Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Injectable hydrogel electrodes as conduction highways to restore native pacing
Injectable hydrogel electrodes as conduction highways to restore native pacing
No preventive treatment addresses the underlying condition that leads to cardiac arrest. Here, researchers developed an injectable hydrogel electrode that achieves pacing that mimics physiological conduction with the potential to eliminate lethal arrhythmias and provide painless defibrillation.
- Gabriel J. Rodriguez-Rivera
- , Allison Post
- & Elizabeth Cosgriff-Hernandez
-
Article
| Open Access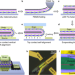 Ultrashort vertical-channel MoS2 transistor using a self-aligned contact
Ultrashort vertical-channel MoS2 transistor using a self-aligned contact
The simultaneous scaling down of the channel length and gate length of 2D transistors remains challenging. Here, the authors report a self-alignment process to fabricate vertical MoS2 transistors with sub-1 nm gate length and sub−50 nm channel length, exhibiting on-off ratios over 105 and on-state currents of 250 μA/μm at 4 V bias.
- Liting Liu
- , Yang Chen
- & Yuan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access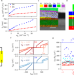 Parity-conserving Cooper-pair transport and ideal superconducting diode in planar germanium
Parity-conserving Cooper-pair transport and ideal superconducting diode in planar germanium
M. Valentini et al. study superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs) where the weak link of the Josephson junctions is a germanium 2D hole gas. They report signatures of the tunneling of pairs of Cooper pairs. For a particular microwave drive power, they observe a 100% efficient superconducting diode effect.
- Marco Valentini
- , Oliver Sagi
- & Georgios Katsaros
-
Article
| Open Access A stabilization rule for metal carbido cluster bearing μ3-carbido single-atom-ligand encapsulated in carbon cage
A stabilization rule for metal carbido cluster bearing μ3-carbido single-atom-ligand encapsulated in carbon cage
Trimetallic carbido clusterfullerenes (CCFs) represent the simplest metal carbido complexes with the ligands being only carbon atoms, but the formation prerequisite is unclear. Herein, the authors report the syntheses of three novel vanadium(V)-based CCFs featuring high vanadium valence state and propose a supplemental Octet Rule
- Runnan Guan
- , Jing Huang
- & Su-Yuan Xie
-
Article
| Open Access High throughput intracellular delivery by viscoelastic mechanoporation
High throughput intracellular delivery by viscoelastic mechanoporation
Scalability of mechanoporation strategies for intracellular delivery remains challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate a microfluidic approach for delivering mRNA and CRISPR-Cas systems to over 250 million cells per minute.
- Derin Sevenler
- & Mehmet Toner
-
Article
| Open Access A light-activatable theranostic combination for ratiometric hypoxia imaging and oxygen-deprived drug activity enhancement
A light-activatable theranostic combination for ratiometric hypoxia imaging and oxygen-deprived drug activity enhancement
Monitoring the level of hypoxia in a tumour is of use when treating by chemotherapy or photodynamic therapy, but can be challenging. Here, the authors report the development of a theranostic combination for light activated hypoxia imaging and modulation, and prodrug activation.
- Lei Ge
- , Yikai Tang
- & Xiqun Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Elastocapillarity-driven 2D nano-switches enable zeptoliter-scale liquid encapsulation
Elastocapillarity-driven 2D nano-switches enable zeptoliter-scale liquid encapsulation
In this work, authors demonstrate programmable nanostructures using two-dimensional materials for nanoscale liquid manipulation. The nanoswitches and capsules can hold zeptoliter liquid volumes, enabling active nanofluidics circuits and confined reactors.
- Nathan Ronceray
- , Massimo Spina
- & Slaven Garaj
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks
Biomimetic chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks
Assembly is an interesting strategy to build chiral hierarchies with premade properties and functionalities. Here, the authors present assembled chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks with dynamical chiroptical activities and employ them as powerful and recoverable platforms for enantioselective recognition of chiral aliphatic substrates.
- Jun Guo
- , Yulong Duan
- & Yi Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Purely self-rectifying memristor-based passive crossbar array for artificial neural network accelerators
Purely self-rectifying memristor-based passive crossbar array for artificial neural network accelerators
Designing memristor-integrated passive crossbar arrays to accelerate artificial neural networks with high reliability remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose a self-rectifying resistive switching device incorporated into a crossbar array with a density of 1 kb whose operational performance is assessed in terms of defected-cell proportion, reading margin, and selection functionality.
- Kanghyeok Jeon
- , Jin Joo Ryu
- & Gun Hwan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic order in 2D antiferromagnets revealed by spontaneous anisotropic magnetostriction
Magnetic order in 2D antiferromagnets revealed by spontaneous anisotropic magnetostriction
Van der Waals antiferromagnets offer a unique platform for studying magnetism in reduced dimensions, however, the low dimensionality, combined with lack of net magnetization, renders investigation challenging with conventional experimental probes. Here, Houmes et al show how van der Waals antiferromagnets can be investigated via the resonances of a vibrating rectangular membranes of this material.
- Maurits J. A. Houmes
- , Gabriele Baglioni
- & Herre S. J. van der Zant
-
Article
| Open Access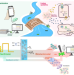 Redox-enabled electronic interrogation and feedback control of hierarchical and networked biological systems
Redox-enabled electronic interrogation and feedback control of hierarchical and networked biological systems
With redox-linked synthetic biology and electrobiofabrication, electronic information can be transmitted in a bidirectional manner between biology and electronics. Here the authors design an electrogenetic platform that allows real time electronic control of biological functions from proteins and gene circuits to cell consortia.
- Sally Wang
- , Chen-Yu Chen
- & William E. Bentley
-
Article
| Open Access Extendable piezo/ferroelectricity in nonstoichiometric 2D transition metal dichalcogenides
Extendable piezo/ferroelectricity in nonstoichiometric 2D transition metal dichalcogenides
Nonstoichiometric transition metal dichalcogenides break symmetry, enabling piezo/ferroelectric effects. Here, the authors propose an approach to integrate these properties with diverse 2D materials, advancing multifunctional materials and devices.
- Yi Hu
- , Lukas Rogée
- & Shu Ping Lau
-
Article
| Open Access 3D microprinting of inorganic porous materials by chemical linking-induced solidification of nanocrystals
3D microprinting of inorganic porous materials by chemical linking-induced solidification of nanocrystals
3D microprinting is considered a next generation manufacturing process for microscale components. Here, authors develop a generalised microscale 3D printing method to produce purely inorganic nanocrystal-linked porous materials that exhibit excellent functionality and hierarchical porosity.
- Minju Song
- , Yoonkyum Kim
- & Jae Sung Son
-
Article
| Open Access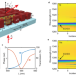 High quality factor metasurfaces for two-dimensional wavefront manipulation
High quality factor metasurfaces for two-dimensional wavefront manipulation
Wavefront manipulation with metasurfaces is typically limited to low quality factors. Here, the authors show how higher-order Mie modes can be leveraged to design high quality factor optical metasurfaces for wavefront manipulation in two dimensions.
- Claudio U. Hail
- , Morgan Foley
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Article
| Open Access A hard molecular nanomagnet from confined paramagnetic 3d-4f spins inside a fullerene cage
A hard molecular nanomagnet from confined paramagnetic 3d-4f spins inside a fullerene cage
Shortening the inter-spin distance is an effective way to enhance magnetic coupling. However, it is typically challenging to change the inter-ion distance in most magnetic systems. Here, Huang et al present a strategy for enhancing magnetic interactions, by confining a molecular magnetic system inside a carbon fullerene cage, leading to enhanced magnetic properties.
- Chenli Huang
- , Rong Sun
- & Song Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrophobically gated memristive nanopores for neuromorphic applications
Hydrophobically gated memristive nanopores for neuromorphic applications
Designing efficient nanoscale and adaptable bioinspired memristors remains a challenge. Here, the authors develop a bioinspired hydrophobically gated memristive nanopore capable of learning, forgetting, and retaining memory through an electrowetting mechanism.
- Gonçalo Paulo
- , Ke Sun
- & Alberto Giacomello
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired mechanical mineralization of organogels
Bioinspired mechanical mineralization of organogels
Mineralization is common in biological materials for selective strengthening, but similar toughening in polymer composites is challenging. Here, the authors report a mechanically-mediated reaction for formation of mineralized microrods within a synthetic material.
- Jorge Ayarza
- , Jun Wang
- & Aaron P. Esser-Kahn
-
Article
| Open Access Fragment-based drug nanoaggregation reveals drivers of self-assembly
Fragment-based drug nanoaggregation reveals drivers of self-assembly
Drug nanoaggregates could be used to improve drug pharmacokinetics when developed for drug delivery, however, the structural features of molecules that drive nanoaggregate formation remain elusive. Here, the authors investigate nanoaggregate self-assembly mechanisms using small molecule fragments to identify the critical molecular forces that contribute to self-assembly, namely aromatic groups and hydrogen bond acceptors/donors.
- Chen Chen
- , You Wu
- & Daniel A. Heller
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular sensitised probe for amino acid recognition within peptide sequences
Molecular sensitised probe for amino acid recognition within peptide sequences
Chemical identification of the building blocks of biopolymers often considerably relies on the presence of markers, extensive simulations, or is not possible at all. Here, the authors report a molecular probe-sensitisation approach addressing the identification of a specific amino acid within different peptides.
- Xu Wu
- , Bogdana Borca
- & Uta Schlickum
-
Article
| Open Access Embedding security into ferroelectric FET array via in situ memory operation
Embedding security into ferroelectric FET array via in situ memory operation
Existing solutions based Advanced Encryption Standard to address the security issues of nonvolatile memories incurs significant performance and power overhead. Here, the authors propose a lightweight XOR-gate based encryption/decryption technique by exploiting in-situ array operations, which achieves significant area/latency/power reduction compared to conventional designs.
- Yixin Xu
- , Yi Xiao
- & Kai Ni
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-dependent Andreev molecules and superconducting gap closing in coherently-coupled Josephson junctions
Phase-dependent Andreev molecules and superconducting gap closing in coherently-coupled Josephson junctions
S. Matsuo et al. report tunneling spectroscopy measurements on a device consisting of two Josephson junctions (JJ) sharing a single superconducting electrode. In isolation, each JJ would host an Andreev bound state (ABS). In their coherently-coupled JJs, the authors report the formation of an Andreev molecule due to hybridization of the two ABSs.
- Sadashige Matsuo
- , Takaya Imoto
- & Seigo Tarucha
-
Comment
| Open Access Excitonic Complexes in Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides
Excitonic Complexes in Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides
The enhanced Coulomb interaction in two dimensions leads to not only tightly bound excitons but also many-particle excitonic complexes: excitons interacting with other quasiparticles, which results in improved and even new exciton properties with better controls. Here, we summarize studies of excitonic complexes in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides and their moiré heterojunctions, envisioning how to utilize them for exploring quantum many-body physics.
- Xiaotong Chen
- , Zhen Lian
- & Su-Fei Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Record high room temperature resistance switching in ferroelectric-gated Mott transistors unlocked by interfacial charge engineering
Record high room temperature resistance switching in ferroelectric-gated Mott transistors unlocked by interfacial charge engineering
Ferroelectric transistors are promising building blocks for developing energy-efficient memory and logic applications. Here, the authors report a record high 300 K resistance on-off ratio achieved in ferroelectric-gated Mott transistors by exploiting a charge transfer layer to tailor the channel carrier density and mitigate the ferroelectric depolarization effect.
- Yifei Hao
- , Xuegang Chen
- & Xia Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Low-dimensional heat conduction in surface phonon polariton waveguide
Low-dimensional heat conduction in surface phonon polariton waveguide
Heat conduction in solids is known to be contributed by phonons and electrons. Here, authors observe enhanced and non-diffusive thermal conductance mediated by surface phonon polaritons in polar dielectric nanoribbon waveguides.
- Yu Pei
- , Li Chen
- & Renkun Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Hot luminescence from single-molecule chromophores electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by tripodal scaffolds
Hot luminescence from single-molecule chromophores electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by tripodal scaffolds
A fundamental challenge for molecular electronics is the change in photophysical properties of molecules upon direct electrical contact. Here, the authors observe hot luminescence emitted by single-molecule chromophores that are electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by a tripodal scaffold.
- Vibhuti Rai
- , Nico Balzer
- & Michal Valášek
-
Article
| Open Access In operando cryo-STEM of pulse-induced charge density wave switching in TaS2
In operando cryo-STEM of pulse-induced charge density wave switching in TaS2
Resistive switching of 1T-TaS2 is promising for next-generation electronics. Here, using in operando electron microscopy, the authors determine that Joule heating drives the switching process, which will aid the engineering of future devices.
- James L. Hart
- , Saif Siddique
- & Judy J. Cha
-
Article
| Open Access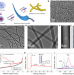 One-dimensionally oriented self-assembly of ordered mesoporous nanofibers featuring tailorable mesophases via kinetic control
One-dimensionally oriented self-assembly of ordered mesoporous nanofibers featuring tailorable mesophases via kinetic control
One-dimensional materials have interesting physiochemical properties, but control over porosity is still a significant challenge. Here, the authors report a self-assembly method for the fabrication of 1D materials with an ordered mesostructure.
- Liang Peng
- , Huarong Peng
- & Dongyuan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic metasurfaces of cellulose nanocrystal matrices with quadrants of aligned gold nanorods for photothermal anti-icing
Plasmonic metasurfaces of cellulose nanocrystal matrices with quadrants of aligned gold nanorods for photothermal anti-icing
Cellulose nanocrystals are very attractive as a matrix material for plasmonic nanoparticles, but controlling particle orientation for patterning is challenging. Here, the authors prepare annular ring patterns with quadrants of aligned gold nanorods for photothermal applications.
- Jeongsu Pyeon
- , Soon Mo Park
- & Hyoungsoo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring gas discharge in contact electrification
Measuring gas discharge in contact electrification
Contact electrification triggers gas breakdown. Using Coulomb force to estimate voltage, this work provides experimental evidence for the Paschen curves that govern such discharge.
- Hongcheng Tao
- & James Gibert
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-50 nm perovskite-type tantalum-based oxynitride single crystals with enhanced photoactivity for water splitting
Sub-50 nm perovskite-type tantalum-based oxynitride single crystals with enhanced photoactivity for water splitting
A trade-off exists between improving crystallinity and minimizing particle size in the synthesis of perovskite-type transition-metal oxynitrides. The authors break this limitation to fabricate sub-50 nm ATaO2N (A = Sr, Ca, Ba) single nanocrystals exhibiting improved photocatalytic water-splitting performance
- Jiadong Xiao
- , Mamiko Nakabayashi
- & Kazunari Domen
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmon mediated coherent population oscillations in molecular aggregates
Plasmon mediated coherent population oscillations in molecular aggregates
The authors uncover a coherent, long-range transport of excitons in organic semiconductors that are strongly coupled to spatially structured plasmon fields by tracing ultrafast Rabi oscillations using two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy.
- Daniel Timmer
- , Moritz Gittinger
- & Christoph Lienau
-
Article
| Open Access Incommensurate grain-boundary atomic structure
Incommensurate grain-boundary atomic structure
Grain boundary atomic structures of crystalline materials have long been believed to be commensurate with the crystal periodicity of the adjacent crystals. Here, the authors discover an incommensurate grain boundary structure based on direct observations and theoretical calculations.
- Takehito Seki
- , Toshihiro Futazuka
- & Naoya Shibata
-
Article
| Open Access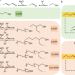 Enabling direct-growth route for highly efficient ethanol upgrading to long-chain alcohols in aqueous phase
Enabling direct-growth route for highly efficient ethanol upgrading to long-chain alcohols in aqueous phase
Achieving efficient carbon chain propagation remains a grand challenge for ethanol upgrading. Here, the authors report sulfur doped Ni@C-Sx catalysts with controllably exposed nickel sites that can dramatically improve direct-growth probability towards long-chain alcohols production.
- Juwen Gu
- , Wanbing Gong
- & Yujie Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance van der Waals antiferroelectric CuCrP2S6-based memristors
High-performance van der Waals antiferroelectric CuCrP2S6-based memristors
Layered thio- and seleno-phosphate ferroelectrics show promise for next-generation memory but have thermal stability issues. Using the electric field-driven phase transition in antiferroelectric CuCrP2S6, the authors introduce a robust memristor, emphasizing the potential of van der Waals antiferroelectrics in advanced neuromorphic computing.
- Yinchang Ma
- , Yuan Yan
- & Xixiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access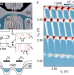 Coherent charge oscillations in a bilayer graphene double quantum dot
Coherent charge oscillations in a bilayer graphene double quantum dot
Graphene quantum dots promise applications for spin and valley qubits; however a demonstration of phase coherent oscillations has been lacking. Here the authors report coherent charge oscillations and measurements of coherence times in highly tuneable double quantum dots in bilayer graphene.
- K. Hecker
- , L. Banszerus
- & C. Stampfer
-
Article
| Open Access Solving complex nanostructures with ptychographic atomic electron tomography
Solving complex nanostructures with ptychographic atomic electron tomography
Transmission electron microscopy is essential for three-dimensional atomic structure determination, but solving complex heterogeneous structures containing light elements remains challenging. Here, authors solve a complex nanostructure using atomic resolution ptychographic electron tomography.
- Philipp M. Pelz
- , Sinéad M. Griffin
- & Colin Ophus
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling the synergistic effects of Cu-Ag tandem catalysts during electrochemical CO2 reduction using nanofocused X-ray probes
Unraveling the synergistic effects of Cu-Ag tandem catalysts during electrochemical CO2 reduction using nanofocused X-ray probes
Combining in situ nanoprobe techniques paves the way for gaining insights into structure-selectivity relations for electrocatalysts. Herein, the dynamic evolution of lattice strain in individual nanoparticles is directly visualized with nanoscale resolution in Cu-Ag tandem catalysts during the electrocatalytic conversion of CO2 into value-added chemicals.
- Marvin L. Frisch
- , Longfei Wu
- & Peter Strasser
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancement of short/medium-range order and thermal conductivity in ultrahard sp3 amorphous carbon by C70 precursor
Enhancement of short/medium-range order and thermal conductivity in ultrahard sp3 amorphous carbon by C70 precursor
sp3 amorphous carbon exhibits exceptional mechanical, thermal, and optical properties, but cannot be synthesized using traditional processes. Here authors report a nearly pure sp3−hybridized amorphous carbon synthesized from C70 which shows more short/medium-range order and enhanced thermal conductivity compared to C60.
- Yuchen Shang
- , Mingguang Yao
- & Bingbing Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Proton and molecular permeation through the basal plane of monolayer graphene oxide
Proton and molecular permeation through the basal plane of monolayer graphene oxide
GO monolayers are presumed to invariably contain a large density of nanoscale pinholes. Here the authors present gas and proton transport measurements which show that GO monolayers can be pinhole-free over micrometer-scale areas.
- Z. F. Wu
- , P. Z. Sun
- & M. Lozada-Hidalgo
-
Article
| Open Access Cryogenic multiplexing using selective area grown nanowires
Cryogenic multiplexing using selective area grown nanowires
The authors demonstrate a large ensemble of quantum dots which is characterized using a cryogenic multiplexer-demultiplexer circuit based on selective area growth nanowires, establishing the feasibility of scaling future quantum circuits.
- Dāgs Olšteins
- , Gunjan Nagda
- & Thomas S. Jespersen
-
Article
| Open Access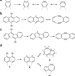 Local probe-induced structural isomerization in a one-dimensional molecular array
Local probe-induced structural isomerization in a one-dimensional molecular array
Achieving unit-by-unit isomerization within a molecular array poses a significant challenge in chemistry. Here, the authors demonstrate tip-induced stereoisomerization of dehydroazulene and diradical units in three-dimensional organometallic compounds on Ag(111).
- Shigeki Kawai
- , Orlando J. Silveira
- & Adam S. Foster
-
Article
| Open Access The role of halogens in Au–S bond cleavage for energy-differentiated catalysis at the single-bond limit
The role of halogens in Au–S bond cleavage for energy-differentiated catalysis at the single-bond limit
Investigation of the reaction process at the single-bond interface is key to understanding the catalytic reaction mechanism. Here, the authors develop a STM-BJ method to monitor the catalytic process from the perspective of single-bond energy.
- Peihui Li
- , Songjun Hou
- & Xuefeng Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Self-activated superhydrophilic green ZnIn2S4 realizing solar-driven overall water splitting: close-to-unity stability for a full daytime
Self-activated superhydrophilic green ZnIn2S4 realizing solar-driven overall water splitting: close-to-unity stability for a full daytime
A superhydrophilic green hollow ZnIn2S4 was fabricated to realize unassisted photocatalytic overall water splitting. This work could provide an innovative aperture for efficient solar-driven green hydrogen production to achieve carbon neutrality.
- Wei-Kean Chong
- , Boon-Junn Ng
- & Siang-Piao Chai
-
Article
| Open Access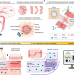 3D bioprinted multilayered cerebrovascular conduits to study cancer extravasation mechanism related with vascular geometry
3D bioprinted multilayered cerebrovascular conduits to study cancer extravasation mechanism related with vascular geometry
Geometrical complexities of blood vessels alter biophysical behaviors of circulating tumor cells, influencing cancer metastasis. Here, the authors develop a 3D bioprinted in vitro brain blood vessel-on-a-chip to investigate continuities between vascular geometry and metastatic cancer development.
- Wonbin Park
- , Jae-Seong Lee
- & Dong-Woo Cho
-
Article
| Open Access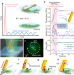 Autonomous nanorobots with powerful thrust under dry solid-contact conditions by photothermal shock
Autonomous nanorobots with powerful thrust under dry solid-contact conditions by photothermal shock
Optically trapping objects, marked by Nobel Prizes in 1997 and 2018 for applications in vacuum and liquids, remains challenging on solid surfaces. Here, the authors demonstrate a breakthrough by using photothermal-shock tweezers and explore nano-conventional robot applications
- Zhaoqi Gu
- , Runlin Zhu
- & Fuxing Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal and electrostatic tuning of surface phonon-polaritons in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures
Thermal and electrostatic tuning of surface phonon-polaritons in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures
Phonon polaritons are promising for infrared applications while it is difficult to tune the phonon polariton properties. Here, authors report a thermal and electrostatic tuning of surface phonon polaritons in heterostructures of LaAlO3/SrTiO3.
- Yixi Zhou
- , Adrien Waelchli
- & Alexey B. Kuzmenko
-
Article
| Open Access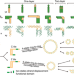 DNA T-shaped crossover tiles for 2D tessellation and nanoring reconfiguration
DNA T-shaped crossover tiles for 2D tessellation and nanoring reconfiguration
DNA tiles lay the foundation for programmable self-assembly of diverse DNA nanostructures. Here, the authors present a set of T-shaped crossover DNA tiles for various 2D tessellation and nanoring reconfiguration.
- Qi Yang
- , Xu Chang
- & Fei Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access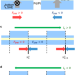 Position error-free control of magnetic domain-wall devices via spin-orbit torque modulation
Position error-free control of magnetic domain-wall devices via spin-orbit torque modulation
For magnetic domain-wall devices, key issue to be addressed is nonstochastic displacement of magnetic domain wall. Here, authors report domain-wall control with a position error-free scheme via spin-orbit torque modulation along nanotrack devices.
- Seong-Hyub Lee
- , Myeonghoe Kim
- & Sug-Bong Choe
-
Article
| Open Access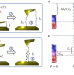 Microscopic theory, analysis, and interpretation of conductance histograms in molecular junctions
Microscopic theory, analysis, and interpretation of conductance histograms in molecular junctions
Conductance histograms are common setups to study molecular junctions, but the dispersion of the signals makes it difficult to interpret at microscopic level. Here the authors develop a physical model of molecular junctions that connects this observable with molecular properties.
- Leopoldo Mejía
- , Pilar Cossio
- & Ignacio Franco

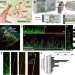 Angiogenesis-on-a-chip coupled with single-cell RNA sequencing reveals spatially differential activations of autophagy along angiogenic sprouts
Angiogenesis-on-a-chip coupled with single-cell RNA sequencing reveals spatially differential activations of autophagy along angiogenic sprouts