Featured
-
-
Letter |
 3D printing of high-strength aluminium alloys
3D printing of high-strength aluminium alloys
Zirconium nanoparticles introduced into aluminium alloy powders control solidification during 3D printing, enabling the production of crack-free materials with strengths comparable to the corresponding wrought material.
- John H. Martin
- , Brennan D. Yahata
- & Tresa M. Pollock
-
News & Views |
 Nanomagnets boost thermoelectric output
Nanomagnets boost thermoelectric output
The direct conversion of heat into electricity — a reversible process known as the thermoelectric effect — can be greatly enhanced in some materials by embedding them with a small number of magnetic nanoparticles. See Letter p.247
- Stephen R. Boona
-
Letter |
 High-temperature crystallization of nanocrystals into three-dimensional superlattices
High-temperature crystallization of nanocrystals into three-dimensional superlattices
A bottom-up process to achieve rapid growth of micrometre-sized three-dimensional nanocrystal superlattices during colloidal synthesis at high temperatures is revealed by in situ small-angle X-ray scattering; the process is applicable to several colloidal materials.
- Liheng Wu
- , Joshua J. Willis
- & Christopher J. Tassone
-
Technology Feature |
 The architecture of structured DNA
The architecture of structured DNA
Researchers are exploiting the structural properties of DNA to build nanoscale models for use in medicine and materials science.
- XiaoZhi Lim
-
Research Highlight |
Nanoprobe detects the force of swimming bacteria
The optical fibre is several times more sensitive than other techniques.
-
News & Views |
 Vibrations mapped by an electron beam
Vibrations mapped by an electron beam
The vibrational excitations of nanostructures have been mapped using state-of-the-art electron microscopy. The results improve our understanding of these excitations, which will aid the design of nanostructures. See Letter p.529
- Christian Colliex
-
Letter |
 Mapping vibrational surface and bulk modes in a single nanocube
Mapping vibrational surface and bulk modes in a single nanocube
Spatial mapping of optical and acoustic, bulk and surface vibrational modes in magnesium oxide nanocubes is demonstrated using a single electron probe.
- Maureen J. Lagos
- , Andreas Trügler
- & Philip E. Batson
-
Letter |
 Amplified stimulated emission in upconversion nanoparticles for super-resolution nanoscopy
Amplified stimulated emission in upconversion nanoparticles for super-resolution nanoscopy
Super-resolution optical microscopy based on stimulated emission depletion effects can now be performed at much lower light intensities than before by using bright upconversion emission from thulium-doped nanoparticles.
- Yujia Liu
- , Yiqing Lu
- & Dayong Jin
-
Letter |
 Photovoltage field-effect transistors
Photovoltage field-effect transistors
A photovoltage field-effect transistor is demonstrated that is very sensitive to infrared light and has high gain.
- Valerio Adinolfi
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
News & Views |
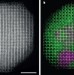 Nanoparticle atoms pinpointed
Nanoparticle atoms pinpointed
The locations of atoms in a metallic alloy nanoparticle have been determined using a combination of electron microscopy and image simulation, revealing links between the particle's structure and magnetic properties. See Letter p.75
- Michael Farle
-
Letter |
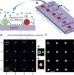 Catalyst support effects on hydrogen spillover
Catalyst support effects on hydrogen spillover
The mechanism of hydrogen spillover is described using a precisely nanofabricated model system, explaining why it is slower on an aluminum oxide catalyst support than on a titanium oxide catalyst support.
- Waiz Karim
- , Clelia Spreafico
- & Jeroen A. van Bokhoven
-
Letter |
 Surface patterning of nanoparticles with polymer patches
Surface patterning of nanoparticles with polymer patches
Surface patterning of nanoparticles with polymer patches is achieved in a poor solvent for the polymer by controlling the ratio between the sizes of polymer molecules and nanoparticles.
- Rachelle M. Choueiri
- , Elizabeth Galati
- & Eugenia Kumacheva
-
News & Views |
 Magnetic nanoparticles line up
Magnetic nanoparticles line up
Certain bacteria contain strings of magnetic nanoparticles and therefore align with magnetic fields. Inspired by these natural structures, researchers have now fabricated synthetic one-dimensional arrays of such particles.
- Damien Faivre
- & Mathieu Bennet
-
Letter |
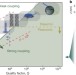 Single-molecule strong coupling at room temperature in plasmonic nanocavities
Single-molecule strong coupling at room temperature in plasmonic nanocavities
Placing a light emitter in an ultra-small optical cavity results in coupling between matter and light, generating new forms of emission that can be exploited in practical or fundamental applications; here, a system is described in which strong light–matter coupling occurs at room temperature and in ambient conditions by aligning single dye molecules in the optical cavities between gold nanoparticles and surfaces.
- Rohit Chikkaraddy
- , Bart de Nijs
- & Jeremy J. Baumberg
-
News |
 Bankruptcy filing worries developers of nanoparticle cancer drugs
Bankruptcy filing worries developers of nanoparticle cancer drugs
Financial woes of leading biotech firm highlight challenges of developing innovative therapies.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Research Highlights |
Exploding bubbles kill cancer cells
-
Letter |
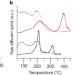 Stable amorphous georgeite as a precursor to a high-activity catalyst
Stable amorphous georgeite as a precursor to a high-activity catalyst
Hydroxycarbonate minerals such as zincian malachite and aurichalcite are well known precursors to catalysts for methanol-synthesis and low-temperature water–gas shift reactions; here, a supercritical antisolvent method is used to prepare highly stable georgeite—a hydroxycarbonate mineral that has hitherto been ignored because of its rarity, but which is found to be a superior catalyst precursor.
- Simon A. Kondrat
- , Paul J. Smith
- & Graham J. Hutchings
-
News & Views |
 Platelet mimicry
Platelet mimicry
Cloaking drug-loaded nanoparticles with platelet membranes enhances the drugs' abilities to target desired cells and tissues. This technology might improve treatments for cardiovascular and infectious diseases. See Letter p.118
- Omid C. Farokhzad
-
News |
 Nanoparticles disguised as blood-cell fragments slip past body's immune defence
Nanoparticles disguised as blood-cell fragments slip past body's immune defence
Drug-delivery systems coated in platelets used to repair damaged blood vessels.
- Elizabeth Gibney
-
Letter |
 Nanoparticle biointerfacing by platelet membrane cloaking
Nanoparticle biointerfacing by platelet membrane cloaking
The authors report a new biomimetic nanodelivery platform in which polymeric nanoparticles enclosed in the plasma membrane of human platelets are used for disease-relevant targeting, and the therapeutic potential of the concept is demonstrated in animal models of coronary restenosis and systemic bacterial infection.
- Che-Ming J. Hu
- , Ronnie H. Fang
- & Liangfang Zhang
-
Letter |
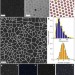 Substitutional doping in nanocrystal superlattices
Substitutional doping in nanocrystal superlattices
Substitutional atomic doping is a process by which atomic defects are introduced into a host material, altering its properties; substitutional doping of cadmium selenide or lead selenide nanocrystal lattices with gold nanocrystals has now been achieved, the key being to ensure that the dopant nanocrystals are similar in size to the host nanocrystals.
- Matteo Cargnello
- , Aaron C. Johnston-Peck
- & Christopher B. Murray
-
News & Views |
 Colourful particles for spectrometry
Colourful particles for spectrometry
A smartphone camera, patterned with arrays of filters made from colloidal suspensions of coloured particles, has been transformed into a powerful tool for spectral analysis. See Letter p.67
- Norm C. Anheier
-
Letter |
 Shape-changing magnetic assemblies as high-sensitivity NMR-readable nanoprobes
Shape-changing magnetic assemblies as high-sensitivity NMR-readable nanoprobes
A shape-changing sensor made of pairs of magnetic disks spaced by swellable hydrogel material removes all need for optical access by operating in the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) radio-frequency spectrum.
- G. Zabow
- , S. J. Dodd
- & A. P. Koretsky
-
Research Highlights |
Nanoparticles stuck on tape
-
Letter |
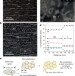 Brittle intermetallic compound makes ultrastrong low-density steel with large ductility
Brittle intermetallic compound makes ultrastrong low-density steel with large ductility
Alloying steel with aluminium improves the material’s strength-to-weight ratio, but the resulting formation of brittle intermetallic compounds within the steel matrix reduces its ductility; here the morphology and distribution of the intermetallic precipitates are controlled to alleviate this problem.
- Sang-Heon Kim
- , Hansoo Kim
- & Nack J. Kim
-
Letter |
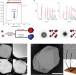 DNA-mediated nanoparticle crystallization into Wulff polyhedra
DNA-mediated nanoparticle crystallization into Wulff polyhedra
Very slow cooling, over several days, of solutions of complementary-DNA-modified nanoparticles through the melting temperature of the system produces nanoparticle assemblies with the Wulff equilibrium crystal structure, thus showing that DNA hybridization can direct nanoparticle assembly along a pathway that mimics atomic crystallization.
- Evelyn Auyeung
- , Ting I. N. G. Li
- & Chad A. Mirkin
-
-
Brief Communications Arising |
Three-dimensional imaging of dislocations
- Peter Rez
- & Michael M. J. Treacy
-
Letter |
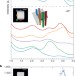 Three-dimensional imaging of localized surface plasmon resonances of metal nanoparticles
Three-dimensional imaging of localized surface plasmon resonances of metal nanoparticles
Localized surface plasmon resonances of an individual silver nanocube are reconstructed in three dimensions using electron energy-loss spectrum imaging, resulting in a better understanding of the optical response of noble-metal nanoparticles.
- Olivia Nicoletti
- , Francisco de la Peña
- & Paul A. Midgley
-
Letter |
 Ultrastable silver nanoparticles
Ultrastable silver nanoparticles
Silver nanoparticles are susceptible to oxidation and have accordingly received less attention than gold nanoparticles; ultrastable silver nanoparticles are now reported, which can be produced in very large quantities as a single-sized molecular product, and the origins of their enhanced stability are elucidated using a single-crystal X-ray structure and first-principles calculations.
- Anil Desireddy
- , Brian E. Conn
- & Terry P. Bigioni
-
-
-
News |
 Nanoparticle blast caught on film
Nanoparticle blast caught on film
Combustion could help to make minuscule matter.
- Eugenie Samuel Reich
-
-
News |
 Scaled-down: new nano device can weigh single molecules
Scaled-down: new nano device can weigh single molecules
A tiny resonating beam, just 10 millionths of a meter in length, can measure the mass of a molecule or nanoparticle in real time.
- John Matson
-
Research Highlights |
Strong and stable nanocrystals
-
News |
 Colour printing reaches its ultimate resolution
Colour printing reaches its ultimate resolution
Images made up of metal-nanostructure pixels could be used for security or optical data storage.
- Katherine Bourzac
-
Research Highlights |
 Nanoparticles home in to clear clots
Nanoparticles home in to clear clots
-
Letter |
 SbsB structure and lattice reconstruction unveil Ca2+ triggered S-layer assembly
SbsB structure and lattice reconstruction unveil Ca2+ triggered S-layer assembly
Nanobody-aided X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy are used to describe the Ca2+-dependent polymerization dynamics of the S-layer of the Geobacillus stearothermophilus cell wall.
- Ekaterina Baranova
- , Rémi Fronzes
- & Han Remaut
-
Research Highlights |
On-demand drug release
-
News |
 Remote-controlled genes trigger insulin production
Remote-controlled genes trigger insulin production
Nanoparticles heated by radio waves switch on genes in mice
- Helen Shen
-
News |
 Nanomaterials offer hope for cerebral palsy
Nanomaterials offer hope for cerebral palsy
Rabbits with brain injuries hop again after treatment with dendrimers.
- Amy Maxmen
-
Research Highlights |
Lasers sort particles by size
-
Letter |
 Electron tomography at 2.4-ångström resolution
Electron tomography at 2.4-ångström resolution
An electron tomography method is demonstrated that can determine the three-dimensional structure of a gold nanoparticle at 2.4 Å resolution, including the locations of some of the individual atoms within the sample.
- M. C. Scott
- , Chien-Chun Chen
- & Jianwei Miao
-
Article |
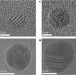 Quantum plasmon resonances of individual metallic nanoparticles
Quantum plasmon resonances of individual metallic nanoparticles
Metal nanoparticles with dimensions below ten nanometres exhibit plasmon resonances governed by quantum mechanical effects, as probed with electron microscopy and spectroscopy
- Jonathan A. Scholl
- , Ai Leen Koh
- & Jennifer A. Dionne
-
News & Views |
 Shape matters
Shape matters
The ligand-mediated binding of colloid particles to each other is more effective if the particles are flat rather than curved. This finding opens up opportunities for the design of self-assembling materials.
- Sharon C. Glotzer
-
Research Highlights |
 Getting past a brain block
Getting past a brain block
-
News |
 Nanoparticle solar cells make light work
Nanoparticle solar cells make light work
Cheap, printable photovoltaics might finally live up to their early promise.
- Philip Ball
-
News |
 Draft guidelines for nanomedicine unveiled
Draft guidelines for nanomedicine unveiled
With hundreds of nanoproducts currently being tested in humans, recommendations aim to safeguard trial participants.
- Jessica Marshall

 Force loading explains spatial sensing of ligands by cells
Force loading explains spatial sensing of ligands by cells Have you ever seen an atom?
Have you ever seen an atom? Looking from both sides
Looking from both sides