Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Elementary steps in electrical doping of organic semiconductors
Elementary steps in electrical doping of organic semiconductors
Molecular doping is routinely used in organic semiconductor devices nowadays, but the physics at play remains unclarified. Tietze et al. describe it as a two-step process and show it costs little, energetically, to dissociate charge transfer complexes due to energetic disorder of organic semiconductors.
- Max L. Tietze
- , Johannes Benduhn
- & Karl Leo
-
Article
| Open Access Explosive dissolution and trapping of block copolymer seed crystallites
Explosive dissolution and trapping of block copolymer seed crystallites
The study of the dissolution of polymer crystals is a challenging task. Here the authors use crystallization-driven self-assembly of coil-crystalline block copolymers as a trapping technique to track the change in length of 1D seed crystallites during annealing.
- Gerald Guerin
- , Paul A. Rupar
- & Mitchell A. Winnik
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic artificial organelles with in vitro and in vivo activity triggered by reduction in microenvironment
Biomimetic artificial organelles with in vitro and in vivo activity triggered by reduction in microenvironment
The efficacy of stimuli-responsive enzyme delivery systems is usually limited to in vitro applications. Here the authors form artificial organelles by inserting stimuli-responsive protein gates in membranes of polymersomes loaded with enzymes and obtain a triggered functionality both in vitro and in vivo.
- T. Einfalt
- , D. Witzigmann
- & C. G. Palivan
-
Article
| Open Access Plasma dye coating as straightforward and widely applicable procedure for dye immobilization on polymeric materials
Plasma dye coating as straightforward and widely applicable procedure for dye immobilization on polymeric materials
Dye coating techniques for colored materials are often cost intensive or cause degradation of the material during processing. Here the authors demonstrate a fast, scalable and cost efficient plasma dye coating procedure, which allows for covalent immobilization of dye molecules on different polymer surfaces.
- Lieselot De Smet
- , Gertjan Vancoillie
- & Richard Hoogenboom
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-liquid-like state in a spin-1/2 square-lattice antiferromagnet perovskite induced by d10–d0 cation mixing
Spin-liquid-like state in a spin-1/2 square-lattice antiferromagnet perovskite induced by d10–d0 cation mixing
Quantum spin liquids are predicted to form in frustrated square lattice magnets but this has been difficult to verify experimentally. Here the authors show that cation mixing in the square perovskite Sr2Cu(Te0.5W0.5)O6 can be used to tune it into the spin liquid regime.
- O. Mustonen
- , S. Vasala
- & M. Karppinen
-
Article
| Open Access Surface plasmon resonance extension through two-block metal-conducting polymer nanorods
Surface plasmon resonance extension through two-block metal-conducting polymer nanorods
Localized surface plasmon resonance can be exploited for a range of applications, but remains difficult to tailor in metal-organic nanostructures. Here the authors synthesize gold-polypyrrole nanorods and observe a unique extended surface plasmon resonance, which they find to be tunable through doping.
- Insub Jung
- , Minkyung Kim
- & Sungho Park
-
Article
| Open Access Cation vacancy stabilization of single-atomic-site Pt1/Ni(OH)x catalyst for diboration of alkynes and alkenes
Cation vacancy stabilization of single-atomic-site Pt1/Ni(OH)x catalyst for diboration of alkynes and alkenes
Development of single-atomic-site catalysts with high metal loading remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a nickel hydroxide nanoboard with abundant Ni2+ vacancy defects serving as the support to achieve high platinum loading by simple wet impregnation.
- Jian Zhang
- , Xi Wu
- & Yadong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-thin enzymatic liquid membrane for CO2 separation and capture
Ultra-thin enzymatic liquid membrane for CO2 separation and capture
Porous membranes show great promise for CO2 separation and capture, but are currently limited by a trade-off between permeance and selectivity. Here, the authors fabricate a bio-inspired, ultra-thin enzymatic liquid membrane that displays exceptional CO2 permeability and selectivity under ambient conditions.
- Yaqin Fu
- , Ying-Bing Jiang
- & C. Jeffrey Brinker
-
Article
| Open Access The role of confined collagen geometry in decreasing nucleation energy barriers to intrafibrillar mineralization
The role of confined collagen geometry in decreasing nucleation energy barriers to intrafibrillar mineralization
Nucleation in highly confined gaps shows distinctly different behavior from nucleation in extrafibrillar spaces. Here, using in situ X-ray scattering and classical nucleation theory, the authors show how confined geometry reduces energy barriers to intrafibrillar mineralization of collagen.
- Doyoon Kim
- , Byeongdu Lee
- & Young-Shin Jun
-
Article
| Open Access Highly stretchable carbon aerogels
Highly stretchable carbon aerogels
Improved compressive elasticity was lately demonstrated for carbon aerogels but the problem of reversible stretchability remained a challenge. Here the authors use a hierarchical structure design and synergistic effects between carbon nanotubes and graphene to achieve high stretchability in carbon aerogels.
- Fan Guo
- , Yanqiu Jiang
- & Chao Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of friction on oxidative graphite intercalation and high-quality graphene formation
Effect of friction on oxidative graphite intercalation and high-quality graphene formation
Scalable graphene production from graphite via an intercalation-oxidation-reduction process is still hampered by low reproducibility and many lattice defects. Here, the authors show that reducing molecular friction by using highly crystalline graphite and mild oxidizing conditions is the key to high quality graphene.
- Steffen Seiler
- , Christian E. Halbig
- & Siegfried Eigler
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum and electrochemical interplays in hydrogenated graphene
Quantum and electrochemical interplays in hydrogenated graphene
Electrochemically-gated graphene field-effect transistors show promise for sensing of charged species in real time. Here, the authors leverage the interplay between electrical in-plane transport and electrochemical activity to explore the sensing performance of hydrogenated graphene.
- Lin Jiang
- , Wangyang Fu
- & Grégory F. Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Retrosynthesis of multi-component metal−organic frameworks
Retrosynthesis of multi-component metal−organic frameworks
The crystal engineering of metal–organic frameworks has led to the construction of complex structures, but has yet to reach the same level of sophistication as organic synthesis. Here, Zhou and colleagues use retrosynthetic chemistry to design and produce complex multi-component frameworks.
- Shuai Yuan
- , Jun-Sheng Qin
- & Hong-Cai Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Oxidation-stable amine-containing adsorbents for carbon dioxide capture
Oxidation-stable amine-containing adsorbents for carbon dioxide capture
Amine-containing solids are promising adsorbents for CO2 capture, but their low oxidative stability has hindered their application. Here, Choi and colleagues develop a strategy to poison the metal impurities present in poly(ethyleneimine)/silica adsorbents, significantly improving their stability towards oxidation.
- Kyungmin Min
- , Woosung Choi
- & Minkee Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Route to high-energy density polymeric nitrogen t-N via He−N compounds
Route to high-energy density polymeric nitrogen t-N via He−N compounds
Polymeric nitrogen has yet to be recovered to ambient conditions, precluding its practical application as high-energy density material. Here, the authors highlight a possible route to the formation of a tetragonal polymeric nitrogen via helium-nitrogen compounds at high pressures.
- Yinwei Li
- , Xiaolei Feng
- & Yanming Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-fouling graphene-based membranes for effective water desalination
Anti-fouling graphene-based membranes for effective water desalination
Intrinsic limitations of nanoporous graphene limit its applications in water treatment. Here the authors produce post-treatment-free, low-cost graphene-based membranes from renewable biomass and demonstrate their high water permeance and antifouling properties using real seawater.
- Dong Han Seo
- , Shafique Pineda
- & Kostya (Ken) Ostrikov
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular-channel driven actuator with considerations for multiple configurations and color switching
Molecular-channel driven actuator with considerations for multiple configurations and color switching
Intrinsic deformation with fast response in commercially available materials that can safely contact skin continues to be a challenge for artificial actuating materials. Here the authors incorporate nanoscale molecular channels within perfluorosulfonic acid ionomer for self-adaptive and ambient-driven actuation.
- Jiuke Mu
- , Gang Wang
- & Meifang Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Stimuli-responsive hydroxyapatite liquid crystal with macroscopically controllable ordering and magneto-optical functions
Stimuli-responsive hydroxyapatite liquid crystal with macroscopically controllable ordering and magneto-optical functions
Liquid crystals comprising inorganic species are far less common than their organic-based counterparts. Here, the authors report a magneto-optically responsive liquid crystal based on nanorods of the biomineral hydroxyapatite, representing a new type of biologically-based, dynamic inorganic material.
- Masanari Nakayama
- , Satoshi Kajiyama
- & Takashi Kato
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly of emissive supramolecular rosettes with increasing complexity using multitopic terpyridine ligands
Self-assembly of emissive supramolecular rosettes with increasing complexity using multitopic terpyridine ligands
Metal coordination of multitopic ligands is a powerful approach to building complex, functional architectures. Here, the authors construct three generations of fluorescent supramolecular rosettes by coordination of aggregation-induced emissive ligands, including a 2nd-generation macrocycle that emits pure white light.
- Guang-Qiang Yin
- , Heng Wang
- & Xiaopeng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast ion sieving using nanoporous polymeric membranes
Ultrafast ion sieving using nanoporous polymeric membranes
Nanoporous membranes show great potential for ionic separations, but the typical trade-off between permeability and selectivity hinders their applicability. Here the authors fabricate nanoporous polymeric membranes with a high density of 0.5 nm pores and demonstrate their exceptional performance for ion sieving.
- Pengfei Wang
- , Mao Wang
- & Yugang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Walking and rolling of crystals induced thermally by phase transition
Walking and rolling of crystals induced thermally by phase transition
Mechanical motions of molecular crystals have been limited to in-place movement or slow crawling. Here, the authors describe chiral azobenzene crystals that walk or roll quickly forward in response to heating or cooling, offering new modes of material locomotion.
- Takuya Taniguchi
- , Haruki Sugiyama
- & Hideko Koshima
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing hole trapping in zinc oxide nanoparticles by time-resolved X-ray spectroscopy
Revealing hole trapping in zinc oxide nanoparticles by time-resolved X-ray spectroscopy
Metal-oxide nanostructures are used in a range of light-driven applications, yet the fundamentals behind their properties are poorly understood. Here the authors probe photoexcited zinc oxide nanoparticles using time-resolved X-ray spectroscopy, identifying photocatalytically-active hole traps as oxygen vacancies in the lattice.
- Thomas J. Penfold
- , Jakub Szlachetko
- & Christopher J. Milne
-
Article
| Open Access Mössbauer spectroscopy of a monolayer of single molecule magnets
Mössbauer spectroscopy of a monolayer of single molecule magnets
Deposition of single molecule magnets onto surfaces is a key step for integration in devices exploiting their magnetic bistability and quantum properties. Here, Sessoli and colleagues exploit synchrotron Mössbauer spectroscopy to assess the effects of molecule-surface interactions on the magnetic properties of Fe(III) SMMs.
- Alberto Cini
- , Matteo Mannini
- & Roberta Sessoli
-
Article
| Open Access Active sites of copper-complex catalytic materials for electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Active sites of copper-complex catalytic materials for electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
The catalytic conversion of carbon dioxide into value-added products requires an understanding of the active species present under working conditions. Here, the authors discover copper-containing complexes to reversibly transform during electrocatalysis into methane-producing copper nanoclusters.
- Zhe Weng
- , Yueshen Wu
- & Hailiang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Fused electron deficient semiconducting polymers for air stable electron transport
Fused electron deficient semiconducting polymers for air stable electron transport
Semiconducting polymers are usually prepared by transition metal mediated coupling reactions that cause problems for sustainability and biological applications. Here the authors synthesise fused electron deficient polymers that are air stable and have high electron affinities, via metal free aldol polymerisation reactions.
- Ada Onwubiko
- , Wan Yue
- & Iain McCulloch
-
Article
| Open Access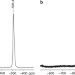 Facile storage and release of white phosphorus and yellow arsenic
Facile storage and release of white phosphorus and yellow arsenic
White phosphorus and yellow arsenic represent useful elemental sources for synthetic applications, but their poor stabilities make their storage highly challenging. Here, Scheer and colleagues encapsulate P4 and As4 molecules within porous activated carbons and demonstrate their use in subsequent chemical reactions.
- Andreas E. Seitz
- , Felix Hippauf
- & Manfred Scheer
-
Article
| Open Access Rotator side chains trigger cooperative transition for shape and function memory effect in organic semiconductors
Rotator side chains trigger cooperative transition for shape and function memory effect in organic semiconductors
Martensitic transition is commonly seen in steel and shape memory alloys but rarely in organic materials. Chung et al. discover martensitic transitions in organic electronics and utilize it in designing field-effect transistors, leading to shape memory effect that in return modifies charge transport properties.
- Hyunjoong Chung
- , Dmytro Dudenko
- & Ying Diao
-
Article
| Open Access Designable and dynamic single-walled stiff nanotubes assembled from sequence-defined peptoids
Designable and dynamic single-walled stiff nanotubes assembled from sequence-defined peptoids
The application potential of organic nanotubes is currently limited by their lack of designable or dynamic properties. Here, Chen et al. use sequence-defined peptoids to assemble a new family of pH-responsive stiff nanotubes whose dimensions, components and functions can be easily tailored.
- Haibao Jin
- , Yan-Huai Ding
- & Chun-Long Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A versatile MOF-based trap for heavy metal ion capture and dispersion
A versatile MOF-based trap for heavy metal ion capture and dispersion
Heavy metal removal from polluted water is of global significance, but current adsorbents are limited by their specificity towards certain metals. Here the authors incorporate a non-specific and strong chelating group into a robust metal-organic framework and demonstrate its versatility for heavy metal adsorption.
- Yaguang Peng
- , Hongliang Huang
- & Chongli Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access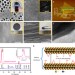 MXene molecular sieving membranes for highly efficient gas separation
MXene molecular sieving membranes for highly efficient gas separation
Two-dimensional materials show great potential for membrane technologies, but their disordered channels hinder their molecular sieving performance. Here, Wang, Gogotsi and colleagues design a MXene membrane with ordered nanochannels that exhibits an excellent H2/CO2 gas separation performance.
- Li Ding
- , Yanying Wei
- & Yury Gogotsi
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic metal-ligand coordination for multicolour and water-jet rewritable paper
Dynamic metal-ligand coordination for multicolour and water-jet rewritable paper
Rewritable paper is environmentally favourable, but its practical realization is stifled by limited ink colour versatility and poor image retention times. Here, the authors exploit the relatively stable but reversible nature of metal–organic coordination bonds to produce long-lasting and multicoloured inks for rewritable paper.
- Yun Ma
- , Pengfei She
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access In situ inward epitaxial growth of bulk macroporous single crystals
In situ inward epitaxial growth of bulk macroporous single crystals
Porous single crystals are desirable for optoelectronic applications, but their fabrication remains challenging. Here the authors produce centimetre-sized macroporous GaN single crystals with electron mobility comparable to that of bulk crystals via in situ inward epitaxial growth on parent LiGaO2 crystals.
- Chenlong Chen
- , Shujing Sun
- & Kui Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Sixteen isostructural phosphonate metal-organic frameworks with controlled Lewis acidity and chemical stability for asymmetric catalysis
Sixteen isostructural phosphonate metal-organic frameworks with controlled Lewis acidity and chemical stability for asymmetric catalysis
Asymmetric synthesis predominantly falls within the realm of homogeneous catalysis. Here, the authors synthesized 16 chiral metal–organic frameworks differing in the nature of the transition metal and demonstrate their excellent stability, catalytic activity and recyclability in a number of enantioselective reactions.
- Xu Chen
- , Yongwu Peng
- & Yong Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Electrical semiconduction modulated by light in a cobalt and naphthalene diimide metal-organic framework
Electrical semiconduction modulated by light in a cobalt and naphthalene diimide metal-organic framework
Photoactive and semiconducting metal-organic frameworks are desirable for electrical and photoelectrical devices, but remain rare. Here Demets and co-workers design a naphthalene diimide and cobalt based MOF with anisotropic electrical semiconductivity and a high responsivity of 2.5 × 105 A W−1.
- Evandro Castaldelli
- , K. D. G. Imalka Jayawardena
- & Grégoire Jean-François Demets
-
Article
| Open Access Giant coercivity and high magnetic blocking temperatures for N2
3− radical-bridged dilanthanide complexes upon ligand dissociation
Giant coercivity and high magnetic blocking temperatures for N2
3− radical-bridged dilanthanide complexes upon ligand dissociation
Single-molecule magnets typically only retain information in the presence of an applied magnetic field and at very low temperatures. Here, Demir, Long and co-workers design N2 3– radical-bridged dilanthanide complexes that exhibit giant coercivities and 100-s magnetic blocking temperatures of up to 20 K.
- Selvan Demir
- , Miguel I. Gonzalez
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering active precursors in colloidal quantum dot synthesis
Uncovering active precursors in colloidal quantum dot synthesis
Little is understood about the chemical evolution of precursors to quantum dots. Here, the authors find that under the high temperature conditions typical of CdSe quantum dot synthesis, precursors decompose into highly reactive species in a critical first step before forming monomers and finally nanocrystals.
- Leah C. Frenette
- & Todd D. Krauss
-
Article
| Open Access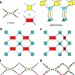 Redox-switchable breathing behavior in tetrathiafulvalene-based metal–organic frameworks
Redox-switchable breathing behavior in tetrathiafulvalene-based metal–organic frameworks
Modulating the adsorption behaviours of metal-organic frameworks using external stimuli is desirable, but challenging to achieve. Here, Zhou and colleagues design an indium-based MOF in which tetrathiafulvalene ligands undergo reversible redox reactions that alter the framework breathing behaviour.
- Jian Su
- , Shuai Yuan
- & Hong-Cai Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access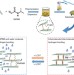 Bioinspired graphene membrane with temperature tunable channels for water gating and molecular separation
Bioinspired graphene membrane with temperature tunable channels for water gating and molecular separation
The smart regulation of substance permeability is highly desirable for membrane separation technologies. Here, the authors design a poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-grafted graphene oxide membrane with temperature tunable lamellar spaces, allowing for water gating and size-variable molecular separations.
- Jingchong Liu
- , Nü Wang
- & Yong Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Existence of multi-radical and closed-shell semiconducting states in post-graphene organic Dirac materials
Existence of multi-radical and closed-shell semiconducting states in post-graphene organic Dirac materials
The lack of band gap controllability in graphene severely restricts its use in nanoelectronics. Here, the authors predict that post-graphene organic Dirac materials should allow for exceptional electronic tunability between graphene-like semimetallicity and multi-radical and/or closed-shell semiconducting states.
- Isaac Alcón
- , Francesc Viñes
- & Stefan T. Bromley
-
Article
| Open Access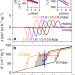 Giant barocaloric effects over a wide temperature range in superionic conductor AgI
Giant barocaloric effects over a wide temperature range in superionic conductor AgI
Barocaloric materials offer promise in solid-state cooling devices, but few materials have been show to display giant barocaloric effects near room temperature. Here, the authors demonstrate that solid electrolyte AgI displays giant inverse barocaloric effects near its superionic phase transition at ~420 K.
- Araceli Aznar
- , Pol Lloveras
- & Lluís Mañosa
-
Article
| Open Access A rapidly-reversible absorptive and emissive vapochromic Pt(II) pincer-based chemical sensor
A rapidly-reversible absorptive and emissive vapochromic Pt(II) pincer-based chemical sensor
Solid state Pt(II)-pincer complexes exhibiting vapochromic responses show promise for chemical sensing applications, but their slow responses typically limit their utility. Here, Raithby and colleagues design a Pt(II)-pincer complex with a subsecond, highly-selective vapochromic response to water and methanol.
- M. J. Bryant
- , J. M. Skelton
- & P. R. Raithby
-
Article
| Open Access Nano-enabled pancreas cancer immunotherapy using immunogenic cell death and reversing immunosuppression
Nano-enabled pancreas cancer immunotherapy using immunogenic cell death and reversing immunosuppression
Pancreatic cancer remains difficult to treat mainly due to the drug delivery challenges posed by a strong stromal component. Here the authors develop nanocarriers that improve drug delivery efficiency and engage the host immune system against the tumor resulting in reduction of tumor growth and metastasis.
- Jianqin Lu
- , Xiangsheng Liu
- & Andre E. Nel
-
Article
| Open Access Forming a three-dimensional porous organic network via solid-state explosion of organic single crystals
Forming a three-dimensional porous organic network via solid-state explosion of organic single crystals
Porous organic networks are of great fundamental and technological interest. Here, the authors synthesize a three-dimensional porous organic network with high specific surface area via a solid-state explosive reaction of hexaethynyl triptycene single crystals containing primer molecules.
- Seo-Yoon Bae
- , Dongwook Kim
- & Jong-Beom Baek
-
Article
| Open Access Interference-like patterns of static magnetic fields imprinted into polymer/nanoparticle composites
Interference-like patterns of static magnetic fields imprinted into polymer/nanoparticle composites
For materials fabrication, it is most efficient to create various patterns from the same set of templates. Here, the authors show that when magnetic particles are exposed to stacks of periodic magnetic fields, they can form dynamic interference-like patterns that reflect where the magnetic fields overlap.
- Zhijie Yang
- , Jingjing Wei
- & Bartosz A. Grzybowski
-
Article
| Open Access Excavating hidden adsorption sites in metal-organic frameworks using rational defect engineering
Excavating hidden adsorption sites in metal-organic frameworks using rational defect engineering
Defects in metal-organic frameworks have an important impact on the properties of resultant materials. Here, based on computational screening the authors identify 13 frameworks that experience drastic improvements in their methane storage capacities upon introduction of linker vacancy defects.
- Sanggyu Chong
- , Günther Thiele
- & Jihan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access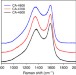 Oxygen-rich microporous carbons with exceptional hydrogen storage capacity
Oxygen-rich microporous carbons with exceptional hydrogen storage capacity
Hydrogen is attractive as a clean fuel for motor vehicles and porous carbons represent promising hydrogen storage materials. Here, Mokaya and colleagues incorporate oxygen-rich functional groups into porous carbons with high microporosity, showing that such materials exhibit significantly enhanced H2 storage capacity.
- L. Scott Blankenship
- , Norah Balahmar
- & Robert Mokaya
-
Article
| Open Access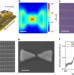 Purcell-enhanced quantum yield from carbon nanotube excitons coupled to plasmonic nanocavities
Purcell-enhanced quantum yield from carbon nanotube excitons coupled to plasmonic nanocavities
Single-walled carbon nanotubes offer exciting optoelectronic applications but generally suffer from low quantum yields. Here, Luo et al. demonstrate that coupling nanotubes to plasmonic antennas can lead to large Purcell enhancement and corresponding increase in quantum yield as well as plasmonic thermometry at the single molecule level.
- Yue Luo
- , Ehsaneh D. Ahmadi
- & Stefan Strauf
-
Article
| Open Access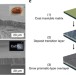 Total morphosynthesis of biomimetic prismatic-type CaCO3 thin films
Total morphosynthesis of biomimetic prismatic-type CaCO3 thin films
The exterior layers of mollusk shells are prismatic in nature, endowing them with stiffness and wear resistance. Inspired by these biominerals, here, Jiang and colleagues grow structurally similar prismatic-type CaCO3 thin films with comparable stiffness and hardness.
- Chuanlian Xiao
- , Ming Li
- & Helmut Cölfen
-
Article
| Open Access A mesoporous cationic thorium-organic framework that rapidly traps anionic persistent organic pollutants
A mesoporous cationic thorium-organic framework that rapidly traps anionic persistent organic pollutants
Cationic metal-organic frameworks provide promising opportunities to capture anionic pollutants, but stable frameworks with sufficiently large pores are lacking. Here the authors present a thorium-based mesoporous, cationic and hydrolytically-stable MOF that can rapidly trap inorganic and organic anionic pollutants.
- Yuxiang Li
- , Zaixing Yang
- & Shuao Wang

 Adsorption-based atmospheric water harvesting device for arid climates
Adsorption-based atmospheric water harvesting device for arid climates