Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Light-induced MOF synthesis enabling composite photothermal materials
Light-induced MOF synthesis enabling composite photothermal materials
Introduced here is a light-induced MOF synthesis, enabled by plasmonic nanoparticles. The method, proven to be rapid and efficient, can also promote the formation of a nanoparticle-MOF composite, imparting photothermal properties to the new material.
- Ofir Shelonchik
- , Nir Lemcoff
- & Yossi Weizmann
-
Article
| Open Access Programming crack patterns with light in colloidal plasmonic films
Programming crack patterns with light in colloidal plasmonic films
Crack formation typically results in random patterns and material failure. Inspired by plant phototropism, the authors use plasmonic absorbers to control crack propagation in colloidal films with light, showcasing a robust, programmable self-assembly process.
- Fanny Thorimbert
- , Mateusz Odziomek
- & Marco Faustini
-
Article
| Open Access Regulating protein corona on nanovesicles by glycosylated polyhydroxy polymer modification for efficient drug delivery
Regulating protein corona on nanovesicles by glycosylated polyhydroxy polymer modification for efficient drug delivery
The dynamic protein corona hinders the uptake of nanocarriers in desired target cell populations, limiting their bench-to-bedside translation. Here the authors reveal that the modification of hydroxyl and amino functional groups on nanovesicles can rationally regulate the composition of protein coronas to improve the efficiency of targeted drug delivery.
- Yunqiu Miao
- , Lijun Li
- & Yong Gan
-
Article
| Open Access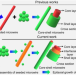 Visualizing the interfacial-layer-based epitaxial growth process toward organic core-shell architectures
Visualizing the interfacial-layer-based epitaxial growth process toward organic core-shell architectures
Organic heterostructures with controlled geometry on the micro and nanoscale are important in nanotechnology, but epitaxial growth processes with high lattice mismatching are challenging to achieve. Here, the authors report a visualisation process for morphology evolution on epitaxial growth.
- Ming-Peng Zhuo
- , Xiao Wei
- & Liang-Sheng Liao
-
Article
| Open Access Multicompartmental coacervate-based protocell by spontaneous droplet evaporation
Multicompartmental coacervate-based protocell by spontaneous droplet evaporation
Coacervate-based compartments are attractive as potential protocells, but formation and control of the compartments can be challenging. Here, the authors report the spontaneous formation of core-shell, cell-sized coacervate compartments driven by droplet evaporation.
- Cheng Qi
- , Xudong Ma
- & Zhou Liu
-
Article
| Open Access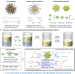 Ultra-stable and highly reactive colloidal gold nanoparticle catalysts protected using multi-dentate metal oxide nanoclusters
Ultra-stable and highly reactive colloidal gold nanoparticle catalysts protected using multi-dentate metal oxide nanoclusters
For catalytic nanoparticles there is often a trade-off between stability and activity. Here the authors report a route to ultra-stable and catalytically active colloidal small (~3 nm) gold nanoparticles using multi-dentate polyoxometalates as protecting agents in nonpolar solvents.
- Kang Xia
- , Takafumi Yatabe
- & Kosuke Suzuki
-
Article
| Open Access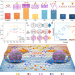 Optimizing potassium polysulfides for high performance potassium-sulfur batteries
Optimizing potassium polysulfides for high performance potassium-sulfur batteries
Potassium-sulfur battery are promising materials for next-generation high energy, low cost batteries. Here the authors explore a tungsten based catalytic composite for optimizing potassium polysulfides and improve K-S electrochemistry in batteries
- Wanqing Song
- , Xinyi Yang
- & Wenbin Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding the AIE phenomenon of nonconjugated rhodamine derivatives via aggregation-induced molecular conformation change
Understanding the AIE phenomenon of nonconjugated rhodamine derivatives via aggregation-induced molecular conformation change
“Understanding the structure-property relationship of organic molecules which exhibit different properties upon aggregation is important for the field of material science. Here, the authors prepare nonconjugated rhodamine-based molecules without aggregation-induced emission building blocks yet displaying typical aggregation-induced emission behavior.”
- Lin-Lin Yang
- , Haoran Wang
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogel dressings with intrinsic antibiofilm and antioxidative dual functionalities accelerate infected diabetic wound healing
Hydrogel dressings with intrinsic antibiofilm and antioxidative dual functionalities accelerate infected diabetic wound healing
Dressings for aiding in chronic wound healing can be beneficial, but often involve additional processes or leave residue. Here, the authors report a hydrogel dressing with antibiofilm and antioxidative properties for the treatment of infected diabetic wounds.
- Dicky Pranantyo
- , Chun Kiat Yeo
- & Mary B. Chan-Park
-
Article
| Open Access Self-compliant ionic skin by leveraging hierarchical hydrogen bond association
Self-compliant ionic skin by leveraging hierarchical hydrogen bond association
Ionic skins have potential in long-term physiological monitoring, but do not always achieve a desirable balance of viscosity and elasticity. Here, the authors report a material with hierarchical topological entanglements allowing desirable viscoelastic properties.
- Huating Ye
- , Baohu Wu
- & Peiyi Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired light-driven chloride pump with helical porphyrin channels
Bioinspired light-driven chloride pump with helical porphyrin channels
Artificial ion channels have potential in a range of applications, but achieving performance comparable to biological channels has been challenging. Here, the authors report an artificial, light-driven chloride pump, inspired by halorhodopsin, with a helical porphyrin channel array.
- Chao Li
- , Yi Zhai
- & Lei Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Generating dual structurally and functionally skin-mimicking hydrogels by crosslinking cell-membrane compartments
Generating dual structurally and functionally skin-mimicking hydrogels by crosslinking cell-membrane compartments
It is desirable to be able to mimic the properties of skin with hydrogels, but challenging to achieve. Here, the authors report the use of functionalised extracellular vesicles as crosslinkers for skin-mimicking hydrogels with good mechanical strength.
- Feng Wu
- , Yusheng Ren
- & Yan Pang
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with nia nets for efficient separation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures
Three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with nia nets for efficient separation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures
The synthesis of three-dimensional (3D) covalent organic frameworks (COFs) with highly connected building blocks presents a significant challenge. Here, the authors report the synthesis of two 3D COFs with the nia topology, by introducing planar hexagonal and triangular prism nodes.
- Jianhong Chang
- , Fengqian Chen
- & Qianrong Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Upcycling poly(succinates) with amines to N-substituted succinimides over succinimide anion-based ionic liquids
Upcycling poly(succinates) with amines to N-substituted succinimides over succinimide anion-based ionic liquids
Ionic liquids have been employed in dissolution and chemical degradation of waste polymers. Here the authors report a cation-anion confined hydrogen-bonding catalysis strategy to deconstruct poly(succinates) into N-substituted succinimides over ionic liquids.
- Fengtian Wu
- , Yuepeng Wang
- & Zhimin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access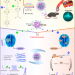 A one-two punch targeting reactive oxygen species and fibril for rescuing Alzheimer’s disease
A one-two punch targeting reactive oxygen species and fibril for rescuing Alzheimer’s disease
Toxic amyloid-beta plaque and harmful inflammation are two leading hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and precise AD therapy is elusive due to the lack of dual-targeting therapy function, limited blood-brain barrier penetration, and low imaging sensitivity. Here, the authors address these issues by designing a near-infrared-II aggregation-induced emission nanotheranostic for precise AD therapy.
- Jiefei Wang
- , Ping Shangguan
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Sublimed C60 for efficient and repeatable perovskite-based solar cells
Sublimed C60 for efficient and repeatable perovskite-based solar cells
Batch-to-batch reproducibility of device performances is crucial for perovskite photovoltaics moving towards industrialization. Here, the authors show that commercial as-received C60 source materials may coalesce during repeated thermal evaporation processes, jeopardizing such reproducibility.
- Ahmed A. Said
- , Erkan Aydin
- & Stefaan De Wolf
-
Article
| Open Access Self-encapsulated ionic fibers based on stress-induced adaptive phase transition for non-contact depth-of-field camouflage sensing
Self-encapsulated ionic fibers based on stress-induced adaptive phase transition for non-contact depth-of-field camouflage sensing
Fabrication methods for ionic conductive hydrogel fibers are challenged by complexity and poor stability. Using a stress-induced adaptive phase transition strategy, Liu et al. fabricate self-encapsulated hydrogel fibers for depth-of-field sensing applications in a sustainable, two-step process.
- Ying Liu
- , Chan Wang
- & Zhou Li
-
Article
| Open Access Self-similar chiral organic molecular cages
Self-similar chiral organic molecular cages
To enhance the utility of organic molecular cages (OMCs), the evolution of OMCs into higher-level chiral OMCs with self-similar superstructures is meaningful yet challenging. Here, the authors report a pair of higher-level 3D tri-bladed chiral helical molecular cages, displaying self-similarity in a discrete self-similar superstructure at different levels.
- Zhen Wang
- , Qing-Pu Zhang
- & Chuan-Feng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks in solution enables continuous and high-crystalline membranes
Hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks in solution enables continuous and high-crystalline membranes
Hydrogen-bonded organic frameworks (HOFs) attract increasing attention as porous materials. Despite the widely studied solid-state properties, little research has been done on the solution state. Here, the authors demonstrate that HOFs fragment into small particles while maintaining their original assemblies upon dispersing in solvents.
- Qi Yin
- , Kuan Pang
- & Tian-Fu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access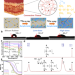 Connective tissue inspired elastomer-based hydrogel for artificial skin via radiation-indued penetrating polymerization
Connective tissue inspired elastomer-based hydrogel for artificial skin via radiation-indued penetrating polymerization
Robust hydrogels offer a promising solution for the development of artificial skin for bionic robots, yet few hydrogels have a comprehensive performance comparable to real human skin. Here, the authors present a general method to convert traditional elastomers into tough hydrogels via a unique radiation-induced penetrating polymerization method.
- Yuan Tian
- , Zhihao Wang
- & Yunlong Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-micro porous thin polymer membranes for discriminating H2 and CO2
Sub-micro porous thin polymer membranes for discriminating H2 and CO2
The fabrication of polymeric membranes with high permeance and remarkable selectivity for simultaneous H2 purification and CO2 capture is challenging. Here, the authors design a polymer membrane with sub-micro pores via controlled transformation of amine-linked polymer films into benzimidazole- and amine-linked polymer layers.
- Xueru Yan
- , Tianqi Song
- & Xinlei Liu
-
Article
| Open Access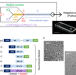 Replicating shear-mediated self-assembly of spider silk through microfluidics
Replicating shear-mediated self-assembly of spider silk through microfluidics
Native spider silk has desirable mechanical properties, but these are challenging to replicate in an artificial material. Here, the authors report the use of a microfluidic system to create continuous fibers based on recombinant spidroin.
- Jianming Chen
- , Arata Tsuchida
- & Keiji Numata
-
Article
| Open Access Lithiated porous silicon nanowires stimulate periodontal regeneration
Lithiated porous silicon nanowires stimulate periodontal regeneration
Prelithiation can introduce controllable amounts of lithium within porous silicon, however it yields a highly reactive material unsuitable for biomedicine. In this study, the authors present a strategy to lithiate porous silicon nanowires, resulting in a biocompatible and bioresorbable material.
- Martti Kaasalainen
- , Ran Zhang
- & Ciro Chiappini
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-selective uranium separation by in-situ formation of π-f conjugated 2D uranium-organic framework
Ultra-selective uranium separation by in-situ formation of π-f conjugated 2D uranium-organic framework
Methodologies to achieve efficient and selective uranium separation originating from nuclear waste are desirable. Here the authors report the in-situ formation of π-f conjugated 2D uranium-organic framework for uranium separation, leading to superior performance in uranium uptake and outstanding uranium generation efficiency from seawater.
- Qing Yun Zhang
- , Lin Juan Zhang
- & Feng Luo
-
Article
| Open Access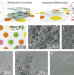 Unusual flexibility of transparent poly(methylsilsesquioxane) aerogels by surfactant-induced mesoscopic fiber-like assembly
Unusual flexibility of transparent poly(methylsilsesquioxane) aerogels by surfactant-induced mesoscopic fiber-like assembly
Aerogels are mechanically friable despite their attractive properties such as visible-light transparency and low thermal conductivity. Here the authors show mechanically flexible, highly transparent aerogels based on fiber-like pore skeletons.
- Ryota Ueoka
- , Yosuke Hara
- & Kazuyoshi Kanamori
-
Article
| Open Access Functionally antagonistic polyelectrolyte for electro-ionic soft actuator
Functionally antagonistic polyelectrolyte for electro-ionic soft actuator
Electro-active ionic soft actuators generally present slow responses and poor durability when are applied as artificial muscles. Here, the authors describe a polyelectrolyte membrane based on the assembly of Nafion molecules into micelles with efficient ionic conducting pathways for electro-ionic soft actuators and soft robotics with fast responses and long durability.
- Van Hiep Nguyen
- , Saewoong Oh
- & Il-Kwon Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of core@shell catalysts guided by Tammann temperature
Synthesis of core@shell catalysts guided by Tammann temperature
The authors report a synthetic strategy to create core@shell catalysts using strong metal-support interactions and low-Tammann-temperature compounds. The resulting materials are highly stable and may be useful in industrial applications.
- Pei Xiong
- , Zhihang Xu
- & Molly Meng-Jung Li
-
Article
| Open Access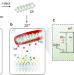 Non-Faradaic optoelectrodes for safe electrical neuromodulation
Non-Faradaic optoelectrodes for safe electrical neuromodulation
Nanoscale optoelectrodes hold the potential to optically stimulate individual neuron. Here, the authors form nanoscale capacitive optoelectrodes by incorporating zinc porphyrin into nanorods, coated by TiO2, a design that allows for far-field optical modulation of neurons with efficiency and negligible side effects.
- Jian Chen
- , Yanyan Liu
- & Wenbo Bu
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling nonconjugated polyesters emit full-spectrum fluorescence from blue to near-infrared
Enabling nonconjugated polyesters emit full-spectrum fluorescence from blue to near-infrared
Near-infrared luminescence is useful for advance applications, but is challenging to achieve through clusteroluminescence. Here, the authors report the use of amine-initiated polyesters for amine-ester clusters with near-infrared emission.
- Bo Chu
- , Xiong Liu
- & Xing-Hong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Active machine learning model for the dynamic simulation and growth mechanisms of carbon on metal surface
Active machine learning model for the dynamic simulation and growth mechanisms of carbon on metal surface
Understanding the surface growth mechanism of carbon nanostructures would help designing better catalysts. Here, the authors combine active machine learning force fields with time-stamped Monte Carlo methods, to dynamically predict carbon growth on metal surfaces.
- Di Zhang
- , Peiyun Yi
- & Hao Li
-
Article
| Open Access One-dimensional single atom arrays on ferroelectric nanosheets for enhanced CO2 photoreduction
One-dimensional single atom arrays on ferroelectric nanosheets for enhanced CO2 photoreduction
The authors report a study preparing single atom (M = Pt, Ag, Fe, Co, and Ni) arrays on Au/Bi4Ti3O12 nanosheets using electric field polarization techniques. Photocatalytic CO2 reduction is shown to proceed effectively over Au/Bi4Ti3O12.
- Lizhen Liu
- , Jingcong Hu
- & Hongwei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Animating hydrogel knotbots with topology-invoked self-regulation
Animating hydrogel knotbots with topology-invoked self-regulation
Soft robots have potential in a number of applications, but the self-regulated steering of the robots under static stimuli is a significant challenge. Here, the authors report the movement of knotbots by symmetry breaking and restoration to achieve tasks including gear rotation and rod climbing.
- Qing Li Zhu
- , Weixuan Liu
- & Zi Liang Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Helical-caging enables single-emitted large asymmetric full-color circularly polarized luminescence
Helical-caging enables single-emitted large asymmetric full-color circularly polarized luminescence
Circularly polarised luminescence (CPL) is essential for asymmetric synthetic photochemistry. Here, the authors integrate white quantum dots with chiral nematic liquid crystal or liquid crystal polymer to achieve single-emitted tuneable full-colour or white CPL for enantioselective polymerization.
- Yajie Zhou
- , Yaxin Wang
- & Taotao Zhuang
-
Article
| Open Access Cation-π interactions enabled water-stable perovskite X-ray flat mini-panel imager
Cation-π interactions enabled water-stable perovskite X-ray flat mini-panel imager
The water stability of perovskites remains challenging due to their intrinsic ionic nature. Here, the authors present water stable perovskite X-ray imager driven by strong cation-π interactions between organic cations and a complete release of microstrain during dimension transformation process.
- Wanting Pan
- , Yuhong He
- & Haotong Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Shape morphing of hydrogels by harnessing enzyme enabled mechanoresponse
Shape morphing of hydrogels by harnessing enzyme enabled mechanoresponse
A change material properties on application of stimuli is a useful property for hydrogels, but mechano-responsiveness in such materials is challenging to achieve. Here, the authors report a strain-responsive hydrogel, controlled by the activity of enzymes within the material.
- Kuan Zhang
- , Yu Zhou
- & Lifei Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable adhesion and morphing of protein hydrogels for underwater robots
Programmable adhesion and morphing of protein hydrogels for underwater robots
Soft robots have potential in carrying out underwater tasks, but achieving the right level of adhesion and shape-changing ability is challenging. Here, the authors report the development of protein-based hydrogels with iron oxide nanoparticles with photothermal and magnetic responsiveness, capable of carrying out complex tasks.
- Sheng-Chen Huang
- , Ya-Jiao Zhu
- & Zhi-Gang Qian
-
Article
| Open Access Surface hydrophobization of hydrogels via interface dynamics-induced network reconfiguration
Surface hydrophobization of hydrogels via interface dynamics-induced network reconfiguration
It is useful to be able to control the surface properties of a hydrogel, but tuning the surface without altering bulk properties of the hydrogel is challenging. Here, the authors report a method for modifying the surface of a hydrogel by grafting of polymer chains to the mold.
- Bo Yi
- , Tianjie Li
- & Liming Bian
-
Article
| Open Access Switching molecular recognition selectivities by temperature in a diffusion-regulatory porous material
Switching molecular recognition selectivities by temperature in a diffusion-regulatory porous material
The design of host-guest systems for switchable recognition of guests upon the change of external stimuli is challenging due to the invariable host-guest affinity. Here, the authors encode a dynamic motion into a porous crystal to regulate the diffusion of CO2 and C2H2 allowing the crystal to switch the gas recognition selectivity by temperature.
- Yan Su
- , Ken-ichi Otake
- & Cheng Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired structural hydrogels with highly ordered hierarchical orientations by flow-induced alignment of nanofibrils
Bioinspired structural hydrogels with highly ordered hierarchical orientations by flow-induced alignment of nanofibrils
Natural materials can combine strength and toughness, but achieving similar well-ordered structures for synthetic materials is challenging. Here, the authors report hydrogels prepared by flow-induced alignment of nanofibrils, with anisotropic structure and good mechanical properties.
- Shuihong Zhu
- , Sen Wang
- & Youhui Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Heparin-network-mediated long-lasting coatings on intravascular catheters for adaptive antithrombosis and antibacterial infection
Heparin-network-mediated long-lasting coatings on intravascular catheters for adaptive antithrombosis and antibacterial infection
Catheter-related infection and thrombosis are serious complications, and preventative coatings are not always suitable. Here, the authors report a heparin mediated coating for to address both infections and thrombosis from catheters simultaneously.
- Lin Liu
- , Huan Yu
- & Hengchong Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Metallopolymer strategy to explore hypoxic active narrow-bandgap photosensitizers for effective cancer photodynamic therapy
Metallopolymer strategy to explore hypoxic active narrow-bandgap photosensitizers for effective cancer photodynamic therapy
Iridium-based photosensitizers exhibit good photocatalytic performance, but the in vivo applications are hindered by conventional O2-dependent Type-II photochemistry and poor absorption. Here, the authors report a general metallopolymerization strategy for engineering iridium complexes exhibiting Type-I photochemistry and enhancing absorption intensity in the blue to near-infrared region.
- Zhao Zhang
- , Zixiang Wei
- & Xuanjun Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Dipeptide coacervates as artificial membraneless organelles for bioorthogonal catalysis
Dipeptide coacervates as artificial membraneless organelles for bioorthogonal catalysis
Coacervate droplets have potential as components for cell-like materials, but are limited by complex molecular structure and control of the internal microenvironment. Here, the authors report stable dipeptide-based coacervates with a microenvironment for the encapsulation of hydrophobic species.
- Shoupeng Cao
- , Tsvetomir Ivanov
- & Lucas Caire da Silva
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks
Biomimetic chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks
Assembly is an interesting strategy to build chiral hierarchies with premade properties and functionalities. Here, the authors present assembled chiral hydrogen-bonded organic-inorganic frameworks with dynamical chiroptical activities and employ them as powerful and recoverable platforms for enantioselective recognition of chiral aliphatic substrates.
- Jun Guo
- , Yulong Duan
- & Yi Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Octopus-inspired deception and signaling systems from an exceptionally-stable acene variant
Octopus-inspired deception and signaling systems from an exceptionally-stable acene variant
The design of multifunctional platforms with tunable spectroscopic and fluorescent properties that span the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared spectral regions remains challenging. Here, the authors report an actuator-type system that leverages a readily-prepared, easily-processable, and exceptionally-stable nonacene-like molecule to achieve multiple complementary dynamic operating modes.
- Preeta Pratakshya
- , Chengyi Xu
- & Alon A. Gorodetsky
-
Article
| Open Access Janus particles with tunable patch symmetry and their assembly into chiral colloidal clusters
Janus particles with tunable patch symmetry and their assembly into chiral colloidal clusters
Janus particles commonly exhibit a high-symmetry patch, constraining the range of possible assemblies. Here, the authors devise a synthetic approach to fine-tune the patch symmetry in Janus particles and showcase the assembly of these particles into chiral colloidal clusters.
- Tianran Zhang
- , Dengping Lyu
- & Yufeng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access 3D microprinting of inorganic porous materials by chemical linking-induced solidification of nanocrystals
3D microprinting of inorganic porous materials by chemical linking-induced solidification of nanocrystals
3D microprinting is considered a next generation manufacturing process for microscale components. Here, authors develop a generalised microscale 3D printing method to produce purely inorganic nanocrystal-linked porous materials that exhibit excellent functionality and hierarchical porosity.
- Minju Song
- , Yoonkyum Kim
- & Jae Sung Son
-
Article
| Open Access Ground-state electron transfer in all-polymer donor:acceptor blends enables aqueous processing of water-insoluble conjugated polymers
Ground-state electron transfer in all-polymer donor:acceptor blends enables aqueous processing of water-insoluble conjugated polymers
Chemical approaches to improve aqueous dispersions of conjugated polymers are limited by the feasibility of modifying the backbone or lead to poor performance. Here, Liu et al. show that ground-state electron transfer in donor:acceptor blends aids aqueous dispersion, for high conductivity and solubility.
- Tiefeng Liu
- , Johanna Heimonen
- & Simone Fabiano
-
Article
| Open Access 3D printing of self-healing personalized liver models for surgical training and preoperative planning
3D printing of self-healing personalized liver models for surgical training and preoperative planning
High-fidelity personalized anatomical models can offer invaluable support for precision medicine. Here, the authors show the 3D printing of self-healing liver models, which can be resected in a trial and-error manner for surgical training to enhance the safety of hepatic surgery.
- Yahui Lu
- , Xing Chen
- & Yuhua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Folk arts-inspired twice-coagulated configuration-editable tough aerogels enabled by transformable gel precursors
Folk arts-inspired twice-coagulated configuration-editable tough aerogels enabled by transformable gel precursors
Aerogels attract considerable attention in various emerging fields in recent decades, but low density and weak mechanical performance make their configuration-editing capability challenging. Here the authors establish an efficient twice-coagulated strategy to fabricate configuration-editable tough aerogels enabled by transformable gel precursors.
- Lishan Li
- , Guandu Yang
- & Xuetong Zhang

 Melt-quenched carboxylate metal–organic framework glasses
Melt-quenched carboxylate metal–organic framework glasses