Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable human histone phosphorylation and gene activation using a CRISPR/Cas9-based chromatin kinase
Programmable human histone phosphorylation and gene activation using a CRISPR/Cas9-based chromatin kinase
Histone phosphorylation is a ubiquitous post-translational modification. Here the authors present a programmable chromatin kinase, dCas9-dMSK1, that enables controlled histone phosphorylation and specific gene activation.
- Jing Li
- , Barun Mahata
- & Isaac B. Hilton
-
Article
| Open Access A glucose meter interface for point-of-care gene circuit-based diagnostics
A glucose meter interface for point-of-care gene circuit-based diagnostics
Getting synthetic biology circuit-based sensors into field applications is still a challenge. Here the authors combine a circuit sensor with a glucose meter for small analyte and nucleic acid detection.
- Evan Amalfitano
- , Margot Karlikow
- & Keith Pardee
-
Article
| Open Access Direct control of CAR T cells through small molecule-regulated antibodies
Direct control of CAR T cells through small molecule-regulated antibodies
Many next-generation antibody therapeutics have enhanced potency but the risk of adverse events. Here the authors develop a conditionally activated, single-module CAR.
- Spencer Park
- , Edward Pascua
- & Javier Chaparro-Riggers
-
Article
| Open Access Posttranslational chemical installation of azoles into translated peptides
Posttranslational chemical installation of azoles into translated peptides
Azoles are five-membered heterocycles found in peptidic natural products and synthetic peptiodomimetics. Here the authors demonstrate a posttranslational chemical modification method for in vitro ribosomal synthesis of peptides with exotic azole groups at specific positions.
- Haruka Tsutsumi
- , Tomohiro Kuroda
- & Hiroaki Suga
-
Article
| Open Access A synthetic BRET-based optogenetic device for pulsatile transgene expression enabling glucose homeostasis in mice
A synthetic BRET-based optogenetic device for pulsatile transgene expression enabling glucose homeostasis in mice
Pulsing cellular dynamics in genetic circuits have been shown to provide critical capabilities to cells in diverse cellular activities. Here the authors show a synthetic BRET-based transgene expression system that allows pulsatile and quantitative activation of gene expression both in live cells and in vivo.
- Ting Li
- , Xianjun Chen
- & Yi Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Orthogonal translation enables heterologous ribosome engineering in E. coli
Orthogonal translation enables heterologous ribosome engineering in E. coli
Synthetic biologists often co-opt heterologous parts to affect new functions in living cells, yet such an approach has rarely been extended to structural components of the ribosome. Here, the authors describe generalizable methods to express ribosomes from divergent microbes in E. coli and maximize their function.
- Natalie S. Kolber
- , Ranan Fattal
- & Ahmed H. Badran
-
Review Article
| Open Access CRISPR technologies and the search for the PAM-free nuclease
CRISPR technologies and the search for the PAM-free nuclease
One of the key limitations of CRISPR-Cas-based genome editing techniques is the PAM dependency. Here, the authors review ongoing efforts towards realizing PAM-free nucleases, address potential consequences of eliminating PAM recognition, and propose an alternative nuclease repertoire covering all possible PAM sequences.
- Daphne Collias
- & Chase L. Beisel
-
Article
| Open Access Heme-binding enables allosteric modulation in an ancient TIM-barrel glycosidase
Heme-binding enables allosteric modulation in an ancient TIM-barrel glycosidase
Family 1 glycosidases (GH1) are present in the three domains of life and share classical TIM-barrel fold. Structural and biochemical analyses of a resurrected ancestral GH1 enzyme reveal heme binding, not known in its modern descendants. Heme rigidifies the TIM-barrel and allosterically enhances catalysis.
- Gloria Gamiz-Arco
- , Luis I. Gutierrez-Rus
- & Jose M. Sanchez-Ruiz
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered dual selection for directed evolution of SpCas9 PAM specificity
Engineered dual selection for directed evolution of SpCas9 PAM specificity
The PAM specificity of SpCas9 can be altered with positive selection during directed evolution. Here the authors use simultaneous positive and negative selection to improve activity on NAG PAMs while reducing activity on NGG PAMs.
- Gregory W. Goldberg
- , Jeffrey M. Spencer
- & Marcus B. Noyes
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed characterization of rationally designed promoter architectures deconstructs combinatorial logic for IPTG-inducible systems
Multiplexed characterization of rationally designed promoter architectures deconstructs combinatorial logic for IPTG-inducible systems
Precisely tuning the genetic response to environmental stimuli is a key step in engineering synthetic biology systems. Here, the authors profile 8269 IPTG-induced promoters to deconstruct the relationship between sequence architecture and gene expression.
- Timothy C. Yu
- , Winnie L. Liu
- & Guillaume Urtecho
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering and elucidation of the lipoinitiation process in nonribosomal peptide biosynthesis
Engineering and elucidation of the lipoinitiation process in nonribosomal peptide biosynthesis
Nonribosomal lipopeptides contain an acyl chain important for bioactivity, but its incorporation into the peptidyl backbone, mediated by the starter condensation (Cs) domain of nonribosomal peptide synthases, is not fully understood. Here, the authors show that acyl chains of different lengths can be obtained by engineering Cs domains and identify residues that determine the selectivity for acyl chains.
- Lin Zhong
- , Xiaotong Diao
- & Xiaoying Bian
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering of a bona fide light-operated calcium channel
Engineering of a bona fide light-operated calcium channel
Existing optogenetic methods to induce calcium mobilisation lack selectivity and specificity. Here, the authors design and engineer a single-component light-operated calcium channel to provide optical control over calcium signals and calcium-dependent physiological responses: LOCa.
- Lian He
- , Liuqing Wang
- & Yubin Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Site-specific incorporation of citrulline into proteins in mammalian cells
Site-specific incorporation of citrulline into proteins in mammalian cells
Citrullination of arginine is crucial for several physiological processes. Here the authors report the site-specific incorporation of citrulline into proteins in mammalian cells using an engineered tRNA synthetase/tRNA pair and a photocaged-citrulline.
- Santanu Mondal
- , Shu Wang
- & Paul R. Thompson
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo diversification of target genomic sites using processive base deaminase fusions blocked by dCas9
In vivo diversification of target genomic sites using processive base deaminase fusions blocked by dCas9
In vivo mutagenesis systems can often show restricted capabilities and deleterious off-site mutations. Here the authors fuse base deaminases to T7 RNA polymerase to mutate a target sequence and use dCas9 to define the boundaries of the diversified DNA.
- Beatriz Álvarez
- , Mario Mencía
- & Luis Ángel Fernández
-
Comment
| Open Access Synthetic biology 2020–2030: six commercially-available products that are changing our world
Synthetic biology 2020–2030: six commercially-available products that are changing our world
Synthetic biology will transform how we grow food, what we eat, and where we source materials and medicines. Here I have selected six products that are now on the market, highlighting the underlying technologies and projecting forward to the future that can be expected over the next ten years.
- Christopher A. Voigt
-
Perspective
| Open AccessThe biosecurity benefits of genetic engineering attribution
A key security challenge with biosecurity threats is determining the responsible actor. In this Perspective, the authors review recent developments in using genetic sequence to assign a lab-of-origin and the potential protection it provides against misuse of synthetic biology.
- Gregory Lewis
- , Jacob L. Jordan
- & Thomas V. Inglesby
-
Review Article
| Open Access Plant-based and cell-based approaches to meat production
Plant-based and cell-based approaches to meat production
Large-scale meat production can have negative impacts on public health, the environment and animal welfare. In this Review, the authors consider plant-based and cell-based approaches to meat production and the challenges they face.
- Natalie R. Rubio
- , Ning Xiang
- & David L. Kaplan
-
Article
| Open Access A machine learning toolkit for genetic engineering attribution to facilitate biosecurity
A machine learning toolkit for genetic engineering attribution to facilitate biosecurity
The potential for accidental or deliberate misuse of biotechnology is of concern for international biosecurity. Here the authors apply machine learning to DNA sequences and associated phenotypic data to facilitate genetic engineering attribution and identify country-of-origin and ancestral lab of engineered DNA sequences.
- Ethan C. Alley
- , Miles Turpin
- & Kevin M. Esvelt
-
Article
| Open Access Pathway engineering in yeast for synthesizing the complex polyketide bikaverin
Pathway engineering in yeast for synthesizing the complex polyketide bikaverin
Bikaverin is a fungal-derived tetracyclic polyketide with antibiotic, antifungal and anticancer properties. Here, the authors employ various pathway engineering strategies to achieve high level production of bikaverin in baker’s yeast.
- Meng Zhao
- , Yu Zhao
- & Jef D. Boeke
-
Perspective
| Open Access Building genomes to understand biology
Building genomes to understand biology
Advances in our ability to manipulate genetics leads to deeper understanding of biological systems. In this Perspective, the authors argue that synthetic genomics facilitates complex modifications that open up new areas of research.
- Alessandro L. V. Coradini
- , Cara B. Hull
- & Ian M. Ehrenreich
-
Article
| Open Access A nanobody suite for yeast scaffold nucleoporins provides details of the nuclear pore complex structure
A nanobody suite for yeast scaffold nucleoporins provides details of the nuclear pore complex structure
Characterizing the assembly of the nuclear pore complex (NPC) remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a set of nanobodies that recognize seven constituent nucleoporins, study their binding characteristics, and apply them to probe accessible and obstructed NPC surfaces in yeast.
- Sarah A. Nordeen
- , Kasper R. Andersen
- & Thomas U. Schwartz
-
Article
| Open Access An expanded palette of improved SPLICS reporters detects multiple organelle contacts in vitro and in vivo
An expanded palette of improved SPLICS reporters detects multiple organelle contacts in vitro and in vivo
The authors have previously reported split-GFP-based contact site sensors (SPLICS) to document endoplasmic reticulum/mitochondria contact sites. Here they extend this work and develop a range of improved SPLICS sensors to detect single and multiple organelle contact sites at different distances.
- Francesca Vallese
- , Cristina Catoni
- & Tito Calì
-
Article
| Open Access UMI-linked consensus sequencing enables phylogenetic analysis of directed evolution
UMI-linked consensus sequencing enables phylogenetic analysis of directed evolution
The success of protein evolution is dependent on the sequence context mutations are introduced into. Here the authors present UMIC-seq that allows consensus generation for closely related genes by using unique molecular identifiers linked to gene variants.
- Paul Jannis Zurek
- , Philipp Knyphausen
- & Florian Hollfelder
-
Article
| Open Access Streamlined inactivation, amplification, and Cas13-based detection of SARS-CoV-2
Streamlined inactivation, amplification, and Cas13-based detection of SARS-CoV-2
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the need for user-friendly diagnostic techniques. Here, the authors present SHINE, a streamlined and optimised Cas13-based method with accompanying smartphone app for visual diagnosis.
- Jon Arizti-Sanz
- , Catherine A. Freije
- & Cameron Myhrvold
-
Article
| Open Access DNA synthesis for true random number generation
DNA synthesis for true random number generation
Large volumes of true random numbers are needed for increasing requirements of secure data encryption. Here the authors use the stochastic nature of DNA synthesis to obtain millions of gigabytes of unbiased randomness.
- Linda C. Meiser
- , Julian Koch
- & Robert N. Grass
-
Article
| Open Access Predictive design of sigma factor-specific promoters
Predictive design of sigma factor-specific promoters
Automated design tools and tailored subunits are beneficial in fine-tuning all components of a complex genetic circuit. Here the authors create E. coli and B. subtilis promoter libraries using FACS and HTS, from which an online promoter design tool has been developed using CNN.
- Maarten Van Brempt
- , Jim Clauwaert
- & Marjan De Mey
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for tuning activity and membrane specificity of bacterial cytolysins
Structural basis for tuning activity and membrane specificity of bacterial cytolysins
Cholesterol-dependent cytolysins (CDCs) are bacterial pore-forming virulence factors. Cryo-EM structure of an early conformation of the CDC ILY from Streptococcus intermedius, bound to the human immune receptor CD59, provides insight into ILY oligomerization and role of cholesterol in membrane lysis.
- Nita R. Shah
- , Tomas B. Voisin
- & Doryen Bubeck
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable continuous evolution for the generation of diverse enzyme variants encompassing promiscuous activities
Scalable continuous evolution for the generation of diverse enzyme variants encompassing promiscuous activities
Generating rich ortholog diversity for biocatalysts can be difficult due to the deep evolutionary processes involved. Here the authors use OrthoRep to rapidly evolve TrpB to produce sequence-diverse variants with altered substrate promiscuity.
- Gordon Rix
- , Ella J. Watkins-Dulaney
- & Chang C. Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Adaptive laboratory evolution of native methanol assimilation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Adaptive laboratory evolution of native methanol assimilation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Methylotrophic metabolism enables growth on methanol, an alternative to sugar fermentation. Here the authors use adaptive laboratory evolution to uncover native methylotrophy capacity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
- Monica I. Espinosa
- , Ricardo A. Gonzalez-Garcia
- & Thomas C. Williams
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid and robust assembly and decoding of molecular tags with DNA-based nanopore signatures
Rapid and robust assembly and decoding of molecular tags with DNA-based nanopore signatures
Molecular tagging using DNA is an attractive option in cases that are not suitable for RFID tags or QR codes. Here, the authors present Porcupine, DNA tags directly classifiable from raw nanopore signals.
- Kathryn Doroschak
- , Karen Zhang
- & Jeff Nivala
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient population modification gene-drive rescue system in the malaria mosquito Anopheles stephensi
Efficient population modification gene-drive rescue system in the malaria mosquito Anopheles stephensi
Gene drives may be impeded by the generation of resistant alleles following NHEJ. Here the authors develop a recoded gene-drive rescue system for the malaria mosquito, Anopheles stephensi, that targets the drive to the kynurenine hydroxylase gene for negative selection against mutated alleles.
- Adriana Adolfi
- , Valentino M. Gantz
- & Anthony A. James
-
Article
| Open Access Gamma estimator of Jarzynski equality for recovering binding energies from noisy dynamic data sets
Gamma estimator of Jarzynski equality for recovering binding energies from noisy dynamic data sets
Measuring interaction energies from experimentally measured single-molecular interactions is challenging. Here, the authors report a gamma work distribution applied to single molecule pulling events for estimating peptide absorption free energy.
- Zhifeng Kuang
- , Kristi M. Singh
- & Rajesh R. Naik
-
Article
| Open Access Developing a pathway-independent and full-autonomous global resource allocation strategy to dynamically switching phenotypic states
Developing a pathway-independent and full-autonomous global resource allocation strategy to dynamically switching phenotypic states
A challenge for biological chemical production is the completion between synthetic circuits and host resources. Here the authors the authors use quorum sensing circuits and global mRNA decay to independently control two phenotypic states.
- Junjun Wu
- , Meijiao Bao
- & Zhijun Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesizing AND gate minigene circuits based on CRISPReader for identification of bladder cancer cells
Synthesizing AND gate minigene circuits based on CRISPReader for identification of bladder cancer cells
Synthetic biology logic gates can be used to distinguish healthy cells from cancer cells. Here the authors design minigene circuits that show more robust identification of cancer cells compared to traditional genetic circuits.
- Yuchen Liu
- , Weiren Huang
- & Zhiming Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered fluoride sensitivity enables biocontainment and selection of genetically-modified yeasts
Engineered fluoride sensitivity enables biocontainment and selection of genetically-modified yeasts
Non-antibiotic selection systems could also serve as biocontainment strategies. Here the authors present a fluoride sensitivity selection system for use in yeast.
- Justin I. Yoo
- , Susanna Seppälä
- & Michelle A. OʼMalley
-
Article
| Open Access Expanding detection windows for discriminating single nucleotide variants using rationally designed DNA equalizer probes
Expanding detection windows for discriminating single nucleotide variants using rationally designed DNA equalizer probes
The design of nucleic acid hybridisation probes is important for their use in DNA nanotechnology and biomedical applications. Here the authors use a DNA equalizer gate approach that expands the detection windows for improved sequence selectivity.
- Guan A. Wang
- , Xiaoyu Xie
- & Feng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Reprogramming bacterial protein organelles as a nanoreactor for hydrogen production
Reprogramming bacterial protein organelles as a nanoreactor for hydrogen production
The extreme oxygen sensitive character of hydrogenases is a longstanding issue for hydrogen production in bacteria. Here, the authors build carboxysome shells in E. coli and incorporate catalytically active hydrogenases and functional partners within the empty shell for the production of hydrogen.
- Tianpei Li
- , Qiuyao Jiang
- & Lu-Ning Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Low cost DNA data storage using photolithographic synthesis and advanced information reconstruction and error correction
Low cost DNA data storage using photolithographic synthesis and advanced information reconstruction and error correction
The current bottleneck for DNA data storage systems is the cost and speed of synthesis. Here, the authors use inexpensive, massively parallel light-directed synthesis and correct for a high error rate with a pipeline of encoding and reconstruction algorithms.
- Philipp L. Antkowiak
- , Jory Lietard
- & Robert N. Grass
-
Article
| Open Access GPAHex-A synthetic biology platform for Type IV–V glycopeptide antibiotic production and discovery
GPAHex-A synthetic biology platform for Type IV–V glycopeptide antibiotic production and discovery
Expansion of the chemical diversity of glycopeptide antibiotics (GPAs) to deal with the emergence and spread of GPA resistance is challenging. Here, the authors report a GPA synthetic biology platform in Streptomyces coelicolor for Type IV–V glycopeptide antibiotic production and discovery.
- Min Xu
- , Wenliang Wang
- & Gerard D. Wright
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering Af1521 improves ADP-ribose binding and identification of ADP-ribosylated proteins
Engineering Af1521 improves ADP-ribose binding and identification of ADP-ribosylated proteins
ADP-ribose binding macro domains facilitate the enrichment and detection of cellular ADP-ribosylation. Here, the authors generate an engineered macro domain with increased ADP-ribose affinity, improving the identification of ADP-ribosylated proteins by proteomics, western blot and immunofluorescence.
- Kathrin Nowak
- , Florian Rosenthal
- & Michael O. Hottiger
-
Comment
| Open Access The second decade of synthetic biology: 2010–2020
The second decade of synthetic biology: 2010–2020
Synthetic biology is among the most hyped research topics this century, and in 2010 it entered its teenage years. But rather than these being a problematic time, we’ve seen synthetic biology blossom and deliver many new technologies and landmark achievements.
- Fankang Meng
- & Tom Ellis
-
Article
| Open Access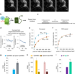 Resonance energy transfer sensitises and monitors in situ switching of LOV2-based optogenetic actuators
Resonance energy transfer sensitises and monitors in situ switching of LOV2-based optogenetic actuators
Cellular optogenetics applications are limited by difficulties in quantification and blue light toxicity. Here the authors design LOV2-based switches that use resonance energy transfer to overcome these concerns.
- Li-Li Li
- , Florence M. Klein
- & Michael J. Courtney
-
Article
| Open Access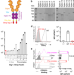 A versatile soluble siglec scaffold for sensitive and quantitative detection of glycan ligands
A versatile soluble siglec scaffold for sensitive and quantitative detection of glycan ligands
Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectins (Siglecs) are a family of immunomodulatory receptors expressed on cells of the hematopoietic lineage. Here the authors demonstrate an approach for the identification of the glycan ligands of Siglecs, which is also applicable to other families of glycan-binding proteins.
- Emily Rodrigues
- , Jaesoo Jung
- & Matthew S. Macauley
-
Article
| Open Access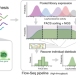 A deep learning approach to programmable RNA switches
A deep learning approach to programmable RNA switches
RNA can be used as a programmable tool for detection of biological analytes. Here the authors use deep neural networks to predict toehold switch functionality in synthetic biology applications.
- Nicolaas M. Angenent-Mari
- , Alexander S. Garruss
- & James J. Collins
-
Article
| Open Access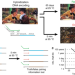 Metastable hybridization-based DNA information storage to allow rapid and permanent erasure
Metastable hybridization-based DNA information storage to allow rapid and permanent erasure
The chemical stability of DNA makes complete erasure of DNA-encoded data difficult. Here the authors mix true and false messages, differentiated by whether a truth marker oligo is bound to it, and show that brief exposure to elevated temperatures randomizes the binding of truth markers preventing data recovery.
- Jangwon Kim
- , Jin H. Bae
- & David Yu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Protease circuits for processing biological information
Protease circuits for processing biological information
In contrast to genetic circuits, here the authors develop protein biocircuits based on proteases. They show these activity-based circuits can execute Boolean logic for programmable drug delivery and perform fuzzy logic to solve a mathematical oracle problem, Learning Parity with Noise.
- Brandon Alexander Holt
- & Gabriel A. Kwong
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancement of trans-cleavage activity of Cas12a with engineered crRNA enables amplified nucleic acid detection
Enhancement of trans-cleavage activity of Cas12a with engineered crRNA enables amplified nucleic acid detection
CRISPR-Cas12a based detection systems can be sensitive down to the picomolar range. Here the authors modify the 3′- and 5′-ends of the crRNA and show this enhances trans-cleavage for improved sensitivity.
- Long T. Nguyen
- , Brianna M. Smith
- & Piyush K. Jain
-
Article
| Open Access Viral gene drive in herpesviruses
Viral gene drive in herpesviruses
Current gene drive strategies are restricted to sexually reproducing species. Here the authors develop a gene drive in herpesviruses that allows the spread of an engineered trait through a viral population.
- Marius Walter
- & Eric Verdin
-
Article
| Open Access A machine learning Automated Recommendation Tool for synthetic biology
A machine learning Automated Recommendation Tool for synthetic biology
Synthetic Biology often lacks the predictive power needed for efficient bioengineering. Here the authors present ART, a machine learning and probabilistic predictive tool to guide synthetic biology design in a systematic fashion.
- Tijana Radivojević
- , Zak Costello
- & Hector Garcia Martin

 Self-assembly and regulation of protein cages from pre-organised coiled-coil modules
Self-assembly and regulation of protein cages from pre-organised coiled-coil modules