattering media is hindered by multiple light scattering. Here, the authors proposed a method to trace multiple scattering trajectories in situ using a recorded reflection matrix and achieved enhanced imaging depth by converting these multiple scattering to signal waves.
- Sungsam Kang
- , Yongwoo Kwon
- & Wonshik Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Polarization structured light 3D depth image sensor for scenes with reflective surfaces
Polarization structured light 3D depth image sensor for scenes with reflective surfaces
Highly reflective surfaces are notorious in 3D sensing because they can cause errors in depth perception. Here, the authors devise a polarization structured light 3D sensor for this problem, in which high-contrast-grating VCSELs are used. Experiments are reported to demonstrate the sensor can be used to see and see through the highly reflective surfaces.
- Xuanlun Huang
- , Chenyang Wu
- & Connie J. Chang-Hasnain
-
Article
| Open Access Polarization-driven reversible actuation in a photo-responsive polymer composite
Polarization-driven reversible actuation in a photo-responsive polymer composite
Light-responsive polymers with polarization-dependent deformation are promising material to develop tunable devices usually limited by irreversible dynamic control. Here, the authors use controlled polarization of visible light to produce arbitrary deformations into amorphous composites containing azopolymer microdomains to unlock the next level of complex actuation in soft lightdriven robots.
- David Urban
- , Niccolò Marcucci
- & Emiliano Descrovi
-
Article
| Open Access Rheological engineering of perovskite suspension toward high-resolution X-ray flat-panel detector
Rheological engineering of perovskite suspension toward high-resolution X-ray flat-panel detector
The film uniformity is essential to the fixed pattern noise (FPN) and resolution of X-ray detectors. Here the authors demonstrate the rheological engineering of the perovskite suspension to achieve low FPN of 1.39% and high resolution of 0.51 lp/pix.
- Zihao Song
- , Xinyuan Du
- & Jiang Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Learning diffractive optical communication around arbitrary opaque occlusions
Learning diffractive optical communication around arbitrary opaque occlusions
Researchers demonstrate robust optical communication around fully opaque occlusions, partially or entirely blocking the light path, using a pair of electronic encoder and passive diffractive decoder that are jointly optimized using deep learning.
- Md Sadman Sakib Rahman
- , Tianyi Gan
- & Aydogan Ozcan
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid sensing of hidden objects and defects using a single-pixel diffractive terahertz sensor
Rapid sensing of hidden objects and defects using a single-pixel diffractive terahertz sensor
Researchers showcase a deep learning-designed diffractive terahertz sensor that rapidly detects hidden defects within 3D samples based on the output spectrum measured by a single-pixel detector, eliminating sample scanning or image formation/processing.
- Jingxi Li
- , Xurong Li
- & Aydogan Ozcan
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reassessing the existence of soft X-ray correlated plasmons
Reassessing the existence of soft X-ray correlated plasmons
- Mohsen Moazzami Gudarzi
- & Seyed Hamed Aboutalebi

 Real-data-driven real-time reconfigurable microwave reflective surface
Real-data-driven real-time reconfigurable microwave reflective surface