Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalously bright single-molecule upconversion electroluminescence
Anomalously bright single-molecule upconversion electroluminescence
The efficiency of upconversion electroluminescence remains very low for single-molecule emitters. Here, the authors report over one order of magnitude improvement in the emission efficiency via engineering energy-level alignments for triplet relayed upconversion involving only carrier injection.
- Yang Luo
- , Fan-Fang Kong
- & Zhen-Chao Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Non-volatile rippled-assisted optoelectronic array for all-day motion detection and recognition
Non-volatile rippled-assisted optoelectronic array for all-day motion detection and recognition
The authors create a rippled-assisted optoelectronic array (18 × 18 pixels) for the all-day motion detection and recognition, possessing negative and positive optical detection as well as memory and computation capabilities.
- Xingchen Pang
- , Yang Wang
- & Peng Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Smart touchless human–machine interaction based on crystalline porous cages
Smart touchless human–machine interaction based on crystalline porous cages
Smart sensors are important components in the development of touchless human-machine interaction systems. Here, the authors describe a smart 3D porous crystalline organic cage-based system that exhibits remarkable responsiveness to fingertip humidity, contributing to the advancement of touchless human-machine interaction technology.
- Jinrong Wang
- , Weibin Lin
- & Niveen M. Khashab
-
Article
| Open Access Inorganic perovskite-based active multifunctional integrated photonic devices
Inorganic perovskite-based active multifunctional integrated photonic devices
Researchers showcase an integrated photonic device with monocrystalline CsPbBr3 perovskite. Employing top-down etching approach, it introduces for micro lasers, beam splitters, X-couplers, Mach-Zehnder interferometers on perovskite films. This opens avenues for integrating perovskite semiconductors into optical chips, promising advancements in information and computing science.
- Qi Han
- , Jun Wang
- & Li Ji
-
Article
| Open Access True amplification of spin waves in magnonic nano-waveguides
True amplification of spin waves in magnonic nano-waveguides
True amplification of spin waves by spin-orbit torque, which manifests itself by an exponential increase in amplitude with propagation distance, has so far remained elusive. Here, the authors realize amplification using clocked nanoseconds-long spin-orbit torque pulses in magnonic nano-waveguides.
- H. Merbouche
- , B. Divinskiy
- & V. E. Demidov
-
Article
| Open Access Current-induced switching of a van der Waals ferromagnet at room temperature
Current-induced switching of a van der Waals ferromagnet at room temperature
Fe3GaTe2 is a van der Waals material with a Curie temperature well above room temperature, making it an attractive material for integration into spintronic devices. Here, Kajale et al demonstrate spin-orbit torque induced switching of the magnetization of Fe3GaTe2, above room temperature, using a Pt spin Hall layer.
- Shivam N. Kajale
- , Thanh Nguyen
- & Deblina Sarkar
-
Article
| Open Access VO2 memristor-based frequency converter with in-situ synthesize and mix for wireless internet-of-things
VO2 memristor-based frequency converter with in-situ synthesize and mix for wireless internet-of-things
Frequency converters for wireless internet of things applications typically require separate circuits for different functions, causing energy and performance inefficiencies. Using an epitaxially grown VO2 memristor array, Liu et al. present a frequency converter with in-situ frequency synthesis and mix functionality.
- Chang Liu
- , Pek Jun Tiw
- & Yuchao Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Photooxidation driven formation of Fe-Au linked ferrocene-based single-molecule junctions
Photooxidation driven formation of Fe-Au linked ferrocene-based single-molecule junctions
Metal-metal interfaces hold promise as contacting moieties for single-molecule devices with tunable functionality, yet the direct bonding has remained a challenge. Here, Lee et al. report the formation of Fe-Au bond without chemical ligand support in ferrocene-based molecular junctions.
- Woojung Lee
- , Liang Li
- & Latha Venkataraman
-
Article
| Open Access Navigating the 16-dimensional Hilbert space of a high-spin donor qudit with electric and magnetic fields
Navigating the 16-dimensional Hilbert space of a high-spin donor qudit with electric and magnetic fields
Qudits, higher-dimensional analogues of qubits, expand quantum state space for information processing using fewer physical units. Here the authors demonstrate control over a 16-dimensional Hilbert space, equivalent to four qubits, using combined electron-nuclear states of a single Sb donor atom in Si.
- Irene Fernández de Fuentes
- , Tim Botzem
- & Andrea Morello
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-EPR-pair separation by conveyor-mode single electron shuttling in Si/SiGe
Spin-EPR-pair separation by conveyor-mode single electron shuttling in Si/SiGe
Electron charge and spin shuttling is a promising technique for connecting distant spin qubits. Here the authors use conveyor-mode shuttling to achieve high-fidelity transport of a single electron spin in Si/SiGe by separation and rejoining of two spin-entangled electrons across a shuttling distance of 560 nm.
- Tom Struck
- , Mats Volmer
- & Lars R. Schreiber
-
Article
| Open Access Functional nanoporous graphene superlattice
Functional nanoporous graphene superlattice
Here, the authors report the synthesis and characterization of doped nanoporous graphene superlattices, showing their improved properties for electromagnetic shielding, energy harvesting, optoelectronic and thermoelectric applications.
- Hualiang Lv
- , Yuxing Yao
- & Xiaoguang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access The role of interfacial donor–acceptor percolation in efficient and stable all-polymer solar cells
The role of interfacial donor–acceptor percolation in efficient and stable all-polymer solar cells
The underlying charge generation dynamics and structure-property relationships in organic solar cells are not fully understood. Here, the authors demonstrate that interfacial donor-acceptor percolation plays a key role in enabling both high charge generation efficiency and device stability.
- Zhen Wang
- , Yu Guo
- & Philip C. Y. Chow
-
Article
| Open Access Memristor-based storage system with convolutional autoencoder-based image compression network
Memristor-based storage system with convolutional autoencoder-based image compression network
Dealing with the explosive growth of diverse image data in the era of big data poses challenges for storage. Feng et al. propose a memristor-based near-storage in-memory processing system to boost the energy and storage efficiency.
- Yulin Feng
- , Yizhou Zhang
- & Jinfeng Kang
-
Article
| Open Access Steep-slope vertical-transport transistors built from sub-5 nm Thin van der Waals heterostructures
Steep-slope vertical-transport transistors built from sub-5 nm Thin van der Waals heterostructures
2D vertical transport transistors (VTFETs) may promote the downscaling of electronic devices, but their performance is usually restricted by the thermionic limit. Here, the authors report the realization of short-channel steep-slope VTFETs based on MoS2/MoTe2 heterojunctions integrated with resistance threshold switching cells.
- Qiyu Yang
- , Zheng-Dong Luo
- & Genquan Han
-
Article
| Open Access Interfacial magnetic spin Hall effect in van der Waals Fe3GeTe2/MoTe2 heterostructure
Interfacial magnetic spin Hall effect in van der Waals Fe3GeTe2/MoTe2 heterostructure
Charge-to-spin conversion allows for the generation and control of spin polarization via a charge current. Typically, this is done with non-magnetic materials with large spin-orbit interactions such as Platinum. Herein, Dai et al demonstrate an intriguing charge-to-spin mechanism, a magnetic spin Hall effect, in a van der Waals heterostructure.
- Yudi Dai
- , Junlin Xiong
- & Feng Miao
-
Article
| Open Access Strong coupling between a microwave photon and a singlet-triplet qubit
Strong coupling between a microwave photon and a singlet-triplet qubit
By coupling a spin-qubit to a superconducting resonator, remote spin-entanglement becomes feasible. Here, Ungerer et al achieve strong coupling between a superconducting resonator and a singlet-triplet spin qubit, in an InAs nanowire.
- J. H. Ungerer
- , A. Pally
- & C. Schönenberger
-
Article
| Open Access Approaching a fully-polarized state of nuclear spins in a solid
Approaching a fully-polarized state of nuclear spins in a solid
Highly polarized nuclear spins can supress decoherence of electron spin qubits, but this requires near-unity polarization. Here the authors implement a protocol combining optical excitation and fast carrier tunnelling to achieve nuclear spin polarizations above 95% in GaAs quantum dots on a timescale of 1 minute.
- Peter Millington-Hotze
- , Harry E. Dyte
- & Evgeny A. Chekhovich
-
Article
| Open Access Non-hermiticity in spintronics: oscillation death in coupled spintronic nano-oscillators through emerging exceptional points
Non-hermiticity in spintronics: oscillation death in coupled spintronic nano-oscillators through emerging exceptional points
Exceptional points emerge in systems with loss and gain when loss and gain in the system are balanced. Due to the careful balancing involved, they are highly sensitive to perturbations, making them exceptionally useful for sensors and other devices. Here, Wittrock et al observe a variety of complex dynamics associated with exceptional points in coupled spintronic nano-oscillators.
- Steffen Wittrock
- , Salvatore Perna
- & Vincent Cros
-
Article
| Open Access Clocked dynamics in artificial spin ice
Clocked dynamics in artificial spin ice
Artificial spin ices are nanomagnetic metamaterials, whose collective magnetization self-organizes into extended domains. However, controlling when, where and how domains change has proven difficult, yet is crucial for technological applications. Here, Jensen and Strømberg et al. introduce astroid clocking, which enables controlled, stepwise growth and reversal of magnetic domains, using only global fields.
- Johannes H. Jensen
- , Anders Strømberg
- & Erik Folven
-
Article
| Open Access Switchable unidirectional emissions from hydrogel gratings with integrated carbon quantum dots
Switchable unidirectional emissions from hydrogel gratings with integrated carbon quantum dots
Directional emission of photoluminescence is an emerging technique for light-emitting fields and nanophotonics. Here, the authors demonstrate a hydrogel grating with integrated quantum dots for switchable unidirectional emission tuning.
- Chenjie Dai
- , Shuai Wan
- & Zhongyang Li
-
Article
| Open Access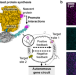 A genetic circuit on a single DNA molecule as an autonomous dissipative nanodevice
A genetic circuit on a single DNA molecule as an autonomous dissipative nanodevice
Achieving genetic circuits on single DNA molecules could have varied applications. Here, authors observed proteins emerging from single DNA molecules through coupled transcription-translation complexes, and show that nascent proteins lingered on DNA, regulating cascaded reactions on the same DNA and allowing the design of a pulsatile genetic circuit.
- Ferdinand Greiss
- , Nicolas Lardon
- & Roy Bar-Ziv
-
Article
| Open Access Pulse irradiation synthesis of metal chalcogenides on flexible substrates for enhanced photothermoelectric performance
Pulse irradiation synthesis of metal chalcogenides on flexible substrates for enhanced photothermoelectric performance
Here, the authors report a low-temperature pulse irradiation synthesis method to prepare thermoelectric metal chalcogenide (Bi2Se3, SnSe2 and Bi2Te3) thin films on various flexible substrates, showing their application for the realization of broadband photothermoelectric detectors.
- Yuxuan Zhang
- , You Meng
- & Johnny C. Ho
-
Article
| Open Access Toward grouped-reservoir computing: organic neuromorphic vertical transistor with distributed reservoir states for efficient recognition and prediction
Toward grouped-reservoir computing: organic neuromorphic vertical transistor with distributed reservoir states for efficient recognition and prediction
Existing neuromorphic hardware, focusing mainly on shallow-reservoir computing, is challenged in providing adequate spatial and temporal scales characteristic for effective computing. Here, Gao et al. report an ultra-short channel organic neuromorphic vertical transistor with distributed reservoir states.
- Changsong Gao
- , Di Liu
- & Huipeng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Powering AI at the edge: A robust, memristor-based binarized neural network with near-memory computing and miniaturized solar cell
Powering AI at the edge: A robust, memristor-based binarized neural network with near-memory computing and miniaturized solar cell
The authors present an AI engine with 32,768 memristors powered by a miniature solar cell. This circuit exploits near-memory computing, naturally adjusting its accuracy depending on the illumination level, and paves the way for self-powered AI.
- Fadi Jebali
- , Atreya Majumdar
- & Jean-Michel Portal
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetoresistive-coupled transistor using the Weyl semimetal NbP
Magnetoresistive-coupled transistor using the Weyl semimetal NbP
L. Rocchino et al. experimentally demonstrate a magnetic field effect transistor based on the Weyl semimetal NbP as the active channel material. A gate magnetic field is generated by current flowing in an integrated superconductor NbN. The device operation relies on the extreme magnetoresistance of the NbP.
- Lorenzo Rocchino
- , Federico Balduini
- & Cezar B. Zota
-
Article
| Open Access Giant tunnelling electroresistance in atomic-scale ferroelectric tunnel junctions
Giant tunnelling electroresistance in atomic-scale ferroelectric tunnel junctions
The authors report ferroelectric tunnel junctions based on samarium-substituted layered bismuth oxide, which show tunnelling electroresistance of 7 × 105 and high endurance over 5 billion cycles, even when the film is down to one nanometer.
- Yueyang Jia
- , Qianqian Yang
- & Rui Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Microwave quantum diode
Microwave quantum diode
Quantum devices exhibiting non-reciprocal behaviour have been attracting attention for fundamental studies and applications. Here the authors report a microwave quantum diode based on a superconducting flux qubit coupled to two resonators, which has the advantage of compactness and scalability.
- Rishabh Upadhyay
- , Dmitry S. Golubev
- & Jukka P. Pekola
-
Article
| Open Access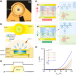 Flexible switch matrix addressable electrode arrays with organic electrochemical transistor and pn diode technology
Flexible switch matrix addressable electrode arrays with organic electrochemical transistor and pn diode technology
Organic neural implants hold considerable promise for biocompatible neural interfaces. Here, the authors employ polymer-based organic electrochemical diodes and transistors to develop neuron-sized complex circuits, enabling multiplexing without crosstalk and demonstrate that, when integrated onto ultra-thin plastic, these circuits achieve high performance while maintaining minimal invasiveness.
- Ilke Uguz
- , David Ohayon
- & Kenneth L. Shepard
-
Article
| Open Access Compact and wideband nanoacoustic pass-band filters for future 5G and 6G cellular radios
Compact and wideband nanoacoustic pass-band filters for future 5G and 6G cellular radios
This work addresses the fundamental challenge of the frequency up-scaling of microacoustic devices. The manuscript presents the first bank of on-chip multi-frequency, low-loss, wideband, and compact passband filters for mobile 5G and 6G applications.
- Gabriel Giribaldi
- , Luca Colombo
- & Matteo Rinaldi
-
Article
| Open Access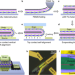 Ultrashort vertical-channel MoS2 transistor using a self-aligned contact
Ultrashort vertical-channel MoS2 transistor using a self-aligned contact
The simultaneous scaling down of the channel length and gate length of 2D transistors remains challenging. Here, the authors report a self-alignment process to fabricate vertical MoS2 transistors with sub-1 nm gate length and sub−50 nm channel length, exhibiting on-off ratios over 105 and on-state currents of 250 μA/μm at 4 V bias.
- Liting Liu
- , Yang Chen
- & Yuan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access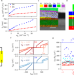 Parity-conserving Cooper-pair transport and ideal superconducting diode in planar germanium
Parity-conserving Cooper-pair transport and ideal superconducting diode in planar germanium
M. Valentini et al. study superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs) where the weak link of the Josephson junctions is a germanium 2D hole gas. They report signatures of the tunneling of pairs of Cooper pairs. For a particular microwave drive power, they observe a 100% efficient superconducting diode effect.
- Marco Valentini
- , Oliver Sagi
- & Georgios Katsaros
-
Article
| Open Access Injectable hydrogel electrodes as conduction highways to restore native pacing
Injectable hydrogel electrodes as conduction highways to restore native pacing
No preventive treatment addresses the underlying condition that leads to cardiac arrest. Here, researchers developed an injectable hydrogel electrode that achieves pacing that mimics physiological conduction with the potential to eliminate lethal arrhythmias and provide painless defibrillation.
- Gabriel J. Rodriguez-Rivera
- , Allison Post
- & Elizabeth Cosgriff-Hernandez
-
Article
| Open Access Elastocapillarity-driven 2D nano-switches enable zeptoliter-scale liquid encapsulation
Elastocapillarity-driven 2D nano-switches enable zeptoliter-scale liquid encapsulation
In this work, authors demonstrate programmable nanostructures using two-dimensional materials for nanoscale liquid manipulation. The nanoswitches and capsules can hold zeptoliter liquid volumes, enabling active nanofluidics circuits and confined reactors.
- Nathan Ronceray
- , Massimo Spina
- & Slaven Garaj
-
Article
| Open Access Purely self-rectifying memristor-based passive crossbar array for artificial neural network accelerators
Purely self-rectifying memristor-based passive crossbar array for artificial neural network accelerators
Designing memristor-integrated passive crossbar arrays to accelerate artificial neural networks with high reliability remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose a self-rectifying resistive switching device incorporated into a crossbar array with a density of 1 kb whose operational performance is assessed in terms of defected-cell proportion, reading margin, and selection functionality.
- Kanghyeok Jeon
- , Jin Joo Ryu
- & Gun Hwan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Extendable piezo/ferroelectricity in nonstoichiometric 2D transition metal dichalcogenides
Extendable piezo/ferroelectricity in nonstoichiometric 2D transition metal dichalcogenides
Nonstoichiometric transition metal dichalcogenides break symmetry, enabling piezo/ferroelectric effects. Here, the authors propose an approach to integrate these properties with diverse 2D materials, advancing multifunctional materials and devices.
- Yi Hu
- , Lukas Rogée
- & Shu Ping Lau
-
Article
| Open Access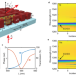 High quality factor metasurfaces for two-dimensional wavefront manipulation
High quality factor metasurfaces for two-dimensional wavefront manipulation
Wavefront manipulation with metasurfaces is typically limited to low quality factors. Here, the authors show how higher-order Mie modes can be leveraged to design high quality factor optical metasurfaces for wavefront manipulation in two dimensions.
- Claudio U. Hail
- , Morgan Foley
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Article
| Open Access A hard molecular nanomagnet from confined paramagnetic 3d-4f spins inside a fullerene cage
A hard molecular nanomagnet from confined paramagnetic 3d-4f spins inside a fullerene cage
Shortening the inter-spin distance is an effective way to enhance magnetic coupling. However, it is typically challenging to change the inter-ion distance in most magnetic systems. Here, Huang et al present a strategy for enhancing magnetic interactions, by confining a molecular magnetic system inside a carbon fullerene cage, leading to enhanced magnetic properties.
- Chenli Huang
- , Rong Sun
- & Song Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrophobically gated memristive nanopores for neuromorphic applications
Hydrophobically gated memristive nanopores for neuromorphic applications
Designing efficient nanoscale and adaptable bioinspired memristors remains a challenge. Here, the authors develop a bioinspired hydrophobically gated memristive nanopore capable of learning, forgetting, and retaining memory through an electrowetting mechanism.
- Gonçalo Paulo
- , Ke Sun
- & Alberto Giacomello
-
Article
| Open Access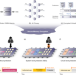 Embedding security into ferroelectric FET array via in situ memory operation
Embedding security into ferroelectric FET array via in situ memory operation
Existing solutions based Advanced Encryption Standard to address the security issues of nonvolatile memories incurs significant performance and power overhead. Here, the authors propose a lightweight XOR-gate based encryption/decryption technique by exploiting in-situ array operations, which achieves significant area/latency/power reduction compared to conventional designs.
- Yixin Xu
- , Yi Xiao
- & Kai Ni
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-dependent Andreev molecules and superconducting gap closing in coherently-coupled Josephson junctions
Phase-dependent Andreev molecules and superconducting gap closing in coherently-coupled Josephson junctions
S. Matsuo et al. report tunneling spectroscopy measurements on a device consisting of two Josephson junctions (JJ) sharing a single superconducting electrode. In isolation, each JJ would host an Andreev bound state (ABS). In their coherently-coupled JJs, the authors report the formation of an Andreev molecule due to hybridization of the two ABSs.
- Sadashige Matsuo
- , Takaya Imoto
- & Seigo Tarucha
-
Article
| Open Access Record high room temperature resistance switching in ferroelectric-gated Mott transistors unlocked by interfacial charge engineering
Record high room temperature resistance switching in ferroelectric-gated Mott transistors unlocked by interfacial charge engineering
Ferroelectric transistors are promising building blocks for developing energy-efficient memory and logic applications. Here, the authors report a record high 300 K resistance on-off ratio achieved in ferroelectric-gated Mott transistors by exploiting a charge transfer layer to tailor the channel carrier density and mitigate the ferroelectric depolarization effect.
- Yifei Hao
- , Xuegang Chen
- & Xia Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Hot luminescence from single-molecule chromophores electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by tripodal scaffolds
Hot luminescence from single-molecule chromophores electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by tripodal scaffolds
A fundamental challenge for molecular electronics is the change in photophysical properties of molecules upon direct electrical contact. Here, the authors observe hot luminescence emitted by single-molecule chromophores that are electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by a tripodal scaffold.
- Vibhuti Rai
- , Nico Balzer
- & Michal Valášek
-
Article
| Open Access In operando cryo-STEM of pulse-induced charge density wave switching in TaS2
In operando cryo-STEM of pulse-induced charge density wave switching in TaS2
Resistive switching of 1T-TaS2 is promising for next-generation electronics. Here, using in operando electron microscopy, the authors determine that Joule heating drives the switching process, which will aid the engineering of future devices.
- James L. Hart
- , Saif Siddique
- & Judy J. Cha
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance van der Waals antiferroelectric CuCrP2S6-based memristors
High-performance van der Waals antiferroelectric CuCrP2S6-based memristors
Layered thio- and seleno-phosphate ferroelectrics show promise for next-generation memory but have thermal stability issues. Using the electric field-driven phase transition in antiferroelectric CuCrP2S6, the authors introduce a robust memristor, emphasizing the potential of van der Waals antiferroelectrics in advanced neuromorphic computing.
- Yinchang Ma
- , Yuan Yan
- & Xixiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Cryogenic multiplexing using selective area grown nanowires
Cryogenic multiplexing using selective area grown nanowires
The authors demonstrate a large ensemble of quantum dots which is characterized using a cryogenic multiplexer-demultiplexer circuit based on selective area growth nanowires, establishing the feasibility of scaling future quantum circuits.
- Dāgs Olšteins
- , Gunjan Nagda
- & Thomas S. Jespersen
-
Article
| Open Access The role of halogens in Au–S bond cleavage for energy-differentiated catalysis at the single-bond limit
The role of halogens in Au–S bond cleavage for energy-differentiated catalysis at the single-bond limit
Investigation of the reaction process at the single-bond interface is key to understanding the catalytic reaction mechanism. Here, the authors develop a STM-BJ method to monitor the catalytic process from the perspective of single-bond energy.
- Peihui Li
- , Songjun Hou
- & Xuefeng Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal and electrostatic tuning of surface phonon-polaritons in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures
Thermal and electrostatic tuning of surface phonon-polaritons in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures
Phonon polaritons are promising for infrared applications while it is difficult to tune the phonon polariton properties. Here, authors report a thermal and electrostatic tuning of surface phonon polaritons in heterostructures of LaAlO3/SrTiO3.
- Yixi Zhou
- , Adrien Waelchli
- & Alexey B. Kuzmenko
-
Article
| Open Access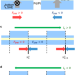 Position error-free control of magnetic domain-wall devices via spin-orbit torque modulation
Position error-free control of magnetic domain-wall devices via spin-orbit torque modulation
For magnetic domain-wall devices, key issue to be addressed is nonstochastic displacement of magnetic domain wall. Here, authors report domain-wall control with a position error-free scheme via spin-orbit torque modulation along nanotrack devices.
- Seong-Hyub Lee
- , Myeonghoe Kim
- & Sug-Bong Choe
-
Article
| Open Access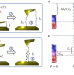 Microscopic theory, analysis, and interpretation of conductance histograms in molecular junctions
Microscopic theory, analysis, and interpretation of conductance histograms in molecular junctions
Conductance histograms are common setups to study molecular junctions, but the dispersion of the signals makes it difficult to interpret at microscopic level. Here the authors develop a physical model of molecular junctions that connects this observable with molecular properties.
- Leopoldo Mejía
- , Pilar Cossio
- & Ignacio Franco

 Motility of an autonomous protein-based artificial motor that operates via a burnt-bridge principle
Motility of an autonomous protein-based artificial motor that operates via a burnt-bridge principle