Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Anoxygenic phototroph of the Chloroflexota uses a type I reaction centre
Anoxygenic phototroph of the Chloroflexota uses a type I reaction centre
Cultivation of a new anoxygenic phototrophic bacterium from Boreal Shield lake water—representing a transition form in the evolution of photosynthesis—offers insights into how the major modes of phototrophy diversified.
- J. M. Tsuji
- , N. A. Shaw
- & J. D. Neufeld
-
Article |
 The episodic resurgence of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5 virus
The episodic resurgence of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5 virus
Recent resurgences of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5 viruses have different origins and virus ecologies as their epicentres shift and viruses evolve, with changes indicating increased adaptation among domestic birds.
- Ruopeng Xie
- , Kimberly M. Edwards
- & Vijaykrishna Dhanasekaran
-
Article
| Open Access Persistent equatorial Pacific iron limitation under ENSO forcing
Persistent equatorial Pacific iron limitation under ENSO forcing
An assessment of variations in phytoplankton nutrient limitation in the tropical Pacific over the past two decades finds that phytoplankton iron limitation is more stable in response to ENSO dynamics than models predict.
- Thomas J. Browning
- , Mak A. Saito
- & Alessandro Tagliabue
-
Article |
 Phototrophy by antenna-containing rhodopsin pumps in aquatic environments
Phototrophy by antenna-containing rhodopsin pumps in aquatic environments
Light energy transfer from abundant hydroxylated carotenoids to the retinal moiety of widespread light-driven proton pumps is detected.
- Ariel Chazan
- , Ishita Das
- & Oded Béjà
-
Perspective |
 Questioning the fetal microbiome illustrates pitfalls of low-biomass microbial studies
Questioning the fetal microbiome illustrates pitfalls of low-biomass microbial studies
This Perspective reviews the evidence for and against the existence of a fetal microbiome and concludes that detected microbial signals are most likely the result of contamination, suggesting that the ‘sterile womb’ hypothesis is correct.
- Katherine M. Kennedy
- , Marcus C. de Goffau
- & Jens Walter
-
Article |
 Microbial predators form a new supergroup of eukaryotes
Microbial predators form a new supergroup of eukaryotes
Provora is an ancient supergroup of microbial predators that are genetically, morphologically and behaviourally distinct from other eukaryotes, and comprise two divergent clades of predators—Nebulidia and Nibbleridia—that differ fundamentally in ultrastructure, behaviour and gene content.
- Denis V. Tikhonenkov
- , Kirill V. Mikhailov
- & Patrick J. Keeling
-
Article |
 Climate change increases cross-species viral transmission risk
Climate change increases cross-species viral transmission risk
Changes in climate and land use will lead to species aggregating in new combinations at high elevations, in biodiversity hotspots and in areas of high human population density in Asia and Africa, driving the cross-species transmission of animal-associated viruses.
- Colin J. Carlson
- , Gregory F. Albery
- & Shweta Bansal
-
Article |
 Discovery of a Ni2+-dependent guanidine hydrolase in bacteria
Discovery of a Ni2+-dependent guanidine hydrolase in bacteria
A bacterial enzyme is characterized and demonstrated to have Ni2+-dependent activity and high specificity for free guanidine enabling the bacteria to use guanidine as the sole nitrogen source for growth.
- D. Funck
- , M. Sinn
- & J. S. Hartig
-
Article |
 Towards the biogeography of prokaryotic genes
Towards the biogeography of prokaryotic genes
A survey of species-level genes from 13,174 publicly available metagenomes shows that most species-level genes are specific to a single habitat, encode a small number of protein families and are under low positive (adaptive) pressure.
- Luis Pedro Coelho
- , Renato Alves
- & Peer Bork
-
Article
| Open Access Terrestrial-type nitrogen-fixing symbiosis between seagrass and a marine bacterium
Terrestrial-type nitrogen-fixing symbiosis between seagrass and a marine bacterium
The N2-fixing symbiont ‘Candidatus Celerinatantimonas neptuna’ lives inside the root tissue of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica, providing ammonia and amino acids to its host in exchange for sugars and enabling highly productive seagrass meadows to thrive in the nitrogen-limited Mediterranean Sea.
- Wiebke Mohr
- , Nadine Lehnen
- & Marcel M. M. Kuypers
-
Article
| Open Access Anaerobic endosymbiont generates energy for ciliate host by denitrification
Anaerobic endosymbiont generates energy for ciliate host by denitrification
‘Candidatus Azoamicus ciliaticola’ transfers energy to its ciliate host in the form of ATP and enables this host to breathe nitrate, demonstrating that eukaryotes with remnant mitochondria can secondarily acquire energy-providing endosymbionts.
- Jon S. Graf
- , Sina Schorn
- & Jana Milucka
-
Article |
 Multi-kingdom ecological drivers of microbiota assembly in preterm infants
Multi-kingdom ecological drivers of microbiota assembly in preterm infants
Absolute microbial abundances delineate longitudinal dynamics of bacteria, fungi and archaea in the infant gut microbiome, uncovering drivers of microbiome development masked by relative abundances and revealing notable parallels to macroscopic ecosystem assemblies.
- Chitong Rao
- , Katharine Z. Coyte
- & Seth Rakoff-Nahoum
-
Article |
 Widespread endogenization of giant viruses shapes genomes of green algae
Widespread endogenization of giant viruses shapes genomes of green algae
The authors show that large endogenous viral elements derived from giant viruses are prominent components of green algal genomes.
- Mohammad Moniruzzaman
- , Alaina R. Weinheimer
- & Frank O. Aylward
-
Article |
 Relatives of rubella virus in diverse mammals
Relatives of rubella virus in diverse mammals
Ruhugu virus and rustrela virus are the first close relatives of rubella virus, providing insights into the zoonotic origin of rubella virus and the epidemiology and evolution of all three viruses.
- Andrew J. Bennett
- , Adrian C. Paskey
- & Tony L. Goldberg
-
Article |
 C9orf72 suppresses systemic and neural inflammation induced by gut bacteria
C9orf72 suppresses systemic and neural inflammation induced by gut bacteria
Reduced abundance of immune-stimulating gut bacteria ameliorated the inflammatory and autoimmune phenotypes of mice with mutations in C9orf72, which in the human orthologue are linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia.
- Aaron Burberry
- , Michael F. Wells
- & Kevin Eggan
-
Article |
 Recycling and metabolic flexibility dictate life in the lower oceanic crust
Recycling and metabolic flexibility dictate life in the lower oceanic crust
Analyses of microbial communities that live 10–750 m below the seafloor at Atlantis Bank, Indian Ocean, provide insights into how these microorganisms survive by coupling energy sources to organic and inorganic carbon resources.
- Jiangtao Li
- , Paraskevi Mara
- & Virginia P. Edgcomb
-
Article |
 Marine Proteobacteria metabolize glycolate via the β-hydroxyaspartate cycle
Marine Proteobacteria metabolize glycolate via the β-hydroxyaspartate cycle
Marine Proteobacteria use the β-hydroxyaspartate cycle to assimilate glycolate, which is secreted by algae on a petagram scale, providing evidence of a previously undescribed trophic interaction between autotrophic phytoplankton and heterotrophic bacterioplankton.
- Lennart Schada von Borzyskowski
- , Francesca Severi
- & Tobias J. Erb
-
Article |
 Human placenta has no microbiome but can contain potential pathogens
Human placenta has no microbiome but can contain potential pathogens
The human placenta does not have a microbiota, suggesting that bacterial infection of the placenta is not a common cause of adverse pregnancy outcome, but group B Streptococcus is found in approximately 5% of placental samples.
- Marcus C. de Goffau
- , Susanne Lager
- & Gordon C. S. Smith
-
Letter |
 Climatic controls of decomposition drive the global biogeography of forest-tree symbioses
Climatic controls of decomposition drive the global biogeography of forest-tree symbioses
A spatially explicit global map of tree symbioses with nitrogen-fixing bacteria and mycorrhizal fungi reveals that climate variables are the primary drivers of the distribution of different types of symbiosis.
- B. S. Steidinger
- , T. W. Crowther
- & Irie Casimir Zo-Bi
-
Letter |
 A widespread coral-infecting apicomplexan with chlorophyll biosynthesis genes
A widespread coral-infecting apicomplexan with chlorophyll biosynthesis genes
A newly identified lineage of apicomplexans, named corallicolids, are intracellular symbionts of many coral species, and possesses a plastid that retains genes for chlorophyll biosynthesis despite lacking photosystem genes.
- Waldan K. Kwong
- , Javier del Campo
- & Patrick J. Keeling
-
Article |
 Structural variation in the gut microbiome associates with host health
Structural variation in the gut microbiome associates with host health
The authors systematically characterize structural variation in the genomes of gut microbiota and show that they are associated with bacterial fitness and with host risk factors, and that examining genes coded in these regions facilitates investigation of mechanisms that may underlie these associations.
- David Zeevi
- , Tal Korem
- & Eran Segal
-
Article |
 Pathogen elimination by probiotic Bacillus via signalling interference
Pathogen elimination by probiotic Bacillus via signalling interference
Lipopeptides secreted by Bacillus bacteria block quorum sensing by Staphylococcus aureus and thereby inhibit the growth of this opportunistic pathogen in the gut, suggesting why people in rural Thailand who are colonized by Bacillus are not also colonized by S. aureus.
- Pipat Piewngam
- , Yue Zheng
- & Michael Otto
-
Letter |
 Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome
Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome
Metagenomic, chemical and biomass analyses of topsoil samples from around the world reveal spatial and environmental trends in microbial community composition and genetic diversity.
- Mohammad Bahram
- , Falk Hildebrand
- & Peer Bork
-
Article |
 Genome-centric view of carbon processing in thawing permafrost
Genome-centric view of carbon processing in thawing permafrost
Analysis of more than 1,500 microbial genomes sheds light on the processing of carbon released as permafrost thaws.
- Ben J. Woodcroft
- , Caitlin M. Singleton
- & Gene W. Tyson
-
Letter |
 Novel soil bacteria possess diverse genes for secondary metabolite biosynthesis
Novel soil bacteria possess diverse genes for secondary metabolite biosynthesis
Metagenomic and soil microcosm analyses identify abundant biosynthetic gene clusters in genomes of microorganisms from a northern Californian grassland ecosystem that provide a potential source for the future development of bacterial natural products.
- Alexander Crits-Christoph
- , Spencer Diamond
- & Jillian F. Banfield
-
Article |
 Environment and host as large-scale controls of ectomycorrhizal fungi
Environment and host as large-scale controls of ectomycorrhizal fungi
Analyses of data from 137 forest plots across 20 European countries show that ectomycorrhizal fungal diversity is strongly influenced by environmental and host species factors and provide thresholds to inform ecosystem assessment tools
- Sietse van der Linde
- , Laura M. Suz
- & Martin I. Bidartondo
-
Letter |
 A major lineage of non-tailed dsDNA viruses as unrecognized killers of marine bacteria
A major lineage of non-tailed dsDNA viruses as unrecognized killers of marine bacteria
Members of a family of marine dsDNA non-tailed bacterial viruses have short, 10-kb genomes, infect a broader range of hosts than tailed viruses and belong to the double jelly roll capsid lineage of viruses, which are associated with diverse bacterial and archaeal hosts.
- Kathryn M. Kauffman
- , Fatima A. Hussain
- & Martin F. Polz
-
Article |
 Dietary trehalose enhances virulence of epidemic Clostridium difficile
Dietary trehalose enhances virulence of epidemic Clostridium difficile
Two hypervirulent ribotypes of the enteric pathogen Clostridium difficile, RT027 and RT078, have independently acquired unique mechanisms to metabolize low concentrations of the disaccharide trehalose, suggesting a correlation between the emergence of these ribotypes and the widespread adoption of trehalose in the human diet.
- J. Collins
- , C. Robinson
- & R. A. Britton
-
Letter
| Open Access Atmospheric trace gases support primary production in Antarctic desert surface soil
Atmospheric trace gases support primary production in Antarctic desert surface soil
Metagenomic and biochemical analyses of soil samples from Antarctic desert regions provides evidence that bacteria in these soils derive carbon and energy from atmospheric CO, H2 and CO2.
- Mukan Ji
- , Chris Greening
- & Belinda C. Ferrari
-
Review Article |
 Progress in and promise of bacterial quorum sensing research
Progress in and promise of bacterial quorum sensing research
A Review of the genetics, biochemistry, ecology and evolution of bacterial quorum sensing.
- Marvin Whiteley
- , Stephen P. Diggle
- & E. Peter Greenberg
-
Letter |
 Nutrient co-limitation at the boundary of an oceanic gyre
Nutrient co-limitation at the boundary of an oceanic gyre
Nutrient amendment experiments at the boundary of the South Atlantic gyre reveal extensive regions in which nitrogen and iron are co-limiting, with other micronutrients also approaching co-deficiency; such limitations potentially increase phytoplankton community diversity.
- Thomas J. Browning
- , Eric P. Achterberg
- & C. Mark Moore
-
Article
| Open Access Strains, functions and dynamics in the expanded Human Microbiome Project
Strains, functions and dynamics in the expanded Human Microbiome Project
Updates from the Human Microbiome Project analyse the largest known body-wide metagenomic profile of human microbiome personalization.
- Jason Lloyd-Price
- , Anup Mahurkar
- & Curtis Huttenhower
-
Letter |
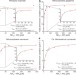 Kinetic analysis of a complete nitrifier reveals an oligotrophic lifestyle
Kinetic analysis of a complete nitrifier reveals an oligotrophic lifestyle
A pure culture of the complete nitrifier Nitrospira inopinata shows a high affinity for ammonia, low maximum rate of ammonia oxidation, high growth yield compared to canonical nitrifiers and genomic potential for alternative metabolisms, probably reflecting an important role in nitrification in oligotrophic environments.
- K. Dimitri Kits
- , Christopher J. Sedlacek
- & Michael Wagner
-
Letter |
 Persistent anthrax as a major driver of wildlife mortality in a tropical rainforest
Persistent anthrax as a major driver of wildlife mortality in a tropical rainforest
An anthrax-causing agent, Bacillus cereus biovar anthracis, is a persistent and widespread cause of death for a broad range of mammalian hosts in a tropical rainforest, with important implications for the conservation of mammals such as chimpanzees.
- Constanze Hoffmann
- , Fee Zimmermann
- & Fabian H. Leendertz
-
Letter |
 Establishment and cryptic transmission of Zika virus in Brazil and the Americas
Establishment and cryptic transmission of Zika virus in Brazil and the Americas
Virus genomes reveal the establishment of Zika virus in Brazil and the Americas, and provide an appropriate timeframe for baseline (pre-Zika) microcephaly in different regions.
- N. R. Faria
- , J. Quick
- & O. G. Pybus
-
Letter |
 Leaf bacterial diversity mediates plant diversity and ecosystem function relationships
Leaf bacterial diversity mediates plant diversity and ecosystem function relationships
A tree biodiversity and ecosystem function experiment shows that leaf bacterial diversity is positively related to plant community productivity, and explains a portion of the variation in productivity that would otherwise be attributed to plant diversity and functional traits.
- Isabelle Laforest-Lapointe
- , Alain Paquette
- & Steven W. Kembel
-
Letter |
 Drivers of salamander extirpation mediated by Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans
Drivers of salamander extirpation mediated by Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans
The authors investigated the disease ecology of the fast-spreading fungal pathogen Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans in fire salamanders; on the basis of their research, they call for Europe-wide monitoring systems and conservation strategies for threatened species.
- Gwij Stegen
- , Frank Pasmans
- & An Martel
-
Letter |
 New CRISPR–Cas systems from uncultivated microbes
New CRISPR–Cas systems from uncultivated microbes
Using a metagenomic approach, three types of CRISPR–Cas systems have been discovered in uncultivated bacterial and archaeal hosts from a variety of different environments.
- David Burstein
- , Lucas B. Harrington
- & Jillian F. Banfield
-
Article |
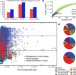 Uncovering Earth’s virome
Uncovering Earth’s virome
An integrated computational approach that explores the viral content of more than 3,000 metagenomic samples collected globally highlights the existing global viral diversity, increases the known number of viral genes by an order of magnitude, and provides detailed insights into viral distribution across diverse ecosystems and into virus–host interactions.
- David Paez-Espino
- , Emiley A. Eloe-Fadrosh
- & Nikos C. Kyrpides
-
Letter |
 Universality of human microbial dynamics
Universality of human microbial dynamics
A new computational method to characterize the dynamics of human-associated microbial communities is applied to data from two large-scale metagenomic studies, and suggests that gut and mouth microbiomes of healthy individuals are subjected to universal (that is, host-independent) dynamics, whereas skin microbiomes are shaped by the host environment; the method paves the way to designing general microbiome-based therapies.
- Amir Bashan
- , Travis E. Gibson
- & Yang-Yu Liu
-
Letter |
 Development of the gut microbiota and mucosal IgA responses in twins and gnotobiotic mice
Development of the gut microbiota and mucosal IgA responses in twins and gnotobiotic mice
The relationship between assembly of the gut community and gut mucosal immunoglobulin A responses during the first 24–36 months of postnatal life in a cohort of 40 twin pairs is defined and modelled in gnotobiotic mice.
- Joseph D. Planer
- , Yangqing Peng
- & Jeffrey I. Gordon
-
Article |
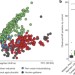 Interconnected microbiomes and resistomes in low-income human habitats
Interconnected microbiomes and resistomes in low-income human habitats
An analysis of bacterial community structure and antibiotic resistance gene content of interconnected human faecal and environmental samples from two low-income communities in Latin America was carried out using a combination of functional metagenomics, 16S sequencing and shotgun sequencing; resistomes across habitats are generally structured along ecological gradients, but key resistance genes can cross these boundaries, and the authors assessed the usefulness of excreta management protocols in the prevention of resistance gene dissemination.
- Erica C. Pehrsson
- , Pablo Tsukayama
- & Gautam Dantas
-
Letter
| Open Access Culturing of ‘unculturable’ human microbiota reveals novel taxa and extensive sporulation
Culturing of ‘unculturable’ human microbiota reveals novel taxa and extensive sporulation
A novel approach is used to cultivate a substantial proportion of the human gut microbiota, representing an important step forward in characterizing the role of these bacteria in health and disease.
- Hilary P. Browne
- , Samuel C. Forster
- & Trevor D. Lawley
-
Article |
 Lytic to temperate switching of viral communities
Lytic to temperate switching of viral communities
An analysis of 24 coral reef viromes challenges the view that lytic phage are believed to predominate when the density of their hosts increase and shows instead that lysogeny is more important at high host densities; the authors also show that this model is consistent with predator–prey dynamics in a range of other ecosystems, such as animal-associated, sediment and soil systems.
- B. Knowles
- , C. B. Silveira
- & F. Rohwer
-
Letter |
 Diet-induced extinctions in the gut microbiota compound over generations
Diet-induced extinctions in the gut microbiota compound over generations
In mice on a low microbiota-accessible carbohydrate (MAC) diet, the diversity of the gut microbiota is depleted, and the effect is transferred and compounded over generations; this phenotype is only reversed after supplementation of the missing taxa via faecal microbiota transplantation, suggesting dietary intervention alone may by insufficient at managing diseases characterized by a dysbiotic microbiota.
- Erica D. Sonnenburg
- , Samuel A. Smits
- & Justin L. Sonnenburg
-
Article |
 Single cell activity reveals direct electron transfer in methanotrophic consortia
Single cell activity reveals direct electron transfer in methanotrophic consortia
The anaerobic oxidation of methane in marine sediments is performed by consortia of methane-oxidizing archaea and sulfate-reducing bacteria; an examination of the role of interspecies spatial positioning on single cell activity reveals that interspecies electron transfer may overcome the requirement for close spatial proximity, a proposition supported by large multi-haem cytochromes in ANME-2 genomes as well as redox-active electron microscopy staining.
- Shawn E. McGlynn
- , Grayson L. Chadwick
- & Victoria J. Orphan
-
Letter |
 Counteraction of antibiotic production and degradation stabilizes microbial communities
Counteraction of antibiotic production and degradation stabilizes microbial communities
Mathematical modelling and simulations reveal that including antibiotic degraders in ecological models of microbial species interaction allows the system to robustly move towards an intermixed stable state, more representative of real-world observations.
- Eric D. Kelsic
- , Jeffrey Zhao
- & Roy Kishony
-
Letter |
 Precision microbiome reconstitution restores bile acid mediated resistance to Clostridium difficile
Precision microbiome reconstitution restores bile acid mediated resistance to Clostridium difficile
A fraction of the intestinal microbiota as precise as a single bacterial species confers infection resistance by synthesizing Clostridium difficile-inhibiting metabolites from host-derived bile salts.
- Charlie G. Buffie
- , Vanni Bucci
- & Eric G. Pamer
-
Letter |
 Methane dynamics regulated by microbial community response to permafrost thaw
Methane dynamics regulated by microbial community response to permafrost thaw
The abundance of key microbial lineages can be used to predict atmospherically relevant patterns in methane isotopes and the proportion of carbon metabolized to methane during permafrost thaw, suggesting that microbial ecology may be important in ecosystem-scale responses to global change.
- Carmody K. McCalley
- , Ben J. Woodcroft
- & Scott R. Saleska

 Streptomyces umbrella toxin particles block hyphal growth of competing species
Streptomyces umbrella toxin particles block hyphal growth of competing species