Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Digital data storage on DNA tape using CRISPR base editors
Digital data storage on DNA tape using CRISPR base editors
DNA is an alternative to data storage materials for its durability, density, and energetics. Here the authors demonstrate the storage of digital information on DNA molecules using base-editing.
- Afsaneh Sadremomtaz
- , Robert F. Glass
- & Reza Zadegan
-
Article
| Open Access Next-generation CRISPR gene-drive systems using Cas12a nuclease
Next-generation CRISPR gene-drive systems using Cas12a nuclease
One method for reducing the impact of vector-borne diseases is through the use of CRISPR-based gene drives, which manipulate insect populations due to their ability to rapidly propagate desired genetic traits into a target population. Here the authors describe a Cas12a gene drive system whose activity can be finetuned in a temperature-dependent manner.
- Sara Sanz Juste
- , Emily M. Okamoto
- & Víctor López Del Amo
-
Article
| Open Access Deep flanking sequence engineering for efficient promoter design using DeepSEED
Deep flanking sequence engineering for efficient promoter design using DeepSEED
Designing promoters with desired properties is crucial in synthetic biology. Here, authors introduce DeepSEED, an AI-aided flanking sequence optimisation framework which combines expert knowledge with deep learning techniques to efficiently design promoters in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
- Pengcheng Zhang
- , Haochen Wang
- & Xiaowo Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoparticle display of prefusion coronavirus spike elicits S1-focused cross-reactive antibody response against diverse coronavirus subgenera
Nanoparticle display of prefusion coronavirus spike elicits S1-focused cross-reactive antibody response against diverse coronavirus subgenera
Most current anti-coronavirus nanoparticle vaccines target epitopes within the RBD. Here, the authors developed nanoparticles displaying an array of spike fusion proteins derived from various coronaviruses and show that immunizing mice with these vaccines elicits broad and potent cross-reactive antibodies.
- Geoffrey B. Hutchinson
- , Olubukola M. Abiona
- & Kizzmekia S. Corbett-Helaire
-
Article
| Open Access A digital twin for DNA data storage based on comprehensive quantification of errors and biases
A digital twin for DNA data storage based on comprehensive quantification of errors and biases
Archiving data in synthetic DNA offers unprecedented storage density and longevity. To understand how experimental choices affect the integrity of digital data stored in DNA, the authors study the evolution of errors and bias and with a digital twin they supply tools for experimental planning and design of error-correcing codes.
- Andreas L. Gimpel
- , Wendelin J. Stark
- & Robert N. Grass
-
Comment
| Open AccessEngineered and natural gene drives: mechanistically the same, yet not same in kind
We propose the use of the terms natural gene drive (NGD) and engineered gene drive (EGD) arguing against James et al.
1 , who think both should be included within the term “gene drive”, based on their mechanistic similarities.- Raul F. Medina
- & Jennifer Kuzma
-
Article
| Open Access A split and inducible adenine base editor for precise in vivo base editing
A split and inducible adenine base editor for precise in vivo base editing
TadA deaminases widely used in many base editors lack post-translational control in cells. Here the authors report a split adenine base editor (sABE) using chemically induced dimerisation (CID) to control the catalytic activity of TadA8e and show this can be used for PCSK9 gene editing in the mouse liver.
- Hongzhi Zeng
- , Qichen Yuan
- & Xue Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable RNA detection with CRISPR-Cas12a
Programmable RNA detection with CRISPR-Cas12a
Cas12a is widely used in diagnostic platforms. Here the authors show that Cas12a can be programmed to directly detect RNA substrates, this is due to the 3’-end of the crRNA tolerating both RNA and DNA substrates: they use this to report a method, SAHARA, to detect RNA sequences.
- Santosh R. Rananaware
- , Emma K. Vesco
- & Piyush K. Jain
-
Article
| Open Access Next generation synthetic memory via intercepting recombinase function
Next generation synthetic memory via intercepting recombinase function
Memory is a basic tenet of intelligent biological systems. Here the authors engineered a programmable and expandable iteration of recombinase-based synthetic memory (interception) that functions post-translation, resulting in faster recombination.
- Andrew E. Short
- , Dowan Kim
- & Corey J. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access CD98hc is a target for brain delivery of biotherapeutics
CD98hc is a target for brain delivery of biotherapeutics
New delivery platforms are needed to allow broader application of biotherapeutics for CNS diseases. Here, the authors show enhanced CNS delivery with a transport vehicle engineered to bind CD98hc, a highly expressed target at the blood-brain barrier.
- Kylie S. Chew
- , Robert C. Wells
- & Mihalis S. Kariolis
-
Article
| Open Access Programming conformational cooperativity to regulate allosteric protein-oligonucleotide signal transduction
Programming conformational cooperativity to regulate allosteric protein-oligonucleotide signal transduction
Conformational cooperativity is a universal molecular effect mechanism and plays a critical role in signalling pathways. Here the authors present a programmable conformational cooperativity strategy to construct the oligo-protein signal transduction platform for logic operations and gene regulations which can be cooperatively regulated by conformational signals.
- Yuan Liang
- , Yunkai Qie
- & Cheng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Biosensor Guided Polyketide Synthases Engineering for Optimization of Domain Exchange Boundaries
Biosensor Guided Polyketide Synthases Engineering for Optimization of Domain Exchange Boundaries
Engineering polyketide synthases can be challenging due to the absence of efficient high-throughput methods. Here, the authors used a solubility biosensor to identify stable variants from libraries of modified polyketide synthases.
- Elias Englund
- , Matthias Schmidt
- & Jay D. Keasling
-
Article
| Open Access Phenotypically complex living materials containing engineered cyanobacteria
Phenotypically complex living materials containing engineered cyanobacteria
Engineered living materials (ELMs) are emerging as a field at the intersection of materials science and synthetic biology. Here, the authors describe a photosynthetic ELM composed of genetically engineered cyanobacteria in a hydrogel matrix, capable of bioremediation and inducible cell death.
- Debika Datta
- , Elliot L. Weiss
- & Jonathan K. Pokorski
-
Article
| Open Access A multiplexed bacterial two-hybrid for rapid characterization of protein–protein interactions and iterative protein design
A multiplexed bacterial two-hybrid for rapid characterization of protein–protein interactions and iterative protein design
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) are crucial for biological functions and have applications ranging from drug design to synthetic cell circuits. Here the authors develop an assay and computational methods to identify more orthogonal coiled-coil pairs, critical for biological processes and drug design.
- W. Clifford Boldridge
- , Ajasja Ljubetič
- & Sriram Kosuri
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and rational engineering of PET hydrolase with both mesophilic and thermophilic PET hydrolase properties
Discovery and rational engineering of PET hydrolase with both mesophilic and thermophilic PET hydrolase properties
Extensive research efforts have been directed towards the development of PET hydrolases with improved activity, but template enzymes used are limited. Here, the authors report a PET hydrolase from Cryptosporangium aurantiacum (CaPETase) that exhibits high thermostability and PET degradation activity at ambient temperatures and determine its crystal structure.
- Hwaseok Hong
- , Dongwoo Ki
- & Kyung-Jin Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered reporter phages for detection of Escherichia coli, Enterococcus, and Klebsiella in urine
Engineered reporter phages for detection of Escherichia coli, Enterococcus, and Klebsiella in urine
Although diagnosis of urinary tract infections has improved through the use of point-of-care molecular technologies, they are however limited by poor specificity and / or sensitivity, and requirement of laboratory resources. In this work, the authors develop a bacteriophage-based diagnostic assay for the detection of prevalent uropathogens.
- Susanne Meile
- , Jiemin Du
- & Samuel Kilcher
-
Article
| Open Access Liver lipophagy ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through extracellular lipid secretion
Liver lipophagy ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through extracellular lipid secretion
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) starts with lipid droplet accumulation in the liver that eventually causes inflammation and fibrosis. Here, authors use lipophagy activators to limit the accumulation of lipids in the liver and show that this can prevent disease progression in a mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
- Yoshito Minami
- , Atsushi Hoshino
- & Satoaki Matoba
-
Article
| Open Access An unnatural enzyme with endonuclease activity towards small non-coding RNAs
An unnatural enzyme with endonuclease activity towards small non-coding RNAs
Endonucleases play crucial roles in various biological processes but endonucleases that target small non-coding RNAs have not been reported. Here, the authors combined the metal binding non-canonical amino acid BpyAla and a high affinity binder to engineer a catalyst that degrades small non-coding RNAs.
- Noreen Ahmed
- , Nadine Ahmed
- & John Paul Pezacki
-
Article
| Open Access Resource-aware construct design in mammalian cells
Resource-aware construct design in mammalian cells
Resource competition can be the cause of unintended coupling between co-expressed genetic constructs. Here the authors quantify the resource load imposed by different mammalian genetic components to identify construct designs with increased performance and reduced resource footprint.
- Roberto Di Blasi
- , Mara Pisani
- & Francesca Ceroni
-
Article
| Open Access Isolation of full-length IgG antibodies from combinatorial libraries expressed in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli
Isolation of full-length IgG antibodies from combinatorial libraries expressed in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli
Discovery of full-length antibodies can be slow and labor intensive. Here, the authors describe a robust genetic assay for facile isolation of IgG antibodies from combinatorial libraries expressed in the cytoplasm of redox-engineered bacteria.
- Michael-Paul Robinson
- , Jinjoo Jung
- & Matthew P. DeLisa
-
Article
| Open Access A single-domain green fluorescent protein catenane
A single-domain green fluorescent protein catenane
Natural proteins exhibit rich structural diversity based on the folds of an invariably linear chain. Here the authors design a single-domain GFP catenane as the counterpart of conventional linear GFP with enhanced thermal resilience and to provide a robust scaffold for making fusion protein catenanes.
- Zhiyu Qu
- , Jing Fang
- & Wen-Bin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic model for core modifying region of human fatty acid synthase in complex with Denifanstat
Atomic model for core modifying region of human fatty acid synthase in complex with Denifanstat
Here, the authors develop a protein engineering method that enables high-resolution structural biology study of human fatty acid synthase. Using this technique, they uncover unique structural features of the enzyme and the mechanism of its inhibition by an anticancer drug Denifanstat.
- S. M. Naimul Hasan
- , Jennifer W. Lou
- & Mohammad T. Mazhab-Jafari
-
Article
| Open Access A Cas3-base editing tool for targetable in vivo mutagenesis
A Cas3-base editing tool for targetable in vivo mutagenesis
In vivo mutagenesis allows improving cell factories through directed evolution. Here, the authors present CoMuTER, a tool for targetable random mutagenesis of complete biosynthetic pathways using a Cas3 enzyme fused to a cytidine deaminase.
- Anna Zimmermann
- , Julian E. Prieto-Vivas
- & Kevin J. Verstrepen
-
Article
| Open Access NERNST: a genetically-encoded ratiometric non-destructive sensing tool to estimate NADP(H) redox status in bacterial, plant and animal systems
NERNST: a genetically-encoded ratiometric non-destructive sensing tool to estimate NADP(H) redox status in bacterial, plant and animal systems
NADP(H) is a crucial cofactor, acting as a reducing agent in numerous pathways in living organisms. Here the authors report a ratiometric biosensor named NERNST, which can be used to estimate the NADP(H) redox status in bacterial, plant and animal cells and organelles.
- Pamela E. Molinari
- , Adriana R. Krapp
- & Matias D. Zurbriggen
-
Article
| Open Access Design of bacteriophage T4-based artificial viral vectors for human genome remodeling
Design of bacteriophage T4-based artificial viral vectors for human genome remodeling
Safe delivery of genes is needed for gene therapy. Here the authors build “artificial viral vectors” (AVVs) by engineering the well-characterised structural components of bacteriophage T4: the large capacity, all-in-one, multiplex, programmable, and phage-based AVV nanomaterials have potential for gene therapy.
- Jingen Zhu
- , Himanshu Batra
- & Venigalla B. Rao
-
Article
| Open Access Post-translational covalent assembly of CAR and synNotch receptors for programmable antigen targeting
Post-translational covalent assembly of CAR and synNotch receptors for programmable antigen targeting
Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) and synthetic Notch (synNotch) receptors are promising platforms for cell-based immunotherapies. Here, the authors develop highly programmable versions of these receptors that can be universally targeted to antigens of interest through covalent enzyme chemistry.
- Elisa Ruffo
- , Adam A. Butchy
- & Jason Lohmueller
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered repeat proteins as scaffolds to assemble multi-enzyme systems for efficient cell-free biosynthesis
Engineered repeat proteins as scaffolds to assemble multi-enzyme systems for efficient cell-free biosynthesis
Multi-enzymatic cascades benefit from precise nanometric organization but achieving this using available scaffolds is challenging. Here the authors present strategy for organizing multienzymatic systems using a protein scaffold based on TRAP domains, and demonstrate improved catalytic output.
- Alba Ledesma-Fernandez
- , Susana Velasco-Lozano
- & Aitziber L. Cortajarena
-
Article
| Open Access A blueprint for a synthetic genetic feedback optimizer
A blueprint for a synthetic genetic feedback optimizer
Genetic modules are sensitive to changes in their context and to environmental perturbations. Here, the authors develop a genetic optimizer based on common synthetic biology parts to ensure optimal and robust cellular performance in diverse contexts.
- Andras Gyorgy
- , Amor Menezes
- & Murat Arcak
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning-driven multifunctional peptide engineering for sustained ocular drug delivery
Machine learning-driven multifunctional peptide engineering for sustained ocular drug delivery
Sustained drug delivery is critical for patient adherence to chronic disease treatments. Here the authors apply machine learning to engineer multifunctional peptides with high melanin binding, high cell-penetration, and low cytotoxicity, enhancing the duration and efficacy of peptide-drug conjugates for sustained ocular delivery.
- Henry T. Hsueh
- , Renee Ti Chou
- & Laura M. Ensign
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering α-carboxysomes into plant chloroplasts to support autotrophic photosynthesis
Engineering α-carboxysomes into plant chloroplasts to support autotrophic photosynthesis
Engineering carboxysomes into crop chloroplasts is a potential route to improve photosynthesis and crop yield. Here, the authors engineer functional CO2-fixing modules into tobacco chloroplasts to improve their photosynthesis and productivity.
- Taiyu Chen
- , Marta Hojka
- & Lu-Ning Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid assembly of SARS-CoV-2 genomes reveals attenuation of the Omicron BA.1 variant through NSP6
Rapid assembly of SARS-CoV-2 genomes reveals attenuation of the Omicron BA.1 variant through NSP6
Omicron BA.1 is attenuated in infection models though the precise nature of this attenuation remains unknown as generating replication-competent viral genomes is challenging. Here the authors present pGLUE, a plasmid-based viral genome assembly and rescue strategy, to systematically characterize Omicron mutations and show that Omicron NSP6 has weakened lipid flow to replication organelles and reduced viral RNA replication.
- Taha Y. Taha
- , Irene P. Chen
- & Melanie Ott
-
Article
| Open Access Trumpet is an operating system for simple and robust cell-free biocomputing
Trumpet is an operating system for simple and robust cell-free biocomputing
Biological computation is becoming a viable and fast-growing alternative to traditional electronic computing. Here the authors present Trumpet, which uses DNA and enzymes to build logic gate circuits with amplified fluorescent readout.
- Judee A. Sharon
- , Chelsea Dasrath
- & Katarzyna P. Adamala
-
Article
| Open Access CAR-neutrophil mediated delivery of tumor-microenvironment responsive nanodrugs for glioblastoma chemo-immunotherapy
CAR-neutrophil mediated delivery of tumor-microenvironment responsive nanodrugs for glioblastoma chemo-immunotherapy
Neutrophil-mediated drug delivery has been investigated as a therapeutic approach for brain tumors. Here the authors report the anti-tumor activity of chlorotoxin-directed CAR neutrophils delivering chemodrug-loaded nanoparticles in preclinical glioblastoma models.
- Yun Chang
- , Xuechao Cai
- & Xiaoping Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable mammalian translational modulators by CRISPR-associated proteins
Programmable mammalian translational modulators by CRISPR-associated proteins
The scarcity of qualified RNA-binding proteins hinders the development of artificial translational regulators and synthetic gene circuits. Here, the authors repurposed CRISPR-Cas proteins as translational regulators to build synthetic circuits.
- Shunsuke Kawasaki
- , Hiroki Ono
- & Hirohide Saito
-
Article
| Open Access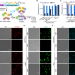 Controlling protein stability with SULI, a highly sensitive tag for stabilization upon light induction
Controlling protein stability with SULI, a highly sensitive tag for stabilization upon light induction
Tools for the spatiotemporal control of protein abundance are valuable in studying diverse complex biological processes. Here, authors engineered a protein tag which is stabilized upon light induction but which quickly degrades the protein of interest in the dark, demonstrating control of protein stability in yeast and zebrafish.
- Miaowei Mao
- , Yajie Qian
- & Yi Yang
-
Article
| Open Access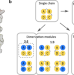 Segmentation strategy of de novo designed four-helical bundles expands protein oligomerization modalities for cell regulation
Segmentation strategy of de novo designed four-helical bundles expands protein oligomerization modalities for cell regulation
New protein assemblies can be introduced through the fusion of selected proteins with di/oligomerization domains, which interact specifically with their partners but not with other cellular proteins. Here the authors demonstrate that a single four-helical bundle protein can be segmented into several different parts, defining up to four interacting molecules for enzyme reconstitution, gene expression, or CAR-T cell regulation.
- Estera Merljak
- , Benjamin Malovrh
- & Roman Jerala
-
Article
| Open Access An integrase toolbox to record gene-expression during plant development
An integrase toolbox to record gene-expression during plant development
Synthetic circuits that can record in vivo signaling networks is critical in elucidating developmental process. Here, the authors describe the engineering and application of synthetic in vivo recorders with different promoters that can drive spatiotemporally-specific integrase switching during lateral root initiation.
- Sarah Guiziou
- , Cassandra J. Maranas
- & Jennifer L. Nemhauser
-
Article
| Open Access Small molecule-nanobody conjugate induced proximity controls intracellular processes and modulates endogenous unligandable targets
Small molecule-nanobody conjugate induced proximity controls intracellular processes and modulates endogenous unligandable targets
Induced proximity can be used to control diverse cellular processes. Here, the authors develop nanobody-based proximity inducers called SNACIPs, which can be used to regulate either tagged or endogenous proteins, and demonstrate their use in blocking microtubule nucleation for tumour growth inhibition in vivo.
- Xiaofeng Sun
- , Chengjian Zhou
- & Xi Chen
-
Article
| Open Access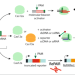 CRISPR-induced DNA reorganization for multiplexed nucleic acid detection
CRISPR-induced DNA reorganization for multiplexed nucleic acid detection
Nucleic acid sensing involving CRISPR technologies is powerful but has certain limitations, such as PAM sequence requirements and limited multiplexing. Here, authors report a CRISPR-based barcoding technology which enables multiple outputs from any target sequence, based on cis- and trans-cleavage.
- Margot Karlikow
- , Evan Amalfitano
- & Keith Pardee
-
Article
| Open Access Improving adenine and dual base editors through introduction of TadA-8e and Rad51DBD
Improving adenine and dual base editors through introduction of TadA-8e and Rad51DBD
There is a low efficiency of A-to-G base conversion in at specific positions using base editors. Here the authors fuse ABE8e with the Rad51 DNA-binding domain to generate a hyperactive ABE allowing improved A-to-G editing efficiency at the region proximal to the PAM and improved simultaneous A/C conversion efficiency.
- Niannian Xue
- , Xu Liu
- & Xiaohui Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access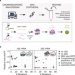 Community science designed ribosomes with beneficial phenotypes
Community science designed ribosomes with beneficial phenotypes
While the ribosome has been harnessed for synthetic biology, designing ribosomes has remained challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate a community science approach for rational design of ribosomes with beneficial properties.
- Antje Krüger
- , Andrew M. Watkins
- & Michael C. Jewett
-
Article
| Open Access DddA homolog search and engineering expand sequence compatibility of mitochondrial base editing
DddA homolog search and engineering expand sequence compatibility of mitochondrial base editing
There is a need to improve and expand mitochondrial base editing tools. Here the authors identify a DddA homolog from Simiaoa sunii (Ddd_Ss) which can efficiently deaminate cytosine in dsDNA; they develop cytosine base editors and introduce mutations at multiple mitochondrial DNA loci.
- Li Mi
- , Ming Shi
- & Yangming Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and optimization of a broadly-neutralizing human monoclonal antibody against long-chain α-neurotoxins from snakes
Discovery and optimization of a broadly-neutralizing human monoclonal antibody against long-chain α-neurotoxins from snakes
The treatment of snakebite envenoming is currently suboptimal. Existing antivenoms often lack efficacy and may cause adverse reactions. Here, the authors derive, develop, and demonstrate the utility of toxin-specific broadly-neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies with established reactivity across related venom toxins from different snake species and show efficacy in rodent models.
- Line Ledsgaard
- , Jack Wade
- & Aneesh Karatt-Vellatt
-
Article
| Open Access Systematically attenuating DNA targeting enables CRISPR-driven editing in bacteria
Systematically attenuating DNA targeting enables CRISPR-driven editing in bacteria
Genome editing in bacteria normally requires efficient recombination and high transformation efficiencies, which often isn’t. Here the authors report that systematically attenuating DNA targeting activity enables RecA-mediated repair in different bacteria, allowing chromosomal cleavage to drive editing.
- Daphne Collias
- , Elena Vialetto
- & Chase L. Beisel
-
Article
| Open Access Germline T cell receptor exchange results in physiological T cell development and function
Germline T cell receptor exchange results in physiological T cell development and function
The currently available transgenic T cell receptor (TCR) models represent high affinity antigen-TCR interactions. Authors here present an alternative approach to target an exogenous TCR into the physiological Trac locus in the germline of mice, which uncovers that the natural genomic context for TCRs can enhance the antigen sensitivity of lower affinity TCRs and enables the physiologic range of antigen-TCR interaction and a gene dosage dependent mechanism of central tolerance.
- Meagan R. Rollins
- , Jackson F. Raynor
- & Ingunn M. Stromnes
-
Article
| Open Access A split ribozyme that links detection of a native RNA to orthogonal protein outputs
A split ribozyme that links detection of a native RNA to orthogonal protein outputs
RNA provides a unique readout of a cell’s identity, physiologic status, and phenotype. Here the authors deliver an RNA sensing system that can use the information contained within cellular RNA to selectively control the activity of genetic programs.
- Lauren Gambill
- , August Staubus
- & James Chappell
-
Article
| Open Access A modular vaccine platform enabled by decoration of bacterial outer membrane vesicles with biotinylated antigens
A modular vaccine platform enabled by decoration of bacterial outer membrane vesicles with biotinylated antigens
Antigen display on outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) can be difficult to control and highly variable. Here, the authors describe a universal approach called AvidVax for linking biotinylated antigens to the exterior of OMVs and enabling rapid vaccine assembly.
- Kevin B. Weyant
- , Ayomide Oloyede
- & Matthew P. DeLisa
-
Article
| Open Access TadA orthologs enable both cytosine and adenine editing of base editors
TadA orthologs enable both cytosine and adenine editing of base editors
Properties of cytidine and adenosine deaminases lead to off-target effects for cytosine base editors (CBEs) and adenine base editors (ABEs). Here the authors report that 25 TadA orthologs could be engineered to generate functional ABEs, CBEs or ACBEs via single/double mutations with minimised off-targets.
- Shuqian Zhang
- , Bo Yuan
- & Tian-Lin Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access TadA reprogramming to generate potent miniature base editors with high precision
TadA reprogramming to generate potent miniature base editors with high precision
Hypercompact CRISPR-Cas12f systems have been engineered to generate miniABEs but these have limitations. Here the authors generate Cas12f-derived miniCBEs and develop miniABEs with improved editing and targeting scopes; they use these to correct pathogenic mutations in cell lines and introduce mutations in vivo.
- Shuqian Zhang
- , Liting Song
- & Tian-Lin Cheng

 A robust yeast biocontainment system with two-layered regulation switch dependent on unnatural amino acid
A robust yeast biocontainment system with two-layered regulation switch dependent on unnatural amino acid