Featured
-
-
Article |
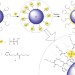 Core@shell bimetallic nanoparticle synthesis via anion coordination
Core@shell bimetallic nanoparticle synthesis via anion coordination
Bimetallic core@shell nanoparticles often have properties that are different from those of single-metal or alloy nanoparticles. Here, a route to such nanoparticles that binds the second metal to the core surface prior to reduction is described. The unique catalytic properties of the nanoparticles are demonstrated in the selective production of chloroaniline.
- Christopher J. Serpell
- , James Cookson
- & Paul D. Beer
-
News & Views |
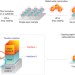
 Where the action is
Where the action is
Heterogeneous catalyst systems comprising metals supported on oxides are widespread. Evidence now suggests that it is the interfacial regions that are most catalytically active, and this has been exploited to create a tandem nanocatalyst system.
- Peter C. Stair
-
Article |
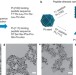 Platinum nanocrystals selectively shaped using facet-specific peptide sequences
Platinum nanocrystals selectively shaped using facet-specific peptide sequences
Crystal growth in nature is controlled by biomolecules to produce precisely engineered crystal shapes. Now, facet-specific peptide sequences that have been rationally selected through a biomimetic evolution process are used as regulating agents for predictable synthesis of platinum nanocrystals with selectively exposed crystal surfaces.
- Chin-Yi Chiu
- , Yujing Li
- & Yu Huang
-
Article |
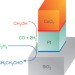
 Nanocrystal bilayer for tandem catalysis
Nanocrystal bilayer for tandem catalysis
The development of high-performance ‘smart’ catalysts will rely on the rational design of nanoscale metal–metal oxide interfaces. A tandem catalyst that has both CeO2-Pt and Pt-SiO2 interfaces is now reported, and is capable of catalysing sequential reactions to convert methanol into ethylene.
- Yusuke Yamada
- , Chia-Kuang Tsung
- & Peidong Yang
-
Article |
 Biodegradable nanostructures with selective lysis of microbial membranes
Biodegradable nanostructures with selective lysis of microbial membranes
Macromolecules with antimicrobial properties are promising materials for combating multi-drug-resistant microbes. Now, it has been shown that amphiphilic cationic polycarbonates that are biodegradable can self-assemble into micellar nanoparticles that can kill gram-positive bacteria, MRSA and fungi efficiently, even at low concentrations. Moreover, no significant toxicity is observed during in vivo studies in mice.
- Fredrik Nederberg
- , Ying Zhang
- & Yi-Yan Yang
-
Article |
 Palladium-mediated intracellular chemistry
Palladium-mediated intracellular chemistry
Palladium nanoparticles trapped within polystyrene beads can enter cells and mediate a variety of Pd0-catalysed reactions, including allylcarbamate cleavage and Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling. The methodology presented provides the basis for the customization of heterogeneous unnatural catalysts as tools for carrying out artificial chemistries within cells.
- Rahimi M. Yusop
- , Asier Unciti-Broceta
- & Mark Bradley
-
News & Views |
 Detection by failure
Detection by failure
Testing for enzymes is important for diagnosing various medical conditions but can be problematic because of the complexity of physiological media such as blood. Now, a method of detecting phospholipases has been developed that neatly couples their concentration with the aggregation of gold nanoparticles.
- Nicholas A. Melosh
-
Research Highlights |
 An extra layer
An extra layer
Introducing a layer of gold alloy between the outer platinum shell and palladium core of a nanoparticle improves its activity as a catalyst for oxygen reduction.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
Research Highlights |
Matters of size
Differences in nanoparticle surface energies account for varying phase stabilities on the nanoscale compared with bulk.
- Neil Withers
-
Research Highlights |
 Get rhythm
Get rhythm
An oscillatory reaction has been used to drive the rhythmical assembly and disassembly of gold nanoparticles.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
Article |
 Recognition-mediated activation of therapeutic gold nanoparticles inside living cells
Recognition-mediated activation of therapeutic gold nanoparticles inside living cells
Application of supramolecular chemistry in living systems is challenging because of the inherent chemical complexity of cellular environments. Now, the use of a carefully designed host–guest system featuring diaminohexane-terminated gold nanoparticles and complementary cucurbit[7]uril macrocycles has been shown to provide triggered activation of a therapeutic system in living cells.
- Chaekyu Kim
- , Sarit S. Agasti
- & Vincent M. Rotello
-
News & Views |
 Capturing hot electrons
Capturing hot electrons
The efficiency of photovoltaic materials is compromised by their inability to capture all the energy absorbed when excited by high-energy photons. Such absorption creates 'hot' electrons, and now their transfer from excited lead selenide nanocrystals to an electron acceptor provides a necessary initial step towards tapping their 'lost' energy.
- Prashant V. Kamat
-
Article |
 A polyhedron made of tRNAs
A polyhedron made of tRNAs
Whereas synthetic DNA nanostructures are widely studied, the use of RNA as a structural building block is much less common. Now, it has been shown that tRNA molecules can be designed to assemble into a rigid and thermally stable square antiprism structure that may prove useful for delivery applications inside cells.
- Isil Severcan
- , Cody Geary
- & Luc Jaeger
-
News & Views |
 Illuminated oxides
Illuminated oxides
A photo-reversible metal–semiconductor phase transition can be induced in a nanocrystalline transition-metal oxide at room temperature by short-wavelength light irradiation, holding promise for the development of new optical storage media.
- Kosmas Prassides
-
Article |
 Synthesis of a metal oxide with a room-temperature photoreversible phase transition
Synthesis of a metal oxide with a room-temperature photoreversible phase transition
Optically driven phase transitions are widely used in optical memory devices, and the materials showing this effect are normally chalcogenides or organic compounds. Now a room-temperature light-induced phase transition between metal and semiconducting phases has been observed in a titanium oxide material.
- Shin-ichi Ohkoshi
- , Yoshihide Tsunobuchi
- & Hiroko Tokoro
-
Article |
 Lattice-strain control of the activity in dealloyed core–shell fuel cell catalysts
Lattice-strain control of the activity in dealloyed core–shell fuel cell catalysts
The rational design of catalytic materials requires synthetic control over their reactive properties. Now, the activity of dealloyed Pt–Cu bimetallic nanoparticles, which catalyse the oxygen reduction reaction, can be tuned through control of the geometric strain at their surface.
- Peter Strasser
- , Shirlaine Koh
- & Anders Nilsson
-
Article |
 Rapid preparation of flexible porous coordination polymer nanocrystals with accelerated guest adsorption kinetics
Rapid preparation of flexible porous coordination polymer nanocrystals with accelerated guest adsorption kinetics
Porous coordination polymers — PCPs, also known as metal–organic framework materials — have been widely investigated for their useful properties, but controlling their size and shape in a nanocrystalline form is difficult. Now, a rapid method of preparing porous crystalline nanosized PCPs that uses a microemulsion system under ultrasonic irradiation has been reported.
- Daisuke Tanaka
- , Artur Henke
- & Juergen Groll
-
News & Views |
 Protons on tap
Protons on tap
Electrochemistry has so far been mostly centred around measuring factors and coefficients. Through the reversible reduction and oxidation of an electrode coating formed from three-dimensional hybrid aniline–gold nanoparticles, it has now moved on to controlling the pH of a solution, thus triggering specific reactions.
- Reginald M. Penner
-
Article |
 Quantum size effects in ambient CO oxidation catalysed by ligand-protected gold clusters
Quantum size effects in ambient CO oxidation catalysed by ligand-protected gold clusters
Gold nanoparticles can catalyse oxidation reactions in remarkably mild conditions and have excited much interest in recent years. With experimental studies disagreeing over the size of the most active nanoparticles, density functional calculations have now shown that limiting the particle size to below two nanometres is crucial.
- Olga Lopez-Acevedo
- , Katarzyna A. Kacprzak
- & Hannu Häkkinen
-
Research Highlights |
Sunscreen size studies
A comparison of models for the sun-protection factor, transparency and production of reactive oxygen species leads to a prediction of the optimum size of titania nanoparticles for use in sunscreen.
- Stephen Davey
-
Article |
 Loading and selective release of cargo in DNA nanotubes with longitudinal variation
Loading and selective release of cargo in DNA nanotubes with longitudinal variation
Nanotubular structures made from different materials are being investigated for applications ranging from sensing to drug delivery, but controlling how they interact with ‘cargo’ molecules has proved challenging. Now, the selective uptake, precise positioning and triggered release of gold nanoparticles has been achieved with nanotubes assembled from triangular DNA building blocks.
- Pik Kwan Lo
- , Pierre Karam
- & Hanadi F. Sleiman
-
-
Article |
 Nanocrystalline intermetallics on mesoporous carbon for direct formic acid fuel cell anodes
Nanocrystalline intermetallics on mesoporous carbon for direct formic acid fuel cell anodes
Formic acid fuel cells require nanosized intermetallic nanoparticles as anode catalysts, but current techniques are poor at producing the small size required. Now, surface-modified ordered mesoporous carbons have been used to produce nanocrystallites as small as 1.5 nm that are extremely active catalysts.
- Xiulei Ji
- , Kyu Tae Lee
- & Linda F. Nazar
-
Research Highlights |
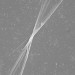 An illuminating twist
An illuminating twist
The slow oxidation of tellurium in semiconductor cadmium telluride nanoparticles, accompanied by the replacement of tellurium by sulfur, has led to CdS/CdTe nanoparticles that self-assemble under visible light into twisted nanoribbons.
- Anne Pichon
-
Research Highlights |
 Nanoparticles ring the changes
Nanoparticles ring the changes
More predictable chemical patterns have been created by using nanoparticles instead of ions.
- Neil Withers
-
News & Views |
 The best of both worlds
The best of both worlds
Embedding platinum nanoparticles in a polymer matrix produces a system that reacts like a homogeneous catalyst, but provides the stability and separation advantages of a heterogeneous one.
- Gadi Rothenberg
-
News & Views |
 Producing 'perfect' particles
Producing 'perfect' particles
Synthetic procedures for making nanoparticles often result in samples that contain a range of different particle sizes. By using hollow self-assembled metal–organic spheres as templates, however, it is possible to make silica nanoparticles with uniform shapes and sizes in a precisely controlled fashion.
- Boris Breiner
- & Jonathan R. Nitschke

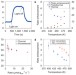 Visible-light-enhanced catalytic oxidation reactions on plasmonic silver nanostructures
Visible-light-enhanced catalytic oxidation reactions on plasmonic silver nanostructures Nanoparticles ring the changes
Nanoparticles ring the changes