Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Perspective
| Open Access Roadmapping the next generation of silicon photonics
Roadmapping the next generation of silicon photonics
In order to complete the transition to the era of large-scale integration, silicon photonics will have to overcome several challenges. Here, the authors outline what these challenges are and what it will take to tackle them.
- Sudip Shekhar
- , Wim Bogaerts
- & Bhavin J. Shastri
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast hot-carrier dynamics in ultrathin monocrystalline gold
Ultrafast hot-carrier dynamics in ultrathin monocrystalline gold
Progress has been made in the development of low-loss monocrystalline plasmonic metals, opening up opportunities for ultrathin nanophotonic architectures. Here, the authors reveal differences in hot-electron thermalisation dynamics between ultrathin monocrystalline and polycrystalline gold films.
- Can O. Karaman
- , Anton Yu. Bykov
- & Anatoly V. Zayats
-
Article
| Open Access Active mid-infrared ring resonators
Active mid-infrared ring resonators
Multifunctional active mid-infrared ring resonators and directional couplers with quantum cascade laser cores allow electrical control of resonant frequency and quality factors, tunable filtering and frequency comb generation.
- Dmitry Kazakov
- , Theodore P. Letsou
- & Federico Capasso
-
Article
| Open Access Giant optical polarisation rotations induced by a single quantum dot spin
Giant optical polarisation rotations induced by a single quantum dot spin
Light-matter interfaces implementing arbitrary conditional operations on incoming photons would have several applications in quantum computation and communications. Here, the authors demonstrate conditional polarization rotation induced by a single quantum dot spin embedded in an electrically contacted micropillar, spanning up to a pi flip.
- E. Mehdi
- , M. Gundín
- & L. Lanco
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable nano-architecture for stable near-blackbody solar absorption at high temperatures
Scalable nano-architecture for stable near-blackbody solar absorption at high temperatures
Nanostructures are generally unstable above 850 °C in air, limiting their use in high-temperature solar thermal applications. Here, a scalable ceramic nano-architecture layer can significantly enhance and stabilise the absorption of an arbitrary solar absorber.
- Yifan Guo
- , Kaoru Tsuda
- & Juan F. Torres
-
Article
| Open Access Theory predicts 2D chiral polaritons based on achiral Fabry–Pérot cavities using apparent circular dichroism
Theory predicts 2D chiral polaritons based on achiral Fabry–Pérot cavities using apparent circular dichroism
2D chiral polaritons are light-matter states with select angular momentum holding technological promise. Here, the authors present the theory of such states, and propose their realisation based on a phenomenon called “apparent circular dichroism”.
- Andrew H. Salij
- , Randall H. Goldsmith
- & Roel Tempelaar
-
Article
| Open Access Creating pairs of exceptional points for arbitrary polarization control: asymmetric vectorial wavefront modulation
Creating pairs of exceptional points for arbitrary polarization control: asymmetric vectorial wavefront modulation
The authors report the chiral inversion of exceptional points (EPs) through a structural mirror-symmetric operation, extending the application of EP to any desired polarization states, surpassing the inherent limitation of conventional EP systems.
- Zijin Yang
- , Po-Sheng Huang
- & Qinghua Song
-
Article
| Open Access Direct laser-written optomechanical membranes in fiber Fabry-Perot cavities
Direct laser-written optomechanical membranes in fiber Fabry-Perot cavities
Authors showcase 3D direct laser writing to fabricate optically interfaced mechanical resonators. The membrane-type structures are placed inside fiber Fabry-Perot cavities to realize a miniaturized optical cavity. Further, the optomechanical properties reveal the coupling mechanism and a significant tuning of the mechanical resonator frequency.
- Lukas Tenbrake
- , Alexander Faßbender
- & Hannes Pfeifer
-
Perspective
| Open Access Planar hyperbolic polaritons in 2D van der Waals materials
Planar hyperbolic polaritons in 2D van der Waals materials
In this Perspective, the authors illustrate the physics of hyperbolic polaritons in anisotropic 2D and 1D materials, proposing new potential material candidates, forward looking opportunities and technological applications.
- Hongwei Wang
- , Anshuman Kumar
- & Tony Low
-
Article
| Open Access Direct and integrating sampling in terahertz receivers from wafer-scalable InAs nanowires
Direct and integrating sampling in terahertz receivers from wafer-scalable InAs nanowires
Authors report on nanofacet engineering of wafer‐scalable InAs nanowires enabling the operation of THz photodetectors in direct or integrating sampling mode, with performance comparable to commercial InP technology.
- Kun Peng
- , Nicholas Paul Morgan
- & Michael B. Johnston
-
Article
| Open Access Photogating-assisted tunneling boosts the responsivity and speed of heterogeneous WSe2/Ta2NiSe5 photodetectors
Photogating-assisted tunneling boosts the responsivity and speed of heterogeneous WSe2/Ta2NiSe5 photodetectors
Photodetectors based on 2D materials can exhibit high photoresponsivity, but usually at the cost of their response speed. Here, the authors report a strategy based on photogating-assisted tunneling to overcome this trade-off in WSe2/Ta2NiSe5 heterostructures.
- Mingxiu Liu
- , Jingxuan Wei
- & Shaojuan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Dual-wavelength metalens enables Epi-fluorescence detection from single molecules
Dual-wavelength metalens enables Epi-fluorescence detection from single molecules
The requirement for sophisticated objective lenses hinders the miniaturisation of single molecule fluorescence spectroscopy for portable sensing applications. Here, the authors demonstrate a dual-wavelength metalens for real-time monitoring of individual fluorescent nanoparticles.
- Aleksandr Barulin
- , Yeseul Kim
- & Inki Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum plasmonics pushes chiral sensing limit to single molecules: a paradigm for chiral biodetections
Quantum plasmonics pushes chiral sensing limit to single molecules: a paradigm for chiral biodetections
Chiroptic sensing of single molecule is extremely challenging. Here the authors unveil an extreme nanophotonic system based on nanoparticle-on-mirror shows exceptional high sensitivity of chiral supramolecules, which can resolve enantiomer access of a racemate monolayer, exhibiting great potential for single chiral molecule sensing.
- Chi Zhang
- , Huatian Hu
- & Tao Ding
-
Article
| Open Access High quality factor metasurfaces for two-dimensional wavefront manipulation
High quality factor metasurfaces for two-dimensional wavefront manipulation
Wavefront manipulation with metasurfaces is typically limited to low quality factors. Here, the authors show how higher-order Mie modes can be leveraged to design high quality factor optical metasurfaces for wavefront manipulation in two dimensions.
- Claudio U. Hail
- , Morgan Foley
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Article
| Open Access Probing optical anapoles with fast electron beams
Probing optical anapoles with fast electron beams
Optical anapoles in nanoresonators result in strong suppression of the electromagnetic radiation, which is challenging to detect in ideal settings. Here, the authors show that fast electrons are a powerful tool to circumvent this challenge due to their ability to access dark modes.
- Carlos Maciel-Escudero
- , Andrew B. Yankovich
- & Timur O. Shegai
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-narrow inhomogeneous spectral distribution of telecom-wavelength vanadium centres in isotopically-enriched silicon carbide
Ultra-narrow inhomogeneous spectral distribution of telecom-wavelength vanadium centres in isotopically-enriched silicon carbide
Several solid-state defect platforms have been proposed for application as a spin-photon interface in quantum communication networks. Here the authors report spin-selective optical transitions and narrow inhomogeneous spectral distribution of V centers in isotopically-enriched SiC emitting in the telecom O-band.
- Pasquale Cilibrizzi
- , Muhammad Junaid Arshad
- & Cristian Bonato
-
Article
| Open Access All-optical geometric image transformations enabled by ultrathin metasurfaces
All-optical geometric image transformations enabled by ultrathin metasurfaces
Metasurfaces enable all-optical geometric coordinate transformations, converting images with altered pixel spatial relations, which can facilitate fast, energy-efficient preprocessing for tasks like object tracking, or aid in laser manufacturing.
- Xingwang Zhang
- , Xiaojie Zhang
- & Xingjie Ni
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent light scattering from a telecom C-band quantum dot
Coherent light scattering from a telecom C-band quantum dot
Developing quantum networks would require reliable sources of coherent quantum light at telecom wavelengths. Here, the authors employ elastic scattering of excitation laser photons on InAs/InP quantum dots to demonstrate the emission of telecom photons with coherence times longer than the Fourier limit.
- L. Wells
- , T. Müller
- & A. J. Shields
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time photonic blind interference cancellation
Real-time photonic blind interference cancellation
The authors demonstrate real-time blind photonic interference cancellation using FPGA-photonic coordinated processing with zero calibration micro-ring resonator control and sub-second cancellation weight identification.
- Joshua C. Lederman
- , Weipeng Zhang
- & Paul R. Prucnal
-
Article
| Open Access Mid-infrared supermirrors with finesse exceeding 400 000
Mid-infrared supermirrors with finesse exceeding 400 000
The researchers showcase all-crystalline and hybrid mid-infrared supermirrors with the lowest optical losses ever demonstrated in this wavelength range, representing an unprecedented improvement over any existing mirrors made with any production technology.
- Gar-Wing Truong
- , Lukas W. Perner
- & Garrett D. Cole
-
Article
| Open Access Real-data-driven real-time reconfigurable microwave reflective surface
Real-data-driven real-time reconfigurable microwave reflective surface
The authors demonstrate how flexible metasurfaces powered by artificial neural network can dynamically manipulate the EM scattering behavior from an arbitrary surface - an ultimate ambition for many EM stealth and communication problems.
- Erda Wen
- , Xiaozhen Yang
- & Daniel F. Sievenpiper
-
Article
| Open Access Synchronous micromechanically resonant programmable photonic circuits
Synchronous micromechanically resonant programmable photonic circuits
MEMS-based photonic integrated circuits (PICs) are often limited in speed by mechanical resonances. Here the authors report a programmable architecture for PICs which uses mechanical eigenmodes for synchronized, resonantly enhanced optical modulation.
- Mark Dong
- , Julia M. Boyle
- & Dirk Englund
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasmall and tunable TeraHertz surface plasmon cavities at the ultimate plasmonic limit
Ultrasmall and tunable TeraHertz surface plasmon cavities at the ultimate plasmonic limit
In this work, the authors use a surface plasmonic mechanism to efficiently confine TeraHertz photons inside ultrasmall cavities. These plasmonic-based TeraHertz cavities are shown to operate until the ultimate limit that is allowed fundamentally and at which plasmons start to behave in a nonlocal fashion.
- Ian Aupiais
- , Romain Grasset
- & Yannis Laplace
-
Article
| Open Access Optomechanical ring resonator for efficient microwave-optical frequency conversion
Optomechanical ring resonator for efficient microwave-optical frequency conversion
The authors showed a high-efficiency microwave-optical conversion using optomechanical rings where co-resonant traveling photons and phonons induce enhanced interconversion, which enables transduction application in quantum and classical domains.
- I-Tung Chen
- , Bingzhao Li
- & Mo Li
-
Article
| Open Access Strong transient magnetic fields induced by THz-driven plasmons in graphene disks
Strong transient magnetic fields induced by THz-driven plasmons in graphene disks
The authors provide an experimental demonstration of magnetic field generation in graphene disks via the inverse Faraday effect. When the disks are illuminated with circularly polarized radiation in resonance with the graphene plasmon frequency, the corresponding rotational motion of the charge carriers gives rise to a unipolar magnetic field.
- Jeong Woo Han
- , Pavlo Sai
- & Martin Mittendorff
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering chirality at wafer scale with ordered carbon nanotube architectures
Engineering chirality at wafer scale with ordered carbon nanotube architectures
Methods for generating macroscopic chiral matter struggle with limited scalability. Here, the authors show two vacuum filtration methods - twist stacking and mechanical rotation - to align carbon nanotubes into chiral structures at wafer scale with tunable circular dichroism.
- Jacques Doumani
- , Minhan Lou
- & Weilu Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Bulk-local-density-of-state correspondence in topological insulators
Bulk-local-density-of-state correspondence in topological insulators
Current approaches to distinguish topological phases from topologically-trivial phases have limited general applicability. Here, in a photonic-crystal context, the authors demonstrate that in trivial structures the bulk local density of states (LDOS) extends all the way to the edges and corners, while in topological structures the bulk LDOS actually avoids the edges and corners.
- Biye Xie
- , Renwen Huang
- & Shuang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic construction of refractive index-dependent vibrations using surface plasmon-phonon polaritons
Dynamic construction of refractive index-dependent vibrations using surface plasmon-phonon polaritons
Molecular vibrations serve as valuable signatures for the constituent elements and bonding in compounds. Here, using Surface-Enhanced Infrared Absorption spectroscopy, the authors study refractive index dependent vibrations of surface phonon polaritons and surface plasmon platform, targeting dynamic biomonitoring.
- Hong Zhou
- , Zhihao Ren
- & Chengkuo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Metafiber transforming arbitrarily structured light
Metafiber transforming arbitrarily structured light
Structured light has proven useful for numerous photonic applications. However, its current use in optical fibers is severely limited. The authors report a highly integrated metafiber platform based on 3D laser nanoprinting, capable of creating arbitrarily structured light.
- Chenhao Li
- , Torsten Wieduwilt
- & Haoran Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Accessible hotspots for single-protein SERS in DNA-origami assembled gold nanorod dimers with tip-to-tip alignment
Accessible hotspots for single-protein SERS in DNA-origami assembled gold nanorod dimers with tip-to-tip alignment
The identification of individual proteins is highly desirable in diagnostics. Here, the authors report on DNA-origami assembled dimers of gold nanorod with accessible hotspots to capture and identify single proteins from solution by SERS.
- Francis Schuknecht
- , Karol Kołątaj
- & Theobald Lohmueller
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable Tamm plasmon cavity as a scalable biosensing platform for surface enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy
Tunable Tamm plasmon cavity as a scalable biosensing platform for surface enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy
The researchers present a scalable Tamm plasmon cavity using phase change material with large resonance tunability and demonstrated tunable SERS by matching the plasmonic resonance with the molecule absorption for sensitivity enhanced biosensing.
- Kandammathe Valiyaveedu Sreekanth
- , Jayakumar Perumal
- & Jinghua Teng
-
Article
| Open Access Negative capacitors and inductors enabling wideband waveguide metatronics
Negative capacitors and inductors enabling wideband waveguide metatronics
The authors showcase a method to design negative lumped elements by engineering the effective permittivity within the waveguide, which enables realizations of wideband waveguide metatronics and promises performance enhancement in various fields.
- Xu Qin
- , Pengyu Fu
- & Yue Li
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene/silicon heterojunction for reconfigurable phase-relevant activation function in coherent optical neural networks
Graphene/silicon heterojunction for reconfigurable phase-relevant activation function in coherent optical neural networks
Designing an efficient activation function for optical neural networks remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a modulator-detector-in-one graphene/silicon heterojunction ring resonators enabling on-chip reconfigurable activation function devices with phase activation capability for optical neural networks.
- Chuyu Zhong
- , Kun Liao
- & Hongtao Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Organic photodiodes with bias-switchable photomultiplication and photovoltaic modes
Organic photodiodes with bias-switchable photomultiplication and photovoltaic modes
Preparation of photodiodes with photomultiplication/photovoltaic two operating modes is promising but challenging. Here, the authors report a bias-switchable dual-mode organic photodiode by adopting traps and blocking layer, achieving detectivity of 1012 Jones and fast response speed in both modes.
- Qingxia Liu
- , Lingfeng Li
- & Yadong Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Polarization-driven reversible actuation in a photo-responsive polymer composite
Polarization-driven reversible actuation in a photo-responsive polymer composite
Light-responsive polymers with polarization-dependent deformation are promising material to develop tunable devices usually limited by irreversible dynamic control. Here, the authors use controlled polarization of visible light to produce arbitrary deformations into amorphous composites containing azopolymer microdomains to unlock the next level of complex actuation in soft lightdriven robots.
- David Urban
- , Niccolò Marcucci
- & Emiliano Descrovi
-
Article
| Open Access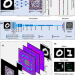 Learning diffractive optical communication around arbitrary opaque occlusions
Learning diffractive optical communication around arbitrary opaque occlusions
Researchers demonstrate robust optical communication around fully opaque occlusions, partially or entirely blocking the light path, using a pair of electronic encoder and passive diffractive decoder that are jointly optimized using deep learning.
- Md Sadman Sakib Rahman
- , Tianyi Gan
- & Aydogan Ozcan
-
Article
| Open Access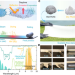 Atmospheric-moisture-induced polyacrylate hydrogels for hybrid passive cooling
Atmospheric-moisture-induced polyacrylate hydrogels for hybrid passive cooling
Gan et al. have developed sodium polyacrylate-based films for passive radiative cooling that can be fabricated using atmospheric moisture alone, offering radiative and evaporative cooling, reducing temperatures by up to 5 °C under partly cloudy skies.
- Roisul Hasan Galib
- , Yanpei Tian
- & Qiaoqiang Gan
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale reshaping of resonant dielectric microstructures by light-driven explosions
Nanoscale reshaping of resonant dielectric microstructures by light-driven explosions
Laser machining can modify and reshape materials on the scale comparable to light’s wavelength. Here, authors use tailored microstructures to push the limit of laser machining to a scale that is almost 100 times smaller than a wavelength of light.
- Maxim R. Shcherbakov
- , Giovanni Sartorello
- & Gennady Shvets
-
Article
| Open Access All-dielectric scale invariant waveguide
All-dielectric scale invariant waveguide
The Authors present an exciting dielectric waveguide mechanism that can confine light in regions of varying sizes, unlike conventional designs. The platform offers a unique blend of properties by leveraging radiation modes while minimizing optical losses. This work holds promise for serving as the next generation of fundamental building blocks for integrated photonics applications.
- Janderson R. Rodrigues
- , Utsav D. Dave
- & Michal Lipson
-
Article
| Open Access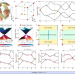 Real higher-order Weyl photonic crystal
Real higher-order Weyl photonic crystal
Here, the authors experimentally discover a class of higher-order Weyl semimetal phase in a three-dimensional photonic crystal, exhibiting the concurrence of the surface and hinge Fermi arcs from the nonzero Chern number and the nontrivial generalized real Chern number, respectively, coined a real higher-order Weyl photonic crystals.
- Yuang Pan
- , Chaoxi Cui
- & Yihao Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Asymptotic dispersion engineering for ultra-broadband meta-optics
Asymptotic dispersion engineering for ultra-broadband meta-optics
The authors present a comprehensive framework for on-demand dispersion control with a single-layer metasurface, particularly in an ultra-broad bandwidth. An achromatic metalens spanning the visible and near-infrared spectra is experimentally demonstrated.
- Yueqiang Hu
- , Yuting Jiang
- & Huigao Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Resonant cavity phosphor
Resonant cavity phosphor
Phosphor efficiency can be improved via materials development or structural engineering, the latter only begun lately. Here the authors propose and investigate simple vertical resonant cavity as a platform for nanostructurally engineered phosphor.
- Tae-Yun Lee
- , Yeonsang Park
- & Heonsu Jeon
-
Article
| Open Access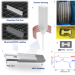 4D Optical fibers based on shape-memory polymers
4D Optical fibers based on shape-memory polymers
The authors demonstrate here a method for the production of arbitrarily long, light-guiding microstructured fibers with shape-memory properties. The showcased design of adaptative fibers here holds potential for the development of functional actuators and sensors.
- Clément Strutynski
- , Marianne Evrard
- & Frédéric Smektala
-
Article
| Open Access Metasurface enabled broadband all optical edge detection in visible frequencies
Metasurface enabled broadband all optical edge detection in visible frequencies
Here, the Authors demonstrate a 2D isotropic, polarization-independent, broadband edge detection with high transmission efficiency under both coherent and incoherent illumination along the visible range using a metasurface based on Fourier optics principles.
- Ibrahim Tanriover
- , Sina Abedini Dereshgi
- & Koray Aydin
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-THz wireless transmission based on graphene-integrated optoelectronic mixer
Sub-THz wireless transmission based on graphene-integrated optoelectronic mixer
Here, the authors report the realization of a sub-THz wireless data link based on a graphene-integrated optoelectronic mixer with a >96 GHz bandwidth, −44 dB upconversion efficiency and <0.1 mm2 footprint, providing an alternative approach for the realization of millimeter-wave transmitters.
- Alberto Montanaro
- , Giulia Piccinini
- & Marco Romagnoli
-
Article
| Open Access High-Q lasing via all-dielectric Bloch-surface-wave platform
High-Q lasing via all-dielectric Bloch-surface-wave platform
Integrating coherent light sources on surface wave platforms would offer opportunities for sensing and data processing. The authors realize a microfabricated coherent light source based on the stimulated emission of a guided Bloch surface wave mode.
- Yang-Chun Lee
- , Ya-Lun Ho
- & Jean-Jacques Delaunay
-
Article
| Open Access Cascaded metasurfaces for high-purity vortex generation
Cascaded metasurfaces for high-purity vortex generation
The authors demonstrate an efficient way to generate high-purity vortex beams by applying optical neural networks to cascaded phase-only metasurfaces. Specifically, they present record-high-quality Laguerre-Gaussian (LGp,l) optical modes with polynomial orders p = 10 and l = 200 with purity in p, l and relative conversion efficiency of 96%, 85%, and 70%, respectively.
- Feng Mei
- , Geyang Qu
- & Shumin Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated reconstructive spectrometer with programmable photonic circuits
Integrated reconstructive spectrometer with programmable photonic circuits
Recent years have seen a growing need for miniaturized spectroscopic tools. Here, authors present a novel integrated spectrometer with programmable photonic circuits, achieving record-high resolution and bandwidth via only a few filtering components.
- Chunhui Yao
- , Kangning Xu
- & Richard Penty
-
Article
| Open Access Morphogenetic metasurfaces: unlocking the potential of turing patterns
Morphogenetic metasurfaces: unlocking the potential of turing patterns
Inspired by Alan Turing’s last works on morphogenesis, this research introduces a technique for generating metasurfaces through the emergence of anisotropic patterns capable of self-structuring in response to electromagnetic constraints.
- Thomas Fromenteze
- , Okan Yurduseven
- & Cyril Decroze

 Thermo-optic epsilon-near-zero effects
Thermo-optic epsilon-near-zero effects