Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access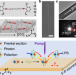 Room temperature exciton–polariton Bose–Einstein condensation in organic single-crystal microribbon cavities
Room temperature exciton–polariton Bose–Einstein condensation in organic single-crystal microribbon cavities
The use of room temperature exciton–polariton Bose–Einstein condensation is limited by the need for external high-finesse microcavities. The authors generate room temperature EPs with single-crystal microribbons as waveguide Fabry–Pérot microcavities, and demonstrate controllable output of coherent light.
- Ji Tang
- , Jian Zhang
- & Yong Sheng Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access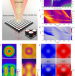 All-dielectric chiral-field-enhanced Raman optical activity
All-dielectric chiral-field-enhanced Raman optical activity
Raman optical activity (ROA) is useful for studying conformational structure and behavior of chiral molecules, but is limited by the weak signals. Here, the authors demonstrate 100x signal enhancement via an all-dielectric approach, using a silicon nanodisk array and exploiting its dark mode.
- Ting-Hui Xiao
- , Zhenzhou Cheng
- & Keisuke Goda
-
Article
| Open Access A luminescent view of the clickable assembly of LnF3 nanoclusters
A luminescent view of the clickable assembly of LnF3 nanoclusters
Precisely controlling the chemical composition and structure of nanoclusters is an ongoing challenge. Here, the authors report a clickable assembly strategy to construct widely varied lanthanide nanoclusters with synergized optical functionalities.
- Jie Zhou
- , Yang Wei
- & Ling Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Expanding the chemistry of borates with functional [BO2]− anions
Expanding the chemistry of borates with functional [BO2]− anions
Borates offer extended structural diversity and promise in diverse applications. Here the authors report a borate with linear BO2 units as well as NMR spectroscopy characterization that provides a quantitative basis for identification of BO2 units in polycrystalline and non-crystalline samples.
- Chunmei Huang
- , Miriding Mutailipu
- & Shilie Pan
-
Article
| Open Access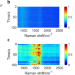 A rich catalog of C–C bonded species formed in CO2 reduction on a plasmonic photocatalyst
A rich catalog of C–C bonded species formed in CO2 reduction on a plasmonic photocatalyst
In situ vibrational spectroscopy affords a powerful tool for probing elementary chemical processes on catalytic surfaces. Using surface enhanced Raman scattering, authors identify an array of multicarbon species formed on a Ag nanoparticle catalyst in plasmon-driven reduction of CO2 in water.
- Dinumol Devasia
- , Andrew J. Wilson
- & Prashant K. Jain
-
Article
| Open Access The diversity of three-dimensional photonic crystals
The diversity of three-dimensional photonic crystals
Photonic crystals have a range of desirable properties for manipulating light. Here, the authors calculate and use the photonic band gap for thousands of such crystals to examine heuristics for their design and predict new photonic crystal structures.
- Rose K. Cersonsky
- , James Antonaglia
- & Sharon C. Glotzer
-
Article
| Open Access Optical spin-state polarization in a binuclear europium complex towards molecule-based coherent light-spin interfaces
Optical spin-state polarization in a binuclear europium complex towards molecule-based coherent light-spin interfaces
Rare-earth ion (REI)-doped systems are well suited for realising coherent light-spin interfaces, but demonstrations of spectral hole burning (SHB) in optical transitions of REI-based systems have been so far limited to REIs dispersed in matrices. Here, the authors report on transient SHB in a binuclear Eu(III) complex.
- Kuppusamy Senthil Kumar
- , Diana Serrano
- & Mario Ruben
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic upconversion multicolour editing enabled by molecule-assisted opto-electrochemical modulation
Dynamic upconversion multicolour editing enabled by molecule-assisted opto-electrochemical modulation
Though upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) are attractive for infrared detecting and modulating photonic devices, devising strategies to electrically manipulate upconversion emission remain a challenge. Here, the authors report molecule-assisted opto-electrochemical modulation of UCNP luminescence.
- Yiming Wu
- , Jiahui Xu
- & Xiaogang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic lattice distortions driven by surface trapping in semiconductor nanocrystals
Dynamic lattice distortions driven by surface trapping in semiconductor nanocrystals
Charge trapping can lead to severe nonradiative losses in colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals (NCs). The authors report femtosecond electron diffraction measurements on photoexcited NCs to reveal atomic-scale insights into how localization of charges at trap sites induce surface deformations.
- Burak Guzelturk
- , Benjamin L. Cotts
- & Aaron M. Lindenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Light-activated shape morphing and light-tracking materials using biopolymer-based programmable photonic nanostructures
Light-activated shape morphing and light-tracking materials using biopolymer-based programmable photonic nanostructures
Programmable optical actuation in a material provides special possibilities for applications. Here, the authors combine photonic crystals with elastomers to provide material composites with tunable deformation and actuation as a function of moving light.
- Yu Wang
- , Meng Li
- & Fiorenzo G. Omenetto
-
Article
| Open Access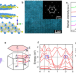 High-frequency rectifiers based on type-II Dirac fermions
High-frequency rectifiers based on type-II Dirac fermions
High-frequency rectifiers at terahertz regime are pivotal components in modern communication, whereas the drawbacks in semiconductor junctions-based devices inhibit their usages. Here, the authors report electromagnetic rectification with high signal-to-noise ratio driven by chiral Bloch-electrons in type-II Dirac semimetal NiTe2-based device allowing for efficient THz detection.
- Libo Zhang
- , Zhiqingzi Chen
- & Wei Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrastable liquid crystalline blue phase from molecular synergistic self-assembly
Ultrastable liquid crystalline blue phase from molecular synergistic self-assembly
Blue phases are spatially ordered yet fragile liquid crystalline structures, bearing applications in optoelectronics and photonics. Hu et al. show that self-assembly within a mixture of different mesogens may significantly broaden the temperature range over which they are stable.
- Wei Hu
- , Ling Wang
- & Huai Yang
-
Article
| Open Access General molten-salt route to three-dimensional porous transition metal nitrides as sensitive and stable Raman substrates
General molten-salt route to three-dimensional porous transition metal nitrides as sensitive and stable Raman substrates
Fabrication of transition metal nitrides generally requires harsh conditions due to the high activation energy barrier for nucleation. Here, the authors report a mild molten-salt route for the synthesis of three-dimensional porous metal nitrides, VN, MoN, WN, and TiN.
- Haomin Guan
- , Wentao Li
- & Guangcheng Xi
-
Article
| Open Access Giant nonlinear optical activity in two-dimensional palladium diselenide
Giant nonlinear optical activity in two-dimensional palladium diselenide
Strong nonlinearities in 2D materials can lead to interesting applications in optoelectronics. Here the authors investigate the optical nonlinearity of palladium diselenide, determine the layer dependent two photon absorption efficiency and the saturable absorption modulation depth.
- Juan Yu
- , Xiaofei Kuang
- & Yanping Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Radiative lifetime-encoded unicolour security tags using perovskite nanocrystals
Radiative lifetime-encoded unicolour security tags using perovskite nanocrystals
Designing effective covert security features is highly regarded to deter counterfeit of goods and currency in the global markets. Here, the authors present an electrohydrodynamically printed unicolour multifluorescent-lifetime security tag system based on perovskite to provide an alternative yet affordable solution.
- Sergii Yakunin
- , Jana Chaaban
- & Maksym V. Kovalenko
-
Article
| Open Access In3SbTe2 as a programmable nanophotonics material platform for the infrared
In3SbTe2 as a programmable nanophotonics material platform for the infrared
Here, the authors introduce In3SbTe2 (IST) as a programmable material platform for plasmonics and nanophotonics in the infrared. They demonstrate direct optical writing, modifying and erasing of metallic crystalline IST nanoantennas, tuning their resonances, as well as nanoscale screening and soldering.
- Andreas Heßler
- , Sophia Wahl
- & Thomas Taubner
-
Article
| Open Access Giant optical anisotropy in transition metal dichalcogenides for next-generation photonics
Giant optical anisotropy in transition metal dichalcogenides for next-generation photonics
Optical anisotropy in a broad spectral range is pivotal to efficient light manipulation. Here, the authors measure a birefringence of 1.5 in the infrared range and 3 in the visible light for MoS2.
- G. A. Ermolaev
- , D. V. Grudinin
- & V. S. Volkov
-
Article
| Open Access Geminate labels programmed by two-tone microdroplets combining structural and fluorescent color
Geminate labels programmed by two-tone microdroplets combining structural and fluorescent color
Creating an enhanced-security-level label that carries entirely distinct information in different optical states has proven challenging. Here, the authors design geminate labels by programming fluorescent cholesteric liquid crystal microdroplets to encrypt fluorescent security information behind colorful reflective patterns.
- Lang Qin
- , Xiaojun Liu
- & Yanlei Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Mixed halide perovskites for spectrally stable and high-efficiency blue light-emitting diodes
Mixed halide perovskites for spectrally stable and high-efficiency blue light-emitting diodes
Achieving bright and efficient blue emission in metal halide perovskite light-emitting diodes has proven to be challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate high EQE and spectrally stable blue light-emitting diodes based on mixed halide perovskites, with emission from 490 to 451 nm by using a vapour-assisted crystallization technique.
- Max Karlsson
- , Ziyue Yi
- & Feng Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Giant topological longitudinal circular photo-galvanic effect in the chiral multifold semimetal CoSi
Giant topological longitudinal circular photo-galvanic effect in the chiral multifold semimetal CoSi
Quantized circular photogalvanic effect (CPGE) is predicted in chiral topological semimetals, but the experimental observation remains challenging. Here, Ni et al. observe a large topological longitudinal photocurrent in CoSi, which is much larger than the photocurrent in any other chiral crystals, indicating quantized CPGE within reach upon doping and increase of the hot-carrier lifetime.
- Zhuoliang Ni
- , K. Wang
- & Liang Wu
-
Article
| Open Access π-Extended perylene diimide double-heterohelicenes as ambipolar organic semiconductors for broadband circularly polarized light detection
π-Extended perylene diimide double-heterohelicenes as ambipolar organic semiconductors for broadband circularly polarized light detection
In organic semiconducting molecules materials, distorted π-systems enable strong coupling with circular polarized light while planar π-stacking systems are necessary for high charge-carrier mobility. Here, the authors address this dilemma by introducing a skeleton merging approach through distortion of a perylene diimide core with four fused heteroaromatics to form a π-extended double helicene.
- Li Zhang
- , Inho Song
- & Jianbin Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Structural multi-colour invisible inks with submicron 4D printing of shape memory polymers
Structural multi-colour invisible inks with submicron 4D printing of shape memory polymers
Four-dimensional (4D) printing of shape memory polymer (SMP) imparts time responsive properties to 3D structures. Here, the authors explore 4D printing of a SMP in the submicron length scale, extending its applications to nanophononics.
- Wang Zhang
- , Hao Wang
- & Joel K. W. Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Nanorods with multidimensional optical information beyond the diffraction limit
Nanorods with multidimensional optical information beyond the diffraction limit
Development of functional nanostructures can enable a range of applications in imaging and nanoscale science. Here, the authors fabricate and characterize complex heterogeneous nanorods with diverse, tunable sub-wavelength structures.
- Shihui Wen
- , Yongtao Liu
- & Dayong Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable analog thermal material
Tunable analog thermal material
Thermal metamaterials are able to produce unconventional physical properties. Here, the authors demonstrate a thermal metamaterial with conductivity that can be continuously tuned over a very large range.
- Guoqiang Xu
- , Kaichen Dong
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Lithography-free IR polarization converters via orthogonal in-plane phonons in α-MoO3 flakes
Lithography-free IR polarization converters via orthogonal in-plane phonons in α-MoO3 flakes
Here, the authors investigate the polarization-dependent optical characteristics of cavities formed using α-MoO3 to extend the degrees of freedom in the design of IR photonic components exploiting the in-plane anisotropy of this material. Absorption over 80% and polarization conversion is reported without the need for nanoscale fabrication.
- Sina Abedini Dereshgi
- , Thomas G. Folland
- & Koray Aydin
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling the dimension of the quantum resonance in CdTe quantum dot superlattices fabricated via layer-by-layer assembly
Controlling the dimension of the quantum resonance in CdTe quantum dot superlattices fabricated via layer-by-layer assembly
Designing quantum dot superlattices remains a challenge. Here, the authors present CdTe quantum dot superlattices via the layer-by-layer assembly and verify the miniband formation by measuring the excitation energy the dependence of the photoluminescence spectra and the detection energy dependence of the excitation spectra.
- TaeGi Lee
- , Kazushi Enomoto
- & DaeGwi Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Suppressing material loss in the visible and near-infrared range for functional nanophotonics using bandgap engineering
Suppressing material loss in the visible and near-infrared range for functional nanophotonics using bandgap engineering
Large absorption of high-index semiconductors has hindered the application of all dielectric nanostructures in the visible range. Here, the authors present bandgap-engineered hydrogenated amorphous Si nanoparticles with Q-factors up to 100 and their integration with photochromic molecules as tunable meta-atoms.
- Mingsong Wang
- , Alex Krasnok
- & Yuebing Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Suppression of external quantum efficiency rolloff in organic light emitting diodes by scavenging triplet excitons
Suppression of external quantum efficiency rolloff in organic light emitting diodes by scavenging triplet excitons
Though organic light-emitting diodes are highly desirable for display and lighting applications, efficiency roll-off at high current densities limits its applicability. Here, the authors report a triplet scavenging strategy for improved triplet exciton management and reduced efficiency roll-off.
- Buddhika S. B. Karunathilaka
- , Umamahesh Balijapalli
- & Chihaya Adachi
-
Article
| Open Access Lead halide perovskite vortex microlasers
Lead halide perovskite vortex microlasers
Integration of III-V semiconductor microlasers into modern Si or Si3N4 based photonic integrated circuits remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a perovskite vortex microlaser with highly directional outputs and well-controlled topological charges that is highly compatible with most materials.
- Wenzhao Sun
- , Yilin Liu
- & Shumin Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Transition from light diffusion to localization in three-dimensional amorphous dielectric networks near the band edge
Transition from light diffusion to localization in three-dimensional amorphous dielectric networks near the band edge
Localisation of light in 3D materials is still not fully verified. Here the authors numerically study wave propagation in 3D hyperuniform dielectric networks in order to observe the transition to localization at the mobility edge.
- Jakub Haberko
- , Luis S. Froufe-Pérez
- & Frank Scheffold
-
Article
| Open Access Porous carbon nanowire array for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Porous carbon nanowire array for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
SERS can be unreliable for biomedical use. The authors demonstrate a metal-free nanostructure composed of porous carbon nanowires in an array as a SERS substrate. It offers 106 signal enhancement due to strong broadband charge-transfer resonance and substrate-to-substrate, spot-to-spot and time-to-time consistency in the SERS spectrum.
- Nan Chen
- , Ting-Hui Xiao
- & Keisuke Goda
-
Article
| Open Access High-speed III-V nanowire photodetector monolithically integrated on Si
High-speed III-V nanowire photodetector monolithically integrated on Si
Direct epitaxial growth of III-V on Si for optical emitters and detectors remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate in-plane monolithic integration of an InGaAs nanostructure p-i-n photodetector on Si capable of high-speed optical data reception at 32 Gbps enabled by a 3 dB bandwidth exceeding 25 GHz.
- Svenja Mauthe
- , Yannick Baumgartner
- & Kirsten E. Moselund
-
Article
| Open Access Highly efficient eco-friendly X-ray scintillators based on an organic manganese halide
Highly efficient eco-friendly X-ray scintillators based on an organic manganese halide
Scintillation-based X-ray detection is promising for applications in various areas ranging from security to healthcare, and low-cost and eco-friendly scintillation materials would be beneficial. Here the authors report a facile solution growth of organic manganese halide for efficient X-ray scintillation.
- Liang-Jin Xu
- , Xinsong Lin
- & Biwu Ma
-
Article
| Open Access X-ray radiation excited ultralong (>20,000 seconds) intrinsic phosphorescence in aluminum nitride single-crystal scintillators
X-ray radiation excited ultralong (>20,000 seconds) intrinsic phosphorescence in aluminum nitride single-crystal scintillators
Phosphorescence emission from extrinsic rare-earth element and organic component remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate an ultraviolet ultralong intrinsic phosphorescence (UIP, >20,000 seconds) in aluminum nitride (AlN) single-crystal scintillator through X-ray excitation.
- Richeng Lin
- , Wei Zheng
- & Feng Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Charge and exciton dynamics of OLEDs under high voltage nanosecond pulse: towards injection lasing
Charge and exciton dynamics of OLEDs under high voltage nanosecond pulse: towards injection lasing
Though efforts toward electrically-pumped lasers based on simple organic light-emitting diode (OLED) structures have been reported, a comprehensive model is needed to elucidate key optoelectronic processes. Here, the authors report a model describing OLED operation under high current densities.
- Viqar Ahmad
- , Jan Sobus
- & Ebinazar B. Namdas
-
Article
| Open Access Transparent near-infrared perovskite light-emitting diodes
Transparent near-infrared perovskite light-emitting diodes
Xie et al. report a transparent near-infrared light-emitting diode based on semiconducting lead halide perovskite. This technology could enable security and sensing features on space constrained smart-watches, phones, gaming consoles and augmented or virtual reality headsets.
- Chenchao Xie
- , Xiaofei Zhao
- & Zhi-Kuang Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Large cation ethylammonium incorporated perovskite for efficient and spectra stable blue light-emitting diodes
Large cation ethylammonium incorporated perovskite for efficient and spectra stable blue light-emitting diodes
Blue light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are critical for displays. Employing a large organic cation into a quasi-two dimensional perovskite with green emission, Chu et al. achieve LEDs exhibiting a high external quantum efficiency of 12.1% and stable spectra in the sky-blue region.
- Zema Chu
- , Yang Zhao
- & Jingbi You
-
Article
| Open Access Petahertz non-linear current in a centrosymmetric organic superconductor
Petahertz non-linear current in a centrosymmetric organic superconductor
Here the authors show second harmonic generation (SHG) from a centrosymmetric organic superconductor κ-(BEDT-TTF)2Cu[N(CN)2]Br. They find unusual temperature dependence and CEP-sensitive nature of the SHG which are explained in terms of nonlinear current.
- Y. Kawakami
- , T. Amano
- & S. Iwai
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic design of iridescent insect cuticles with tailored, self-organized cholesteric patterns
Biomimetic design of iridescent insect cuticles with tailored, self-organized cholesteric patterns
Replicating biological patterns is promising for designing materials with multifaceted properties but replication of twisted cholesteric liquid crystal patterns found in insects is extremely difficult. Here, the authors use liquid crystal oligomers to reproduce the textural, structural and color properties of biological liquid crystals.
- Adriana Scarangella
- , Vanessa Soldan
- & Michel Mitov
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmon-driven synthesis of individual metal@semiconductor core@shell nanoparticles
Plasmon-driven synthesis of individual metal@semiconductor core@shell nanoparticles
Light-driven heating of plasmonic metal nanoparticles can activate temperature-sensitive reactions at the nanoscale. Here, the authors exploit such nanoscale plasmonic reactors to drive, control, and spectroscopically track the growth of single metal@semiconductor core@shell nanoparticles.
- Rifat Kamarudheen
- , Gayatri Kumari
- & Andrea Baldi
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetic prediction of reverse intersystem crossing in organic donor–acceptor molecules
Kinetic prediction of reverse intersystem crossing in organic donor–acceptor molecules
Understanding and predicting the kinetics of reverse intersystem crossing (RISC) facilitates the design of materials. Here, the authors demonstrate a theoretical expression that reproduces experimental RISC rate constants ranging over five orders of magnitude in selected molecules.
- Naoya Aizawa
- , Yu Harabuchi
- & Yong-Jin Pu
-
Article
| Open Access Structural order in plasmonic superlattices
Structural order in plasmonic superlattices
Superlattices of nanoparticles promise new properties emerging from the periodic order. Here, the authors describe the synthesis of superlattices of plasmonic gold nanoparticles with high crystallinity and demonstrate how new plasmon-polariton modes appear in the structures.
- Florian Schulz
- , Ondřej Pavelka
- & Holger Lange
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of topological transport quantization by dissipation in fast Thouless pumps
Observation of topological transport quantization by dissipation in fast Thouless pumps
Topological quantized transport has been limited to slow varying potentials. Here, the authors report that a topological band structure and associated quantized transport can be restored by non-Hermitian Floquet engineering at a driving frequency as large as the system’s band gap.
- Zlata Fedorova
- , Haixin Qiu
- & Johann Kroha
-
Article
| Open Access Broadband infrared LEDs based on europium-to-terbium charge transfer luminescence
Broadband infrared LEDs based on europium-to-terbium charge transfer luminescence
Broadband near-infrared (IR) light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are desirable for smart devices and bio-imaging applications, but the efficiency is limited by the phosphor materials. The authors report broadband emission in Eu-Tb co-doped CaS due to metal-to-metal charge transfer between dopants, and build a broadband near-IR LED with output surpassing the state of the art.
- Jonas J. Joos
- , David Van der Heggen
- & Luis Seijo
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrashort laser pulse doubling by metal-halide perovskite multiple quantum wells
Ultrashort laser pulse doubling by metal-halide perovskite multiple quantum wells
Laser pulse multiplication is desired in many applications but has been challenging to realize by gain medium. Here Guo et al. achieve double-pulsed stimulated emission in quasi-2D metal-halide perovskites due to the two-channel carrier funneling effect in their multiple-quantum-wells structure.
- Jia Guo
- , Tanghao Liu
- & Guichuan Xing
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid and high-resolution patterning of microstructure and composition in organic semiconductors using ‘molecular gates’
Rapid and high-resolution patterning of microstructure and composition in organic semiconductors using ‘molecular gates’
Although high‐resolution methods such as photolithography allow for organic semiconductor patterning, they are often limited by their high complexity. Here, the authors report a versatile “molecular gate”‐based method for micro‐patterning organic semiconductor films.
- Aleksandr Perevedentsev
- & Mariano Campoy-Quiles
-
Article
| Open Access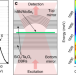 Highly nonlinear trion-polaritons in a monolayer semiconductor
Highly nonlinear trion-polaritons in a monolayer semiconductor
Here, the authors report the creation of trion-polaritons in monolayer MoSe2 in an open microcavity exhibiting strong nonlinear interactions, one order of magnitude bigger than those observed for exciton polaritons in GaAs.
- R. P. A. Emmanuele
- , M. Sich
- & D. N. Krizhanovskii
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-single exciton optical gain threshold in colloidal semiconductor quantum wells with gradient alloy shelling
Sub-single exciton optical gain threshold in colloidal semiconductor quantum wells with gradient alloy shelling
Colloidal quantum wells are highly promising for applications of solution-processed lasers, but their performance is limited by multi-excitonic nature of the materials. Here, the authors demonstrate optical gain in graded alloy core/shell CdSe/CdS@CdZnS quantum wells at less than one exciton per particle resulting in ultralow thresholds.
- Nima Taghipour
- , Savas Delikanli
- & Hilmi Volkan Demir
-
Article
| Open Access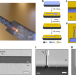 Overcoming evanescent field decay using 3D-tapered nanocavities for on-chip targeted molecular analysis
Overcoming evanescent field decay using 3D-tapered nanocavities for on-chip targeted molecular analysis
Plasmon-enhanced fluorescence is strictly dependent on molecule size and surface position, restricting application of diversely sized molecules. Here, the authors overcome this by introducing a 3D tapered gap plasmon nanocavity with fluidic access and near homogeneous confinement of the electromagnetic fields.
- Shailabh Kumar
- , Haeri Park
- & Hyuck Choo

 Wide-range lifetime-tunable and responsive ultralong organic phosphorescent multi-host/guest system
Wide-range lifetime-tunable and responsive ultralong organic phosphorescent multi-host/guest system