Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Arbitrary lattice symmetries via block copolymer nanomeshes
Arbitrary lattice symmetries via block copolymer nanomeshes
Nanoscale patterning methods based on self-assembly promise to revolutionize the fabrication of high-tech devices, but suffer from a limited number of possible lattice symmetries. Here, the authors use a laser zone annealing technique to pattern block copolymers into any 2D mesh motif they desire.
- Pawel W. Majewski
- , Atikur Rahman
- & Kevin G. Yager
-
Article
| Open Access Colloidal metasurfaces displaying near-ideal and tunable light absorbance in the infrared
Colloidal metasurfaces displaying near-ideal and tunable light absorbance in the infrared
Metasurfaces are arrays of subwavelength structures that are tailored to produce specific optical responses. Rozin et al.show that large-area metasurfaces can be readily fabricated by self-assembly of colloidal nanocrystals of different geometries, producing tunable reflectance and absorbance properties.
- Matthew J. Rozin
- , David A. Rosen
- & Andrea R. Tao
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing the planar chemistry of two-dimensional heterostructures at the atomic level
Revealing the planar chemistry of two-dimensional heterostructures at the atomic level
The properties of 2D materials such as graphene can vary according to the quality and, for vertical devices, the interfaces between materials. Here, the authors report a method using TOF-SIMS, micro-Raman spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy to give high levels of detail of vertical 2D heterostructures.
- Harry Chou
- , Ariel Ismach
- & Andrei Dolocan
-
Article |
 Spin transport and Hanle effect in silicon nanowires using graphene tunnel barriers
Spin transport and Hanle effect in silicon nanowires using graphene tunnel barriers
Graphene forms low-resistance tunnel barriers for spin injection from a ferromagnet into silicon. Here, the authors fabricate silicon nanowire non-local spin valves with graphene tunnel barriers, evidencing spin accumulation and transport via Hanle spin precession measurements.
- O. M. J. van ’t Erve
- , A. L. Friedman
- & B. T. Jonker
-
Article
| Open Access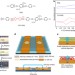 Role of redox centre in charge transport investigated by novel self-assembled conjugated polymer molecular junctions
Role of redox centre in charge transport investigated by novel self-assembled conjugated polymer molecular junctions
To date, conjugated polymers have not yet been used in molecular junctions despite the fact that they transport charge more efficiently than small-molecular systems. Here, Wang et al.showcase the self-assembly of conjugated polymers into ultrathin films in a planar manner for device construction.
- Zongrui Wang
- , Huanli Dong
- & Wenping Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Light-induced crawling of crystals on a glass surface
Light-induced crawling of crystals on a glass surface
Creating the motion of nanosized or microsized objects is essential for building robots at small scales. Here, Uchida et al.move photoresponsive organic crystals on a glass substrate using two lamps, which crystallize and melt the crystal front and the rear, respectively, to generate the moving force.
- Emi Uchida
- , Reiko Azumi
- & Yasuo Norikane
-
Article
| Open Access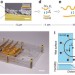 Scaling up nanoscale water-driven energy conversion into evaporation-driven engines and generators
Scaling up nanoscale water-driven energy conversion into evaporation-driven engines and generators
Harvesting energy from evaporation is constrained by the limited transport kinetics of materials and the slowly changing humidity of the environment. Chen et al. follow hierarchical design strategies to overcome these problems and create engines that start and run when placed at air-water interfaces.
- Xi Chen
- , Davis Goodnight
- & Ozgur Sahin
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable photonic crystals enabled by pressure-responsive shape-memory polymers
Reconfigurable photonic crystals enabled by pressure-responsive shape-memory polymers
Smart shape-memory polymers based on pressure stimuli have potential biomedical and aerospace applications but are largely unexplored. Here, Fang et al.present a reconfigurable photonic crystal that is reprogrammed at ambient conditions by a pressure-responsive shape-memory polymer.
- Yin Fang
- , Yongliang Ni
- & Peng Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Ambient solid-state mechano-chemical reactions between functionalized carbon nanotubes
Ambient solid-state mechano-chemical reactions between functionalized carbon nanotubes
Direct coupling between chemical groups on individual nanostructures may lead to new architectures and reactions. Here, the authors report an ambient mechano-chemical reaction between two different reactant carbon nanotube varieties, which produces condensation products and unzipping of the nanotube structure.
- Mohamad A. Kabbani
- , Chandra Sekhar Tiwary
- & Pulickel M. Ajayan
-
Article
| Open Access Noncontact friction via capillary shear interaction at nanoscale
Noncontact friction via capillary shear interaction at nanoscale
The contribution from water bridges at nanoscale between rough surfaces is important for macroscopic friction under ambient conditions. Here, Lee et al. show that water nanobridge produce noncontact friction originated from the pinning–depinning dynamics of the contact line at the interface.
- Manhee Lee
- , Bongsu Kim
- & Wonho Jhe
-
Article
| Open Access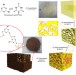 Synthesis of three-dimensionally interconnected sulfur-rich polymers for cathode materials of high-rate lithium–sulfur batteries
Synthesis of three-dimensionally interconnected sulfur-rich polymers for cathode materials of high-rate lithium–sulfur batteries
There is intensive research underway into the cathode development of lithium–sulphur batteries. Here, the authors present a battery with organosulfur-containing polymers as the cathode active materials which displays promising electrochemical performance.
- Hoon Kim
- , Joungphil Lee
- & Moon Jeong Park
-
Article
| Open Access General synthesis of complex nanotubes by gradient electrospinning and controlled pyrolysis
General synthesis of complex nanotubes by gradient electrospinning and controlled pyrolysis
Nanowires and nanotubes are ideal candidates for energy applications but inorganic multielement oxides are less well studied. Here, the authors propose a gradient-electrospinning followed by controlled-pyrolysis method to synthesize various controllable one dimensional metal oxide nanostructures.
- Chaojiang Niu
- , Jiashen Meng
- & Liqiang Mai
-
Article
| Open Access Polarization-independent actively tunable colour generation on imprinted plasmonic surfaces
Polarization-independent actively tunable colour generation on imprinted plasmonic surfaces
Plasmonic nanostructures are a promising alternative to conventional pixels, where their characteristics at the nanoscale offer many benefits. Franklin et al. combine plasmonic surfaces with liquid crystals to create voltage-tunable polarization-independent color pixels for reflective displays.
- Daniel Franklin
- , Yuan Chen
- & Debashis Chanda
-
Article
| Open Access Highly active oxygen reduction non-platinum group metal electrocatalyst without direct metal–nitrogen coordination
Highly active oxygen reduction non-platinum group metal electrocatalyst without direct metal–nitrogen coordination
The active site of many non-noble metal cathodic oxygen reduction catalysts consists of a nitrogen-corodinated transition metal. Here, the authors report an iron-based electrocatalyst devoid of iron–nitrogen coordination, and demonstrate its high activity in acid and alkaline media.
- Kara Strickland
- , Elise Miner
- & Sanjeev Mukerjee
-
Article
| Open Access Phase stability and dynamics of entangled polymer–nanoparticle composites
Phase stability and dynamics of entangled polymer–nanoparticle composites
The lowering of polymer viscosity upon addition of small amounts of nanoparticles is counter-intuitive and has puzzled researchers. Here, Mangal et al. explain this intriguing phenomenon using a model polymer–nanocomposite system comprised of well-dispersed nanoparticles in an entangled polymer melt.
- Rahul Mangal
- , Samanvaya Srivastava
- & Lynden A. Archer
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging screw dislocations at atomic resolution by aberration-corrected electron optical sectioning
Imaging screw dislocations at atomic resolution by aberration-corrected electron optical sectioning
Although screw dislocations impact on the properties of various engineering materials, their investigation on the atomic scale has been challenging. Here, the authors use optical sectioning in a scanning transmission electron microscope to achieve direct imaging of screw displacements around a screw dislocation core in GaN.
- H. Yang
- , J. G. Lozano
- & P. D. Nellist
-
Article
| Open Access Phase and composition controllable synthesis of cobalt manganese spinel nanoparticles towards efficient oxygen electrocatalysis
Phase and composition controllable synthesis of cobalt manganese spinel nanoparticles towards efficient oxygen electrocatalysis
It is challenging to synthesize cobalt manganese spinels with controlled phase and composition. Here the authors present a solution-based synthesis method for the spinels, which show potential in catalysing oxygen reduction reactions.
- Chun Li
- , Xiaopeng Han
- & Jun Chen
-
Article
| Open Access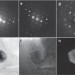 Scanning precession electron tomography for three-dimensional nanoscale orientation imaging and crystallographic analysis
Scanning precession electron tomography for three-dimensional nanoscale orientation imaging and crystallographic analysis
High-resolution microscopy allows imaging of information on the atomic scale. Here, by combining precession electron diffraction with scanning transmission electron microscopy, the authors demonstrate an efficient, alternative technique to determine the three-dimensional orientation of materials.
- Alexander S. Eggeman
- , Robert Krakow
- & Paul A. Midgley
-
Article
| Open Access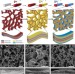 Self-assembled three-dimensional and compressible interdigitated thin-film supercapacitors and batteries
Self-assembled three-dimensional and compressible interdigitated thin-film supercapacitors and batteries
It is challenging to construct three-dimensional thin-film energy-storage devices. Here the authors present supercapacitors and batteries based on layer-by-layer self-assembly of interdigitated thin films inside aerogels, demonstrating energy storage as well as compressibility in three-dimensional devices.
- Gustav Nyström
- , Andrew Marais
- & Mahiar M. Hamedi
-
Article
| Open Access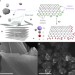 Antimony-doped graphene nanoplatelets
Antimony-doped graphene nanoplatelets
Heteroatom doping of graphitic networks has been shown to modify electrocatalytic performance. Here, the authors fabricate semimetal antimony doped graphene nanoplatelet based catalysts and demonstrate their enhanced stability for oxygen reduction, due to the multiple accessible antimony oxidation states.
- In-Yup Jeon
- , Min Choi
- & Jong-Beom Baek
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional patterning of solid microstructures through laser reduction of colloidal graphene oxide in liquid-crystalline dispersions
Three-dimensional patterning of solid microstructures through laser reduction of colloidal graphene oxide in liquid-crystalline dispersions
Existing lithographic methods for the micropatterning of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) are limited by mask production. Here, the authors fabricate fully 3D rGO microstructures in an aqueous nematic liquid crystal of two-dimensional GO flakes via a scalable, mask-free pulsed near-infrared laser approach.
- Bohdan Senyuk
- , Natnael Behabtu
- & Ivan I. Smalyukh
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic cavity-apertures as dynamic pixels for the simultaneous control of colour and intensity
Plasmonic cavity-apertures as dynamic pixels for the simultaneous control of colour and intensity
The increased miniaturization of optical technologies necessitates ever smaller pixels, but most routes fix pixel colours upon fabrication. Yun et al. show that combined plasmonic cavities and nanoapertures offer a route to nanoscale pixels whose colour and intensity can be dynamically tuned via polarization.
- Hansik Yun
- , Seung-Yeol Lee
- & Byoungho Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent perfect absorption in deeply subwavelength films in the single-photon regime
Coherent perfect absorption in deeply subwavelength films in the single-photon regime
Understanding the nature of coherent absorption is essential for exploiting it in new technologies. Here, the authors show that a metamaterial can deterministically absorb photons from a travelling wave with nearly unitary probability, down to the single-photon level.
- Thomas Roger
- , Stefano Vezzoli
- & Daniele Faccio
-
Article
| Open Access STED nanoscopy with fluorescent quantum dots
STED nanoscopy with fluorescent quantum dots
STED nanoscopy enables sub-diffraction imaging with a wide range of fluorescent probes. Here, the authors show that a bright and very photostable class of fluorescent quantum dots can be super-resolved with STED as biolabels in cellular contexts.
- Janina Hanne
- , Henning J. Falk
- & Stefan W. Hell
-
Article |
 Clean carbon nanotubes coupled to superconducting impedance-matching circuits
Clean carbon nanotubes coupled to superconducting impedance-matching circuits
Radio-frequency circuits offer fast low-noise detection of signals in carbon nanotubes, but incompatibilities in fabrication degrade the performance of the hybrid device. Here, the authors use a deterministic mechanical transfer to couple pristine nanotubes to a gigahertz superconducting matching circuit.
- V. Ranjan
- , G. Puebla-Hellmann
- & C. Schönenberger
-
Article |
 A carbon nanotube wall membrane for water treatment
A carbon nanotube wall membrane for water treatment
Carbon nanotubes have been proposed for many forms of water treatment, although ultrafiltration nanotube-based membranes with very high flow rates remain rare. Here, the authors fabricate a membrane delivering water permeability close to 30,000 litres per square meter per hour at 1 bar.
- Byeongho Lee
- , Youngbin Baek
- & Yong Hyup Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Wearable red–green–blue quantum dot light-emitting diode array using high-resolution intaglio transfer printing
Wearable red–green–blue quantum dot light-emitting diode array using high-resolution intaglio transfer printing
Deformable and high-resolution LEDs have attracted great interest for wearable electronics, but full-colour display is still challenging. Using a stamp printing technology, Choi et al. build ultra-thin RGB quantum dot pixel arrays with luminous efficiency of 14,000 cd m−2operated at low voltage of 7 V.
- Moon Kee Choi
- , Jiwoong Yang
- & Dae-Hyeong Kim
-
Article
| Open Access High-speed multiple-mode mass-sensing resolves dynamic nanoscale mass distributions
High-speed multiple-mode mass-sensing resolves dynamic nanoscale mass distributions
Nanomechanical resonators are sensitive to tiny changes in their mass. Here, the authors demonstrate a method for quickly measuring many resonator modes and use it to analyse the mass and position of multiple nanoparticles flowing in a fluid channel with a precision of 40 attograms and 150 nm, respectively.
- Selim Olcum
- , Nathan Cermak
- & Scott R. Manalis
-
Article
| Open Access Quantification of thickness and wrinkling of exfoliated two-dimensional zeolite nanosheets
Quantification of thickness and wrinkling of exfoliated two-dimensional zeolite nanosheets
Two-dimensional sheets of zeolites can function as molecular sieves for applications such as membranes or as catalysts. Here, the authors demonstrate a method using electron diffraction patterns to accurately measure the thickness and wrinkles of thin zeolite nanosheets.
- Prashant Kumar
- , Kumar Varoon Agrawal
- & K. Andre Mkhoyan
-
Article
| Open Access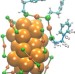 Chirality transfer from gold nanocluster to adsorbate evidenced by vibrational circular dichroism
Chirality transfer from gold nanocluster to adsorbate evidenced by vibrational circular dichroism
The transfer of chirality from surfaces to molecular species may have implications in areas from the origin of homochirality to heterogeneous catalysis. Here, the authors show that a chiral gold cluster can transfer its inherent chirality to adsorbed, achiral molecules, causing them to adopt chiral conformations.
- Igor Dolamic
- , Birte Varnholt
- & Thomas Bürgi
-
Article
| Open Access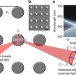 Surface lattice resonances and magneto-optical response in magnetic nanoparticle arrays
Surface lattice resonances and magneto-optical response in magnetic nanoparticle arrays
By incorporating magnetic materials into periodic nanostructures, additional control over the magneto-optical response of the system can be introduced. Kataja et al. show that arrays of magnetic nanoparticles exhibit Fano-type surface plasmon resonances with cross-coupling tuned by the lattice symmetry.
- M. Kataja
- , T. K. Hakala
- & P. Törmä
-
Article |
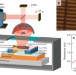 Electronic modulation of infrared radiation in graphene plasmonic resonators
Electronic modulation of infrared radiation in graphene plasmonic resonators
Graphene’s exotic properties make it suitable for many different optoelectronic devices. Brar et al. show that graphene plasmonic resonators can be exploited to produce narrow spectral emission in the mid-infrared, whose frequency and intensity can be modulated by electrostatic gating.
- Victor W. Brar
- , Michelle C. Sherrott
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Article
| Open Access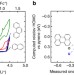 Electrochemical polymerization of pyrene derivatives on functionalized carbon nanotubes for pseudocapacitive electrodes
Electrochemical polymerization of pyrene derivatives on functionalized carbon nanotubes for pseudocapacitive electrodes
Electrochemically active organic molecules are an important class of electrode materials for energy storage. Here, the authors report organic electrodes made of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and functionalized few-walled carbon nanotubes, which show promising electrochemical performance.
- John C. Bachman
- , Reza Kavian
- & Seung Woo Lee
-
Article |
 Tuning the acoustic frequency of a gold nanodisk through its adhesion layer
Tuning the acoustic frequency of a gold nanodisk through its adhesion layer
The mechanical properties of metal nanostructures depend on nature of the adhesion layer attaching it to a substrate. Chang et al.find that the properties of phonons in gold nanodisks vary with adhesion layer thickness, and that this response can act as a probe of the metallic composition of the disk.
- Wei-Shun Chang
- , Fangfang Wen
- & Stephan Link
-
Article
| Open Access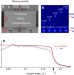 X-ray photonic microsystems for the manipulation of synchrotron light
X-ray photonic microsystems for the manipulation of synchrotron light
Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) are essential in a wide range of photonics applications but have not been demonstrated for X-ray optics. Here, Mukhopadhyay et al.use single-crystal silicon to demonstrate a MEMS system that can preserve and manipulate the spatial, temporal and spectral correlations of the X-rays.
- D. Mukhopadhyay
- , D. A. Walko
- & G. K. Shenoy
-
Article |
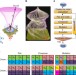 Ultrahigh-capacity non-periodic photon sieves operating in visible light
Ultrahigh-capacity non-periodic photon sieves operating in visible light
Miniaturization of optical structures allows light control in the nanoscale, but handling a large-scale device with aperiodic and random nanostructures is challenging. Here, Huang et al.design and fabricate a non-periodic photon sieve with control over amplitude, phase and polarization in visible light.
- Kun Huang
- , Hong Liu
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article |
 Sequential growth of long DNA strands with user-defined patterns for nanostructures and scaffolds
Sequential growth of long DNA strands with user-defined patterns for nanostructures and scaffolds
Assembling defined sequences of DNA is important for many applications, but the synthesis becomes more difficult as the target size increases. Here, the authors report a method for assembling DNA by combining smaller strands, with the final structure determined by the order of addition of the fragments.
- Graham D. Hamblin
- , Janane F. Rahbani
- & Hanadi F. Sleiman
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetically induced forward scattering at visible wavelengths in silicon nanosphere oligomers
Magnetically induced forward scattering at visible wavelengths in silicon nanosphere oligomers
A weak and narrow electric dipole has limited the use of silicon nanospheres in nanophotonic applications requiring strong interaction between electric and magnetic modes. Here, Yan et al.demonstrate effective coupling between the magnetic resonance and the electric gap mode in nearly touching silicon nanospheres.
- J. H. Yan
- , P. Liu
- & G. W. Yang
-
Article
| Open Access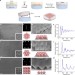 Nanoscale surface chemistry directs the tunable assembly of silver octahedra into three two-dimensional plasmonic superlattices
Nanoscale surface chemistry directs the tunable assembly of silver octahedra into three two-dimensional plasmonic superlattices
The self-assembly of anisotropic nanoparticles into large-area superlattices remains challenging. Here the authors exploit surface chemistry to tune the wettability of silver nano-octahedra, and direct a continuous superlattice structural evolution, from close-packed to progressively open structures.
- Yih Hong Lee
- , Wenxiong Shi
- & Xing Yi Ling
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable definition of nanogap electronic devices using self-inhibited reagent depletion
Programmable definition of nanogap electronic devices using self-inhibited reagent depletion
The miniaturization of electronic circuitry requires the reproducible fabrication of electrodes with nanoscale separations. Here, the authors present a robust manufacturing technology that enables programmably placed nanoscale three-dimensional nanogaps on an integrated circuit.
- Brian Lam
- , Wendi Zhou
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article
| Open Access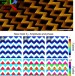 A magneto-electro-optical effect in a plasmonic nanowire material
A magneto-electro-optical effect in a plasmonic nanowire material
Metamaterials can be engineered to provide electric and magnetic responses that cannot be achieved in natural media. Here, the authors present a metamaterial based on plasmonic chevron nanowires that it exhibits a large reciprocal magneto-electro-optical effect driven by the Lorentz force.
- João Valente
- , Jun-Yu Ou
- & Nikolay I. Zheludev
-
Article
| Open Access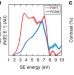 Sub-nanometre resolution imaging of polymer–fullerene photovoltaic blends using energy-filtered scanning electron microscopy
Sub-nanometre resolution imaging of polymer–fullerene photovoltaic blends using energy-filtered scanning electron microscopy
Morphological characterization of organic photovoltaic active layers is restricted by the lack of accurate chemical mapping tools. Here, the authors demonstrate an energy-filtered scanning electron microscopy technique, which enables sub-nanometre resolution imaging of an organic photovoltaic blend.
- Robert C. Masters
- , Andrew J. Pearson
- & Cornelia Rodenburg
-
Article
| Open Access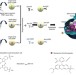 Single-band upconversion nanoprobes for multiplexed simultaneous in situ molecular mapping of cancer biomarkers
Single-band upconversion nanoprobes for multiplexed simultaneous in situ molecular mapping of cancer biomarkers
The excitation–emission profiles of upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) make them attractive biological probes. Here the authors present a lanthanide UCNP for the in situmultiplexed detection of cancer biomarkers, with different single-colour upconversion emissions.
- Lei Zhou
- , Rui Wang
- & Fan Zhang
-
Article |
 Na+ intercalation pseudocapacitance in graphene-coupled titanium oxide enabling ultra-fast sodium storage and long-term cycling
Na+ intercalation pseudocapacitance in graphene-coupled titanium oxide enabling ultra-fast sodium storage and long-term cycling
There are intensive efforts in developing anode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Here, the authors present a graphene-titanium dioxide composite as an anode material and show that sodium ion intercalation pseudocapacitance charge storage leads to excellent electrochemical properties.
- Chaoji Chen
- , Yanwei Wen
- & Yunhui Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional nanoscale molecular imaging by extreme ultraviolet laser ablation mass spectrometry
Three-dimensional nanoscale molecular imaging by extreme ultraviolet laser ablation mass spectrometry
Mass spectral analysis is used to map the composition of materials and surfaces in numerous fields. Here, the authors report a mass spectral technique based on extreme ultraviolet laser ablation that allows three-dimensional imaging of chemical composition in addition to giving highly sensitive nanoscale resolution.
- Ilya Kuznetsov
- , Jorge Filevich
- & Carmen S. Menoni
-
Article
| Open Access Superlattices assembled through shape-induced directional binding
Superlattices assembled through shape-induced directional binding
Controlling self-assembly of nanoparticles into superlattices is an important approach to build functional materials. Here, Lu et al. use directional binding provided by DNA-encoded polyhedral blocks—cubes or octahedrons—to guide spherical nanoparticles into clusters and three-dimensional lattices.
- Fang Lu
- , Kevin G. Yager
- & Oleg Gang
-
Article
| Open Access Metallic glass nanostructures of tunable shape and composition
Metallic glass nanostructures of tunable shape and composition
The nanoscale manipulation of the shape and composition of metallic glasses is challenging. Here, the authors employ a multitarget carousel oblique angle deposition strategy to synthesize metallic glass nanoarchitectures, and demonstrate applicability to a range of glass-forming alloys.
- Yanhui Liu
- , Jingbei Liu
- & Jan Schroers
-
Article
| Open Access Subcontinuum mass transport of condensed hydrocarbons in nanoporous media
Subcontinuum mass transport of condensed hydrocarbons in nanoporous media
Shale gas and oil are trapped in nanoscale porous networks of ultra-low permeability. Here, the authors develop a molecular model of alkane transport through nanoporous materials, showing that the mechanisms controlling flow at the nanoscale lead to a simple scaling of permeance with hydrocarbon size and density.
- Kerstin Falk
- , Benoit Coasne
- & Lydéric Bocquet
-
Article |
 The role of random nanostructures for the omnidirectional anti-reflection properties of the glasswing butterfly
The role of random nanostructures for the omnidirectional anti-reflection properties of the glasswing butterfly
The transparent wings of the glasswing butterfly have a low reflectance over the visible spectrum thanks to the nanopillars distributed across them. Siddique et al. show that this behaviour still works at high angles of incidence because of the random height distribution of the pillars.
- Radwanul Hasan Siddique
- , Guillaume Gomard
- & Hendrik Hölscher

 Membranes with artificial free-volume for biofuel production
Membranes with artificial free-volume for biofuel production