Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Nano-enabled pancreas cancer immunotherapy using immunogenic cell death and reversing immunosuppression
Nano-enabled pancreas cancer immunotherapy using immunogenic cell death and reversing immunosuppression
Pancreatic cancer remains difficult to treat mainly due to the drug delivery challenges posed by a strong stromal component. Here the authors develop nanocarriers that improve drug delivery efficiency and engage the host immune system against the tumor resulting in reduction of tumor growth and metastasis.
- Jianqin Lu
- , Xiangsheng Liu
- & Andre E. Nel
-
Article
| Open Access Forming a three-dimensional porous organic network via solid-state explosion of organic single crystals
Forming a three-dimensional porous organic network via solid-state explosion of organic single crystals
Porous organic networks are of great fundamental and technological interest. Here, the authors synthesize a three-dimensional porous organic network with high specific surface area via a solid-state explosive reaction of hexaethynyl triptycene single crystals containing primer molecules.
- Seo-Yoon Bae
- , Dongwook Kim
- & Jong-Beom Baek
-
Article
| Open Access Interference-like patterns of static magnetic fields imprinted into polymer/nanoparticle composites
Interference-like patterns of static magnetic fields imprinted into polymer/nanoparticle composites
For materials fabrication, it is most efficient to create various patterns from the same set of templates. Here, the authors show that when magnetic particles are exposed to stacks of periodic magnetic fields, they can form dynamic interference-like patterns that reflect where the magnetic fields overlap.
- Zhijie Yang
- , Jingjing Wei
- & Bartosz A. Grzybowski
-
Article
| Open Access Excavating hidden adsorption sites in metal-organic frameworks using rational defect engineering
Excavating hidden adsorption sites in metal-organic frameworks using rational defect engineering
Defects in metal-organic frameworks have an important impact on the properties of resultant materials. Here, based on computational screening the authors identify 13 frameworks that experience drastic improvements in their methane storage capacities upon introduction of linker vacancy defects.
- Sanggyu Chong
- , Günther Thiele
- & Jihan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Oxygen-rich microporous carbons with exceptional hydrogen storage capacity
Oxygen-rich microporous carbons with exceptional hydrogen storage capacity
Hydrogen is attractive as a clean fuel for motor vehicles and porous carbons represent promising hydrogen storage materials. Here, Mokaya and colleagues incorporate oxygen-rich functional groups into porous carbons with high microporosity, showing that such materials exhibit significantly enhanced H2 storage capacity.
- L. Scott Blankenship
- , Norah Balahmar
- & Robert Mokaya
-
Article
| Open Access Purcell-enhanced quantum yield from carbon nanotube excitons coupled to plasmonic nanocavities
Purcell-enhanced quantum yield from carbon nanotube excitons coupled to plasmonic nanocavities
Single-walled carbon nanotubes offer exciting optoelectronic applications but generally suffer from low quantum yields. Here, Luo et al. demonstrate that coupling nanotubes to plasmonic antennas can lead to large Purcell enhancement and corresponding increase in quantum yield as well as plasmonic thermometry at the single molecule level.
- Yue Luo
- , Ehsaneh D. Ahmadi
- & Stefan Strauf
-
Article
| Open Access Total morphosynthesis of biomimetic prismatic-type CaCO3 thin films
Total morphosynthesis of biomimetic prismatic-type CaCO3 thin films
The exterior layers of mollusk shells are prismatic in nature, endowing them with stiffness and wear resistance. Inspired by these biominerals, here, Jiang and colleagues grow structurally similar prismatic-type CaCO3 thin films with comparable stiffness and hardness.
- Chuanlian Xiao
- , Ming Li
- & Helmut Cölfen
-
Article
| Open Access A mesoporous cationic thorium-organic framework that rapidly traps anionic persistent organic pollutants
A mesoporous cationic thorium-organic framework that rapidly traps anionic persistent organic pollutants
Cationic metal-organic frameworks provide promising opportunities to capture anionic pollutants, but stable frameworks with sufficiently large pores are lacking. Here the authors present a thorium-based mesoporous, cationic and hydrolytically-stable MOF that can rapidly trap inorganic and organic anionic pollutants.
- Yuxiang Li
- , Zaixing Yang
- & Shuao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon dioxide capture and conversion by an acid-base resistant metal-organic framework
Carbon dioxide capture and conversion by an acid-base resistant metal-organic framework
Increasing CO2 emissions pose serious environmental issues. Here, the authors report the synthesis of a robust metal-organic framework which displays high volumetric uptake of post-combustion CO2 under ambient conditions and can catalyze CO2 fixation into cyclic carbonates.
- Linfeng Liang
- , Caiping Liu
- & Maochun Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Transformation of doped graphite into cluster-encapsulated fullerene cages
Transformation of doped graphite into cluster-encapsulated fullerene cages
An understanding of how caged carbon materials self-assemble from doped graphite is a long-standing challenge. Here, the authors show that distinct bottom-up processes lead to the synthesis of high-symmetry clusterfullerenes.
- Marc Mulet-Gas
- , Laura Abella
- & Paul W. Dunk
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-modal mechanophores based on cinnamate dimers
Multi-modal mechanophores based on cinnamate dimers
Mechanochemistry offers exciting opportunities for molecular engineering of stress-responsive properties of polymers. Here the authors show that macrocyclic cinnamate dimers in a polymer chain can undergo dissociation on the sub-second timescale under 1–2 nN stretching to yield a chromophore that then can be optically healed.
- Huan Zhang
- , Xun Li
- & Roman Boulatov
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrathin two-dimensional porous organic nanosheets with molecular rotors for chemical sensing
Ultrathin two-dimensional porous organic nanosheets with molecular rotors for chemical sensing
Molecular rotors that fluoresce upon restriction are useful components in functional materials. Here, the authors incorporate molecular rotors into 2D porous organic nanosheets, creating sensitive and selective fluorescent sensors for volatile organic compounds and metal ions.
- Jinqiao Dong
- , Kang Zhang
- & Dan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Stable and ordered amide frameworks synthesised under reversible conditions which facilitate error checking
Stable and ordered amide frameworks synthesised under reversible conditions which facilitate error checking
Irreversible bond formation in covalent organic frameworks leads to amorphous materials. Here, the authors show that crystalline and ultra-stable covalent amide frameworks can be accessed by devitrification of amorphous polyamide networks.
- David Stewart
- , Dmytro Antypov
- & Matthew J. Rosseinsky
-
Article
| Open Access Spin crossover-induced colossal positive and negative thermal expansion in a nanoporous coordination framework material
Spin crossover-induced colossal positive and negative thermal expansion in a nanoporous coordination framework material
Controlling mechanical motions in solid state devices is highly desirable for the development of nanoscale machines. Here, Kepert and colleagues exploit an ultra-flexible coordination framework in which thermally-controlled Fe(II) spin transitions result in remarkable flexing of the crystal lattice.
- Benjamin R. Mullaney
- , Laurence Goux-Capes
- & Cameron J. Kepert
-
Article
| Open Access Ferrotoroidic ground state in a heterometallic {CrIIIDyIII
6} complex displaying slow magnetic relaxation
Ferrotoroidic ground state in a heterometallic {CrIIIDyIII
6} complex displaying slow magnetic relaxation
Coupling molecular toroids via ferrotoroidic interactions represents an important opportunity to enhance ground state toroidicity, but is challenging to achieve. Here the authors isolate a {CrIIIDyIII 6} complex with a ferrotoroidic ground state and an enhanced toroidal moment, arising solely from intramolecular dipolar interactions.
- Kuduva R. Vignesh
- , Alessandro Soncini
- & Gopalan Rajaraman
-
Article
| Open Access Firefly-mimicking intensive and long-lasting chemiluminescence hydrogels
Firefly-mimicking intensive and long-lasting chemiluminescence hydrogels
Great efforts have been devoted to the development of chemiluminescence systems that emit light with high intensity over long periods of time. Here the authors show, firefly-mimicking intensive and long-lasting chemiluminescence hydrogels consisting of chitosan, N-(4-aminobutyl)-N-ethylisoluminol (ABEI) and catalyst Co2+.
- Yating Liu
- , Wen Shen
- & Hua Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Regulating p-block metals in perovskite nanodots for efficient electrocatalytic water oxidation
Regulating p-block metals in perovskite nanodots for efficient electrocatalytic water oxidation
Electrocatalysts that possess high densities of surface defects show great promise for efficient water oxidation. Here the authors demonstrate that regulating the p-block metal content in perovskite nanodots imparts these materials with abundant surface defects and excellent electrocatalytic activity.
- Bo-Quan Li
- , Zi-Jing Xia
- & Qiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding seed-mediated growth of gold nanoclusters at molecular level
Understanding seed-mediated growth of gold nanoclusters at molecular level
Synthetic nanochemistry currently lacks the molecular step-by-step routes afforded to organic chemistry by total synthesis. Here, the authors track the seeded growth of atom-precise gold nanoclusters using mass spectrometry, revealing that the clusters evolve through a series of intermediates in two-electron steps.
- Qiaofeng Yao
- , Xun Yuan
- & Jianping Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical signal activation of an organocatalyst enables control over soft material formation
Chemical signal activation of an organocatalyst enables control over soft material formation
Enzymes regulated by chemical signals are common in biology, but few such artificial catalysts exist. Here, the authors design an aniline catalyst that, when activated by a chemical trigger, catalyses formation of hydrazone-based gels, demonstrating signal response in a soft material.
- Fanny Trausel
- , Chandan Maity
- & Rienk Eelkema
-
Article
| Open Access Coulomb spin liquid in anion-disordered pyrochlore Tb2Hf2O7
Coulomb spin liquid in anion-disordered pyrochlore Tb2Hf2O7
Experimental studies of frustrated spin systems such as pyrochlore magnetic oxides test our understanding of quantum many-body physics. Here the authors show experimentally that Tb2Hf2O7 may be a model material for investigating how structural disorder can stabilize a quantum spin liquid phase.
- Romain Sibille
- , Elsa Lhotel
- & Michel Kenzelmann
-
Article
| Open Access Strict molecular sieving over electrodeposited 2D-interspacing-narrowed graphene oxide membranes
Strict molecular sieving over electrodeposited 2D-interspacing-narrowed graphene oxide membranes
Producing graphene oxide membranes with narrow channels is desirable for small molecule separations, but methods to narrow the 2D spacing typically result in membrane damage. Here the authors exploit electrophoresis-deposition to prepare GO membranes that are reduced in situ, leading to narrow and uniform 2D channels.
- Benyu Qi
- , Xiaofan He
- & Yuhan Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging the polymerization of multivalent nanoparticles in solution
Imaging the polymerization of multivalent nanoparticles in solution
Few models exist that describe the spontaneous organization of colloids into materials. Here, the authors combine liquid-phase TEM and single particle tracking to observe the dynamics of gold nanoprisms, finding that nanoscale self-assembly can be understood within the framework of atomic polymerization.
- Juyeong Kim
- , Zihao Ou
- & Qian Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Continual reproduction of self-assembling oligotriazole peptide nanomaterials
Continual reproduction of self-assembling oligotriazole peptide nanomaterials
Molecules that act as both autocatalysts and material precursors offer exciting prospects for self-synthesizing materials. Here, the authors design a triazole peptide that self-replicates and then self-assembles into nanostructures, coupling autocatalytic and assembly pathways to realize a reproducing supramolecular system.
- Roberto J. Brea
- & Neal K. Devaraj
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding activity trends in electrochemical water oxidation to form hydrogen peroxide
Understanding activity trends in electrochemical water oxidation to form hydrogen peroxide
Producing hydrogen peroxide via electrochemical oxidation of water is an attractive route to this valuable product. Here the authors theoretically and experimentally investigate hydrogen peroxide production activity trends for a range of metal oxides and identify the optimal bias ranges for high Faraday efficiencies.
- Xinjian Shi
- , Samira Siahrostami
- & Jens K. Nørskov
-
Article
| Open Access Pseudo-topotactic conversion of carbon nanotubes to T-carbon nanowires under picosecond laser irradiation in methanol
Pseudo-topotactic conversion of carbon nanotubes to T-carbon nanowires under picosecond laser irradiation in methanol
T-carbon is a previously predicted but so far unobserved allotrope of carbon, with a crystal structure similar to diamond, but with each atomic lattice position replaced by a carbon tetrahedron. Here, the authors produce T-carbon nanowires via laser-irradiating a suspension of carbon nanotubes in methanol.
- Jinying Zhang
- , Rui Wang
- & Chunming Niu
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrodeoxygenation of water-insoluble bio-oil to alkanes using a highly dispersed Pd–Mo catalyst
Hydrodeoxygenation of water-insoluble bio-oil to alkanes using a highly dispersed Pd–Mo catalyst
Bio-oil is a potential major source of renewable fuels and chemicals. Here, the authors report a palladium-molybdenum mixed catalyst for the selective hydrodeoxygenation of water-insoluble bio-oil to mixtures of alkanes with high carbon yield.
- Haohong Duan
- , Juncai Dong
- & Dermot O’Hare
-
Article
| Open Access Infused-liquid-switchable porous nanofibrous membranes for multiphase liquid separation
Infused-liquid-switchable porous nanofibrous membranes for multiphase liquid separation
Separating immiscible liquids with small surface energy differences remains a challenge. Here, the authors develop a polarity-based strategy for the separation of multiphase mixtures of immiscible liquids, even those with surface energy differences as small as 2 mJ m-2.
- Yang Wang
- , Jiancheng Di
- & Jihong Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Distinguishing faceted oxide nanocrystals with 17O solid-state NMR spectroscopy
Distinguishing faceted oxide nanocrystals with 17O solid-state NMR spectroscopy
The exposed facets of oxide nanocrystals are key to their properties. Here, the authors use 17O solid-state NMR spectroscopy to discriminate between oxygen species on different facets of anatase titania nanocrystals, providing compelling evidence for the value of NMR spectroscopy in characterizing faceted oxides.
- Yuhong Li
- , Xin-Ping Wu
- & Luming Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular analogue of the perovskite repeating unit and evidence for direct MnIII-CeIV-MnIII exchange coupling pathway
Molecular analogue of the perovskite repeating unit and evidence for direct MnIII-CeIV-MnIII exchange coupling pathway
Perovskite manganites exhibit intriguing but poorly understood properties, including multiferroicity. Here, the authors synthesize a Ce3Mn8 cluster that structurally resembles a perovskite repeat unit, and use this molecular analogue to elucidate mechanisms driving bulk perovskite properties.
- Annaliese E. Thuijs
- , Xiang-Guo Li
- & George Christou
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-triggered solvent-free metamorphosis of polymeric materials
Photo-triggered solvent-free metamorphosis of polymeric materials
The design of organic and polymeric soft materials showing isothermal reversible liquid–nonliquid conversion is challenging. Here, the authors show solvent-free repeatable molecular architectural transformation between liquid-star and non-liquid-network polymers by the cleavage and reformation of covalent bonds in the polymer chain.
- Satoshi Honda
- & Taro Toyota
-
Article
| Open Access 3D calcite heterostructures for dynamic and deformable mineralized matrices
3D calcite heterostructures for dynamic and deformable mineralized matrices
Minerals are rarely explored as building blocks for dynamic inorganic materials. Here, the authors derive inspiration from fish scales to create mutable surfaces based on arrays of calcite crystals, in which one end of each crystal is immobilized in and regenerated from silicone, and the other functional end is left exposed.
- Jaeseok Yi
- , Yucai Wang
- & Bozhi Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Capture of organic iodides from nuclear waste by metal-organic framework-based molecular traps
Capture of organic iodides from nuclear waste by metal-organic framework-based molecular traps
Capturing radioactive organic iodides from nuclear waste is important for safe nuclear energy usage, but remains a significant challenge. Here, Li and co-workers fabricate a stable metal–organic framework functionalized with tertiary amine groups that exhibits high capacities for radioactive organic iodides uptake.
- Baiyan Li
- , Xinglong Dong
- & Jing Li
-
Article
| Open Access White light emission from a single organic molecule with dual phosphorescence at room temperature
White light emission from a single organic molecule with dual phosphorescence at room temperature
The development of single molecule white light-emitters is extremely challenging for pure phosphorescent metal-free systems at room temperature. Here the authors show a single pure organic room temperature phosphor, 4-chlorobenzoyldibenzothiophene, utilizing the emission from both T1 and T2 states.
- Zikai He
- , Weijun Zhao
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access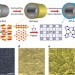 Ultrathin metal–organic framework membrane production by gel–vapour deposition
Ultrathin metal–organic framework membrane production by gel–vapour deposition
MOF-based membranes have shown great promise in separation applications, but producing thin membranes that allow for high fluxes remains challenging. Here, the authors use a gel–vapour deposition strategy to fabricate composite membranes with less than 20 nm thicknesses and high gas permeances and selectivities.
- Wanbin Li
- , Pengcheng Su
- & Eddy Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Photoelectrochemical oxidation of organic substrates in organic media
Photoelectrochemical oxidation of organic substrates in organic media
Photoelectrochemical water splitting is a promising method for H2 fuel production, but the O2 by-product generated has little economic value. Here, Berlinguette and colleagues demonstrate that BiVO4 photoanodes immersed in organic media can instead perform valuable alcohol oxidation and C–H functionalization reactions.
- Tengfei Li
- , Takahito Kasahara
- & Curtis P. Berlinguette
-
Article
| Open Access High-quality monolayer superconductor NbSe2 grown by chemical vapour deposition
High-quality monolayer superconductor NbSe2 grown by chemical vapour deposition
Two-dimensional superconductors will likely have applications not only in devices, but also in the study of fundamental physics. Here, Wang et al. demonstrate the CVD growth of superconducting NbSe2 on a variety of substrates, making these novel materials increasingly accessible.
- Hong Wang
- , Xiangwei Huang
- & Zheng Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Formation pathways of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with dodecagonal tiling
Formation pathways of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with dodecagonal tiling
Probing the growth pathways of quasicrystalline materials, where tiling units arrange with local but no long-range order, remains challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate that dodecagonal tiling of mesoporous silica nanoparticles occurs via irreversible packing of micelles with non-uniform size distribution.
- Yao Sun
- , Kai Ma
- & Ulrich Wiesner
-
Article
| Open Access A promising high-energy-density material
A promising high-energy-density material
High energy density materials are of interest, but density is the limiting factor for many organic compounds. Here the authors show the formation of a high density energetic compound from a two-step reaction between commercially available compounds that exhibit good heat thermal stability and detonation properties.
- Wenquan Zhang
- , Jiaheng Zhang
- & Qinghua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Non-aqueous selective synthesis of orthosilicic acid and its oligomers
Non-aqueous selective synthesis of orthosilicic acid and its oligomers
Orthosilicic acid is essential to many natural and synthetic materials but notoriously difficult to isolate, limiting its use in materials synthesis. Here, the authors successfully synthesize and stabilize orthosilicic acid and its oligomers, making available a new family of building blocks for silicon oxide-based materials.
- Masayasu Igarashi
- , Tomohiro Matsumoto
- & Shigeru Shimada
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic components embedded in a single graphene nanoribbon
Electronic components embedded in a single graphene nanoribbon
Adding functional electronic components to graphene nanoribbons requires precise control over their atomic structure. Here, the authors use a bottom-up approach to build a metal-semiconductor junction and a tunnel barrier directly into a single graphene nanoribbon, an exciting development for graphene-based electronic devices
- P. H. Jacobse
- , A. Kimouche
- & I. Swart
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible interlocked porous frameworks allow quantitative photoisomerization in a crystalline solid
Flexible interlocked porous frameworks allow quantitative photoisomerization in a crystalline solid
Organizing photochromic molecules into 3D networks is a key strategy to access photoresponsive materials, but framework rigidity typically limits conversion efficiency. Here, the authors exploit a flexible metal-organic framework to achieve quantitative and reversible photoisomerization in a porous crystalline solid.
- Yongtai Zheng
- , Hiroshi Sato
- & Susumu Kitagawa
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of ordered carbonaceous frameworks from organic crystals
Synthesis of ordered carbonaceous frameworks from organic crystals
Carbon-based materials are promising alternatives to noble metal catalysts, but their structures are typically disordered and difficult to control. Here, the authors obtain ordered carbonaceous frameworks with advantageous electrocatalytic properties via the carbonization of nickel-containing porphyrin dimer networks.
- Hirotomo Nishihara
- , Tetsuya Hirota
- & Fumito Tani
-
Article
| Open Access Multifunctional nanoparticles as a tissue adhesive and an injectable marker for image-guided procedures
Multifunctional nanoparticles as a tissue adhesive and an injectable marker for image-guided procedures
The use of tissue adhesives for the closure of wounds is of growing interest for surgery and trauma management. Here, the authors develop an adhesive that is biocompatible, enables tissue adhesion and also permits real-time imaging due to the presence of contrast agents for multiple modalities.
- Kwangsoo Shin
- , Jin Woo Choi
- & Taeghwan Hyeon
-
Article
| Open Access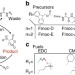 Non-equilibrium dissipative supramolecular materials with a tunable lifetime
Non-equilibrium dissipative supramolecular materials with a tunable lifetime
Biological systems vital functions are based on non-equilibrium states driven by consumption of chemical fuels. Here the authors show a spatiotemporal control over the formation of hydrophobic colloids, hydrogels or inks through a chemical reaction network of dicarboxylate compounds fuelled by carbodiimide.
- Marta Tena-Solsona
- , Benedikt Rieß
- & Job Boekhoven
-
Article
| Open Access Single molecule magnet with an unpaired electron trapped between two lanthanide ions inside a fullerene
Single molecule magnet with an unpaired electron trapped between two lanthanide ions inside a fullerene
Single molecule magnets have demonstrated promise for information storage, molecular spintronics and quantum computing, but are limited by their low operational temperatures. Here, Popov and coworkers prepare a SMM with a high blocking temperature of 18 K by trapping two lanthanide ions with a single-electron bond inside a fullerene.
- Fupin Liu
- , Denis S. Krylov
- & Alexey A. Popov
-
Article
| Open Access A volumetric three-dimensional digital light photoactivatable dye display
A volumetric three-dimensional digital light photoactivatable dye display
Despite living in a three-dimensional world, almost all information in our society is conveyed in a two-dimensional format. Here, the authors provide a technique for the generation of spatially accurate and high-resolution three-dimensional images using fluorescent photoswitch chemistry.
- Shreya K. Patel
- , Jian Cao
- & Alexander R. Lippert
-
Article
| Open Access Wafer-scale single-crystal perovskite patterned thin films based on geometrically-confined lateral crystal growth
Wafer-scale single-crystal perovskite patterned thin films based on geometrically-confined lateral crystal growth
Wafer-scale deposition of uniform metal halide perovskite single-crystals is a step towards commercialisation. Using geometrically-confined lateral crystal growth, Leeet al., report patterned thin films of highly-aligned single-crystals and achieve lateral solar cells with efficiencies up to 4.83%.
- Lynn Lee
- , Jangmi Baek
- & Myung M. Sung
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast water sensing and thermal imaging by a metal-organic framework with switchable luminescence
Ultrafast water sensing and thermal imaging by a metal-organic framework with switchable luminescence
Fast and sensitive detection of water molecules in organic solvents and gases remains an important challenge. Here, Pan and co-workers design a metal-organic framework capable of ultrafast and reversible water sensing by photoluminescence switching via an excited state intramolecular proton transfer mechanism.
- Ling Chen
- , Jia-Wen Ye
- & Cheng-Yong Su
-
Article
| Open Access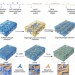 Adaptive and freeze-tolerant heteronetwork organohydrogels with enhanced mechanical stability over a wide temperature range
Adaptive and freeze-tolerant heteronetwork organohydrogels with enhanced mechanical stability over a wide temperature range
Several living organisms can survive subzero temperatures without cell damage. Here, the authors show a heteronetwork organohydrogel with improved elasticity and mechanical features in a wide range of temperatures.
- Hainan Gao
- , Ziguang Zhao
- & Lei Jiang

 A rapidly-reversible absorptive and emissive vapochromic Pt(II) pincer-based chemical sensor
A rapidly-reversible absorptive and emissive vapochromic Pt(II) pincer-based chemical sensor