Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term autophagy is sustained by activation of CCTβ3 on lipid droplets
Long-term autophagy is sustained by activation of CCTβ3 on lipid droplets
The source of phospholipids to generate autophagosomal membranes, particularly after prolonged starvation, is not well characterized. Here, the authors show that CCTβ3, the rate limiting enzyme in phosphatidylcholine synthesis, is activated on lipid droplets and sustains long-term autophagy.
- Yuta Ogasawara
- , Jinglei Cheng
- & Toyoshi Fujimoto
-
Article
| Open Access A global lipid map defines a network essential for Zika virus replication
A global lipid map defines a network essential for Zika virus replication
Zika virus (ZIKV) remodels intracellular membranes for replication, but the role of different lipid types for infection and disease is unclear. Here, the authors perform lipidomics, show perturbation of the lipid network during ZIKV infection and show that ceramides are important for ZIKV infection.
- Hans C. Leier
- , Jules B. Weinstein
- & Fikadu G. Tafesse
-
Article
| Open Access A dietary fatty acid counteracts neuronal mechanical sensitization
A dietary fatty acid counteracts neuronal mechanical sensitization
PIEZO2 is a critical component of the mechanism by which innocuous touch causes pain (tactile allodynia). Here, authors find that the dietary fatty acid margaric acid decreases PIEZO2 function in a dose-dependent manner and counteracts neuronal mechanical sensitization by a proalgesic agent.
- Luis O. Romero
- , Rebeca Caires
- & Valeria Vásquez
-
Article
| Open Access Independent regulation of age associated fat accumulation and longevity
Independent regulation of age associated fat accumulation and longevity
Age-associated metabolic changes include lipid accumulation. Here, the authors show that with replicative aging yeast accumulate lipid droplets which protect cells from cold stress and can be modulated through Biosynthesis of NAD+ 2 (BNA2).
- Anthony O. Beas
- , Patricia B. Gordon
- & Daniel E. Gottschling
-
Article
| Open Access Latitudinal gradient in dairy production with the introduction of farming in Atlantic Europe
Latitudinal gradient in dairy production with the introduction of farming in Atlantic Europe
The transition to agriculture brought major changes to human populations in Europe during the Neolithic period. Here, Cubas and colleagues analyse lipid residues from Neolithic pottery from along the Atlantic coast of Europe to trace the spread of dairy production and shifts in diet.
- Miriam Cubas
- , Alexandre Lucquin
- & Oliver E. Craig
-
Article
| Open Access Obesity-induced overexpression of miR-802 impairs insulin transcription and secretion
Obesity-induced overexpression of miR-802 impairs insulin transcription and secretion
Obesity predisposes to type 2 diabetes, but the mechanisms of obesity-associated β cell dysfunction are incompletely understood. Here the authors report that obesity increases the levels of miR-802, which impairs insulin transcription and secretion by targeting NeuroD1 and Fzd5.
- Fangfang Zhang
- , Dongshen Ma
- & Liang Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Gating mechanism of elongating β-ketoacyl-ACP synthases
Gating mechanism of elongating β-ketoacyl-ACP synthases
The formation of C-C bonds in fatty acid and polyketide biosynthesis depends on β-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP) synthases (KSs). Here, the authors present structures of E.coli KSs bound to substrate mimetic bearing ACPs, providing insights into the catalytic mechanism underlying C-C bond forming reactions.
- Jeffrey T. Mindrebo
- , Ashay Patel
- & Michael D. Burkart
-
Article
| Open Access Lipid analogs reveal features critical for hemolysis and diminish granadaene mediated Group B Streptococcus infection
Lipid analogs reveal features critical for hemolysis and diminish granadaene mediated Group B Streptococcus infection
Granadaene, produced by Group B Streptococcus (GBS), is a long polyene lipid involved in cellular toxicity and hemolytic activity. Here, the authors synthesize and characterize granadaene-like compounds and show that a non-toxic analog diminishes GBS infection in mice when incorporated into a vaccine formulation.
- Blair Armistead
- , Pilar Herrero-Foncubierta
- & Lakshmi Rajagopal
-
Article
| Open Access Acid ceramidase of macrophages traps herpes simplex virus in multivesicular bodies and protects from severe disease
Acid ceramidase of macrophages traps herpes simplex virus in multivesicular bodies and protects from severe disease
Macrophages are critical in limiting replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). Here the authors show how acid ceramidase and its enzymatic product sphingosine enable multivesicular bodies to function as an anti-viral mechanism.
- Judith Lang
- , Patrick Bohn
- & Karl S. Lang
-
Article
| Open Access Lipidomic and biophysical homeostasis of mammalian membranes counteracts dietary lipid perturbations to maintain cellular fitness
Lipidomic and biophysical homeostasis of mammalian membranes counteracts dietary lipid perturbations to maintain cellular fitness
Proper membrane physiology requires maintenance of a narrow range of physicochemical properties, which must be buffered from external perturbations. Here, authors report lipidomic remodeling to preserve membrane physical properties upon exogenous polyunsaturated fatty acids exposure.
- Kandice R. Levental
- , Eric Malmberg
- & Ilya Levental
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure of a lipin/Pah phosphatidic acid phosphatase
Crystal structure of a lipin/Pah phosphatidic acid phosphatase
Lipin/Pah phosphatidic acid phosphatases generate diacylglycerol to regulate triglyceride synthesis and cellular signaling. Here authors determine structures of Tetrahymena thermophila Pah2 and identify an N-terminal amphipathic helix essential for membrane association.
- Valerie I. Khayyo
- , Reece M. Hoffmann
- & Michael V. Airola
-
Article
| Open Access Haploid genetic screens identify SPRING/C12ORF49 as a determinant of SREBP signaling and cholesterol metabolism
Haploid genetic screens identify SPRING/C12ORF49 as a determinant of SREBP signaling and cholesterol metabolism
The transcription factor SREBP is a well-studied and major regulator of sterol and fatty acid metabolism. Here, the authors used haploid genetic screens to identify the Golgi-resident protein SPRING as a new modulator of SREBP by regulating the level of functional SREBP cleavage-activating protein (SCAP).
- Anke Loregger
- , Matthijs Raaben
- & Noam Zelcer
-
Article
| Open Access Alterations in promoter interaction landscape and transcriptional network underlying metabolic adaptation to diet
Alterations in promoter interaction landscape and transcriptional network underlying metabolic adaptation to diet
Metabolic adaptation to different diets results in changes to gene expression. Here, the authors characterise the chromatin landscape and transcriptional network in mice on a diet of high saturated fat, compared to a diet high in carbohydrate, finding a dramatic reprogramming of the liver transcriptional network.
- Yufeng Qin
- , Sara A. Grimm
- & Paul A. Wade
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-talks of glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis with glycosphingolipid biosynthesis and ER-associated degradation
Cross-talks of glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis with glycosphingolipid biosynthesis and ER-associated degradation
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchors are found on many cell surface proteins but their biosynthesis is not fully understood. Here, the authors identify genes involved in GPI galactosylation and reveal functional connections between GPI processing, glycosphingolipid biosynthesis and ER-associated degradation.
- Yicheng Wang
- , Yusuke Maeda
- & Taroh Kinoshita
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of lipid saturation without sensing membrane fluidity
Regulation of lipid saturation without sensing membrane fluidity
Cells maintain membrane fluidity by regulating lipid saturation, but the molecular mechanisms of this homeoviscous adaptation remain poorly understood. Here authors reconstituted the core machinery for regulating lipid saturation in baker’s yeast to directly characterize its response to defined membrane environments and uncover its mode-of-action.
- Stephanie Ballweg
- , Erdinc Sezgin
- & Robert Ernst
-
Article
| Open Access Modular detergents tailor the purification and structural analysis of membrane proteins including G-protein coupled receptors
Modular detergents tailor the purification and structural analysis of membrane proteins including G-protein coupled receptors
Detergents are indispensable reagents in membrane protein structural biology. Here, L. H. Urner and co-workers introduce oligoglycerol detergents (OGDs) and use native mass spectrometry to show how interactions of membrane proteins with native membrane lipids can be preserved during purification.
- Leonhard H. Urner
- , Idlir Liko
- & Kevin Pagel
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale lipid analysis with C=C location and sn-position isomer resolving power
Large-scale lipid analysis with C=C location and sn-position isomer resolving power
Coupling photochemical derivatization with tandem mass spectrometry enables C=C-isomer resolved lipidomics. Here, the authors further develop this approach into a shotgun lipidomics workflow that allows simultaneous characterization of lipid C=C locations and sn-positions in complex biological samples.
- Wenbo Cao
- , Simin Cheng
- & Xiaoxiao Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Relationship between gut microbiota and circulating metabolites in population-based cohorts
Relationship between gut microbiota and circulating metabolites in population-based cohorts
Here, the authors provide an in-depth study of the metabolome in two large population-based prospective cohorts and identify 32 microbial traits associated with various metabolic biomarkers and specific lipoprotein subfractions, providing insights into the role of microbiota in influencing host lipid levels.
- Dina Vojinovic
- , Djawad Radjabzadeh
- & Cornelia M. van Duijn
-
Article
| Open Access Lipid order and charge protect killer T cells from accidental death
Lipid order and charge protect killer T cells from accidental death
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) eliminate virus-infected and cancerous cells by secreting the pore-forming protein (perforin) and pro-apoptotic serine proteases (granzymes). Here authors show that two mechanisms protect the membranes of CTLs from disruption by perforin and granzymes.
- Jesse A. Rudd-Schmidt
- , Adrian W. Hodel
- & Ilia Voskoboinik
-
Article
| Open Access A Chlamydia pneumoniae adhesin induces phosphatidylserine exposure on host cells
A Chlamydia pneumoniae adhesin induces phosphatidylserine exposure on host cells
The Chlamydia pneumoniae adhesin LIPP plays a role in host cell entry and infection. Here, the authors find that LIPP binds to the host plasma membrane and mediates phosphatidylserine translocation, enhancing pathogen internalization without induction of apoptosis.
- Jan N. Galle
- , Tim Fechtner
- & Johannes H. Hegemann
-
Article
| Open Access RORγ is a targetable master regulator of cholesterol biosynthesis in a cancer subtype
RORγ is a targetable master regulator of cholesterol biosynthesis in a cancer subtype
Enhanced cholesterol biosynthesis is associated with cancer progression. Here the authors identify the nuclear receptor RORγ as a novel master regulator of cholesterol metabolism in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) and find that RORγ small-molecule antagonists induce tumor regression in patient-derived xenografts and immunocompetent mouse models.
- Demin Cai
- , Junjian Wang
- & Hong-Wu Chen
-
Article
| Open Access An electrostatic switching mechanism to control the lipid transfer activity of Osh6p
An electrostatic switching mechanism to control the lipid transfer activity of Osh6p
Osh6p and Osh7p are yeast lipid transfer proteins (LTPs) that must transiently interact with membranes but how they escape from the electrostatic attraction of the plasma membrane is unclear. Here authors show that Osh6p reduces its avidity for anionic membranes once it captures PS or PI4P, due to a molecular lid closing its lipid-binding pocket.
- Nicolas-Frédéric Lipp
- , Romain Gautier
- & Guillaume Drin
-
Article
| Open Access The structural basis of lipid scrambling and inactivation in the endoplasmic reticulum scramblase TMEM16K
The structural basis of lipid scrambling and inactivation in the endoplasmic reticulum scramblase TMEM16K
TMEM16K is a member of the TMEM16 family of integral membrane proteins that are either lipid scramblases or chloride channels. Here the authors combine cell biology, electrophysiology measurements, X-ray crystallography, cryo-EM and MD simulations to structurally characterize TMEM16K and show that it is an ER-resident lipid scramblase.
- Simon R. Bushell
- , Ashley C. W. Pike
- & Elisabeth P. Carpenter
-
Article
| Open Access Lysosomal integral membrane protein-2 (LIMP-2/SCARB2) is involved in lysosomal cholesterol export
Lysosomal integral membrane protein-2 (LIMP-2/SCARB2) is involved in lysosomal cholesterol export
Cholesterol transport is tightly regulated in the cell and in lysosomes is regulated by NPC1/2. Here, Heybrock et al. use molecular modeling, knockout mice and cell based studies to show that LIMP-2 also mediates lysosomal cholesterol transport.
- Saskia Heybrock
- , Kristiina Kanerva
- & Dante Neculai
-
Article
| Open Access Mitofusins regulate lipid metabolism to mediate the development of lung fibrosis
Mitofusins regulate lipid metabolism to mediate the development of lung fibrosis
Mitochondria of alveolar type 2 epithelial cells (AEC2) in the lung have been suggested to play a role in the development of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Here the authors show that loss of mitofusin1 and mitofusin2 in murine AEC2 cells leads to the development of lung fibrosis through the regulation of surfactant lipids.
- Kuei-Pin Chung
- , Chia-Lang Hsu
- & Augustine M. K. Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Dietary fatty acids promote lipid droplet diversity through seipin enrichment in an ER subdomain
Dietary fatty acids promote lipid droplet diversity through seipin enrichment in an ER subdomain
Lipid droplets (LDs) are fat storage organelles that are initiated and expanded by seipins at ER contact sites. Here the authors show that the C. elegans seipin ortholog SEIP-1 is recruited to these sites by certain dietary fatty acids to support the expansion of a subset of LDs.
- Zhe Cao
- , Yan Hao
- & Ho Yi Mak
-
Article
| Open Access Marrying chemistry with biology by combining on-chip solution-based combinatorial synthesis and cellular screening
Marrying chemistry with biology by combining on-chip solution-based combinatorial synthesis and cellular screening
High-throughput cell-based screening of compound libraries is utilised in drug development; however, a lack of compatible methods limits direct synthesis and testing. Here, the authors present a diverse chip based synthesis system which can be combined with cell screening and demonstrate the application.
- Maximilian Benz
- , Mijanur R. Molla
- & Pavel A. Levkin
-
Perspective
| Open Access The role of PS 18:0/18:1 in membrane function
The role of PS 18:0/18:1 in membrane function
There are several lines of evidence for interactions between the two membrane leaflets in cells. In this review the authors discuss the transmembrane coupling of lipids, the involvement of phosphatidyl serine species PS 18:0/18:1, and their importance for various cellular processes.
- Tore Skotland
- & Kirsten Sandvig
-
Article
| Open Access Brain leptin reduces liver lipids by increasing hepatic triglyceride secretion and lowering lipogenesis
Brain leptin reduces liver lipids by increasing hepatic triglyceride secretion and lowering lipogenesis
Obesity is associated with leptin resistance and rising blood leptin levels while central leptin exposure may be limited. Here, the authors show that brain leptin infusion reduces hepatic lipid content in rats by increasing hepatic VLDL secretion and lowering liver de novo lipogenesis via a vagal mechanism.
- Martina Theresa Hackl
- , Clemens Fürnsinn
- & Thomas Scherer
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for human sterol isomerase in cholesterol biosynthesis and multidrug recognition
Structural basis for human sterol isomerase in cholesterol biosynthesis and multidrug recognition
Emopamil-Binding Protein (EBP), is an endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein involved in cholesterol biosynthesis, autophagy and oligodendrocyte formation. Here, authors report two crystal structures of human EBP and identify a pharmacological binding site that accommodates multiple different ligands.
- Tao Long
- , Abdirahman Hassan
- & Xiaochun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Local membrane charge regulates β2 adrenergic receptor coupling to Gi3
Local membrane charge regulates β2 adrenergic receptor coupling to Gi3
In the healthy heart, the β2 adrenergic receptor (β2AR) signals through Gs and Gi proteins but the mechanism underlying G protein selectivity is not fully understood. Here, the authors show that membrane charge and intracellular cations modulate the β2AR−Gi3 interaction.
- M. J. Strohman
- , S. Maeda
- & B. K. Kobilka
-
Article
| Open Access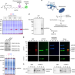 Ceramides bind VDAC2 to trigger mitochondrial apoptosis
Ceramides bind VDAC2 to trigger mitochondrial apoptosis
Ceramides are lipids that act directly on mitochondria to trigger apoptosis, but the underlying mechanism remains largely unclear. Here authors use a photoactivatable ceramide probe combined with a computation approach and functional studies to identify the voltage-dependent anion channel VDAC2 as a direct effector of ceramide-mediated cell death.
- Shashank Dadsena
- , Svenja Bockelmann
- & Joost C. M. Holthuis
-
Article
| Open Access Classification of the human phox homology (PX) domains based on their phosphoinositide binding specificities
Classification of the human phox homology (PX) domains based on their phosphoinositide binding specificities
Phox homology (PX) domains are membrane interacting domains that bind to various lipids. Here authors screen all human PX domains systematically for their phospholipid preferences and define four classes and provide the basis for defining and predicting functional PX-membrane interactions.
- Mintu Chandra
- , Yanni K.-Y. Chin
- & Brett M. Collins
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphatidylethanolamine made in the inner mitochondrial membrane is essential for yeast cytochrome bc1 complex function
Phosphatidylethanolamine made in the inner mitochondrial membrane is essential for yeast cytochrome bc1 complex function
Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) is synthesized by four separate pathways, although surprisingly, perturbing mitochondrial PE synthesis compromises mitochondrial function. Here, the authors show that mitochondrial PE synthesis is required for Complex III function and challenge PE trafficking dogma.
- Elizabeth Calzada
- , Erica Avery
- & Steven M. Claypool
-
Article
| Open Access Coordination of capsule assembly and cell wall biosynthesis in Staphylococcus aureus
Coordination of capsule assembly and cell wall biosynthesis in Staphylococcus aureus
The cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria consists of peptidoglycan modified with other polymers, such as the capsular polysaccharide. Here, the authors reconstitute the biosynthesis of capsular polysaccharide and elucidate its interplay with the cell wall biosynthetic machinery.
- Marvin Rausch
- , Julia P. Deisinger
- & Tanja Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access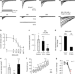 Dietary fatty acids fine-tune Piezo1 mechanical response
Dietary fatty acids fine-tune Piezo1 mechanical response
Piezo channels are mechanosensitive and rely on membrane composition to transduce physical stimuli into electrical signals. Here authors analyse the membrane components that modulate Piezo1 function using lipid profiling which shows that fatty acid metabolism can modulate ion channel activity.
- Luis O. Romero
- , Andrew E. Massey
- & Valeria Vásquez
-
Article
| Open Access Omegasome-proximal PtdIns(4,5)P2 couples F-actin mediated mitoaggregate disassembly with autophagosome formation during mitophagy
Omegasome-proximal PtdIns(4,5)P2 couples F-actin mediated mitoaggregate disassembly with autophagosome formation during mitophagy
Autophagic cells coordinate substrate remodeling with sequestration during autophagosome formation. Here, the authors show that during Parkin-mediated mitophagy, mitochondria are disassembled into progressively smaller aggregates near autophagy initiation sites in a PtdIns(4,5)P2-dependent manner.
- Cheng-Wei Hsieh
- & Wei Yuan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access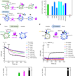 Allosteric enhancement of ORP1-mediated cholesterol transport by PI(4,5)P2/PI(3,4)P2
Allosteric enhancement of ORP1-mediated cholesterol transport by PI(4,5)P2/PI(3,4)P2
Phosphatidylinositol phosphates (PIPs) and cholesterol are known to regulate the function of late endosomes and lysosomes (LELs). Here authors unveil a mechanism by which PI(4,5)P2/PI(3,4)P2 allosterically enhances ORP1-mediated cholesterol exit from LELs.
- Jiangqing Dong
- , Ximing Du
- & Jia-Wei Wu
-
Article
| Open Access A minimal biochemical route towards de novo formation of synthetic phospholipid membranes
A minimal biochemical route towards de novo formation of synthetic phospholipid membranes
The origin of phospholipids, the primary constituents of cell membranes, is uncertain. Here, the authors develop an in vitro system to synthesize phospholipid molecules from water-soluble single-chain amphiphilic precursors via a reaction catalysed by the mycobacterial ligase FadD10.
- Ahanjit Bhattacharya
- , Roberto J. Brea
- & Neal K. Devaraj
-
Article
| Open Access A chemical biology screen identifies a vulnerability of neuroendocrine cancer cells to SQLE inhibition
A chemical biology screen identifies a vulnerability of neuroendocrine cancer cells to SQLE inhibition
Cancer cells are metabolically adaptable and the identification of specific vulnerabilities is challenging. Here the authors identify a subset of neuroendocrine cell lines exquisitely sensitive to inhibition of SQLE, an enzyme in the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway, due to the toxic accumulation of pathway intermediate squalene.
- Christopher E. Mahoney
- , David Pirman
- & Gromoslaw A. Smolen
-
Article
| Open Access Online photochemical derivatization enables comprehensive mass spectrometric analysis of unsaturated phospholipid isomers
Online photochemical derivatization enables comprehensive mass spectrometric analysis of unsaturated phospholipid isomers
Mass spectrometry is widely used for large-scale lipid profiling but distinguishing unsaturated lipid isomers is still challenging. Here, the authors present an analytical platform for high-throughput identification of lipid C=C location isomers in clinical samples, showing that isomer ratios may guide biomarker discovery.
- Wenpeng Zhang
- , Donghui Zhang
- & Yu Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamin-related protein 1 has membrane constricting and severing abilities sufficient for mitochondrial and peroxisomal fission
Dynamin-related protein 1 has membrane constricting and severing abilities sufficient for mitochondrial and peroxisomal fission
Drp1 and Dnm2 have been implicated in mitochondrial fission events, although their specific activities in constriction and scission have been unclear. Here, the authors demonstrate that Drp1 is sufficient to constrict and sever mitochondrial and peroxisomal membranes in the absence of Dnm proteins.
- Sukrut C. Kamerkar
- , Felix Kraus
- & Michael T. Ryan
-
Article
| Open Access Neurohormonal signaling via a sulfotransferase antagonizes insulin-like signaling to regulate a Caenorhabditis elegans stress response
Neurohormonal signaling via a sulfotransferase antagonizes insulin-like signaling to regulate a Caenorhabditis elegans stress response
Reduced insulin-like signaling is required for C. elegans response to many environmental stressors, but how distinct outcomes are achieved is unknown. The authors show that the cytosolic sulfotransferase SSU-1 controls neurohormonal signaling via NHR-1 to specify the animals’ osmotic stress response.
- Nicholas O. Burton
- , Vivek K. Dwivedi
- & H. Robert Horvitz
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of a potent HMG-CoA reductase degrader that eliminates statin-induced reductase accumulation and lowers cholesterol
Discovery of a potent HMG-CoA reductase degrader that eliminates statin-induced reductase accumulation and lowers cholesterol
Accumulated HMG-CoA reductase (HMGCR) limits the cholesterol-lowering effect of statins via a feedback loop. Here the authors developed a compound that degrades HMGCR, thus decreasing cholesterol levels and reducing atherosclerotic plaques.
- Shi-You Jiang
- , Hui Li
- & Bao-Liang Song
-
Article
| Open Access An engineered thermal-shift screen reveals specific lipid preferences of eukaryotic and prokaryotic membrane proteins
An engineered thermal-shift screen reveals specific lipid preferences of eukaryotic and prokaryotic membrane proteins
Membrane bilayers are made up of a myriad of different lipids that affect membrane proteins, but identifying those specific lipid requirements remains a challenge. Here authors present an engineered thermal-shift screen which reveals specific lipid preferences of eukaryotic and prokaryotic membrane proteins.
- Emmanuel Nji
- , Yurie Chatzikyriakidou
- & David Drew
-
Article
| Open Access Direct protein-lipid interactions shape the conformational landscape of secondary transporters
Direct protein-lipid interactions shape the conformational landscape of secondary transporters
Secondary transporters catalyse substrate translocation across the cell membrane but the role of lipids during the transport cycle remains unclear. Here authors used hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry and molecular dynamics simulations to understand how lipids regulate the conformational dynamics of secondary transporters.
- Chloe Martens
- , Mrinal Shekhar
- & Argyris Politis
-
Article
| Open Access C16-ceramide is a natural regulatory ligand of p53 in cellular stress response
C16-ceramide is a natural regulatory ligand of p53 in cellular stress response
Ceramides are important participants of signal transduction, regulating fundamental cellular processes. Here authors show that C16-ceramide binds to the tumor suppressor p53, disrupts its interaction with MDM2 and facilitates p53 accumulation and activation of its downstream targets.
- Baharan Fekry
- , Kristen A. Jeffries
- & Natalia I. Krupenko
-
Article
| Open Access Ancient proteins from ceramic vessels at Çatalhöyük West reveal the hidden cuisine of early farmers
Ancient proteins from ceramic vessels at Çatalhöyük West reveal the hidden cuisine of early farmers
Ancient diets have been reconstructed from archaeological pottery based on lipid remains, but these can lack specificity. Here, Hendy and colleagues analyze ancient proteins from ceramic vessels up to 8000 years old to produce a more nuanced understanding of ancient food processing and diet.
- Jessica Hendy
- , Andre C. Colonese
- & Eva Rosenstock
-
Article
| Open Access Endogenous metabolites of vitamin E limit inflammation by targeting 5-lipoxygenase
Endogenous metabolites of vitamin E limit inflammation by targeting 5-lipoxygenase
Vitamin E metabolites are proposed to have signalling capacity, but how they may regulate immune responses is still unclear. Here the authors show that a vitamin E metabolite, α-T-13′-COOH, can inhibit 5-lipoxygenase and thereby suppress the synthesis of lipid mediators of immune activation and inflammatory responses.
- Helmut Pein
- , Alexia Ville
- & Andreas Koeberle

 CD36 facilitates fatty acid uptake by dynamic palmitoylation-regulated endocytosis
CD36 facilitates fatty acid uptake by dynamic palmitoylation-regulated endocytosis