Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Resonant generation of propagating second-harmonic spin waves in nano-waveguides
Resonant generation of propagating second-harmonic spin waves in nano-waveguides
Spin waves in magnetic nanosystems offer a potential platform for wave-based signal processing and computing, with a variety of advantages compared to optical approaches. Herein, the authors demonstrate resonant phase matched generation of second harmonic spin waves, enabling the generation of short wavelength spin waves that are otherwise difficult to directly excite.
- K. O. Nikolaev
- , S. R. Lake
- & V. E. Demidov
-
Article
| Open Access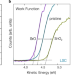 Engineering surface dipoles on mixed conducting oxides with ultra-thin oxide decoration layers
Engineering surface dipoles on mixed conducting oxides with ultra-thin oxide decoration layers
Improving materials for energy devices relates to an optimisation of their surfaces. Here authors show that surface modification with ultrathin oxide layers allows for a tailoring of the surface dipole and the work function of mixed ionic and electronic conducting oxides.
- Matthäus Siebenhofer
- , Andreas Nenning
- & Markus Kubicek
-
Article
| Open Access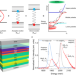 Energy transfer driven brightening of MoS2 by ultrafast polariton relaxation in microcavity MoS2/hBN/WS2 heterostructures
Energy transfer driven brightening of MoS2 by ultrafast polariton relaxation in microcavity MoS2/hBN/WS2 heterostructures
Here, the authors design a microcavity-confined 2D heterojunction to realize the strong coupling among donor exciton, acceptor exciton, and cavity photon mode, leading to an unconventional energy transfer via polariton relaxation with an enhancement factor of ~440.
- Zehua Hu
- , Tanjung Krisnanda
- & Qihua Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule RNA sizing enables quantitative analysis of alternative transcription termination
Single-molecule RNA sizing enables quantitative analysis of alternative transcription termination
The development of RNA technologies demands accurate assessment of transcript size and heterogeneity. Here, authors report a nanopore-based approach to study full-length RNA transcripts at the single-molecule level, identify premature transcription termination and study rolling-circle transcription.
- Gerardo Patiño-Guillén
- , Jovan Pešović
- & Ulrich Felix Keyser
-
Article
| Open Access Creation of a point-of-care therapeutics sensor using protein engineering, electrochemical sensing and electronic integration
Creation of a point-of-care therapeutics sensor using protein engineering, electrochemical sensing and electronic integration
Low-cost point-of-care sensors are vital for precision medicine. Here, the authors have repurposed a glucometer for breast cancer therapeutic detection capable of sensing tamoxifen in human blood, utilizing blood glucose to power and amplify the therapeutic signals
- Rong Cai
- , Chiagoziem Ngwadom
- & Caroline M. Ajo-Franklin
-
Article
| Open Access Targeted delivery of Fc-fused PD-L1 for effective management of acute and chronic colitis
Targeted delivery of Fc-fused PD-L1 for effective management of acute and chronic colitis
Triggering the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint is an attractive therapeutic approach in inflammatory bowel disease, and PD-L1, conjugated to the Fc part of an immunoglobulin (PD-L1-Fc) has been shown to be effective in mouse models. Here authors show that fusing to reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive nanoparticles improves effect of PD-L1-Fc due to targeting to inflammation sites, while systemic toxicity is reduced.
- Xudong Tang
- , Yangyang Shang
- & Lei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access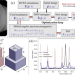 Broadband thermal imaging using meta-optics
Broadband thermal imaging using meta-optics
Exploring the miniaturization of imaging systems, researchers use inverse-design for broadband meta-optics in the LWIR spectrum. Here, authors achieve a six-fold Strehl ratio improvement in image quality over conventional metalenses using a novel design and computational techniques.
- Luocheng Huang
- , Zheyi Han
- & Arka Majumdar
-
Article
| Open Access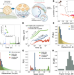 Motility of an autonomous protein-based artificial motor that operates via a burnt-bridge principle
Motility of an autonomous protein-based artificial motor that operates via a burnt-bridge principle
Inspired by biology, great progress has been made in creating artificial molecular motors. Here the authors report the synthesis and characterization of the Lawnmower, an autonomous, protein-based artificial molecular motor and show their design is capable of track-guided motion.
- Chapin S. Korosec
- , Ivan N. Unksov
- & Nancy R. Forde
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalously bright single-molecule upconversion electroluminescence
Anomalously bright single-molecule upconversion electroluminescence
The efficiency of upconversion electroluminescence remains very low for single-molecule emitters. Here, the authors report over one order of magnitude improvement in the emission efficiency via engineering energy-level alignments for triplet relayed upconversion involving only carrier injection.
- Yang Luo
- , Fan-Fang Kong
- & Zhen-Chao Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Non-volatile rippled-assisted optoelectronic array for all-day motion detection and recognition
Non-volatile rippled-assisted optoelectronic array for all-day motion detection and recognition
The authors create a rippled-assisted optoelectronic array (18 × 18 pixels) for the all-day motion detection and recognition, possessing negative and positive optical detection as well as memory and computation capabilities.
- Xingchen Pang
- , Yang Wang
- & Peng Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasmall metal alloy nanozymes mimicking neutrophil enzymatic cascades for tumor catalytic therapy
Ultrasmall metal alloy nanozymes mimicking neutrophil enzymatic cascades for tumor catalytic therapy
Emulating the killing function of neutrophils, which involves the enzymatic cascade of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and myeloperoxidase (MPO), is promising for cancer therapy, but developing SOD-MPO cascade in one nanozyme is challenging. Here the authors report ultrasmall AuPd alloy nanozymes that mimic neutrophil enzymatic cascades for catalytic treatment of tumors.
- Xiangqin Meng
- , Huizhen Fan
- & Kelong Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Smart touchless human–machine interaction based on crystalline porous cages
Smart touchless human–machine interaction based on crystalline porous cages
Smart sensors are important components in the development of touchless human-machine interaction systems. Here, the authors describe a smart 3D porous crystalline organic cage-based system that exhibits remarkable responsiveness to fingertip humidity, contributing to the advancement of touchless human-machine interaction technology.
- Jinrong Wang
- , Weibin Lin
- & Niveen M. Khashab
-
Article
| Open Access Elastic properties and tensile strength of 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene monolayers
Elastic properties and tensile strength of 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene monolayers
The Young’s modulus of the MXene Ti3C2Tx, theoretically predicted to be 0.502 TPa, has not yet been experimentally confirmed. This work supplants previous reports using nanoindentation with the correctly measured Young’s modulus of 0.484 ± 0.013 TPa.
- Chao Rong
- , Ting Su
- & Fu-Zhen Xuan
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneous crystallization of strongly confined CsSnxPb1-xI3 perovskite colloidal quantum dots at room temperature
Spontaneous crystallization of strongly confined CsSnxPb1-xI3 perovskite colloidal quantum dots at room temperature
Photoactive pure-iodine all-inorganic colloidal perovskite quantum dots (QDs) are attractive for optoelectronic applications, however their synthesis at room temperature is challenging. Here the authors report a room temperature strongly confined strategy to synthesize CsSnxPb1-xI3 QDs.
- Louwen Zhang
- , Hai Zhou
- & Guojia Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Open-source microscope add-on for structured illumination microscopy
Open-source microscope add-on for structured illumination microscopy
Researchers developed an open-hardware structured illumination microscopy add-on. This affordable upgrade provides super-resolution capabilities for normal optical microscopes. Detailed instructions enable easy reproduction to help democratize advanced microscopy.
- Mélanie T. M. Hannebelle
- , Esther Raeth
- & Georg E. Fantner
-
Article
| Open Access Inorganic perovskite-based active multifunctional integrated photonic devices
Inorganic perovskite-based active multifunctional integrated photonic devices
Researchers showcase an integrated photonic device with monocrystalline CsPbBr3 perovskite. Employing top-down etching approach, it introduces for micro lasers, beam splitters, X-couplers, Mach-Zehnder interferometers on perovskite films. This opens avenues for integrating perovskite semiconductors into optical chips, promising advancements in information and computing science.
- Qi Han
- , Jun Wang
- & Li Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable nanowrinkle-induced room-temperature exciton localization in monolayer WSe2
Programmable nanowrinkle-induced room-temperature exciton localization in monolayer WSe2
Here, the authors report on the fabrication of strained wrinkles in monolayer WSe2 by placing the material on Au nanoconical substrates. They investigate the correlation between topographical stress factors and localised, quantum-dot-like photoluminescence emission.
- Emanuil S. Yanev
- , Thomas P. Darlington
- & P. James Schuck
-
Article
| Open Access True amplification of spin waves in magnonic nano-waveguides
True amplification of spin waves in magnonic nano-waveguides
True amplification of spin waves by spin-orbit torque, which manifests itself by an exponential increase in amplitude with propagation distance, has so far remained elusive. Here, the authors realize amplification using clocked nanoseconds-long spin-orbit torque pulses in magnonic nano-waveguides.
- H. Merbouche
- , B. Divinskiy
- & V. E. Demidov
-
Article
| Open Access Current-induced switching of a van der Waals ferromagnet at room temperature
Current-induced switching of a van der Waals ferromagnet at room temperature
Fe3GaTe2 is a van der Waals material with a Curie temperature well above room temperature, making it an attractive material for integration into spintronic devices. Here, Kajale et al demonstrate spin-orbit torque induced switching of the magnetization of Fe3GaTe2, above room temperature, using a Pt spin Hall layer.
- Shivam N. Kajale
- , Thanh Nguyen
- & Deblina Sarkar
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid Madelung energy accounts for the huge potential shift in electrochemical systems
Liquid Madelung energy accounts for the huge potential shift in electrochemical systems
Electrode potential in any electrochemical systems has long been discussed by classical Debye-Hückel theory which holds only under extremely dilute concentrations. Here, the authors establish the concept ‘liquid Madelung potential’ to comprehensively describe the potential shift at practical concentrations.
- Norio Takenaka
- , Seongjae Ko
- & Atsuo Yamada
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular co-assembled strategy tuning protein conformation for cartilage regeneration
Molecular co-assembled strategy tuning protein conformation for cartilage regeneration
The assembly of oligopeptide and polypeptide molecules can reconstruct various ordered advanced structures. Here the authors develop a “molecular velcro”-inspired amphiphilic supramolecular co-assembly strategy, which improves the mechanical strength and cartilaginous regeneration efficiency through conformation transition.
- Chengkun Zhao
- , Xing Li
- & Yong Sun
-
Article
| Open Access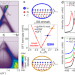 Achieving environmental stability in an atomically thin quantum spin Hall insulator via graphene intercalation
Achieving environmental stability in an atomically thin quantum spin Hall insulator via graphene intercalation
Topological states in atomically thin quantum spin Hall insulators suffer from instability against environmental factors. Here, the authors devise a strategy to preserve topologically protected states in monolayer indenene through graphene intercalation.
- Cedric Schmitt
- , Jonas Erhardt
- & Ralph Claessen
-
Article
| Open Access VO2 memristor-based frequency converter with in-situ synthesize and mix for wireless internet-of-things
VO2 memristor-based frequency converter with in-situ synthesize and mix for wireless internet-of-things
Frequency converters for wireless internet of things applications typically require separate circuits for different functions, causing energy and performance inefficiencies. Using an epitaxially grown VO2 memristor array, Liu et al. present a frequency converter with in-situ frequency synthesis and mix functionality.
- Chang Liu
- , Pek Jun Tiw
- & Yuchao Yang
-
Article
| Open Access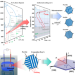 Highly anisotropic Fe3C microflakes constructed by solid-state phase transformation for efficient microwave absorption
Highly anisotropic Fe3C microflakes constructed by solid-state phase transformation for efficient microwave absorption
Fe3C microflakes with high magnetic anisotropy are prepared through solid-state phase transformation and electrochemical dealloying. The magnetic anisotropy can be tuned by adjusting the morphology, resulting in optimized ferromagnetic resonance behavior for microwave absorption
- Rongzhi Zhao
- , Tong Gao
- & Gaowu Qin
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous synthesis of high-entropy alloy nanoparticles by in-flight alloying of elemental metals
Continuous synthesis of high-entropy alloy nanoparticles by in-flight alloying of elemental metals
High-entropy alloy nanoparticles (HEA-NPs) have emerged as new materials in various fields, but their scalable synthesis still remains a challenge. Here, the authors report an ultrafast, one-step method for the continuous synthesis of HEA-NPs based on the thermal plasma jet technology.
- Keun Su Kim
- , Martin Couillard
- & Yu Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Vascular network-inspired fluidic system (VasFluidics) with spatially functionalizable membranous walls
Vascular network-inspired fluidic system (VasFluidics) with spatially functionalizable membranous walls
Functional features in the spatiotemporal regulation of blood chemistry are not much explored. Here authors show vascular network-inspired fluidics, functionalizable for different region-specific trans-wall transport to regulate fluids over space and time.
- Yafeng Yu
- , Yi Pan
- & Ho Cheung Shum
-
Article
| Open Access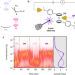 Photooxidation driven formation of Fe-Au linked ferrocene-based single-molecule junctions
Photooxidation driven formation of Fe-Au linked ferrocene-based single-molecule junctions
Metal-metal interfaces hold promise as contacting moieties for single-molecule devices with tunable functionality, yet the direct bonding has remained a challenge. Here, Lee et al. report the formation of Fe-Au bond without chemical ligand support in ferrocene-based molecular junctions.
- Woojung Lee
- , Liang Li
- & Latha Venkataraman
-
Article
| Open Access Biporous silica nanostructure-induced nanovortex in microfluidics for nucleic acid enrichment, isolation, and PCR-free detection
Biporous silica nanostructure-induced nanovortex in microfluidics for nucleic acid enrichment, isolation, and PCR-free detection
Efficient enrichment and isolation of pathogens are crucial for accurate and sensitive disease identification. Here, the authors present a chip equipped with biporous nanofilms that induces a nanovetex in a microfluidic channel for nucleic acid enrichment, isolation, and detection.
- Eunyoung Jeon
- , Bonhan Koo
- & Joonseok Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Navigating the 16-dimensional Hilbert space of a high-spin donor qudit with electric and magnetic fields
Navigating the 16-dimensional Hilbert space of a high-spin donor qudit with electric and magnetic fields
Qudits, higher-dimensional analogues of qubits, expand quantum state space for information processing using fewer physical units. Here the authors demonstrate control over a 16-dimensional Hilbert space, equivalent to four qubits, using combined electron-nuclear states of a single Sb donor atom in Si.
- Irene Fernández de Fuentes
- , Tim Botzem
- & Andrea Morello
-
Article
| Open Access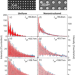 The effect of echoes interference on phonon attenuation in a nanophononic membrane
The effect of echoes interference on phonon attenuation in a nanophononic membrane
Coherent scattering of phonons in a periodic nanostructure leads to interference, which modifies phonon energies. Here, authors observed that a strong interference effect also influences phonon lifetime. Despite its reduction, energy transport is conserved thanks to a hopping of energy among the reflected waves.
- Mohammad Hadi
- , Haoming Luo
- & Valentina M. Giordano
-
Article
| Open Access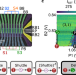 Spin-EPR-pair separation by conveyor-mode single electron shuttling in Si/SiGe
Spin-EPR-pair separation by conveyor-mode single electron shuttling in Si/SiGe
Electron charge and spin shuttling is a promising technique for connecting distant spin qubits. Here the authors use conveyor-mode shuttling to achieve high-fidelity transport of a single electron spin in Si/SiGe by separation and rejoining of two spin-entangled electrons across a shuttling distance of 560 nm.
- Tom Struck
- , Mats Volmer
- & Lars R. Schreiber
-
Article
| Open Access Neuromorphic electro-stimulation based on atomically thin semiconductor for damage-free inflammation inhibition
Neuromorphic electro-stimulation based on atomically thin semiconductor for damage-free inflammation inhibition
Bao et al. report a neuromorphic bionic electro-stimulation solution based on atomic-scale semiconductor floating-gate memory circuit, which enables efficient inhibition of acute inflammation with low stimulation currents that are damage-free to neurons.
- Rong Bao
- , Shuiyuan Wang
- & Shen Liu
-
Article
| Open Access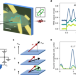 Electric control of optically-induced magnetization dynamics in a van der Waals ferromagnetic semiconductor
Electric control of optically-induced magnetization dynamics in a van der Waals ferromagnetic semiconductor
The combination of strong light-matter interactions and controllable magnetic properties make magnetic semiconductors attractive for both fundamental physics and the development of devices. Here, Hendriks et al show how the optically driven magnetization dynamics in Cr2Ge2Te6 can be controlled via electrostatic gating.
- Freddie Hendriks
- , Rafael R. Rojas-Lopez
- & Marcos H. D. Guimarães
-
Article
| Open Access Functional nanoporous graphene superlattice
Functional nanoporous graphene superlattice
Here, the authors report the synthesis and characterization of doped nanoporous graphene superlattices, showing their improved properties for electromagnetic shielding, energy harvesting, optoelectronic and thermoelectric applications.
- Hualiang Lv
- , Yuxing Yao
- & Xiaoguang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access High intrinsic phase stability of ultrathin 2M WS2
High intrinsic phase stability of ultrathin 2M WS2
Metallic 2M or 1T′-phase transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) are characterized by interesting properties, but they are metastable. Here, the authors demonstrate that the thermal and oxidation stability of 2M WS2 significantly increases as the thickness is reduced down to monolayer, expanding the potential applications of 2M TMDs.
- Xiangye Liu
- , Pingting Zhang
- & Cao Guan
-
Article
| Open Access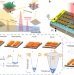 Synergistic-potential engineering enables high-efficiency graphene photodetectors for near- to mid-infrared light
Synergistic-potential engineering enables high-efficiency graphene photodetectors for near- to mid-infrared light
The integration of 2D materials with metasurfaces can enhance their quantum efficiency, but the approach is usually limited to a narrow spectral band. Here, the authors report the realization of gate-tunable graphene photodetectors combined with all-dielectric periodic slits, leading to enhanced photoresponse in the short-to-long-wave infrared.
- Hao Jiang
- , Jintao Fu
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access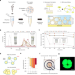 Micrometer-thick and porous nanocomposite coating for electrochemical sensors with exceptional antifouling and electroconducting properties
Micrometer-thick and porous nanocomposite coating for electrochemical sensors with exceptional antifouling and electroconducting properties
It is vital but challenging to develop coating technologies for addressing reliability and durability issues of electrochemical sensors when exposed to diverse and complex biological environments. Here, the authors report a micrometer-thick, porous and robust nanocomposite coating that enables highly sensitive and stable electrochemical sensors.
- Jeong-Chan Lee
- , Su Yeong Kim
- & Donald E. Ingber
-
Article
| Open Access Data-centric artificial olfactory system based on the eigengraph
Data-centric artificial olfactory system based on the eigengraph
Sensitivity-dependent data analysis methods disrupted the development of artificial olfactory technologies. Here, authors present a data-centric artificial olfactory system based on eigengraph that reflects the intrinsic electrochemical interaction.
- Seung-Hyun Sung
- , Jun Min Suh
- & Seong Chan Jun
-
Article
| Open Access The role of interfacial donor–acceptor percolation in efficient and stable all-polymer solar cells
The role of interfacial donor–acceptor percolation in efficient and stable all-polymer solar cells
The underlying charge generation dynamics and structure-property relationships in organic solar cells are not fully understood. Here, the authors demonstrate that interfacial donor-acceptor percolation plays a key role in enabling both high charge generation efficiency and device stability.
- Zhen Wang
- , Yu Guo
- & Philip C. Y. Chow
-
Article
| Open Access Memristor-based storage system with convolutional autoencoder-based image compression network
Memristor-based storage system with convolutional autoencoder-based image compression network
Dealing with the explosive growth of diverse image data in the era of big data poses challenges for storage. Feng et al. propose a memristor-based near-storage in-memory processing system to boost the energy and storage efficiency.
- Yulin Feng
- , Yizhou Zhang
- & Jinfeng Kang
-
Article
| Open Access Interfacial magnetic spin Hall effect in van der Waals Fe3GeTe2/MoTe2 heterostructure
Interfacial magnetic spin Hall effect in van der Waals Fe3GeTe2/MoTe2 heterostructure
Charge-to-spin conversion allows for the generation and control of spin polarization via a charge current. Typically, this is done with non-magnetic materials with large spin-orbit interactions such as Platinum. Herein, Dai et al demonstrate an intriguing charge-to-spin mechanism, a magnetic spin Hall effect, in a van der Waals heterostructure.
- Yudi Dai
- , Junlin Xiong
- & Feng Miao
-
Article
| Open Access Ultracompact mirror device for forming 20-nm achromatic soft-X-ray focus toward multimodal and multicolor nanoanalyses
Ultracompact mirror device for forming 20-nm achromatic soft-X-ray focus toward multimodal and multicolor nanoanalyses
Optics used for X-ray focusing suffer from wavelength dependent effects like chromatic aberration. Here the authors demonstrate fabrication of a ultracompact Kirkpatrick-Baez mirror and use it for achromatic focusing to 20 nm spot for the soft X-ray at 2-keV photon energy.
- Takenori Shimamura
- , Yoko Takeo
- & Hidekazu Mimura
-
Article
| Open Access Dual heterogeneous interfaces enhance X-ray excited persistent luminescence for low-dose 3D imaging
Dual heterogeneous interfaces enhance X-ray excited persistent luminescence for low-dose 3D imaging
High-resolution X-ray imaging requires a high radiation dose. Here, the authors achieve low-dose 3D imaging by increasing the XEPL intensity using a double-shell nanostructure with two heterogeneous interfaces.
- Lei Lei
- , Minghao Yi
- & Shiqing Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Steep-slope vertical-transport transistors built from sub-5 nm Thin van der Waals heterostructures
Steep-slope vertical-transport transistors built from sub-5 nm Thin van der Waals heterostructures
2D vertical transport transistors (VTFETs) may promote the downscaling of electronic devices, but their performance is usually restricted by the thermionic limit. Here, the authors report the realization of short-channel steep-slope VTFETs based on MoS2/MoTe2 heterojunctions integrated with resistance threshold switching cells.
- Qiyu Yang
- , Zheng-Dong Luo
- & Genquan Han
-
Article
| Open Access Programming crack patterns with light in colloidal plasmonic films
Programming crack patterns with light in colloidal plasmonic films
Crack formation typically results in random patterns and material failure. Inspired by plant phototropism, the authors use plasmonic absorbers to control crack propagation in colloidal films with light, showcasing a robust, programmable self-assembly process.
- Fanny Thorimbert
- , Mateusz Odziomek
- & Marco Faustini
-
Article
| Open Access Challenging thermodynamics: combining immiscible elements in a single-phase nano-ceramic
Challenging thermodynamics: combining immiscible elements in a single-phase nano-ceramic
Elemental immiscibility limits the development of solid solution materials. Here, authors create a nonequilibrium flame aerosol method to mix nearly any pair of metal elements in a single-phase nano-ceramic. Also, an exsolution behavior is presented to produce active and stable nanoparticles.
- Shuo Liu
- , Chaochao Dun
- & Mark T. Swihart
-
Article
| Open Access Deceptive orbital confinement at edges and pores of carbon-based 1D and 2D nanoarchitectures
Deceptive orbital confinement at edges and pores of carbon-based 1D and 2D nanoarchitectures
The apparent electronic confinement at nanographene boundaries in scanning tunneling microscopy/spectroscopy is often misinterpreted. Here, the authors explain this phenomenon in terms of the decay of frontier orbitals and confinement at the edges of graphene nanoribbons and pores in nanoporous graphene.
- Ignacio Piquero-Zulaica
- , Eduardo Corral-Rascón
- & Johannes V. Barth
-
Article
| Open Access Localisation-to-delocalisation transition of moiré excitons in WSe2/MoSe2 heterostructures
Localisation-to-delocalisation transition of moiré excitons in WSe2/MoSe2 heterostructures
Stacking two-dimensional crystals creates a moiré superpotential that confines excitons. Here, temperature-/time- and magnetic field-dependent optical spectroscopy allows identifying the conditions under which excitons escape from the moiré potential
- Elena Blundo
- , Federico Tuzi
- & Antonio Polimeni
-
Article
| Open Access Strong coupling between a microwave photon and a singlet-triplet qubit
Strong coupling between a microwave photon and a singlet-triplet qubit
By coupling a spin-qubit to a superconducting resonator, remote spin-entanglement becomes feasible. Here, Ungerer et al achieve strong coupling between a superconducting resonator and a singlet-triplet spin qubit, in an InAs nanowire.
- J. H. Ungerer
- , A. Pally
- & C. Schönenberger

 Epitaxy of wafer-scale single-crystal MoS2 monolayer via buffer layer control
Epitaxy of wafer-scale single-crystal MoS2 monolayer via buffer layer control