Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping global dynamics of benchmark creation and saturation in artificial intelligence
Mapping global dynamics of benchmark creation and saturation in artificial intelligence
Recent studies raised concerns over the state of AI benchmarking, reporting issues such as benchmark overfitting, benchmark saturation and increasing centralization of benchmark dataset creation. To facilitate monitoring of the health of the AI benchmarking ecosystem, the authors introduce methodologies for creating condensed maps of the global dynamics of benchmark.
- Simon Ott
- , Adriano Barbosa-Silva
- & Matthias Samwald
-
Perspective
| Open Access Statistical inference links data and theory in network science
Statistical inference links data and theory in network science
Theoretical models and structures recovered from measured data serve for analysis of complex networks. The authors discuss here existing gaps between theoretical methods and real-world applied networks, and potential ways to improve the interplay between theory and applications.
- Leto Peel
- , Tiago P. Peixoto
- & Manlio De Domenico
-
Article
| Open Access Development and validation of self-monitoring auto-updating prognostic models of survival for hospitalized COVID-19 patients
Development and validation of self-monitoring auto-updating prognostic models of survival for hospitalized COVID-19 patients
Despite rapid and significant changes during the pandemic, prognostic models for COVID-19 patients do not currently account for data drifts. Here, the authors develop a framework for continuously monitoring and updating prognostic models and applied it to predict 28-day survival in COVID-19 patients.
- Todd J. Levy
- , Kevin Coppa
- & Theodoros P. Zanos
-
Article
| Open Access Deep autoencoder for interpretable tissue-adaptive deconvolution and cell-type-specific gene analysis
Deep autoencoder for interpretable tissue-adaptive deconvolution and cell-type-specific gene analysis
Traditional bulk sequencing data lack information about cell-type-specific gene expression. Here, the authors develop a Tissue-AdaPtive autoEncoder (TAPE), a deep learning method connecting bulk RNA-seq and single-cell RNA-seq, and apply it to analyze the cell type fractions and cell-type-specific gene expression in clinical data.
- Yanshuo Chen
- , Yixuan Wang
- & Yu Li
-
Article
| Open Access Bayesian deep learning for error estimation in the analysis of anomalous diffusion
Bayesian deep learning for error estimation in the analysis of anomalous diffusion
Diffusive motions in complex environments such as living biological cells or soft matter systems can be analyzed with single-particle-tracking approaches, where accuracy of output may vary. The authors involve a machine-learning technique for decoding anomalous-diffusion data and provide an uncertainty estimate together with predicted output.
- Henrik Seckler
- & Ralf Metzler
-
Article
| Open Access Uncertainty-informed deep learning models enable high-confidence predictions for digital histopathology
Uncertainty-informed deep learning models enable high-confidence predictions for digital histopathology
Safe clinical deployment of deep learning models for digital pathology requires reliable estimates of predictive uncertainty. Here the authors describe an algorithm for quantifying whole-slide image uncertainty, demonstrating their approach with models trained to distinguish lung cancer subtypes.
- James M. Dolezal
- , Andrew Srisuwananukorn
- & Alexander T. Pearson
-
Article
| Open Access Feature-based volumetric defect classification in metal additive manufacturing
Feature-based volumetric defect classification in metal additive manufacturing
Additively manufactured materials contain different types of volumetric defects. Here, the authors utilize the most distinguishing morphological features among different defect types to propose a defect classification methodology.
- Arun Poudel
- , Mohammad Salman Yasin
- & Nima Shamsaei
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot quantum error correction with the three-dimensional subsystem toric code
Single-shot quantum error correction with the three-dimensional subsystem toric code
Topological quantum error correction is a promising approach towards fault-tolerant quantum computing, but suffers from large time overhead. Here, the authors generalise the stabiliser toric code to a single-shot 3D subsystem toric code, featuring good performance and resilience to measurement errors.
- Aleksander Kubica
- & Michael Vasmer
-
Article
| Open Access Technology readiness levels for machine learning systems
Technology readiness levels for machine learning systems
The development of machine learning systems has to ensure their robustness and reliability. The authors introduce a framework that defines a principled process of machine learning system formation, from research to production, for various domains and data scenarios.
- Alexander Lavin
- , Ciarán M. Gilligan-Lee
- & Yarin Gal
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible learning of quantum states with generative query neural networks
Flexible learning of quantum states with generative query neural networks
The use of machine learning to characterise quantum states has been demonstrated, but usually training the algorithm using data from the same state one wants to characterise. Here, the authors show an algorithm that can learn all states that share structural similarities with the ones used for the training.
- Yan Zhu
- , Ya-Dong Wu
- & Giulio Chiribella
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic model of the El Laco magnetite-apatite deposits by extrusion of iron-rich melt
Genetic model of the El Laco magnetite-apatite deposits by extrusion of iron-rich melt
Can volcanoes erupt ore deposits? This study combines observations, experiments, and simulations to show that iron ore deposits on El Laco volcano formed by eruption of melt sourced from separation of Fe-rich melt from a silicate magma body beneath.
- Tobias Keller
- , Fernando Tornos
- & Jenny Suckale
-
Article
| Open Access Detecting the ultra low dimensionality of real networks
Detecting the ultra low dimensionality of real networks
Reducing of dimension is often necessary to detect and analyze patterns in large datasets and complex networks. Here, the authors propose a method for detection of the intrinsic dimensionality of high-dimensional networks to reproduce their complex structure using a reduced tractable geometric representation.
- Pedro Almagro
- , Marián Boguñá
- & M. Ángeles Serrano
-
Article
| Open Access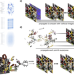 Diffraction-engineered holography: Beyond the depth representation limit of holographic displays
Diffraction-engineered holography: Beyond the depth representation limit of holographic displays
Improving the image depth perception of holograms while maintaining high image quality is a current challenge. Here the authors propose an efficient solution relying on a multi-plane hologram technique that reconstruct different blurred images and sharply focused images depending on a propagation distance.
- Daeho Yang
- , Wontaek Seo
- & Hong-Seok Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Helheim Glacier ice velocity variability responds to runoff and terminus position change at different timescales
Helheim Glacier ice velocity variability responds to runoff and terminus position change at different timescales
Factors driving ice flow variability in Greenland vary by timescale. At seasonal scale, Helheim Glacier ice velocity responds most strongly to meltwater runoff. Glacier terminus position drives velocity variability at longer time scales.
- Lizz Ultee
- , Denis Felikson
- & Bryan Riel
-
Article
| Open Access A neural theory for counting memories
A neural theory for counting memories
It is unclear how the brain keeps track of the number of times different events are experienced. Here, a neural circuit is proposed for this problem inspired by a classic solution in computer science, and evidence of this circuit is shown in the fruit fly brain.
- Sanjoy Dasgupta
- , Daisuke Hattori
- & Saket Navlakha
-
Article
| Open Access Noise-injected analog Ising machines enable ultrafast statistical sampling and machine learning
Noise-injected analog Ising machines enable ultrafast statistical sampling and machine learning
Ising machines are accelerators for computing difficult optimization problems. In this work, Böhm et al. demonstrate a method that extends their use to perform statistical sampling and machine learning orders-of-magnitudes faster than digital computers.
- Fabian Böhm
- , Diego Alonso-Urquijo
- & Guy Van der Sande
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying ethnic segregation in cities through random walks
Quantifying ethnic segregation in cities through random walks
Socioeconomic segregation is one of the main factors behind large-scale inequalities in urban areas and its characterisation remains challenging. The authors propose a family of non-parametric measures to quantify spatial heterogeneity through diffusion, and show how this relates to segregation and deprivation
- Sandro Sousa
- & Vincenzo Nicosia
-
Article
| Open Access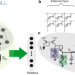 Self-organization of an inhomogeneous memristive hardware for sequence learning
Self-organization of an inhomogeneous memristive hardware for sequence learning
One gap between the neuro-inspired computing and its applications lies in the intrinsic variability of the devices. Here, Payvand et al. suggest a technologically plausible co-design of the hardware architecture which takes into account and exploits the physics behind memristors.
- Melika Payvand
- , Filippo Moro
- & Giacomo Indiveri
-
Article
| Open Access Digitally-enhanced lubricant evaluation scheme for hot stamping applications
Digitally-enhanced lubricant evaluation scheme for hot stamping applications
The digital transformation and Industry 4.0 technologies are rapidly shaping the future of manufacturing. Here, authors use reliable big data to quantitatively evaluate lubricants performance and select desirable candidates for application in target manufacturing processes.
- Xiao Yang
- , Heli Liu
- & Liliang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against Omicron and Delta hospitalisation, a test negative case-control study
Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against Omicron and Delta hospitalisation, a test negative case-control study
SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern have been associated with reduced vaccine effectiveness, even after a booster dose. In this study, authors aim to estimate vaccine effectiveness against hospitalisation with the Omicron and Delta variants, using different definitions of hospitalisation in secondary care data.
- Julia Stowe
- , Nick Andrews
- & Jamie Lopez Bernal
-
Article
| Open Access Adversarial attacks and adversarial robustness in computational pathology
Adversarial attacks and adversarial robustness in computational pathology
Artificial Intelligence can support diagnostic workflows in oncology, but they are vulnerable to adversarial attacks. Here, the authors show that convolutional neural networks are highly susceptible to white- and black-box adversarial attacks in clinically relevant classification tasks.
- Narmin Ghaffari Laleh
- , Daniel Truhn
- & Jakob Nikolas Kather
-
Article
| Open Access Autonomous optimization of non-aqueous Li-ion battery electrolytes via robotic experimentation and machine learning coupling
Autonomous optimization of non-aqueous Li-ion battery electrolytes via robotic experimentation and machine learning coupling
Human-operated optimization of non-aqueous Li-ion battery liquid electrolytes is a time-consuming process. Here, the authors propose an automated workflow that couples robotic experiments with machine learning to optimize liquid electrolyte formulations without human intervention.
- Adarsh Dave
- , Jared Mitchell
- & Venkatasubramanian Viswanathan
-
Article
| Open Access Noise-resilient and high-speed deep learning with coherent silicon photonics
Noise-resilient and high-speed deep learning with coherent silicon photonics
The challenge of high-speed and high-accuracy coherent photonic neurons for deep learning applications lies to solve noise related issues. Here, Mourgias-Alexandris et al. address this problem by introducing a noise-resilient hardware architectural and a deep learning training platform.
- G. Mourgias-Alexandris
- , M. Moralis-Pegios
- & N. Pleros
-
Article
| Open Access Clustering by measuring local direction centrality for data with heterogeneous density and weak connectivity
Clustering by measuring local direction centrality for data with heterogeneous density and weak connectivity
Clustering is a powerful machine learning method for discovering similar patterns according to the proximity of elements in feature space. Here the authors propose a local direction centrality clustering algorithm that copes with heterogeneous density and weak connectivity issues.
- Dehua Peng
- , Zhipeng Gui
- & Huayi Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding Braess’ Paradox in power grids
Understanding Braess’ Paradox in power grids
Increasing the capacity of existing lines or adding new lines in power grids may, counterintuitively, reduce the system performance and promote blackouts. The authors propose an approach for prediction of edges that lower system performance and defining potential constrains for grid extensions.
- Benjamin Schäfer
- , Thiemo Pesch
- & Marc Timme
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning for twelve hour precipitation forecasts
Deep learning for twelve hour precipitation forecasts
Can AI learn from atmospheric data and improve weather forecasting? The neural network MetNet-2 achieves this by forecasting the fast changing variable of precipitation up to 12 h ahead more accurately and efficiently than traditional models based on hand-coded physics.
- Lasse Espeholt
- , Shreya Agrawal
- & Nal Kalchbrenner
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesizing theories of human language with Bayesian program induction
Synthesizing theories of human language with Bayesian program induction
Humans can infer rules for building words in a new language from a handful of examples, and linguists also can infer language patterns across related languages. Here, the authors provide an algorithm which models these grammatical abilities by synthesizing human-understandable programs for building words.
- Kevin Ellis
- , Adam Albright
- & Timothy J. O’Donnell
-
Article
| Open Access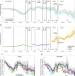 Comparison of the 2021 COVID-19 roadmap projections against public health data in England
Comparison of the 2021 COVID-19 roadmap projections against public health data in England
The ’Roadmap’ for relaxation of COVID-19 restrictions in England in 2021 was informed by mathematical modelling. Here, the authors perform a retrospective assessment of the accuracy of modelling predictions and identify the main sources of uncertainty that led to observed values deviating from projections.
- Matt J. Keeling
- , Louise Dyson
- & Samuel Moore
-
Article
| Open Access Generalization in quantum machine learning from few training data
Generalization in quantum machine learning from few training data
The power of quantum machine learning algorithms based on parametrised quantum circuits are still not fully understood. Here, the authors report rigorous bounds on the generalisation error in variational QML, confirming how known implementable models generalize well from an efficient amount of training data.
- Matthias C. Caro
- , Hsin-Yuan Huang
- & Patrick J. Coles
-
Article
| Open Access Impedance-based forecasting of lithium-ion battery performance amid uneven usage
Impedance-based forecasting of lithium-ion battery performance amid uneven usage
Accurate forecasts of lithium-ion battery performance will ease concerns about the reliability of electric vehicles. Here, the authors leverage electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and machine learning to show that future capacity can be predicted amid uneven use, with no historical data requirement.
- Penelope K. Jones
- , Ulrich Stimming
- & Alpha A. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Secure human action recognition by encrypted neural network inference
Secure human action recognition by encrypted neural network inference
Advanced computer vision technology can provide near real-time home monitoring to support "aging in place” by detecting falls and symptoms related to seizures and stroke. In this paper, the authors propose a strategy that uses homomorphic encryption, which guarantees information confidentiality while retaining action detection.
- Miran Kim
- , Xiaoqian Jiang
- & Shayan Shams
-
Article
| Open Access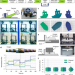 Generalisable 3D printing error detection and correction via multi-head neural networks
Generalisable 3D printing error detection and correction via multi-head neural networks
3D printing is prone to errors and continuous monitoring and real-time correction during processing remains a significant challenge limiting its applied potential. Here, authors train a neural network to detect and correct diverse errors in real time across many geometries, materials and even printing setups.
- Douglas A. J. Brion
- & Sebastian W. Pattinson
-
Article
| Open Access Extraction of accurate cytoskeletal actin velocity distributions from noisy measurements
Extraction of accurate cytoskeletal actin velocity distributions from noisy measurements
Dynamic remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton underlies cell movement, but is challenging to characterize at the molecular level. Here, the authors present a method to extract actin filament velocities in living cells, and compare their results to current models of cytoskeletal dynamics.
- Cayla M. Miller
- , Elgin Korkmazhan
- & Alexander R. Dunn
-
Article
| Open Access Practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution with composable security
Practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution with composable security
Continuous-variable QKD protocols are usually easier to implement than discrete-variables ones, but their security analyses are less developed. Here, the authors propose and demonstrate in the lab a CVQKD protocol that can generate composable keys secure against collective attacks.
- Nitin Jain
- , Hou-Man Chin
- & Ulrik L. Andersen
-
Article
| Open Access Functional control of oscillator networks
Functional control of oscillator networks
In network systems governed by oscillatory activity, such as brain networks or power grids, configurations of synchrony may define network functions. The authors introduce a control approach for the formation of desired synchrony patterns through optimal interventions on the network parameters.
- Tommaso Menara
- , Giacomo Baggio
- & Fabio Pasqualetti
-
Article
| Open Access Explaining a series of models by propagating Shapley values
Explaining a series of models by propagating Shapley values
Series of machine learning models, relevant for tasks in biology, medicine, and finance, usually involve complex feature attribution techniques. The authors introduce a tractable method to compute local feature attributions for a series of machine learning models inspired by connections to the Shapley value.
- Hugh Chen
- , Scott M. Lundberg
- & Su-In Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time 3D analysis during electron tomography using tomviz
Real-time 3D analysis during electron tomography using tomviz
High-throughput electron tomography has been challenging due to time-consuming alignment and reconstruction. Here, the authors demonstrate real-time tomography with dynamic 3D tomographic visualization integrated in tomviz, an open-source 3D data analysis tool.
- Jonathan Schwartz
- , Chris Harris
- & Robert Hovden
-
Article
| Open Access ProtGPT2 is a deep unsupervised language model for protein design
ProtGPT2 is a deep unsupervised language model for protein design
Protein design aims to build novel proteins customized for specific purposes, thereby holding the potential to tackle many environmental and biomedical problems. Here the authors apply some of the latest advances in natural language processing, generative Transformers, to train ProtGPT2, a language model that explores unseen regions of the protein space while designing proteins with nature-like properties.
- Noelia Ferruz
- , Steffen Schmidt
- & Birte Höcker
-
Article
| Open Access Lead federated neuromorphic learning for wireless edge artificial intelligence
Lead federated neuromorphic learning for wireless edge artificial intelligence
Designing energy-efficient computing solution for the implementation of AI algorithms in edge devices remains a challenge. Yang et al. proposes a decentralized brain-inspired computing method enabling multiple edge devices to collaboratively train a global model without a fixed central coordinator.
- Helin Yang
- , Kwok-Yan Lam
- & H. Vincent Poor
-
Article
| Open Access Stress-testing the resilience of the Austrian healthcare system using agent-based simulation
Stress-testing the resilience of the Austrian healthcare system using agent-based simulation
As mass quarantines, absences due to sickness, or other shocks thin out patient-physician networks, the system might be pushed to a tipping point where it loses its ability to deliver care. Here, the authors propose a data-driven framework to quantify regional resilience to such shocks via an agent-based model.
- Michaela Kaleta
- , Jana Lasser
- & Peter Klimek
-
Article
| Open Access Intratumor graph neural network recovers hidden prognostic value of multi-biomarker spatial heterogeneity
Intratumor graph neural network recovers hidden prognostic value of multi-biomarker spatial heterogeneity
Cancer prognosis using multiregion sampling is costly and not completely reliable due to the required biomarker homogenisation step. Here, the authors develop an intratumor graph neural network for prognosis in multiregion cancer samples based on in situ biomarkers and gene expression that does not need homogenisation.
- Lida Qiu
- , Deyong Kang
- & Haohua Tu
-
Article
| Open Access Surrogate- and invariance-boosted contrastive learning for data-scarce applications in science
Surrogate- and invariance-boosted contrastive learning for data-scarce applications in science
Deep learning techniques usually require a large quantity of training data and may be challenging for scarce datasets. The authors propose a framework that involves contrastive and transfer learning and reduces data requirements for training while keeping the prediction accuracy.
- Charlotte Loh
- , Thomas Christensen
- & Marin Soljačić
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical intelligence for learning embodied sensor-object relationships
Mechanical intelligence for learning embodied sensor-object relationships
Information-based search strategies are relevant for the learning of interacting agents dynamics and usually need predefined data. The authors propose a method to collect data for learning a predictive sensor model, without requiring domain knowledge, human input, or previously existing data.
- Ahalya Prabhakar
- & Todd Murphey
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying multicellular spatiotemporal organization of cells with SpaceFlow
Identifying multicellular spatiotemporal organization of cells with SpaceFlow
A critical task in spatial transcriptomics analysis is to understand inherently spatial relationships among cells. Here, the authors present a deep learning framework to integrate spatial and transcriptional information, spatially extending pseudotime and revealing spatiotemporal organization of cells.
- Honglei Ren
- , Benjamin L. Walker
- & Qing Nie
-
Article
| Open Access Instant diagnosis of gastroscopic biopsy via deep-learned single-shot femtosecond stimulated Raman histology
Instant diagnosis of gastroscopic biopsy via deep-learned single-shot femtosecond stimulated Raman histology
Diagnosis of gastric cancer currently requires gastroscopic biopsy, which requires time and expertize to perform. Here, the authors demonstrate a femto-SRS imaging method which showed high accuracy in diagnosing gastric cancer without the need for pathologistbased diagnosis.
- Zhijie Liu
- , Wei Su
- & Minbiao Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear speed and cycle length co-vary with local density during syncytial blastoderm formation in a cricket
Nuclear speed and cycle length co-vary with local density during syncytial blastoderm formation in a cricket
Early in insect embryo development, many nuclei share one large cell, travel varied paths and self-organize into a single layer. Donoughe et al. illuminate this process with live-imaging, modeling, and experimental changes to the embryo’s shape.
- Seth Donoughe
- , Jordan Hoffmann
- & Cassandra G. Extavour
-
Article
| Open Access Optimised weight programming for analogue memory-based deep neural networks
Optimised weight programming for analogue memory-based deep neural networks
Device-level complexity represents a big shortcoming for the hardware realization of analogue memory-based deep neural networks. Mackin et al. report a generalized computational framework, translating software-trained weights into analogue hardware weights, to minimise inference accuracy degradation.
- Charles Mackin
- , Malte J. Rasch
- & Geoffrey W. Burr
-
Article
| Open Access Automated detection and segmentation of non-small cell lung cancer computed tomography images
Automated detection and segmentation of non-small cell lung cancer computed tomography images
Correct interpretation of computer tomography (CT) scans is important for the correct assessment of a patient’s disease but can be subjective and timely. Here, the authors develop a system that can automatically segment the non-small cell lung cancer on CT images of patients and show in an in silico trial that the method was faster and more reproducible than clinicians.
- Sergey P. Primakov
- , Abdalla Ibrahim
- & Philippe Lambin
-
Article
| Open Access A framework for the general design and computation of hybrid neural networks
A framework for the general design and computation of hybrid neural networks
Hybrid neural networks combine advantages of spiking and artificial neural networks in the context of computing and biological motivation. The authors propose a design framework with hybrid units for improved flexibility and efficiency of hybrid neural networks, and modulation of hybrid information flows.
- Rong Zhao
- , Zheyu Yang
- & Luping Shi

 An AI approach for managing financial systemic risk via bank bailouts by taxpayers
An AI approach for managing financial systemic risk via bank bailouts by taxpayers