Featured
-
-
Article |
 Silicon-in-silica spheres via axial thermal gradient in-fibre capillary instabilities
Silicon-in-silica spheres via axial thermal gradient in-fibre capillary instabilities
Silicon nanospheres could be of interest for applications in electronics and optoelectronics. Here, Gumenniket al. demonstrate a nanosphere fabrication process based on an optical fibre drawing technique that is able to produce p and n-type spheres paired into rectifying bispherical junctions.
- Alexander Gumennik
- , Lei Wei
- & Yoel Fink
-
Article
| Open Access Nano-structured smart hydrogels with rapid response and high elasticity
Nano-structured smart hydrogels with rapid response and high elasticity
Smart hydrogels are 3D networks composed of cross-linked polymer chains that can alter their shape and properties in response to environmental stimuli. Xiaet al.demonstrate a smart hydrogel with rapid response and high elasticity, due to its nano-scale structure.
- Lie-Wen Xia
- , Rui Xie
- & Liang-Yin Chu
-
Article |
 Interfacial assembly of protein–polymer nano-conjugates into stimulus-responsive biomimetic protocells
Interfacial assembly of protein–polymer nano-conjugates into stimulus-responsive biomimetic protocells
Proteins are ideal building blocks for self-assembly of artificial cell-like architectures, but their realization is rare. Huang et al.report an interfacial assembly of protein–polymer conjugates, which exhibit cellular properties such as encapsulating guest molecules and switching enzyme activity.
- Xin Huang
- , Mei Li
- & Stephen Mann
-
Article |
 Fast low-voltage electroactive actuators using nanostructured polymer electrolytes
Fast low-voltage electroactive actuators using nanostructured polymer electrolytes
Ionic polymer actuators are becoming popular for biomimetic applications because of their mechanical robustness and easy fabrication at low cost. Kim et al.push them one step closer to practice by achieving a subsecond actuation response at an operation voltage less than 1 V.
- Onnuri Kim
- , Tae Joo Shin
- & Moon Jeong Park
-
Article
| Open Access Helicity-dependent single-walled carbon nanotube alignment on graphite for helical angle and handedness recognition
Helicity-dependent single-walled carbon nanotube alignment on graphite for helical angle and handedness recognition
The alignment of carbon nanotubes on a surface is of importance to deploy them in electronic devices. Here, Chen et al.achieve the orientation of carbon nanotubes according to their helical angle and handedness, thus separating nanotubes of different electronic properties.
- Yabin Chen
- , Ziyong Shen
- & Jin Zhang
-
Article |
 Real-time electrical detection of nitric oxide in biological systems with sub-nanomolar sensitivity
Real-time electrical detection of nitric oxide in biological systems with sub-nanomolar sensitivity
The real-time monitoring of nitric oxide levels in the human body is critical for understanding the roles it has in biological processes. Jiang et al. report a graphene-based sensor for selective detection of nitric oxide in living cells with direct electrical read-out and sub-nanomole sensitivity.
- Shan Jiang
- , Rui Cheng
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Article |
 Hyperthin nanochains composed of self-polymerizing protein shackles
Hyperthin nanochains composed of self-polymerizing protein shackles
The sophisticated structure of protein fibrils suggests that they may be useful nanomaterials. Here the authors design a series of self-polymerizing protein monomers, the reactions of which are controlled by redox chemistry, and show that functional units may also be incorporated into the extended structures.
- Ryo Matsunaga
- , Saeko Yanaka
- & Kouhei Tsumoto
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ ultra-sensitive infrared absorption spectroscopy of biomolecule interactions in real time with plasmonic nanoantennas
In-situ ultra-sensitive infrared absorption spectroscopy of biomolecule interactions in real time with plasmonic nanoantennas
Infrared absorption spectroscopy provides important information about molecules, but is hampered by the absorption of water. Adato and Altug exploit the plasmonic enhancement from nanoantennas to overcome this, enabling chip-based monitoring of biological samples in aqueous environments.
- Ronen Adato
- & Hatice Altug
-
Article
| Open Access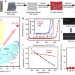 One hundred fold increase in current carrying capacity in a carbon nanotube–copper composite
One hundred fold increase in current carrying capacity in a carbon nanotube–copper composite
High electrical conductivity and ampacity are usually mutually exclusive properties. Here, in a carbon nanotube–copper composite, Subramaniam et al. achieve a similar conductivity to copper, but with a hundred fold increase in current carrying capacity.
- Chandramouli Subramaniam
- , Takeo Yamada
- & Kenji Hata
-
Article |
 Rare-earth-doped biological composites as in vivo shortwave infrared reporters
Rare-earth-doped biological composites as in vivo shortwave infrared reporters
The short-wavelength infrared spectral region is of interest for bio-imaging applications as biological tissue is transparent to such light. Here Naczynski et al. fabricate rare-earth-based nanomaterials and demonstrate multispectral, real-time short-wavelength infrared in-vivoimaging.
- D. J. Naczynski
- , M. C. Tan
- & P. V. Moghe
-
Article |
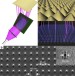 Desktop nanofabrication with massively multiplexed beam pen lithography
Desktop nanofabrication with massively multiplexed beam pen lithography
The development of a desktop nanofabrication tool allowing high-resolution patterning and high-throughput synthesis is a long-standing goal in many nanoscience fields. Here, the authors report a system that can write arbitrary patterns composed of diffraction-unlimited features over square centimetre areas.
- Xing Liao
- , Keith A. Brown
- & Chad A. Mirkin
-
Article |
 Interfacial liquid-state surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Interfacial liquid-state surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Assembly of functional colloidal nanoparticles has many technological applications, but its three-dimensional realization remains challenging. Kim et al.report a spontaneous self-orientation of gold nanorods at an oil/water interface and use it to amplify signal in surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy.
- Kihoon Kim
- , Hye Soo Han
- & Taewook Kang
-
Article
| Open Access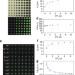 Femtolitre chemistry assisted by microfluidic pen lithography
Femtolitre chemistry assisted by microfluidic pen lithography
Chemical reactions on femtolitre scales are necessary to study confined biological processes. Here, the authors use a microfluidic pen lithography technique to perform a series of discrete femtoscale acid-base and synthetic reactions, and crystallizations on a surface with high registration accuracy.
- Carlos Carbonell
- , Kyriakos C. Stylianou
- & Daniel Maspoch
-
Article |
 Strain and curvature induced evolution of electronic band structures in twisted graphene bilayer
Strain and curvature induced evolution of electronic band structures in twisted graphene bilayer
The electronic properties of graphene are known to be sensitive to strain and geometry. Yan et al.find that the introduction of strain and high curvature to bilayer graphene strongly affects the electronic landscape, resulting in changes in the band structure.
- Wei Yan
- , Wen-Yu He
- & Lin He
-
Article |
 Nanoporous gold supported cobalt oxide microelectrodes as high-performance electrochemical biosensors
Nanoporous gold supported cobalt oxide microelectrodes as high-performance electrochemical biosensors
Metal oxides are proposed as replacements for expensive enzymes in electrochemical biosensors, but their wide use is currently limited by poor electronic conductivity. Lang et al. engineer the nanoarchitecture of electrodes to reduce contact resistances, which leads to an ultrahigh sensitivity to glucose.
- Xing-You Lang
- , Hong-Ying Fu
- & Qing Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmon-mediated magneto-optical transparency
Plasmon-mediated magneto-optical transparency
Magneto-optical effects, where magnetic fields affect light propagating through a material, are of interest for photonic devices such as switches. The magneto-optical effect discovered here in metal-dielectric nanostructures shows a strong light modulation that is suitable for nanophotonic applications.
- V. I. Belotelov
- , L. E. Kreilkamp
- & M. Bayer
-
Article
| Open Access Protein analysis by time-resolved measurements with an electro-switchable DNA chip
Protein analysis by time-resolved measurements with an electro-switchable DNA chip
The comprehensive bioanalysis of proteins usually requires multi-step surface and mobile phase measurements. Here, the authors use chips functionalized with dynamically actuated nanolevers—DNA strands that can be switched in an electric field—to obtain motional dynamic measurements of proteins on a chip.
- Andreas Langer
- , Paul A. Hampel
- & Ulrich Rant
-
Article |
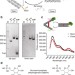 A DNA tweezer-actuated enzyme nanoreactor
A DNA tweezer-actuated enzyme nanoreactor
The control of regulatory enzymes is essential for the modulation of biochemical cellular pathways. Here, the authors fabricate a tweezer-like DNA nanodevice to actuate the activity of an enzyme/cofactor pair, and are able to control enzyme inhibition and activation over multiple cycles.
- Minghui Liu
- , Jinglin Fu
- & Hao Yan
-
Article |
 Strengthening effect of single-atomic-layer graphene in metal–graphene nanolayered composites
Strengthening effect of single-atomic-layer graphene in metal–graphene nanolayered composites
Suppressing the movement of dislocations is critical in enhancing the strength of crystalline metals. Kim et al. demonstrate in Cu– and Ni–graphene nanolayered systems that single-layer graphene is effective in suppressing dislocation movement, resulting in a maximum strength of 4.0 GPa.
- Youbin Kim
- , Jinsup Lee
- & Seung Min Han
-
Article |
 Chemical vapour deposition growth of large single crystals of monolayer and bilayer graphene
Chemical vapour deposition growth of large single crystals of monolayer and bilayer graphene
The growth of high-quality graphene over large areas is essential for the realization of graphene-based electronic devices. Zhou et al.report a new pathway to grow single crystalline graphene of up to 5 mm in size, with very good electronic performance and high uniformity.
- Hailong Zhou
- , Woo Jong Yu
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Article
| Open Access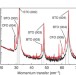 Electric in-plane polarization in multiferroic CoFe2O4/BaTiO3 nanocomposite tuned by magnetic fields
Electric in-plane polarization in multiferroic CoFe2O4/BaTiO3 nanocomposite tuned by magnetic fields
Multiferroics, materials that exhibit two or more ferroic orders, are potentially useful for data storage if the coupling between these orders can be exploited. Here the authors elucidate how the magnetism in ferrimagnetic nanopillars can control the electric polarization of a surrounding matrix.
- Carolin Schmitz-Antoniak
- , Detlef Schmitz
- & Heiko Wende
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional deep sub-diffraction optical beam lithography with 9 nm feature size
Three-dimensional deep sub-diffraction optical beam lithography with 9 nm feature size
The fabrication of three-dimensional nanoscale structures is important to nanophotonic applications where light is guided and controlled. The optical beam lithography scheme developed by Gan and colleagues enables the fabrication of three-dimensional structures with feature sizes down to 9 nm.
- Zongsong Gan
- , Yaoyu Cao
- & Min Gu
-
Article |
 Spin readout and addressability of phosphorus-donor clusters in silicon
Spin readout and addressability of phosphorus-donor clusters in silicon
The spin of an electron bound to a single phosphorus atom in silicon is of interest for spin-based electronics such as quantum computing. Here, Büch et al. show these spin properties are retained even for clusters of a few phosphorus atoms, providing an additional means for quantum bit addressability.
- H. Büch
- , S. Mahapatra
- & M. Y. Simmons
-
Article |
 Two-barrier stability that allows low-power operation in current-induced domain-wall motion
Two-barrier stability that allows low-power operation in current-induced domain-wall motion
Controlling magnetic domain wall motion in nanowires requires a thorough knowledge of the depinning mechanisms. Here, the authors show that current-induced intrinsic depinning has a different energy barrier than magnetic field-induced extrinsic depinning, and succeed in quantifying the respective barriers.
- Kab-Jin Kim
- , Ryo Hiramatsu
- & Teruo Ono
-
Article |
 Giant cationic polyelectrolytes generated via electrochemical oxidation of single-walled carbon nanotubes
Giant cationic polyelectrolytes generated via electrochemical oxidation of single-walled carbon nanotubes
Reduced carbon nanotube anions can be effectively processed and functionalized. Here, the authors prepare discrete nanotube cations by electrochemical oxidation, and the confirmation of their reactivity towards nucleophiles suggests a new library of covalent nanotube modifications.
- Stephen A. Hodge
- , Mustafa K. Bayazit
- & Milo S. P. Shaffer
-
Article |
 A ladder polysilane as a template for folding palladium nanosheets
A ladder polysilane as a template for folding palladium nanosheets
Since the isolation of graphene, there has been extensive interest in other two-dimensional structures including metallic nanosheets. Here, the authors report the use of ladder polysilane ligands for the synthesis of palladium clusters containing eleven metal ions, made up of two heptametallic nanosheets.
- Yusuke Sunada
- , Ryohei Haige
- & Hideo Nagashima
-
Article
| Open Access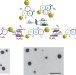 Powering the programmed nanostructure and function of gold nanoparticles with catenated DNA machines
Powering the programmed nanostructure and function of gold nanoparticles with catenated DNA machines
DNA nanotechnology, including DNA machines and devices for computing, is a rapidly expanding field of research. Here, the authors fabricate DNA catenane machines for the programmable arrangement of gold nanoparticle cargoes, and study their switchable spectroscopic features.
- Johann Elbaz
- , Alessandro Cecconello
- & Itamar Willner
-
Article |
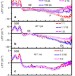 Uncovering loss mechanisms in silver nanoparticle-blended plasmonic organic solar cells
Uncovering loss mechanisms in silver nanoparticle-blended plasmonic organic solar cells
Metallic nanoparticles are commonly used to facilitate light trapping in organic solar cells, but they can also reduce cell performance. Wu et al.demonstrate that a trap-assisted recombination of charge carriers leads to degradation, irrespective of an initially enhanced absorption and excitation.
- Bo Wu
- , Xiangyang Wu
- & Tze Chien Sum
-
Article |
 Suppression of electron–vibron coupling in graphene nanoribbons contacted via a single atom
Suppression of electron–vibron coupling in graphene nanoribbons contacted via a single atom
Graphene nanostructures have a tremendous potential for electronic applications, although contacting them with atomic precision remains a challenge. Here, van der Lit and colleagues achieve contacting graphene nanoribbons via only a single atom, without affecting its electronic structure.
- Joost van der Lit
- , Mark P. Boneschanscher
- & Ingmar Swart
-
Article |
 Dual origin of defect magnetism in graphene and its reversible switching by molecular doping
Dual origin of defect magnetism in graphene and its reversible switching by molecular doping
Local magnetic properties that can be controlled by an applied electric field are desirable for spintronics applications. Nair et al.show that tuning carrier concentration by molecular doping or electric field can be used to control adatoms magnetism on graphene, enabling magnetic moments to be switched on and off.
- R.R. Nair
- , I.-L. Tsai
- & I.V. Grigorieva
-
Article
| Open Access Integrating DNA strand-displacement circuitry with DNA tile self-assembly
Integrating DNA strand-displacement circuitry with DNA tile self-assembly
DNA tile self-assembly and DNA strand displacement circuits are well-developed frameworks in DNA nanotechnology. Here, the two approaches are combined to give programmable kinetic control of DNA nanotube self-assembly.
- David Yu Zhang
- , Rizal F. Hariadi
- & Erik Winfree
-
Article |
 Solution-based circuits enable rapid and multiplexed pathogen detection
Solution-based circuits enable rapid and multiplexed pathogen detection
Rapid, highly multiplexed molecular detection platforms may enable more specific and effective disease diagnosis. Here, a solution-based circuit is reported that enables the analysis of samples for panels of pathogens and antibiotic-resistance profiles at clinically relevant levels in less than 2 min.
- Brian Lam
- , Jagotamoy Das
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
Article
| Open Access Atomistics of vapour–liquid–solid nanowire growth
Atomistics of vapour–liquid–solid nanowire growth
The vapour–liquid–solid method is used to produce semiconducting nanowires but the fundamental processes involved are poorly understood. Wang et al.use atomic-scale simulations to elucidate the mechanisms involved in the growth and stability of gold-catalysed silicon nanowires.
- Hailong Wang
- , Luis A. Zepeda-Ruiz
- & Moneesh Upmanyu
-
Article
| Open Access Tailorable stimulated Brillouin scattering in nanoscale silicon waveguides
Tailorable stimulated Brillouin scattering in nanoscale silicon waveguides
Exploiting photon–phonon coupling in nanoscale silicon waveguides could enable a host of powerful features in photonic devices. Using a hybrid photonic–phononic waveguide structure, Shin et al. show stimulated Brillouin scattering nonlinearities and gain, which offers new on-chip signal-processing abilities.
- Heedeuk Shin
- , Wenjun Qiu
- & Peter T. Rakich
-
Article |
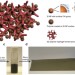 Stable Li-ion battery anodes by in-situ polymerization of conducting hydrogel to conformally coat silicon nanoparticles
Stable Li-ion battery anodes by in-situ polymerization of conducting hydrogel to conformally coat silicon nanoparticles
Nanostructured silicon is a promising anode material for lithium ion batteries but needs to tolerate large volume increase upon lithiation. Wu et al. solve this problem by binding silicon nanoparticles to a conducting polymer hydrogel via in-situpolymerization, which also improves cycling stability.
- Hui Wu
- , Guihua Yu
- & Yi Cui
-
Article |
 Ultrafast charge and discharge biscrolled yarn supercapacitors for textiles and microdevices
Ultrafast charge and discharge biscrolled yarn supercapacitors for textiles and microdevices
Strong, flexible supercapacitors are desirable for miniaturized electronic devices, but realizing a combination of high energy and power density is challenging. Lee et al. address this with a demonstration of high-performance supercapacitor yarns that could be useful for electronic textiles.
- Jae Ah Lee
- , Min Kyoon Shin
- & Seon Jeong Kim
-
Article |
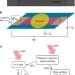 Photocurrent in graphene harnessed by tunable intrinsic plasmons
Photocurrent in graphene harnessed by tunable intrinsic plasmons
By patterning graphene with sub-wavelength features to introduce plasmonic modes, its optical properties can be tailored. Freitag et al. show how tunable plasmons in graphene nanoribbons can be exploited to form polarization-sensitive graphene photodetectors in the mid-infrared spectral region.
- Marcus Freitag
- , Tony Low
- & Phaedon Avouris
-
Article
| Open Access Millisecond charge-parity fluctuations and induced decoherence in a superconducting transmon qubit
Millisecond charge-parity fluctuations and induced decoherence in a superconducting transmon qubit
Superconducting circuits are promising for quantum computing, but quasiparticle tunnelling across Josephson junctions introduces qubit decoherence. Ristè et al. convert a transmon qubit into its own real-time quasiparticle tunnelling detector and accurately measure induced decoherence in the millisecond range.
- D. Ristè
- , C. C. Bultink
- & L. DiCarlo
-
Article
| Open Access Active and stable carbon nanotube/nanoparticle composite electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction
Active and stable carbon nanotube/nanoparticle composite electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction
Cheap, efficient oxygen reduction reaction catalysts are vital for the development of fuel cells and lithium-air batteries. Here, the authors report the scalable synthesis of a nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube/nanoparticle hybrid material that outperforms several platinum-based catalysts.
- Hoon T. Chung
- , Jong H. Won
- & Piotr Zelenay
-
Article |
 Layer-by-layer assembly of vertically conducting graphene devices
Layer-by-layer assembly of vertically conducting graphene devices
Vertically assembled graphene devices have received less attention than the typical two dimensional arrangements. Chen et al. show that an Au/graphene/Au assembly exhibits a large magnetoresistance ratio of up to 400%, while a Co/graphene/Co device displays a spin valve effect at room temperature.
- Jing-Jing Chen
- , Jie Meng
- & Da-Peng Yu
-
Article |
 Photo-switchable molecular monolayer anchored between highly transparent and flexible graphene electrodes
Photo-switchable molecular monolayer anchored between highly transparent and flexible graphene electrodes
The realization of molecular monolayers with graphene electrodes may allow for superior flexible, transparent and stable electronics. Here, a photo-switchable molecular monolayer device is demonstrated, which has one side physically attached, and the other chemically bonded, to graphene.
- Sohyeon Seo
- , Misook Min
- & Hyoyoung Lee
-
Article |
 Monodisperse silicon nanocavities and photonic crystals with magnetic response in the optical region
Monodisperse silicon nanocavities and photonic crystals with magnetic response in the optical region
Metamaterials offer optical functionality, such as cloaking, that is impossible to achieve with natural bulk materials. Here, Shi and colleagues fabricate colloidal metamaterials made from silicon whose magneto-optical response considerably exceeds that of related bulk materials.
- Lei Shi
- , Justin T Harris
- & Francisco Meseguer
-
Article |
 Delivery of therapeutic agents by nanoparticles made of grapefruit-derived lipids
Delivery of therapeutic agents by nanoparticles made of grapefruit-derived lipids
Nanoparticles released from living cells can be used as drug delivery vehicles, but scaling up their production is challenging. Here, Wang and colleagues create nanoparticles from natural lipids contained in grapefruit juice that can encapsulate various types of therapeutics and deliver them to cells in vitro and in vivo.
- Qilong Wang
- , Xiaoying Zhuang
- & Huang-Ge Zhang
-
Article |
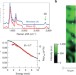 Quantum Faraday and Kerr rotations in graphene
Quantum Faraday and Kerr rotations in graphene
Graphene exhibits interesting optical and electronic properties, resulting from a Dirac dispersion of electrons. Shimano et al.observe quantum magneto-optical Faraday and Kerr effects in the terahertz regime, where plateaus are observed at the quantum-Hall steps.
- R. Shimano
- , G. Yumoto
- & H. Aoki
-
Article |
 Magnetically ultraresponsive nanoscavengers for next-generation water purification systems
Magnetically ultraresponsive nanoscavengers for next-generation water purification systems
Silver nanoparticles are useful antimicrobial agents in water purification systems. Here the fabrication of silver nanoparticles that include a magnetic layer could lead to improved purification systems as it allows the recovery of the nanoparticles by magnetic fields.
- Mingliang Zhang
- , Xing Xie
- & Shan X. Wang
-
Article |
 Broadband high photoresponse from pure monolayer graphene photodetector
Broadband high photoresponse from pure monolayer graphene photodetector
Graphene holds great potential for use in photodetectors, owing to its ability to absorb light over a wide range of wavelengths. Here Zhang et al. report a large photoresponsivity of 8.6 AW-1 over a broad wavelength range in pure monolayer graphene.
- By Yongzhe Zhang
- , Tao Liu
- & Qi Jie Wang
-
Article |
 Engineering fluid flow using sequenced microstructures
Engineering fluid flow using sequenced microstructures
A versatile strategy is needed to engineer fluid streams in channels for different purposes. Amini et al.develop an approach to decompose complicated fluid motion into an ensemble of fluid transformations around individual cylindrical pillars, which allows control without simulations.
- Hamed Amini
- , Elodie Sollier
- & Dino Di Carlo
-
Article
| Open Access Top–down fabrication of sub-nanometre semiconducting nanoribbons derived from molybdenum disulfide sheets
Top–down fabrication of sub-nanometre semiconducting nanoribbons derived from molybdenum disulfide sheets
Fabricating semiconductor devices with dimensions below 10 nm presents significant challenges. Here, Liu et al. use controlled electron irradiation to remove atoms in an MoS2 sheet, creating Mo5S4nanoribbons with a uniform width of 0.35 nm and a theoretical band gap of 0.77 eV.
- Xiaofei Liu
- , Tao Xu
- & Wanlin Guo
-
Article
| Open Access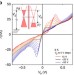 Resonant tunnelling and negative differential conductance in graphene transistors
Resonant tunnelling and negative differential conductance in graphene transistors
Multilayer stacks of graphene and related two-dimensional crystals can be tailored to create new classes of functional materials. Britnell et al. report resonant tunnelling of Dirac fermions and tunable negative differential conductance in a graphene-boron nitride-graphene transistor.
- L. Britnell
- , R. V. Gorbachev
- & L. Eaves

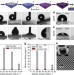 Transparency and damage tolerance of patternable omniphobic lubricated surfaces based on inverse colloidal monolayers
Transparency and damage tolerance of patternable omniphobic lubricated surfaces based on inverse colloidal monolayers