Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A dynamic and multi-responsive porous flexible metal–organic material
A dynamic and multi-responsive porous flexible metal–organic material
Stimuli-responsive porous materials are attractive for a range of applications, but each material typically exhibits only one type of transformation. Here, the authors report on a metal–organic material that exhibits six distinct phases as a result of four types of structural transformation in response to different stimuli.
- Mohana Shivanna
- , Qing-Yuan Yang
- & Michael J. Zaworotko
-
Article
| Open Access Ba3Mg3(BO3)3F3 polymorphs with reversible phase transition and high performances as ultraviolet nonlinear optical materials
Ba3Mg3(BO3)3F3 polymorphs with reversible phase transition and high performances as ultraviolet nonlinear optical materials
Nonlinear optical crystals suitable for the UV spectral region could simplify short-wavelength generation and make it more efficient. Here, the authors design and demonstrate that one of two asymmetric borate polymorphs exhibits promising optical and mechanical properties for generating UV light.
- Miriding Mutailipu
- , Min Zhang
- & Shilie Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Highly sensitive switching of solid-state luminescence by controlling intersystem crossing
Highly sensitive switching of solid-state luminescence by controlling intersystem crossing
The development of intelligent materials, in particular those showing the highly sensitive mechanoresponsive luminescence (MRL), remains challenging. Here the authors report a strategy for constructing high performance On-Off MRL materials by introducing nitrophenyl groups to molecules with aggregation-induced emission characteristic.
- Weijun Zhao
- , Zikai He
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Block copolymer crystalsomes with an ultrathin shell to extend blood circulation time
Block copolymer crystalsomes with an ultrathin shell to extend blood circulation time
In block copolymer vesicles, crystallization often leads to defects and renders the structures leaky that undermines their potential biomedical application. Here the authors use an emulsion solution method to control the crystallization of an amphiphilic block copolymer at the curved liquid/liquid interface to improve the blood circulation time.
- Hao Qi
- , Hao Zhou
- & Christopher Y. Li
-
Article
| Open Access Long range electronic phase separation in CaFe3O5
Long range electronic phase separation in CaFe3O5
Electronic phase separation is an important feature of many correlated perovskite compounds but hasn’t been seen in other complex oxides with similar physical behaviour such as magnetite. Hong et al. find phase separation between a magnetite-like charge ordered phase and a charge averaged phase in CaFe3O5.
- Ka. H. Hong
- , Angel M. Arevalo-Lopez
- & J. Paul Attfield
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of cooperativity in the spin transition of an iron(II) complex on a graphite surface
Evolution of cooperativity in the spin transition of an iron(II) complex on a graphite surface
Spin-crossover molecules offer a potential route towards molecular spintronics, but retaining the bistability of the spin state upon surface deposition is challenging. Here, the authors study the spin-crossover behaviours of an Fe(II) complex deposited on graphite, determining the scale limit at which cooperative spin switching becomes effective.
- Lalminthang Kipgen
- , Matthias Bernien
- & Wolfgang Kuch
-
Article
| Open Access A facile strategy for realizing room temperature phosphorescence and single molecule white light emission
A facile strategy for realizing room temperature phosphorescence and single molecule white light emission
The demonstration of pure organic room temperature phosphorescence (RTP) luminogens with complementary emission is a key requirement for developing low-cost white light emitters. Here, the authors construct RTP-active organic salt compounds by exchanging the counterion with a heavy halide ion.
- Jianguo Wang
- , Xinggui Gu
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Drug capture materials based on genomic DNA-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles
Drug capture materials based on genomic DNA-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles
Chemotherapy agents are prone to producing severe side-effects, and their sequestration prior to their entering of the circulatory system is thus highly desirable. Here, the authors functionalize iron oxide nanoparticles with genomic DNA and achieve sequestration of doxorubicin, cisplatin, and epirubicin from biological solutions.
- Carl M. Blumenfeld
- , Michael D. Schulz
- & Robert H. Grubbs
-
Article
| Open Access Nano-photosensitizer based on layered double hydroxide and isophthalic acid for singlet oxygenation and photodynamic therapy
Nano-photosensitizer based on layered double hydroxide and isophthalic acid for singlet oxygenation and photodynamic therapy
Usually, several components are needed for efficient 2-photon photodynamic therapy (PDT). Here, the authors sandwiched carboxylic acids between layered double hydroxide nanosheets to obtain a single-handed biocompatible photosensitizer that generates singlet oxygen in high quantum yield.
- Rui Gao
- , Xuan Mei
- & Min Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically tunable conductive interpenetrating network hydrogels that mimic the elastic moduli of biological tissue
Mechanically tunable conductive interpenetrating network hydrogels that mimic the elastic moduli of biological tissue
Conductive and stretchable materials that match the elastic moduli of biological tissue are desired for enhanced interfacial and mechanical stability. Here the authors show a method for fabricating highly conductive hydrogels comprising two interpenetrating networks.
- Vivian R. Feig
- , Helen Tran
- & Zhenan Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembly of metal–organic polyhedra into supramolecular polymers with intrinsic microporosity
Self-assembly of metal–organic polyhedra into supramolecular polymers with intrinsic microporosity
Porosity in metal–organic materials typically relies on highly ordered crystalline networks, which hinders material processing and morphological control. Here, the authors use metal–organic polyhedra as porous monomers in supramolecular polymerization to produce colloidal spheres and gels with intrinsic microporosity.
- Arnau Carné-Sánchez
- , Gavin A. Craig
- & Shuhei Furukawa
-
Article
| Open Access Domino-like multi-emissions across red and near infrared from solid-state 2-/2,6-aryl substituted BODIPY dyes
Domino-like multi-emissions across red and near infrared from solid-state 2-/2,6-aryl substituted BODIPY dyes
The class of BODIPY dyes has high solubility and high quantum yields and is widely used in imaging applications. Here Tian et al. synthesize new dye molecules and demonstrate extended emission properties and application scope controllable both by the excitation wavelength and aggregation states.
- Dan Tian
- , Fen Qi
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Collective molecular switching in hybrid superlattices for light-modulated two-dimensional electronics
Collective molecular switching in hybrid superlattices for light-modulated two-dimensional electronics
Photochromic molecules offer the unique opportunity to demonstrate multifunctional devices with light-tunable electrical characteristics. Gobbi et al. build light-switchable electronic heterojunctions based on atomically precise, photo-reversible molecular superlattices on graphene and MoS2.
- Marco Gobbi
- , Sara Bonacchi
- & Paolo Samorì
-
Article
| Open Access Single-layer graphene membranes by crack-free transfer for gas mixture separation
Single-layer graphene membranes by crack-free transfer for gas mixture separation
Graphene shows great promise for gas separation applications, but obtaining large membranes that are free of cracks and tears remains highly challenging. Here, the authors realize monolayer, crack-free, millimeter-scale graphene membranes that exhibit selective gas permeation solely thanks to their intrinsic defects
- Shiqi Huang
- , Mostapha Dakhchoune
- & Kumar Varoon Agrawal
-
Article
| Open Access A coronene-based semiconducting two-dimensional metal-organic framework with ferromagnetic behavior
A coronene-based semiconducting two-dimensional metal-organic framework with ferromagnetic behavior
Endowing metal–organic frameworks with both high electrical conductivity and magnetic ordering could make such materials useful for spintronics. Here the authors design a layer-stacking coronene-based 2D MOF that exhibits a semiconducting feature with an electrical conductivity of ~10 S cm−1 at 300 K, as well as ferromagnetism below ~20 K.
- Renhao Dong
- , Zhitao Zhang
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Universal geometric frustration in pyrochlores
Universal geometric frustration in pyrochlores
The family of pyrochlore complex oxides includes many materials of fundamental or practical interest, such as spin ices and dielectrics. Trump et al. show that flexibility of the pyrochlores’ structure leads to local displacements that explain some of their unusual physical properties.
- B. A. Trump
- , S. M. Koohpayeh
- & T. M. McQueen
-
Article
| Open Access Spin–phonon couplings in transition metal complexes with slow magnetic relaxation
Spin–phonon couplings in transition metal complexes with slow magnetic relaxation
Transition metal complexes that display slow magnetic relaxation show promise for information storage, but our mechanistic understanding of the magnetic relaxation of such compounds remains limited. Here, the authors spectroscopically and computationally characterize the strength of spin–phonon couplings, which play an important role in the relaxation process.
- Duncan H. Moseley
- , Shelby E. Stavretis
- & Zi-Ling Xue
-
Article
| Open Access Control over the emerging chirality in supramolecular gels and solutions by chiral microvortices in milliseconds
Control over the emerging chirality in supramolecular gels and solutions by chiral microvortices in milliseconds
Symmetry breaking and chiral amplification are fundamental principles in chemistry and biology but the control of initial chiral bias remains a great challenge. Here the authors show that chiral microvortices can lead to a selection of initial chiral bias of supramolecular systems composed of achiral molecules.
- Jiashu Sun
- , Yike Li
- & Minghua Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Topochemical conversion of an imine- into a thiazole-linked covalent organic framework enabling real structure analysis
Topochemical conversion of an imine- into a thiazole-linked covalent organic framework enabling real structure analysis
Stabilization of covalent organic frameworks (COFs) by post-synthetic locking is a powerful tool to push the limits of COF utilization. Here the authors demonstrate a sulfur-assisted conversion of an imine-linked COF into a thiazole-linked COF, with retention of crystallinity and porosity, allowing for direct imaging of defects in COFs.
- Frederik Haase
- , Erik Troschke
- & Bettina V. Lotsch
-
Article
| Open Access Vapor sublimation and deposition to build porous particles and composites
Vapor sublimation and deposition to build porous particles and composites
Fabrication of porous nanoparticles is often hampered by low efficiency production methods, challenging isolation of the material and poor control over the fabrication process. Here the authors demonstrate a facile ice-template vapor-phase synthesis which allows for production of porous poly-para-xylylene particles on a large scale.
- Hsing-Ying Tung
- , Zhen-Yu Guan
- & Hsien-Yeh Chen
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance bifunctional porous non-noble metal phosphide catalyst for overall water splitting
High-performance bifunctional porous non-noble metal phosphide catalyst for overall water splitting
Water electrolysis provides a carbon-neutral means to generate hydrogen fuel from water, but the process typically requires expensive, rare metal catalysts. Here, the authors prepare hydrogen- and oxygen-evolving electrocatalysts from earth-abundant elements that outperform noble-metal counterparts.
- Fang Yu
- , Haiqing Zhou
- & Zhifeng Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding crystallization pathways leading to manganese oxide polymorph formation
Understanding crystallization pathways leading to manganese oxide polymorph formation
Minor variations in synthesis conditions can redirect crystallization pathways through different nonequilibrium intermediates. Here, the authors present a theoretical framework to predict which polymorphs appear during MnO2 precipitation, which is validated by in situ X-ray scattering of reaction progression.
- Bor-Rong Chen
- , Wenhao Sun
- & Laura T. Schelhas
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerating the discovery of insensitive high-energy-density materials by a materials genome approach
Accelerating the discovery of insensitive high-energy-density materials by a materials genome approach
The synthesis of explosive materials that are stable, highly dense, and have low sensitivity to external stimuli is a challenge. Here, the authors use a genomic approach to accelerate the discovery of insensitive high explosive molecules with good detonation and low sensitivity properties.
- Yi Wang
- , Yuji Liu
- & Yong Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic design of superaerophobic nanotube-array electrode comprised of transition-metal sulfides for overall water splitting
Systematic design of superaerophobic nanotube-array electrode comprised of transition-metal sulfides for overall water splitting
Water splitting by nanostructured, abundant catalysts provides a renewable means to make carbon neutral fuels, but the ideal material morphology and composition remain uncertain. Here, the authors prepare superaerophobic, multi-metallic sulfide nanotube arrays as bifunctional water splitting catalysts.
- Haoyi Li
- , Shuangming Chen
- & Xun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring exciton and excimer emission in an exfoliated ultrathin 2D metal-organic framework
Tailoring exciton and excimer emission in an exfoliated ultrathin 2D metal-organic framework
Two dimensional (2D) metal-organic frameworks have demonstrated unique photophysical properties compared to their bulk analogs. Here, the authors demonstrate that exfoliation of 2D MOFs can suppress interlayer exciton-related emission, allowing for modulation of the overall emission color and switching of optical memory states.
- Wei-Ming Liao
- , Jian-Hua Zhang
- & Cheng-Yong Su
-
Article
| Open Access Out-of-equilibrium microcompartments for the bottom-up integration of metabolic functions
Out-of-equilibrium microcompartments for the bottom-up integration of metabolic functions
Generating artificial cells able to carry out metabolic activities out-of-equilibrium is a current challenge in synthetic biology. Here the authors use a microfluidic platform for integration and analysis of minimal metabolic reactions in artificial microcompartments formed of water-in-oil droplets.
- Thomas Beneyton
- , Dorothee Krafft
- & Jean-Christophe Baret
-
Article
| Open Access Recipes for improper ferroelectricity in molecular perovskites
Recipes for improper ferroelectricity in molecular perovskites
In layered inorganic materials lattice distortions can couple to break inversion symmetry and drive improper ferroelectricity, but in perovskites, symmetry prohibits such an effect. Here, the authors use group-theoretical analysis to provide crystal engineering design principles for improper ferroelectricity in molecular perovskites.
- Hanna L. B. Boström
- , Mark S. Senn
- & Andrew L. Goodwin
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid phase blending of metal-organic frameworks
Liquid phase blending of metal-organic frameworks
The recently introduced glass and liquid states of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) provide opportunities to design and explore new properties for this class of material. Here, the authors show that a MOF liquid can be blended with another MOF component to produce domain-structured MOF glasses with single, tailorable glass transitions.
- Louis Longley
- , Sean M. Collins
- & Thomas D. Bennett
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis of poly(p-phenylene ethynylene) molecular wires via in situ formation of carbon-carbon triple bond
On-surface synthesis of poly(p-phenylene ethynylene) molecular wires via in situ formation of carbon-carbon triple bond
Incorporating carbon-carbon triple bonds into conjugated chains typically requires acetylenic precursors. Here, the authors synthesize poly(p-phenylene ethynylene) molecular wires on Cu(111) by directly coupling trichloromethyl-containing precursors, forming C-C triple bonds in situ
- Chen-Hui Shu
- , Meng-Xi Liu
- & Pei-Nian Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled synthesis of highly-branched plasmonic gold nanoparticles through peptoid engineering
Controlled synthesis of highly-branched plasmonic gold nanoparticles through peptoid engineering
Peptoids are promising crystallization agents, as they offer the molecular recognition capabilities of proteins and peptides but with higher stability and synthetic tunability. Here, the authors show that sequence-defined peptoids can controllably template the formation and shape evolution of gold nanostructures with defined morphologies.
- Feng Yan
- , Lili Liu
- & Chun-Long Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Topologically frustrated dynamics of crowded charged macromolecules in charged hydrogels
Topologically frustrated dynamics of crowded charged macromolecules in charged hydrogels
Diffusion of molecules in crowded environment is important for various living systems, but the dynamics of charged molecules in charged matrices remains still unexplored. Here the authors report a dynamics of DNA and polyelectrolytes in a charged hydrogel where the guest molecules do not diffuse but experience topologically frustrated dynamics.
- Di Jia
- & Murugappan Muthukumar
-
Article
| Open Access Crosslinking of fibrous hydrogels
Crosslinking of fibrous hydrogels
Unlike synthetic hydrogels, biological gels are made of fibrous networks which give rise to unique properties, such as high porosity and mechanical responsiveness. Here the authors use polyisocyanide-based gels and selectively crosslink inside the bundles to lock the fibrous network and thus control the architecture and the mechanics.
- Daniël C. Schoenmakers
- , Alan E. Rowan
- & Paul H. J. Kouwer
-
Article
| Open Access Transient modes of zeolite surface growth from 3D gel-like islands to 2D single layers
Transient modes of zeolite surface growth from 3D gel-like islands to 2D single layers
While zeolites are industrially relevant as molecular sieves and catalysts, their growth mechanisms remain widely debated. Here, Rimer and colleagues probe the crystallization pathway of zeolite LTA with spatiotemporal resolution, identifying a distinctive nonclassical pathway, and demonstrating that growth is highly dependent on synthetic conditions.
- Manjesh Kumar
- , Madhuresh K. Choudhary
- & Jeffrey D. Rimer
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-plane coherent acoustic phonons in two-dimensional organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites
Cross-plane coherent acoustic phonons in two-dimensional organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites
Two-dimensional, organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites have sustained research interest due to attractive optoelectronic and excitonic properties. Here, Guo et al. systematically investigate coherent acoustic phonon transport versus layer thickness in these materials with strong acoustic impedance mismatch
- Peijun Guo
- , Constantinos C. Stoumpos
- & Richard D. Schaller
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoparticle-templated nanofiltration membranes for ultrahigh performance desalination
Nanoparticle-templated nanofiltration membranes for ultrahigh performance desalination
Nanofiltration membranes are important for water desalination technologies, but designing membranes that achieve both high permeance and high salt rejection remains challenging. Here, the authors use sacrificial nanoparticles in the membrane fabrication process, leading to crumpled structures with ultrahigh permeance.
- Zhenyi Wang
- , Zhangxin Wang
- & Jian Jin
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution AFM structure of DNA G-wires in aqueous solution
High-resolution AFM structure of DNA G-wires in aqueous solution
DNA and RNA G-quadruplexes can stack to form higher-order structures called G-wires. Here the authors report high-resolution AFM images of higher-order DNA G-quadruplexes in aqueous solution that could impact the design of G-wire based nanodevices and the understanding of G-wires in biology.
- Krishnashish Bose
- , Christopher J. Lech
- & Anh Tuân Phan
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing isoelectronic size conversion dynamics of metal nanoclusters by a noncrystallization approach
Revealing isoelectronic size conversion dynamics of metal nanoclusters by a noncrystallization approach
How metal nanoclusters evolve in size is poorly understood, particularly at the atomic level. Here, the authors use mass spectrometry to study the size conversion dynamics between two isoelectronic gold nanoclusters with atomic resolution, revealing that the growth reaction proceeds through a distinct balanced equation.
- Qiaofeng Yao
- , Victor Fung
- & Jianping Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Hollow organic capsules assemble into cellular semiconductors
Hollow organic capsules assemble into cellular semiconductors
Perylene diimide-bithiophene macrocycles are electroactive and shape-persistent hosts. Here, the authors describe their self-assembly into a cellular organic semiconducting film whose voids are electrically sensitive to different guests, and which can function as the active layer in a field-effect transistor device.
- Boyuan Zhang
- , Raúl Hernández Sánchez
- & Colin Nuckolls
-
Article
| Open Access Nanographenes as electron-deficient cores of donor-acceptor systems
Nanographenes as electron-deficient cores of donor-acceptor systems
Nanographenes in donor-acceptor π-systems generally serve as electron-donating moieties but the reversed structures are hardly reported. Here, the authors present a facile synthetic protocol towards reversed donor-acceptor nanographenes by amination and demonstrate fine property tuning by varying the donating ability of the aniline groups.
- Yu-Min Liu
- , Hao Hou
- & Klaus Müllen
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent superconductivity in an iron-based honeycomb lattice initiated by pressure-driven spin-crossover
Emergent superconductivity in an iron-based honeycomb lattice initiated by pressure-driven spin-crossover
Up to now, all iron-based high-Tc superconductors contain a square iron lattice. Here, Wang et al. report the observation of superconductivity in an iron honeycomb lattice accompanied with pressure-driven spin-crossover, in-plane lattice collapse and insulator-metal transition.
- Yonggang Wang
- , Jianjun Ying
- & Ho-kwang Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Self-organizing layers from complex molecular anions
Self-organizing layers from complex molecular anions
Using ions of one polarity to form functional layers on surfaces is usually challenging because of counter ions which are inevitably present in the condensed phase. Here the authors demonstrate accumulation of mass-selected anions and neutral molecules from the gas phase to form a self-organizing liquid-like layer on a surface.
- Jonas Warneke
- , Martin E. McBriarty
- & Julia Laskin
-
Article
| Open Access Sculpting and fusing biomimetic vesicle networks using optical tweezers
Sculpting and fusing biomimetic vesicle networks using optical tweezers
Assembly of higher-order artificial vesicles can unlock new applications. Here, the authors use optical tweezers to construct user-defined 2D and 3D architectures of chemically distinct vesicles and demonstrate inter-vesicle communication and light-enabled compartment merging.
- Guido Bolognesi
- , Mark S. Friddin
- & Yuval Elani
-
Article
| Open Access Light-driven transformable optical agent with adaptive functions for boosting cancer surgery outcomes
Light-driven transformable optical agent with adaptive functions for boosting cancer surgery outcomes
The combination of imaging techniques in cancer treatment often involves a trade-off in properties due to the opposite working mechanisms. Here, the authors report on a material that avoids the trade-off by switching from photoacoustic imaging to fluorescence imaging upon an external light trigger
- Ji Qi
- , Chao Chen
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Supramolecular Kandinsky circles with high antibacterial activity
Supramolecular Kandinsky circles with high antibacterial activity
Nested structures are common throughout nature and art, yet remain challenging synthetic targets in supramolecular chemistry. Here, the authors design multitopic terpyridine ligands that coordinate into nested concentric hexagons, and show that these discrete supramolecules display potent antimicrobial activity.
- Heng Wang
- , Xiaomin Qian
- & Xiaopeng Li
-
Article
| Open Access A self-destructive nanosweeper that captures and clears amyloid β-peptides
A self-destructive nanosweeper that captures and clears amyloid β-peptides
Cerebral amyloid β-peptide accumulation is a causative factor in Alzheimer’s Disease. Here the authors design a 'nanosweeper' that binds amyloid β-peptide and induces autophagy to clear the accumulated plagues.
- Qiang Luo
- , Yao-Xin Lin
- & Hao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ visualization of solute-driven phase coexistence within individual nanorods
In-situ visualization of solute-driven phase coexistence within individual nanorods
Compared to thin films and other geometries, nanorods can exhibit particularly high performance in solute-intercalation-based energy and information storage devices. Here, the authors use in situ electron microscopy and spectroscopy to study the hydrogenation of palladium nanorods, revealing relationships between nanorod structure and device cyclability and capacity.
- Fariah Hayee
- , Tarun C. Narayan
- & Jennifer A. Dionne
-
Article
| Open Access Topologically guided tuning of Zr-MOF pore structures for highly selective separation of C6 alkane isomers
Topologically guided tuning of Zr-MOF pore structures for highly selective separation of C6 alkane isomers
The separation of C6 alkane isomers is crucial to the petroleum refining industry, but the distillation methods in place are energy intensive. Here, the authors design a series of topologically-guided zirconium-based metal-organic frameworks with optimized pore structures for efficient C6 alkane isomer separations.
- Hao Wang
- , Xinglong Dong
- & Jing Li
-
Article
| Open Access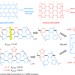 A modular synthetic approach for band-gap engineering of armchair graphene nanoribbons
A modular synthetic approach for band-gap engineering of armchair graphene nanoribbons
Effective band-gap engineering of armchair graphene nanoribbons calls for control over both width and edge structure. Here, the authors report a modular synthesis of narrow N = 6 armchair graphene nanoribbons whose edges can be unsymmetrically modified with heteroarenes, introducing a simple way to tune band gap.
- Gang Li
- , Ki-Young Yoon
- & Guangbin Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical diversity in a metal–organic framework revealed by fluorescence lifetime imaging
Chemical diversity in a metal–organic framework revealed by fluorescence lifetime imaging
Metal-organic frameworks are typically characterized by a variety of techniques, but most only provide information on properties as an average of a bulk sample. Here, Wuttke and colleagues demonstrate that fluorescence imaging and lifetime analysis allows access to local information on defects and functional groups.
- Waldemar Schrimpf
- , Juncong Jiang
- & Stefan Wuttke

 Crystalline polymeric carbon dioxide stable at megabar pressures
Crystalline polymeric carbon dioxide stable at megabar pressures