Abstract
The discovery of iron-based superconductors (FeSCs), with the highest transition temperature (Tc) up to 55 K, has attracted worldwide research efforts over the past ten years. So far, all these FeSCs structurally adopt FeSe-type layers with a square iron lattice and superconductivity can be generated by either chemical doping or external pressure. Herein, we report the observation of superconductivity in an iron-based honeycomb lattice via pressure-driven spin-crossover. Under compression, the layered FePX3 (X = S, Se) simultaneously undergo large in-plane lattice collapses, abrupt spin-crossovers, and insulator-metal transitions. Superconductivity emerges in FePSe3 along with the structural transition and vanishing of magnetic moment with a starting Tc ~ 2.5 K at 9.0 GPa and the maximum Tc ~ 5.5 K around 30 GPa. The discovery of superconductivity in iron-based honeycomb lattice provides a demonstration for the pursuit of transition-metal-based superconductors via pressure-driven spin-crossover.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Since the discovery of 26 K superconductivity (SC) in LaO1−xF x FeAs in 20081, the Fe-based superconductors (FeSCs) have attracted enormous research interest, owing to their rich compositional and structural varieties1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12. The rapid development on this new SC family has led to the highest critical temperature (Tc) up to 55 K in F-doped SmFeAsO2 and the discovery of a large number of FeSCs with various structure types3,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12. Similar to the high-Tc cuprate family unexceptionally adopting square CuO2 layers, all of these FeSCs structurally possess infinite antifluorite-like Fe2X2 layers comprising the stacks of edge-sharing FeX4 tetrahedra (X denotes a pnictide or a chalcogenide element). Therefore, it is widely believed that the common Fe2X2 layer is the essential building unit for the rational structure design of FeSCs, similar in nature to the CuO2 unit in cuprate SCs. And this viewpoint is verified by the discovery of high-Tc SC in a large number of FeSe-derived layered compounds such as A x Fe2−ySe2 (A = alkali metals)9,10, Li x (NH2) y (NH3)1−yFe2Se211, and (Li0.8Fe0.2)OHFeSe12. Another key feature of FeSCs is a well-recognized fact that in most cases the high-Tc SC can emerge by suppressing the long-range antiferromagnetic (AFM) order in the stoichiometric parent compounds. Experimentally, two general routes are adopted to achieve this purpose: first, chemical doping or substitution, such as F doping in REFeAsO1 (RE = rare earth elements) and interlayer cation doping (alkali metals or NH3)9,10,11; second, application of chemical or external pressure, such as the replacement of X in Fe2X2 by congeners with bigger or smaller atomic radii or the substitution of smaller RE ions for La ions2.
Under applied high pressure (HP), materials undergo direct structural evolutions including the shortening of metal-ligand bond length, the distortions in the nearest neighbor environment, and the introduction of stress. These structural evolutions make HP significant in the researches on SCs, and many unanticipated SCs have been discovered with this powerful tool. A recent famous example is the observation of conventional SC with high-Tc in hydrogen-rich systems, H x S, and PH313,14, under HPs up to megabar scale. Besides, unexpected SC phase diagrams (e.g., MnP15, Tl0.6Rb0.4Fe1.67Se2, and K0.8Fe1.7+δSe216) and greatly enhanced Tc values in both cuprates and FeSCs (e.g., LaO1−xF x FeAs17, HgBa2Ca2Cu3O8+δ18, and β-Fe1.01Se19) have also been successfully achieved by pressure tuning. Moreover, applying external pressure to transition metal (TM) systems may also lead to other significant phenomena such as large-volume collapse20,21,22, spin-crossover (SCO)22,23,24, charge disproportionation25, and insulator-metal transition (IMT). Regarding the pressure-driven SCO, in which magnetic ions undergo high-to-low spin-state transition, it is possible to produce a nonmagnetic phase through the pressure-induced spin-quenching (S = 0). Keeping the relationship between magnetism and SC in mind, an adventurous but meaningful idea is: can we make new nonmagnetic FeSCs without the FeSe-type structure via pressure-driven spin-quenching? If so, Fe2+ with d6 electrical configuration in a sixfold-coordinated environment should be an ideal candidate to ensure a nonmagnetic HP phase with zero spin ground state (S = 2 to S = 0).
In the pursuit of abrupt pressure-driven SCOs in TM chalcogenides, we became aware of the essential role of the TM-sublattice dimensions in the cooperativeness of SCO26,27. We have discovered abrupt pressure-driven phase transitions accompanied by a high-to-low spin-state transition of Mn2+ in the transition from three-dimensional (3D) NaCl-type MnX to two-dimensional (2D) MnPX3 (X = S, Se) with an Mn2+ honeycomb lattice. Subsequent experiments showed that similar cooperative SCO phenomenon also exists in the iron homologs FePX3, in which Fe2+ ions (d6) arranged on a nearly perfect honeycomb lattice undergo a sharp magnetic-to-nonmagnetic transition (S = 2 to S = 0). This 2D system apparently meets all the above-mentioned prerequisites for the emergence of SC. In this letter, we report our discoveries in the course of HP studies of the layered compound FePX3 (X = S, Se). Along with the pressure-driven SCO, in-plane lattice collapse, and semiconductor-to-metal transition, SC emerges around 3 ~ 5 K in the nonmagnetic HP phase of FePSe3. The physical property and the phase diagram of FePX3 under HP are discussed along with the structural analyses results.
Results
Pressure-induced large-volume collapse
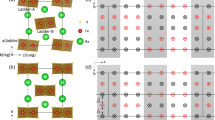
FePX3 (X = S, Se) compounds adopt a 2D crystal structure with Fe2+ ions arranged in a nearly perfect honeycomb lattice and weak interlayer van der Walls interactions28. Figure 1a, b display the crystal structure of the low-pressure (LP) phase of FePS3 and FePSe3 with an ideal trigonal symmetry. Each layer is composed of two layers of S/Se atoms, octahedrally coordinated Fe2+ ions, and phosphorous pairs. All the FeX6 octahedra share their edges with three neighbors to form the honeycomb lattice, and with P = P dimers locating in the center of the sixfold mesh. The shortest Fe–Fe distances in FePX3 are ~3.44 Å for X = S and 3.62 Å for X = Se, respectively, and both compounds are narrow-band semiconductors at ambient conditions. Under compression, FePX3 undergo isostructural or quasi-isostructural phase transitions at ~13 GPa for X = S and ~8 GPa for X = Se, respectively (Supplementary Fig. 1). The discontinuous shifts of the diffraction peaks ((113)/(20-2) of FePS3 and (113) of FePSe3, as shown in Fig. 1c, d) indicate abruptly shrinking of the lattice parameters concomitant with the pressure-driven phase transition, in particular, the collapses in the ab-plane lattice spacings.
The crystal structure and pressure-induced phase transition of FePX3. a, b Ambient crystal structure of FePX3 (X = S, Se) viewed along c- and a/b-axis showing the layered structure feature and the Fe2+ honeycomb lattice. c, d Two-dimensional PXRD data showing abrupt pressure-induced changes of the (131) and (20-2) peaks for FePS3 and the (113) peak for FePSe3, respectively. e The derived cell volume values as a function of applied pressure for the LP and HP phases of FePS3 and FePSe3. The derived bulk moduli are: B0 = 61.1(2) and 162(9) GPa for LP and HP FePS3; B0 = 82.8(7) and 201(8) GPa for LP and HP FePSe3, respectively. Error bars represent ± S.D. f The cell parameters of FePSe3 with a pseudo-trigonal unit cell showing an in-plane collapse along with the pressure-induced phase transition
Judging from the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns, monoclinic unit cells with the space group C2/m were adopted for the Le Bail fitting analyses for both FePS3 and FePSe3 (Supplementary Fig. 2). Figure 1e presents the evolution of the cell volumes of FePX3 as a function of applied pressure. Large cell volume decreases (10.5% for X = S and 10.6% for X = Se) dominate the P–V profiles along with the first-order phase transitions, indicating remarkable changes of the atomic arrangement. Such large-volume collapses (>5%) are usually associated with the pressure-driven SCO on the origin21,22. The decrease of Fe2+ ionic radii from 0.78 Å (high spin (HS), S = 2) to 0.61 Å (low spin (LS), S = 0) results in the shortening of Fe-(S/Se) bond lengths and the possible symmetry lowering of the hexagonal lattice. To sententiously analysis the anisotropic compressibility of FePX3, a pseudo-trigonal space group R-3 is adopted for the XRD refinements of FePSe3 (Fig. 1f). The dramatic decreases of a and b during the phase transition clearly indicate that the volume collapses origin from the shrinkages of the Fe2+ honeycomb lattices, which also indicate the formation of in-plane intermetallic Fe–Fe bonding. Similar in-plane lattice collapse is also observed in FePS3 with monoclinic symmetry (Supplementary Fig. 3).
Pressure-induced spin-crossover
We have proposed that the pressure-driven cooperative SCO, i.e., large-volume collapse accompanied with SCO and IMT, should be a universal behavior of 3d TM chalcogenides26,27. FePX3, as an ideal low-dimensional confined system similar to MnPX327, thus is highly expected to achieve a nonmagnetic HP phase via pressure-driven cooperative SCO. In situ X-ray emission spectroscopy (XES)23 measurements were performed to study the spin-state transitions of FePX3 under HP and the results are presented in Fig. 2a, b. It is generally recognized that the K β lines are the characteristic emissions originated from the 3p → 1s transition, and the shapes of K β lines are determined by the interactions between the 3p core hole and the partially filled 3d shell electrons. Therefore, it allows qualitative distinction of the HS/LS states from the relative intensities of satellite K β ′ and the peak positions of Kβ1,3. In the LP phases of FePX3, well-defined K β ′ satellite peaks are observed with a HS state (S = 2). Concomitant with the structural phase transition, the K β ′ peaks drop suddenly and the Kβ1,3 lines shift to lower energy correspondingly, both of which indicate the occurrence of SCO of Fe2+ within the honeycomb lattice.
XES data of FePS3 and FePSe3 showing the spin-crossover of Fe2+ under compression. a, b Fe K β XES of FePS3 and FePSe3 as a function of applied pressure. Inset of a shows the XES process from 3p to 1s orbital, and the relationship with 3d spin state. c The derived IAD values and corresponding magnetic moment numbers of FePS3 and FePSe3 as a function of pressure. Error bars represent ± S.D. estimated for the IAD analyses
Quantitative analysis of the XES data has been conducted using the integrals of the absolute values of the difference spectra (IAD) method29, and the differential curves are provided in Supplementary Fig. 4. The pressure dependence of the Fe2+ spin state in FePX3 is presented in Fig. 2c. At ambient conditions, the two compounds have a HS state of Fe2+ (3d6) with S = 2 (IAD = 0). The HS state of Fe2+ is stable until the applied pressure exceeds the LP-to-HP structural transition points. The IAD values of FePX3 increase to ~2.5 (S = 0) abruptly, indicating a complete collapse of the Fe2+ spin moments. Like the pressure effect on MnPX3 system27, the abrupt pressure-driven SCO in FePX3 is attributed to their 2D crystal structures, where the spins located on the honeycomb lattice can more collectively communicate with neighboring spins than those on 3D lattices.
Pressure-induced semiconductor-to-metal transition
In situ transport measurements of FePX3 show IMT along with the pressure-driven structural phase transition and SCO (as shown in Fig. 3). During the IMT process, the electrical resistances of FePX3 drop by more than five orders of magnitude at room temperature. The R–T curves under HP also indicate a change from a semi-conductive behavior of the LP phases to metallic behavior of the HP phases, concomitant with the structural and electronic configuration transitions. Since the Fe–Fe intermetallic bonding can only form in the honeycomb layer, it is reasonable to see that the HP phases exhibit a bad-metal and an anisotropic transporting behavior. The conductivity measurements on the single crystal of FePSe3 confirm that the in-plane metallization contributes most to the overall IMT phenomenon (Fig. 3c). What needs to be pointed out here is, all the data obtained in our transport measurements are original resistances rather than absolute resistivity, which may be converted to each other by normalizing the ambient resistivity values inside and outside the diamond anvil cell (DAC).
Pressure-induced semiconductor-to-metal transitions in FePS3 and FePSe3. a, b Electrical resistances of compressed powder of FePX3 (X = S, Se) as a function of pressure. Insets of a, b show the temperature dependence (R–T) of the resistance of FePS3 and FePSe3 under high pressure, respectively. c Electrical resistance measurements on a FePSe3 single crystal showing an in-plane metallization behavior. Inset of c shows the photograph of the FePSe3 single crystal with four Au probes inside a DAC. The scale bar is 100 μm
Observation of superconductivity
Figure 4a presents the resistance R of FePSe3 as a function of temperature T for pressure in the range of 9.0–29.6 GPa. A sharp drop of R at an onset temperature of ~2.5 K is clearly observed near the critical pressure Pc ≈ 9.0 GPa, which is just above the pressure-driven structural phase transition point and indicates the occurrence of SC within the HP phase of FePSe3. During further pressure increase, the onset Tc suddenly increases to 5.5 K above 20 GPa, while the transition becomes much broader. The superconducting transition becomes sharper with zero resistivity reached at 3 K around 30 GPa. Above 29.6 GPa, the Tc of FePSe3 shows a slight tendency to decrease with the pressure increase, but the SC state remains up to 41.4 GPa (the highest pressure in our measurements, as shown in Fig. 4b). The zero resistance has been reached in the experiment for most of the pressure points. All these evidences highlight the fact that the emerging SC state is an intrinsic behavior of the HP phase of FePSe3.
Emergence of superconductivity under high pressure and temperature–pressure phase diagram in FePSe3. a The in-plane electrical resistivity of FePSe3 single crystal as a function of temperature, and applied pressures 9.0, 10.8, 12.5, 17.1, 23.2, 25.5, and 29.6 GPa. b The in-plane electrical resistivity of FePSe3 single crystal as a function of temperature, and applied pressures 29.6, 33.6, 38.0, and 41.4 GPa. Insets of a, b show the enlarged low-temperature parts of the measured resistivity. Line colors are the same as those used in a, b. Inset of b shows the photograph of a single-crystal FePSe3 inside a DAC for resistivity measurements. The scale bar is 100 μm. c The temperature dependence of the electrical resistivity of FePSe3 at 29.6 GPa under magnetic fields of 0, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, and 5 T. Inset shows the field dependence of Tc for FePSe3 at 29.6 GPa. d Temperature–pressure phase diagram of FePSe3, where solid circles represent the pressure dependence of the onset superconducting transition temperatures (5*Tc), and the blue triangles represent the pressure dependence of Hall coefficient. TN represents the Neel temperature of FePSe3
We have also applied magnetic field to suppress the SC. Under the constant pressure of 29.6 GPa, temperature dependences of resistance of FePSe3 at various magnetic fields are shown in Fig. 4c. During the increase of the magnetic field, the transition is gradually suppressed, which further confirms that it is the superconducting transition. We have obtained the upper critical field (Hc2) as shown in the inset of Fig. 4c. The Hc2 shows an upturn curve, which may be related to the multiband SC in a 2D system. The Tc values obtained from the above measurements along with the structural and spin-state transitions are plotted in the temperature–pressure phase diagram of FePSe3, as shown in Fig. 4d. The application of HP drives the phase transition from the LP, HS, and magnetic insulator (or semiconductor) state to a HP, LS, nonmagnetic, and metallic state in FePSe3. SC emerges with a starting Tc ~ 2.5 K at 9.0 GPa and a maximum Tc ~ 5.5 K at 29.6 GPa and sustains within the HP phase of FePSe3 up to 40 GPa. The SC originated from the parent AFM materials has strong similarities with the unconventional superconductors such as high-Tc cuprate SCs, FeSCs, and heavy Fermion SCs. These findings demonstrate a successful exploration of new nonmagnetic phases with SC via pressure-driven spin-quenching. The positive Hall coefficient measured at 10 K indicates that holes are the main carriers in the SC phase. The sudden increase of Tc above 20 GPa, coincident with the anomaly of the Hall coefficient, indicates a possible Fermi surface reconstruction.
Discussion
The honeycomb layers of FePX3 can survive through the pressure-driven quasi-isostructural phase transition. However, the in-plane lattice collapse is proved to be anisotropic and the symmetry breaking down to pseudo-trigonal monoclinic is expected to happen, as shown in Fig. 5a, b. First, the formation of shorter Fe–Fe intermetallic bonding favors the occurrence of cooperative SCO and is consistent with the IMT scenario27. Second, the results of in situ-extended X-ray absorption fine structure measurements on Fe K-edge support the HP-mode-2, where the Fe–Fe bonds split into two groups: an intermetallic bond with the Fe–Fe distance of 3.24 Å and an elongated Fe–Fe distance of 3.78 Å, as shown in Supplementary Fig. 5. Therefore, the HP phases of FePX3 adopt exactly a distorted honeycomb-like Fe2+ lattice. The valence of iron is verified to be +2 in the HP phase of FePSe3 (Supplementary Fig. 6), and the increases of the pre-edge peaks indicate the distortion of FeX6 octahedra along with the formation of Fe–Fe intermetallic bonding. Figure 5c presents the typical tetragonal lattice of FeSe, which is adopted by all the high-Tc FeSCs discovered so far. The HP phase of FePSe3 with an Fe2+ honeycomb lattice presents a unique example of FeSCs without a FeSe-type tetragonal or tetragonal-like lattice. Obviously, the discovery of 3d TM-based SC in a new structure prototype will greatly arouse the passion of pursuing high-Tc SCs.
High-pressure structure modes of Fe2+ honeycomb lattice and comparison with FeSe-type tetragonal Fe2+ lattice. a The proposed HP-mode-1 for FePSe3 with slightly distorted Fe2+ honeycomb lattice. b The proposed HP-mode-2 for FePSe3 with seriously distorted Fe2+ honeycomb lattice. The shortest or the near-shortest Fe–Fe bond lengths are highlighted by black and gray lines in the HP-mode-1 and black and yellow lines in the HP-mode-2, respectively. c Tetragonal Fe2+ lattice in most Fe-based high-Tc superconductors with FeSe-type layered structures
We have made significant efforts to determine the HP crystal structures of FePX3, including repeating powder and single-crystal XRD measurements. However, the detailed structural features, such as the exact space group (symmetry) and atomic positions, are still not well-determined currently due to the difficulty of handling the less than perfect-quality data obtained under HP conditions. The HP crystal structure requires more efforts to be precisely determined in future investigations. In our experiments, SC is only observed in FePSe3. The HP phase of FePS3 may be either non-superconducting or with a very low Tc beyond our measurement capability (below 2 K). Moreover, the determination of a detailed P–T phase diagram of FePX3 involving the AFM transition temperatures is now in progress, which may provide more evidence to the SC mechanism within an Fe2+ honeycomb lattice and most importantly whether it is an unconventional SC or not. We would also point out that the SC, the route to SC, and the unique Fe2+ lattice in FePSe3 are obviously different from those in superconducting, nonmagnetic iron metal under compression30. There are many other candidates with low-dimensional Fe2+ lattices or 3d TM-based low-dimensional lattices with d6 electronic configuration. In principle, they can be tuned to superconducting phases via pressure-driven SCO. Modern structure design and theoretical prediction could facilitate the exploration of such new high-Tc SCs based on this principle.
Methods
Material syntheses
All chemicals were of reagent-grade quality. They were purchased from commercial sources and used as received. FePS3 and FePSe3 powders were synthesized by heating stoichiometric Fe, P, and S/Se powders at 700 °C in sealed quartz tubes for 24 h. High-quality single crystals were grown by chemical vapor transport method in a two-zone furnace31. For both compounds, the temperatures of the two zones were 720–700 °C with iodine as the transport medium. The growth experiments were carried out for a week, and the resulting single crystals were platelets of ~0.01–0.1 mm in thickness and ~0.5–1 mm2 in size with black appearance.
High-pressure structural characterizations
A symmetric DAC with a pair of 300 μm diameter culet-sized diamond anvils was used for all the in situ measurements under HP. Typically, a steel gasket was pre-indented to 40 μm in thickness and a 120 μm diameter hole was laser-drilled to serve as the sample chamber. FePS3 and FePSe3 powders were pre-compressed into pellets before use. In all the experiments, silicone oil was used as the pressure-transmitting medium (PTM). Ruby balls were used as the pressure gauge and the pressures were calibrated according to the ruby fluorescence method32. The in situ XRD measurements were performed at 16 BM-D station of the High Pressure Collaborative Access Team (HPCAT) at Advanced Photon Source (APS) of Argonne National Laboratory (ANL). A focused monochromatic X-ray beam with ~5 μm in diameter (full width at half maximum) and 0.3100 Å wavelength was used, and the diffraction patterns were recorded by using a MAR345 image plate.
High-pressure spectral studies
HP XES experiments were performed at the 16 ID-D station of HPCAT. Be gaskets were used to confine and pressurize the sample and silicone oil was used as the PTM. X-ray absorption spectrum (XAS) measurements at the Fe K-edge were performed at the 20 ID-C, APS, ANL. A pair of nano-diamond anvils was used to avoid the diffraction glitches from regular single-crystal diamonds. No PTM was used to ensure the uniformity of the thickness.
High-pressure transport measurements
Electrical resistances of FePS3 and FePSe3 powders were measured using a four-point-probe resistance measurement system consisting of a Keithley 6221 current source, a 2182A nanovoltmeter, and a 7001 voltage/current switch. Cubic boron nitride layers were inserted into the DAC between the steel gasket and diamond anvils to provide electrical insulation. Four gold wires were arranged to contact the surface of the sample in the chamber.
We conducted the HP electric transport measurements on a FePSe3 single crystal under pressure by using the miniature diamond anvil cell33. Diamond anvils with 300 μm culet and c-BN gasket with sample chambers of diameter 140 μm were used. A FePSe3 single crystal was cut with the dimensions of 60 × 60 × 10 μm3. Four Pt wires were adhered to the sample using the silver epoxy. Daphne oil 7373 was used as the PTM. Resistance and Hall coefficient were measured using the Quantum Design PPMS-9.
Data analyses
The 2D XRD patterns were integrated using the Dioptas program34. Unit cell parameter refinements were performed with FULLPROF program35. The quantitative analyses of the XES data were carried out through IAD (IAD method)29.
Data availability
All data supporting the findings of this work are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
Kamihara, Y., Watanabe, T., Hirano, M. & Hosono, H. Iron-based layered superconductor La[O1−xF x ]FeAs (x=0.05–0.12) with T c=26 K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 3296–3297 (2008).
Ren, Z.-A. et al. Superconductivity at 55 K in iron-based F-doped layered quaternary compound Sm[O1−xF x ]FeAs. Chin. Phys. Lett. 25, 2215–2216 (2008).
Paglione, J. & Greene, R. L. High-temperature superconductivity in iron-based materials. Nat. Phys. 6, 645–658 (2010).
Kotegawa, H., Sugawara, H. & Tou, H. Abrupt emergence of pressure-induced superconductivity of 34 K in SrFe2As2: a resistivity study under pressure. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 78, 013709 (2009).
Sun, Y.-L. et al. Ba2Ti2Fe2As4O: a new superconductor containing Fe2As2 layers and Ti2O sheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 12893–12896 (2012).
Iyo, A. et al. New-structure-type Fe-based superconductors: CaAFe4As4 (A=K, Rb, Cs) and SrAFe4As4 (A=Rb, Cs). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 3410–3415 (2016).
Wang, Z.-C. et al. Superconductivity in KCa2Fe4As4F2 with separate double Fe2As2 layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 7856–7859 (2016).
Wang, C. et al. A new ZrCuSiAs-type superconductor: ThFeAsN. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 2170–2173 (2016).
Ying, T. P. et al. Observation of superconductivity at 30 ~ 46K in A x Fe2Se2 (A=Li, Na, Ba, Sr, Ca, Yb, and Eu). Sci. Rep. 2, 426 (2012).
Ying, T. et al. Superconducting phases in potassium-intercalated iron selenides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 2951–2954 (2013).
Burrard-Lucas, M. et al. Enhancement of the superconducting transition temperature of FeSe by intercalation of a molecular spacer layer. Nat. Mater. 12, 15–19 (2013).
Lu, X. F. et al. Coexistence of superconductivity and antiferromagnetism in (Li0.8Fe0.2)OHFeSe. Nat. Mater. 14, 325–329 (2015).
Drozdov, A. P., Erements, M. I., Troyan, I. A., Ksenofontov, V. & Shylin, S. I. Conventional superconductivity at 203 kelvin at high pressures in the sulfur hydride system. Nature 525, 73–76 (2015).
Drozdov, A. P., Eremets, M. I. & Troyan, I. A. Superconductivity above 100 K in PH3 at high pressures. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1508.06224 (2015).
Cheng, J.-G. et al. Pressure induced superconductivity on the border of magnetic order in MnP. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 117001 (2015).
Sun, L. et al. Re-emerging superconductivity at 48 kelvin in iron chalcogenides. Nature 483, 67–69 (2012).
Takahashi, H. et al. Superconductivity at 43 K in an iron-based layered compound LaO1−xF x FeAs. Nature 453, 376–378 (2008).
Chu, C. W. et al. Superconductivity above 150 K in HgBa2Ca2Cu3O8+δ at high pressures. Nature 365, 323–325 (1993).
Medvedev, S. et al. Electronic and magnetic phase diagram of β-Fe1.01Se with superconductivity at 36.7 K under pressure. Nat. Mater. 8, 630–633 (2009).
Rosner, H. et al. Magneto-elastic lattice collapse in YCo5. Nat. Phys. 2, 469–472 (2006).
Kuneš, J. et al. Collapse of magnetic moment drives the Mott transition in MnO. Nat. Mater. 7, 198–202 (2008).
Kimber, S. A. J. et al. Giant pressure-induced volume collapse in the pyrite mineral MnS2. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111, 5106–5110 (2014).
Rueff, J.-P. et al. Pressure-induced high-spin to low-spin transition in FeS evidenced by X-ray emission spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 3284–3287 (1999).
Kawakami, T. et al. Spin transition in a four-coordinate iron oxide. Nat. Chem. 1, 371–376 (2009).
Cheng, J. et al. Charge disproportionation and the pressure-induced insulator-metal transition in cubic perovskite PbCrO3. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 1670–1674 (2015).
Wang, Y. et al. Giant pressure-driven lattice collapse coupled with intermetallic bonding and spin-state transition in manganese chalcogenides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 55, 10350–10353 (2016).
Wang, Y. et al. Pressure-driven cooperative spin-crossover, large-volume collapse, and semiconductor-to-metal transition in manganese(II) honeycomb lattices. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 15751–15757 (2016).
Wiedenmann, A., Rossat-Mignod, J., Louisy, A., Brec, R. & Rouxel, J. Neutron diffraction study of the layered compounds MnPSe3 and FePSe3. Solid State Commun. 40, 1067–1072 (1981).
Vankó, G. et al. Probing the 3d spin momentum with X-ray emission spectroscopy: the case of molecular-spin transitions. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 11647–11653 (2006).
Shimizu, K. et al. Superconductivity in the nonmagnetic state of iron under pressure. Nature 412, 316–318 (2001).
Klingen, V. W., Ott, R. & Hahn, H. Preparation and properties of hexaghio- and hexaselenohypodiphosphates. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 396, 271–278 (1973).
Mao, H. K., Xu, J. & Bell, P. M. Calibration of the ruby pressure gauge to 800 kbar under quasi-hydrostatic conditions. J. Geophys. Res. 91, 4673–4676 (1986).
Gavriliuk, A. G., Mironovich, A. A. & Struzhkin, V. V. Miniature diamond anvil cell for broad range of high pressure measurements. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80, 043906 (2009).
Prescher, C. & Prakapenka, V. B. DIOPTAS: a program for reduction of two-dimensional X-ray diffraction data and data exploration. High Press. Res. 35, 223–230 (2015).
Rodriguez-Carvajal, J. Recent advances in magnetic structure determination by neutron powder diffraction. Phys. B 192, 55–69 (1993).
Acknowledgements
HPCAT operations are supported by DOE-NNSA under award no. DE-NA0001974, with partial instrumentation funding by NSF. J. Ying, Y. Xiao and P. Chow acknowledge the support of DOE-BES/DMSE under Award DE-FG02-99ER45775. APS is supported by DOE-BES, under contract no. DE-AC02-06CH11357. The HP XAS measurements were performed at 20 ID-C, APS, ANL. This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51527801 and U1530402). We gratefully acknowledge Professor T. Irifune for providing nanodiamonds for the HP XAS measurements, L.X. Yang (HPSTAR), C.J. Sun (XSD), and C. Park (HPCAT) for their support in the in situ HP measurements, and P. Cifligu (UNLV) for his help with the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.S., W.Y., V.V.S., and Y.Z. conceived the project. Y.W., J.Y., and Z.Z. designed the experiments. Z.Z. synthesized the powder and single-crystal samples. Y.W. performed the in situ XRD, XES, XAS, and resistance measurements. J.Y. carried out the SC and Hall coefficient measurements. N.L. and Q.Z. performed quantitative analyses of the XRD and XES data. Y.W., Z.Z., and J.Y. wrote and revised the paper. All authors participated in discussing the results and editing the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Ying, J., Zhou, Z. et al. Emergent superconductivity in an iron-based honeycomb lattice initiated by pressure-driven spin-crossover. Nat Commun 9, 1914 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04326-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04326-1
This article is cited by
-
Pressure-induced transition from a Mott insulator to a ferromagnetic Weyl metal in La2O3Fe2Se2
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Insulator–metal transition in CrSiTe3 triggered by structural distortion under pressure
npj 2D Materials and Applications (2023)
-
Symmetry progression and possible polar metallicity in NiPS3 under pressure
npj 2D Materials and Applications (2022)
-
p + ip-wave pairing symmetry at type-II van Hove singularities
Frontiers of Physics (2021)
-
Dimensional crossover tuned by pressure in layered magnetic NiPS3
Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.