Featured
-
-
News |
 Landmark study links microplastics to serious health problems
Landmark study links microplastics to serious health problems
People who had tiny plastic particles lodged in a key blood vessel were more likely to experience heart attack, stroke or death during a three-year study.
- Max Kozlov
-
Article
| Open Access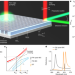 Directive giant upconversion by supercritical bound states in the continuum
Directive giant upconversion by supercritical bound states in the continuum
An experimental design consisting of a photonic-crystal nanoslab covered with upconversion nanoparticles demonstrates the phenomenon of supercritical coupling, resulting in giant enhancement of upconversion by photonic bound states in the continuum.
- Chiara Schiattarella
- , Silvia Romano
- & Gianluigi Zito
-
Research Briefing |
 Atomic electron tomography reveals chemical order in medium- and high-entropy alloys
Atomic electron tomography reveals chemical order in medium- and high-entropy alloys
Medium- and high-entropy alloys are hugely promising materials in metallurgy and catalysis, but their atomic-scale structure — and how that relates to their properties — is not well understood. A powerful method is beginning to reveal their secrets, with hopes for engineering better materials in the future.
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional atomic structure and local chemical order of medium- and high-entropy nanoalloys
Three-dimensional atomic structure and local chemical order of medium- and high-entropy nanoalloys
Atomic electron tomography is used to determine the 3D atomic positions and chemical species of medium- and high-entropy alloy nanoparticles and quantitatively characterize the local lattice distortion, strain tensor, twin boundaries, dislocation cores and chemical short-range order.
- Saman Moniri
- , Yao Yang
- & Jianwei Miao
-
Research Briefing |
 Divide and conquer: exploiting entropy to grow nanoscale barrier materials
Divide and conquer: exploiting entropy to grow nanoscale barrier materials
The full promise of materials structured at the nanoscale can be realized only if they can be manufactured more efficiently and at the sizes required for device integration. An innovative method takes advantage of thermodynamic and kinetic effects to control the growth of stacked 2D nanosheets that can be used for practical applications from the nanoscale to the macroscale.
-
Research Briefing |
 Nanoparticles containing diverse elements made using liquid metal
Nanoparticles containing diverse elements made using liquid metal
The synthesis of high-entropy alloy nanoparticles (HEA-NPs) — small particles each containing multiple principal metal elements — typically requires extreme conditions to ensure adequate mixing of constituents. Innovative experiments show that the liquid metal can act as a mixing reservoir to facilitate the synthesis of a diverse range of such nanoparticles in mild conditions.
-
Article |
 Liquid metal for high-entropy alloy nanoparticles synthesis
Liquid metal for high-entropy alloy nanoparticles synthesis
We discovered that liquid metal endowing negative mixing enthalpy with other elements could provide a stable thermodynamic condition and act as a desirable dynamic mixing reservoir, realizing the synthesis of high-entropy alloy nanoparticles.
- Guanghui Cao
- , Jingjing Liang
- & Lei Fu
-
Article |
 Indefinite and bidirectional near-infrared nanocrystal photoswitching
Indefinite and bidirectional near-infrared nanocrystal photoswitching
This study reports unlimited near-infrared photoswitching in inorganic avalanching nanoparticles via a discrete shift of threshold intensity mediated by internal defect-based colour centres.
- Changhwan Lee
- , Emma Z. Xu
- & P. James Schuck
-
Article
| Open Access Photochromism from wavelength-selective colloidal phase segregation
Photochromism from wavelength-selective colloidal phase segregation
A simple spectral selective active colloidal system is designed in which TiO2 colloidal species are coded with dyes to form a photochromic swarm that adapts the appearance of incident light due to layered phase segregation.
- Jing Zheng
- , Jingyuan Chen
- & Jinyao Tang
-
Research Highlight |
 Gut microbes ‘eat’ nanoparticles — leading to microbiome changes
Gut microbes ‘eat’ nanoparticles — leading to microbiome changes
Humans can accidentally ingest nanomaterials in consumer products, with unknown effects.
-
Article |
 Constrained C2 adsorbate orientation enables CO-to-acetate electroreduction
Constrained C2 adsorbate orientation enables CO-to-acetate electroreduction
A study using a copper-in-silver dilute alloy catalyst in a high-pressure gas flow reactor reports highly selective electrosynthesis of acetate from carbon monoxide.
- Jian Jin
- , Joshua Wicks
- & Yuanjie Pang
-
News & Views |
 Bow-tie particles boast a tunable twist
Bow-tie particles boast a tunable twist
Particles that self-assemble from nanoribbons into bow-tie-shaped structures can be tailored to change the degree of their twist. A search for how best to quantify this twist homes in on a measure of how the bow ties respond to light.
- Bart Kahr
-
Research Briefing |
 Stretchy electronic devices assembled in a Lego-like way
Stretchy electronic devices assembled in a Lego-like way
In current stretchable electronic devices, connection points between modules are made using commercially available pastes and break easily under mechanical deformation. An innovative connection interface has been developed to enable robust stretchable devices to be reliably assembled in a Lego‑like manner by simply pressing the interfaces of two modules together without pastes.
-
Research Briefing |
 Designer silicon nanowires produce hydrogen from water and light
Designer silicon nanowires produce hydrogen from water and light
Silicon nanowires that can convert light into electricity were engineered to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. When integrated with co-catalysts and suspended in water, these light-activated nanoreactors produced hydrogen gas under visible and infrared light.
-
Research Briefing |
 Array of chiral nanoparticles discriminates between enantiomers
Array of chiral nanoparticles discriminates between enantiomers
When circularly polarized light hits an array of chiral gold nanoparticles, it generates polarized electric and magnetic waves across the surface of the nanoparticles. Chiral molecules can alter these resonances, providing a highly sensitive method to determine and quantify molecular chirality, even at very low concentrations.
-
Article |
 Enantioselective sensing by collective circular dichroism
Enantioselective sensing by collective circular dichroism
An array of 2D crystals of isotropic, 432-symmetric chiral gold nanoparticles is shown to exhibit collective resonances with a strong and uniform chiral near field, allowing enantioselective detection by the collective circular dichroism.
- Ryeong Myeong Kim
- , Ji-Hyeok Huh
- & Ki Tae Nam
-
Article |
 Chiral assemblies of pinwheel superlattices on substrates
Chiral assemblies of pinwheel superlattices on substrates
Chiroptically active pinwheel assemblies on substrates are formed by tetrahedral gold nanoparticles from the effective ‘compression’ of a perovskite-like, low-density phase, thereby enabling the manufacture of metastructured coatings with special chiroptical characteristics as identified by photon-induced near-field electron microscopy and chirality measures.
- Shan Zhou
- , Jiahui Li
- & Qian Chen
-
Article |
 Shape memory in self-adapting colloidal crystals
Shape memory in self-adapting colloidal crystals
Preparing crystals held together with macromolecular bonds can create shape memory materials that can be engineered to exhibit a wide range of reversible changes useful for chemical sensing, optics and robotics.
- Seungkyu Lee
- , Heather A. Calcaterra
- & Chad A. Mirkin
-
News Round-Up |
 Levitating nanoparticles, medieval-burial mystery and ancient femur
Levitating nanoparticles, medieval-burial mystery and ancient femur
The latest science news, in brief.
-
News |
 ‘Levitating’ nanoparticles could push the limits of quantum entanglement
‘Levitating’ nanoparticles could push the limits of quantum entanglement
Interaction between glass spheres suspended in a vacuum might one day lead to advances in quantum computing.
- Davide Castelvecchi
-
Nature Index |
 How cross-border collaboration underpins the nanoscience revolution
How cross-border collaboration underpins the nanoscience revolution
Five highly cited papers that have drawn on the strengths of international partnership.
- Bec Crew
- , David Payne
- & Benjamin Plackett
-
Technology Feature |
 Light-based sensors set to revolutionize on-site testing
Light-based sensors set to revolutionize on-site testing
Nanophotonic biosensors exploit light’s properties to detect molecular interactions in real time at the point of need.
- Diana Kwon
-
News |
 Molecular motor is ‘DNA origami’ milestone
Molecular motor is ‘DNA origami’ milestone
Rotating device driven by Brownian motion could pave the way for more advanced nanoscale machines.
- Davide Castelvecchi
-
Article |
 Triplet fusion upconversion nanocapsules for volumetric 3D printing
Triplet fusion upconversion nanocapsules for volumetric 3D printing
. Triplet fusion upconversion nanocapsules dispersed in a photopolymerizable resin allow for volumetric 3D printing at low-power continuous-wave excitation without support structures.
- Samuel N. Sanders
- , Tracy H. Schloemer
- & Daniel N. Congreve
-
Article |
 Metastable hexagonal close-packed palladium hydride in liquid cell TEM
Metastable hexagonal close-packed palladium hydride in liquid cell TEM
A metastable palladium hydride is synthesized where the unique environment in the liquid cell, namely the limited quantity of Pd precursors and the continuous supply of H, resulted in the formation of the hcp phase.
- Jaeyoung Hong
- , Jee-Hwan Bae
- & Dong Won Chun
-
News & Views |
 Nanoparticle asymmetry shapes an immune response
Nanoparticle asymmetry shapes an immune response
The chirality, or handedness, of nanoparticles is shown to be a key factor in determining how well such particles engage with the immune system — a finding that might help to inform the design of vaccines and anticancer therapeutics.
- Alexander Hooftman
- & Luke A. J. O’Neill
-
Article |
 Mastering the surface strain of platinum catalysts for efficient electrocatalysis
Mastering the surface strain of platinum catalysts for efficient electrocatalysis
By depositing platinum shells on palladium-based nanocubes, the strain can be controlled by through phosphorization and dephosphorization, making it possible to tune the electrocatalytic activity of the platinum shells.
- Tianou He
- , Weicong Wang
- & Mingshang Jin
-
News & Views |
 Hybrid light–matter states formed in self-assembling cavities
Hybrid light–matter states formed in self-assembling cavities
Tiny flakes of metal suspended in a solution have been observed to self-assemble into pairs separated by a narrow gap — offering a tunable system for studying combinations of light and matter known as polaritons.
- Johannes Feist
-
Article |
 Tunable self-assembled Casimir microcavities and polaritons
Tunable self-assembled Casimir microcavities and polaritons
Gold nanoflake pairs form by self-assembly in an aqueous ligand solution and offer stable and tunable microcavities by virtue of equilibrium between attractive Casimir forces and repulsive electrostatic forces.
- Battulga Munkhbat
- , Adriana Canales
- & Timur O. Shegai
-
Article |
 Perovskite-type superlattices from lead halide perovskite nanocubes
Perovskite-type superlattices from lead halide perovskite nanocubes
Through precise structural engineering, perovskite nanocrystals are co-assembled with other nanocrystal materials to form a range of binary and ternary perovskite-type superlattices that exhibit superfluorescence.
- Ihor Cherniukh
- , Gabriele Rainò
- & Maksym V. Kovalenko
-
Article |
 Macroscopic materials assembled from nanoparticle superlattices
Macroscopic materials assembled from nanoparticle superlattices
Polymer-covered inorganic nanoparticles are designed to self-assemble into micrometre-sized superlattice crystallites that can subsequently be built into freestanding centimetre-scale solids with hierarchical order across seven orders of magnitude.
- Peter J. Santos
- , Paul A. Gabrys
- & Robert J. Macfarlane
-
Article |
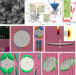 Thermally reconfigurable monoclinic nematic colloidal fluids
Thermally reconfigurable monoclinic nematic colloidal fluids
Dispersion of colloidal disks in a nematic liquid crystal reveals several low-symmetry phases, including monoclinic colloidal nematic order, with interchange between them achieved through variations in temperature, concentration and surface charge.
- Haridas Mundoor
- , Jin-Sheng Wu
- & Ivan I. Smalyukh
-
News & Views |
 Giant photon avalanches observed in nanoparticles
Giant photon avalanches observed in nanoparticles
In some materials, the absorption of a single photon can trigger a chain reaction that produces a large burst of light. The discovery of these photon avalanches in nanostructures opens the way to imaging and sensing applications.
- Andries Meijerink
- & Freddy T. Rabouw
-
Article |
 Giant nonlinear optical responses from photon-avalanching nanoparticles
Giant nonlinear optical responses from photon-avalanching nanoparticles
Room-temperature photon avalanching realized in single thulium-doped upconverting nanocrystals enables super-resolution imaging at near-infrared wavelengths of maximal biological transparency and provides a material platform potentially suitable for other optical technologies.
- Changhwan Lee
- , Emma Z. Xu
- & P. James Schuck
-
Article |
 Spin-enhanced nanodiamond biosensing for ultrasensitive diagnostics
Spin-enhanced nanodiamond biosensing for ultrasensitive diagnostics
Lateral-flow in vitro diagnostic assays based on fluorescent nanodiamonds, in which microwave-based spin manipulation is used to increase sensitivity, are demonstrated using the biotin–avidin model and by the single-copy detection of HIV-1 RNA.
- Benjamin S. Miller
- , Léonard Bezinge
- & Rachel A. McKendry
-
Article |
 Plasmonic enhancement of stability and brightness in organic light-emitting devices
Plasmonic enhancement of stability and brightness in organic light-emitting devices
Plasmonic effects in organic light-emitting devices, which are normally considered a source of energy loss, are harnessed to enhance the stability of these devices while maintaining operational efficiency.
- Michael A. Fusella
- , Renata Saramak
- & Julia J. Brown
-
Review Article |
 Single-particle spectroscopy for functional nanomaterials
Single-particle spectroscopy for functional nanomaterials
Single-particle spectroscopic techniques that provide insights into the fundamental photophysical properties of functional nanomaterials are reviewed.
- Jiajia Zhou
- , Alexey I. Chizhik
- & Dayong Jin
-
Article |
 Design and synthesis of multigrain nanocrystals via geometric misfit strain
Design and synthesis of multigrain nanocrystals via geometric misfit strain
Heteroepitaxy is used to precisely control the growth of Mn3O4 shells on the faces of a Co3O4 nanocube crystal, producing uniform grain boundary defects and highly ordered multigrain nanostructures.
- Myoung Hwan Oh
- , Min Gee Cho
- & Taeghwan Hyeon
-
News & Views |
 Crystallization tracked atom by atom
Crystallization tracked atom by atom
Atoms of a metal alloy have been tracked as they form crystal nuclei — the first ordered clusters of atoms or molecules produced during crystallization. The findings might help to develop a general nucleation theory.
- Peter G. Vekilov
-
Letter |
 Observing crystal nucleation in four dimensions using atomic electron tomography
Observing crystal nucleation in four dimensions using atomic electron tomography
Atomic electron tomography captures crystal nucleation in four dimensions in FePt nanoparticles, with the observed early-stage nucleation not consistent with classical nucleation theory.
- Jihan Zhou
- , Yongsoo Yang
- & Jianwei Miao
-
News |
 Night-vision ‘super-mice’ created using light-converting nanoparticles
Night-vision ‘super-mice’ created using light-converting nanoparticles
The particles bind to photoreceptors in the eyes and convert infrared wavelengths to visible light.
- Matthew Warren
-
Letter |
 Superstructures generated from truncated tetrahedral quantum dots
Superstructures generated from truncated tetrahedral quantum dots
Truncated tetrahedral nanocrystals can self-assemble into one-, two- and three-dimensional superstructures.
- Yasutaka Nagaoka
- , Rui Tan
- & Ou Chen
-
News |
 Making a microscopic swarm move through a maze
Making a microscopic swarm move through a maze
This magnetic ‘microswarm' makes manouvering around a maze look… mostly manageable, despite being made of millions of individual nanoparticles.
- Shamini Bundell
-
Letter |
 All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystal scintillators
All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystal scintillators
All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystals containing caesium and lead provide low-cost, flexible and solution-processable scintillators that are highly sensitive to X-ray irradiation and emit radioluminescence that is colour-tunable across the visible spectrum.
- Qiushui Chen
- , Jing Wu
- & Xiaogang Liu
-
Letter |
 Self-assembly of highly symmetrical, ultrasmall inorganic cages directed by surfactant micelles
Self-assembly of highly symmetrical, ultrasmall inorganic cages directed by surfactant micelles
Machine-learning algorithms are used to generate single-particle three-dimensional reconstructions, revealing that highly symmetrical dodecahedral silica cages, around 10 nm in size, self-assemble in the presence of surfactant micelles.
- Kai Ma
- , Yunye Gong
- & Ulrich Wiesner
-
Letter |
 Amino-acid- and peptide-directed synthesis of chiral plasmonic gold nanoparticles
Amino-acid- and peptide-directed synthesis of chiral plasmonic gold nanoparticles
Chirality can be ‘encoded’ into gold nanoparticles by introducing chiral amino acids or peptides during the growth process, leading to the formation of helicoid morphologies.
- Hye-Eun Lee
- , Hyo-Yong Ahn
- & Ki Tae Nam
-
Letter |
 Bright triplet excitons in caesium lead halide perovskites
Bright triplet excitons in caesium lead halide perovskites
The lowest-energy exciton state in caesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals is shown to be a bright triplet state, contrary to expectations that lowest-energy excitons should always be dark.
- Michael A. Becker
- , Roman Vaxenburg
- & Alexander L. Efros
-
Nature Podcast |
 Podcast: Electric-eel batteries, magma viscocity, and protein shells
Podcast: Electric-eel batteries, magma viscocity, and protein shells
-
Letter |
 Evolution of a designed protein assembly encapsulating its own RNA genome
Evolution of a designed protein assembly encapsulating its own RNA genome
Computationally designed icosahedral protein-based assemblies can protect their genetic material and evolve in biochemical environments, suggesting a route to the custom design of synthetic nanomaterials for non-viral drug delivery.
- Gabriel L. Butterfield
- , Marc J. Lajoie
- & David Baker

 Nanoparticle fix opens up tricky technique to forensic applications
Nanoparticle fix opens up tricky technique to forensic applications