Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Facet-dependent electrooxidation of propylene into propylene oxide over Ag3PO4 crystals
Facet-dependent electrooxidation of propylene into propylene oxide over Ag3PO4 crystals
The electrooxidation of propylene into propylene oxide is important in many industrial sectors. Here, the authors demonstrate efficient and facet-selective formation of propylene oxide using Ag3PO4 cubes and investigate the reaction mechanism.
- Jingwen Ke
- , Jiankang Zhao
- & Zhigang Geng
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast charge transfer dynamics in 2D covalent organic frameworks/Re-complex hybrid photocatalyst
Ultrafast charge transfer dynamics in 2D covalent organic frameworks/Re-complex hybrid photocatalyst
Re complexes within covalent organic frameworks have emerged as promising photocatalysts for CO2 reduction. Here, authors identify a high-energy electron transfer pathway during CO2 reduction that results in longer-lived excited states than a low-energy electron transfer pathway.
- Qinying Pan
- , Mohamed Abdellah
- & Kaibo Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Time- and site-resolved kinetic NMR for real-time monitoring of off-equilibrium reactions by 2D spectrotemporal correlations
Time- and site-resolved kinetic NMR for real-time monitoring of off-equilibrium reactions by 2D spectrotemporal correlations
Time-resolved NMR spectra provide unique structural and dynamical information, but their measurement in systems undergoing chemical reactions is challenging. Here the authors, combining single-scan spectroscopic imaging, rapid mixing and continuous flow techniques, obtain chemically resolved snapshots of a reacting system throughout the reaction coordinate.
- Michael J. Jaroszewicz
- , Mengxiao Liu
- & Lucio Frydman
-
Article
| Open Access Associative detachment in anion-atom reactions involving a dipole-bound electron
Associative detachment in anion-atom reactions involving a dipole-bound electron
Associative electronic detachment (AED) reactions of anions play a key role in many natural processes. Here, Hassan and colleagues investigate AED reactions between hydroxyl anions and ultracold rubidium atoms in a hybrid atom-ion trap, revealing different dynamics for collisions with ground and electronically excited state rubidium.
- Saba Zia Hassan
- , Jonas Tauch
- & Matthias Weidemüller
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional excited-state dynamics in the concerted benzyl (C7H7) radical self-reaction to anthracene (C14H10)
Unconventional excited-state dynamics in the concerted benzyl (C7H7) radical self-reaction to anthracene (C14H10)
The reaction of benzyl radical self-reaction to anthracene opens-up a previously overlooked avenue for a more efficient synthesis of aromatic, multi-ringed structures via excited state dynamics in the gas phase.
- Ralf. I. Kaiser
- , Long Zhao
- & Alexander M. Mebel
-
Article
| Open Access Determining the charge distribution and the direction of bond cleavage with femtosecond anisotropic x-ray liquidography
Determining the charge distribution and the direction of bond cleavage with femtosecond anisotropic x-ray liquidography
Tracking the flow of charge in reacting molecules may provide key insight into reaction mechanisms, but is particularly challenging in liquid solutions. Here the authors, by analyzing the isotropic and anisotropic scattering signal in femtosecond time resolved X-ray liquidography, determine the charge localization and structural changes during photodissociation of the triiodide anion I3-
- Jun Heo
- , Jong Goo Kim
- & Hyotcherl Ihee
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental identification of aminomethanol (NH2CH2OH)—the key intermediate in the Strecker Synthesis
Experimental identification of aminomethanol (NH2CH2OH)—the key intermediate in the Strecker Synthesis
The Strecker synthesis is considered a viable route to amino acids formation on the primordial Earth. Here the authors succeed in observing its elusive intermediate aminomethanol, formed by insertion of an electronically excited oxygen atom in methylamine and stabilized by an icy matrix, using isomer-selective photoionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry during thermal desorption of the ice mixture.
- Santosh K. Singh
- , Cheng Zhu
- & Ralf I. Kaiser
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the broadband circular dichroism of copolymer films with supramolecular chirality in time and space
Mapping the broadband circular dichroism of copolymer films with supramolecular chirality in time and space
Time-resolved circular dichroism spectra can reveal changes in chirality on ultrashort time scales, but achieving sub-picosecond time resolution is still a challenge. Here the authors demonstrate 100-femtosecond time-resolved CD mapping of polyfluorene copolymer thin films, revealing a supramolecular origin of their chiroptical response.
- Marius Morgenroth
- , Mirko Scholz
- & Thomas Lenzer
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of the ponderomotive effect in non-valence bound states of polyatomic molecular anions
Observation of the ponderomotive effect in non-valence bound states of polyatomic molecular anions
The ponderomotive effect experienced by electrons in a molecule under a transient electric field impacts the reactivity, but has been difficult to detect. The authors observe a ponderomotive force on the excess quasi-free electron in the non-valence bound state of three molecular anions, by measuring the photodetachment spectrum under irradiation with a non-resonant wavelength.
- Do Hyung Kang
- , Jinwoo Kim
- & Sang Kyu Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular-level insights into the electronic effects in platinum-catalyzed carbon monoxide oxidation
Molecular-level insights into the electronic effects in platinum-catalyzed carbon monoxide oxidation
A molecular-level understanding of the electronic effects remains a grand challenge in heterogeneous catalysis. Here, the authors report an unconventional kinetics strategy for bridging the upscaling gap between the microscopic fingerprints of active sites and the macroscopic catalytic performance.
- Wenyao Chen
- , Junbo Cao
- & Xuezhi Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Time-resolved relaxation and fragmentation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons investigated in the ultrafast XUV-IR regime
Time-resolved relaxation and fragmentation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons investigated in the ultrafast XUV-IR regime
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons play an important role in interstellar chemistry, where interaction with high energy photons can induce ionization and fragmentation reactions. Here the authors, with XUV-IR pump-probe experiments, investigate the ultrafast photoinduced dynamics of fluorene, phenanthrene and pyrene, providing insight into their preferred reaction channels.
- J. W. L. Lee
- , D. S. Tikhonov
- & M. Schnell
-
Article
| Open Access Conformer-specific polar cycloaddition of dibromobutadiene with trapped propene ions
Conformer-specific polar cycloaddition of dibromobutadiene with trapped propene ions
Identifying a concerted or stepwise mechanism in Diels–Alder reactions is experimentally challenging. Here the authors demonstrate the coexistence of both mechanisms in the reaction of 2,3-dibromobuta-1,3-diene with propene ions, using a conformationally controlled molecular beam reacting with trapped ions and ab initio computations
- Ardita Kilaj
- , Jia Wang
- & Stefan Willitsch
-
Article
| Open Access Quantification of the Li-ion diffusion over an interface coating in all-solid-state batteries via NMR measurements
Quantification of the Li-ion diffusion over an interface coating in all-solid-state batteries via NMR measurements
Development of all-solid-state batteries requires stable solid electrolyte-electrode interfaces. Here, via exchange-NMR measurements, the authors investigate the positive electrode-solid electrolyte interface, revealing the impact of an inorganic coating on the Li-ion transport properties.
- Ming Liu
- , Chao Wang
- & Marnix Wagemaker
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic level fluxional behavior and activity of CeO2-supported Pt catalysts for CO oxidation
Atomic level fluxional behavior and activity of CeO2-supported Pt catalysts for CO oxidation
In heterogeneous catalysts, the nature of the atomic-scale dynamics taking place at nanoparticle surfaces during catalysis is not understood. Here, we employ electron microscopy to show that activity directly correlates with fluxional behavior of the surface and interface atoms.
- Joshua L. Vincent
- & Peter A. Crozier
-
Article
| Open Access Filming ultrafast roaming-mediated isomerization of bismuth triiodide in solution
Filming ultrafast roaming-mediated isomerization of bismuth triiodide in solution
The roaming reaction is a common process in the gas phase and in solution, but observation of the involved atomic movements has been challenging. The authors, using femtosecond time-resolved X-ray liquidography, resolve the detailed structural dynamics at the onset of a roaming reaction in the photoinduced isomerization of BiI3 in solution.
- Eun Hyuk Choi
- , Jong Goo Kim
- & Hyotcherl Ihee
-
Article
| Open Access Visualization of gaseous iodine adsorption on single zeolitic imidazolate framework-90 particles
Visualization of gaseous iodine adsorption on single zeolitic imidazolate framework-90 particles
Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks are promising as high-capacity iodine adsorbents. Here the authors image the gaseous I2 adsorption on single ZIF-90 particles, clarifying the inter-particle heterogeneity in adsorption reactivity and performance improvement after introduction of linker defects .
- Yuting Lei
- , Guihua Zhang
- & Yi He
-
Article
| Open Access Ubiquitous organic molecule-based free-standing nanowires with ultra-high aspect ratios
Ubiquitous organic molecule-based free-standing nanowires with ultra-high aspect ratios
Extension of nanostructure fabrication in the single-nm regime is a promising but fabrication of nanostructures with high aspect ratios remains challenging. Here, the authors use high energy charged particles to produce free-standing 1D organic nanostructures with extremely high aspect ratios and controlled number density.
- Koshi Kamiya
- , Kazuto Kayama
- & Shu Seki
-
Article
| Open Access Active coacervate droplets are protocells that grow and resist Ostwald ripening
Active coacervate droplets are protocells that grow and resist Ostwald ripening
Active coacervate droplets are droplets coupled to a chemical reaction that maintains them out of equilibrium, which can be used to drive active processes, but coacervates are still subject to passive processes that compete with or mask growth. Here, the authors present a nucleotide-based model for active coacervate droplets that form and grow by fuel-driven synthesis of ATP, and, importantly, do not undergo Ostwald ripening.
- Karina K. Nakashima
- , Merlijn H. I. van Haren
- & Evan Spruijt
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast coherent motion and helix rearrangement of homodimeric hemoglobin visualized with femtosecond X-ray solution scattering
Ultrafast coherent motion and helix rearrangement of homodimeric hemoglobin visualized with femtosecond X-ray solution scattering
Femtosecond time-resolved X-ray solution scattering (fs-TRXSS) measurements provide information on the structural dynamics of proteins in solution. Here, the authors present a structure refinement method for the analysis of fs-TRXSS data and use it to characterise the ultrafast structural changes of homodimeric haemoglobin.
- Yunbeom Lee
- , Jong Goo Kim
- & Hyotcherl Ihee
-
Article
| Open Access Motion of water monomers reveals a kinetic barrier to ice nucleation on graphene
Motion of water monomers reveals a kinetic barrier to ice nucleation on graphene
The dynamics of water molecules at interfaces controls natural and artificial processes, but experimental investigations have been challenging. Here the authors investigate water molecules on a graphene surface using helium spin-echo spectroscopy, and reveal a regime where freely mobile molecules undergo strong repulsive mutual interactions which inhibit ice nucleation.
- Anton Tamtögl
- , Emanuel Bahn
- & William Allison
-
Article
| Open Access Autocatalytic and oscillatory reaction networks that form guanidines and products of their cyclization
Autocatalytic and oscillatory reaction networks that form guanidines and products of their cyclization
So far, only a few chemical oscillators based on organic reactions have been developed. Here, the authors report both autocatalytic and oscillatory reaction networks that form substituted guanidines from thiouronium salts; when coupled to cascade cyclization, this reaction network produces oscillations in the production of pyrimidine-based heterocycles.
- Alexander I. Novichkov
- , Anton I. Hanopolskyi
- & Sergey N. Semenov
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting wavelength-dependent photochemical reactivity and selectivity
Predicting wavelength-dependent photochemical reactivity and selectivity
Predicting the conversion and selectivity of a photochemical reactions is challenging. Here, the authors introduce a framework for the quantitative prediction of the time-dependent progress of a photoligation reaction and predict LED-light induced conversion through a wavelength-resolved numerical simulation.
- Jan P. Menzel
- , Benjamin B. Noble
- & Christopher Barner-Kowollik
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanism for rapid autoxidation in α-pinene ozonolysis
Molecular mechanism for rapid autoxidation in α-pinene ozonolysis
Oxidation of volatile organic compounds leads to aerosol formation in the atmosphere, but the mechanism of some fast reactions is still unclear. The authors, using quantum chemical modelling and experiments, reveal that in key monoterpenes the cyclobutyl ring that would hinder the reactivity is broken in the early exothermic steps of the reaction.
- Siddharth Iyer
- , Matti P. Rissanen
- & Theo Kurtén
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic spin separation induced by nuclear motion near conical intersections
Electronic spin separation induced by nuclear motion near conical intersections
Spin polarization is at the basis of quantum information and underlies some natural processes, but many aspects still need to be explored. Here, the authors, by quantum mechanical computations, show that even a weak spin-orbit coupling near a conical intersection can induce large spin selection, with consequences for spin manipulation in photochemical or electrochemical reactions.
- Yanze Wu
- & Joseph E. Subotnik
-
Article
| Open Access Defect-driven selective metal oxidation at atomic scale
Defect-driven selective metal oxidation at atomic scale
Crystal defects critically influence surface chemical reactions in nanomaterials, yet the basic mechanisms at play are still elusive. Here, the authors show the atomic-scale dynamics of surface oxidation at coherent planar defects in Ag and Pd, revealing how twins and stacking-faults selectively oxidize metallic nanocrystals.
- Qi Zhu
- , Zhiliang Pan
- & Jiangwei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Differential guest location by host dynamics enhances propylene/propane separation in a metal-organic framework
Differential guest location by host dynamics enhances propylene/propane separation in a metal-organic framework
Porous materials acting as molecular sieves for propylene/propane separation are important for the petrochemical industry. Here the authors show an example of how specific guest-host interactions can result in structural changes in the porous host and shut down diffusion of one of the two similar guest molecules.
- Dmytro Antypov
- , Aleksander Shkurenko
- & Matthew S. Dyer
-
Article
| Open Access How Rh surface breaks CO2 molecules under ambient pressure
How Rh surface breaks CO2 molecules under ambient pressure
Direct observation of carbon dioxide dissociation provides an origin of catalytic conversion for industrial chemical reactions. Here, the authors reveal their molecular interactions on the rhodium catalyst at near-ambient pressure by interface science techniques and computational calculations.
- Jeongjin Kim
- , Hyunwoo Ha
- & Jeong Young Park
-
Article
| Open Access Confinement in crystal lattice alters entire photocycle pathway of the Photoactive Yellow Protein
Confinement in crystal lattice alters entire photocycle pathway of the Photoactive Yellow Protein
Protein structural dynamics can be studied by time-resolved crystallography (TRC) and ultrafast transient spectroscopic methods. Here, the authors perform electronic and vibrational transient absorption measurements to characterise the full photocycle of Photoactive Yellow Protein (PYP) both in the crystalline and solution state and find that the photocycle kinetics and structural intermediates of PYP deviate in the crystalline state, which must be taken into consideration when planning TRC experiments.
- Patrick E. Konold
- , Enis Arik
- & Marie Louise Groot
-
Article
| Open Access Adsorption and activation of molecular oxygen over atomic copper(I/II) site on ceria
Adsorption and activation of molecular oxygen over atomic copper(I/II) site on ceria
Precise control over the energy of atomic metal sites is key to unlocking novel reaction pathways. Here, the authors achieve selective oxygen activation by the isolated copper site on ceria, due to its reduced 3d orbital energy via cerium induced electron withdrawing effect.
- Liqun Kang
- , Bolun Wang
- & Feng Ryan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Polypeptide formation in clusters of β-alanine amino acids by single ion impact
Polypeptide formation in clusters of β-alanine amino acids by single ion impact
Formation of peptide bonds in cold gas-phase environments might represent a prebiotic synthesis route of polypeptides. Here, the authors show the formation of up to tetra-peptide species in the collision of He2+ ions, with kinetic energies typical for solar wind ions, with cold β-alanine clusters.
- Patrick Rousseau
- , Dariusz G. Piekarski
- & Bernd A. Huber
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging spatiotemporal evolution of molecules and active sites in zeolite catalyst during methanol-to-olefins reaction
Imaging spatiotemporal evolution of molecules and active sites in zeolite catalyst during methanol-to-olefins reaction
Imaging zeolites in catalysis relies on the use of probe molecules or model catalysts. Here the authors show the synergy of a multiscale reaction-diffusion model and structured illumination microscopy to illustrate spatiotemporal evolution of molecules and acid sites in SAPO-34 zeolites in methanol-to-olefins reaction.
- Mingbin Gao
- , Hua Li
- & Zhongmin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of the geometric phase effect in the H+HD→H2+D reaction below the conical intersection
Observation of the geometric phase effect in the H+HD→H2+D reaction below the conical intersection
The geometric phase effect associated with a conical intersection between the ground and first excited electronic state has been predicted in the H3 system below the conical intersection energy. The authors, by a crossed molecular beam technique and quantum dynamic calculations, provide experimental evidence and insight into its origin.
- Daofu Yuan
- , Yin Huang
- & Xueming Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of a Feshbach resonance by coincidence detection of ions and electrons in Penning ionization collisions
Direct observation of a Feshbach resonance by coincidence detection of ions and electrons in Penning ionization collisions
Here the authors use ion-electron coincidence imaging method to explore collision dynamics. They observe Feshbach resonance in the Penning ionization collision of argon and excited helium atoms, resulting in singly charged argon ion and ground state helium.
- Baruch Margulis
- , Julia Narevicius
- & Edvardas Narevicius
-
Article
| Open Access In situ observation of oscillatory redox dynamics of copper
In situ observation of oscillatory redox dynamics of copper
How a catalyst behaves microscopically under reaction conditions, and what kinds of active sites transiently exist on its surface, is still very much a mystery to the scientific community. Here the authors report on in situ observation of a redox active copper catalyst by a combination of in situ imaging and spectroscopy tools.
- Jing Cao
- , Ali Rinaldi
- & Marc Willinger
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering the effects of interface-induced ordering of liquid on crystal growth using machine learning
Uncovering the effects of interface-induced ordering of liquid on crystal growth using machine learning
Crystallization is a challenging process to model quantitatively. Here the authors use machine learning and atomistic simulations together to uncover the role of the liquid structure on the process of crystallization and derive a predictive kinetic model of crystal growth.
- Rodrigo Freitas
- & Evan J. Reed
-
Article
| Open Access Heavy N+ ion transfer in doubly charged N2Ar van der Waals cluster
Heavy N+ ion transfer in doubly charged N2Ar van der Waals cluster
There are multiple ways by which energy and charge transfer occur in weakly bound systems. Here the authors reveal a heavy ion N+ transfer in a doubly charged Van der Waals cluster produced in collisions of the highly charged Ne8+ ion with N2Ar, leading to fragmentation of N+ and NAr+ via Coulomb explosion.
- XiaoLong Zhu
- , XiaoQing Hu
- & X. Ma
-
Article
| Open Access The unique interplay between copper and zinc during catalytic carbon dioxide hydrogenation to methanol
The unique interplay between copper and zinc during catalytic carbon dioxide hydrogenation to methanol
In spite of numerous works, the nature of high activity of Cu/ZnO catalyst in methanol synthesis remains the subject of intensive debate. Here, the authors study the carbon dioxide hydrogenation mechanism using high-pressure operando techniques which allow them to unify different, seemingly contradicting, models.
- Maxim Zabilskiy
- , Vitaly L. Sushkevich
- & Jeroen A. van Bokhoven
-
Article
| Open Access Water acting as a catalyst for electron-driven molecular break-up of tetrahydrofuran
Water acting as a catalyst for electron-driven molecular break-up of tetrahydrofuran
Reactions induced by low-energy electrons in hydrated systems are central to radiation therapy, but a full understanding of their mechanism is lacking. Here the authors investigate the electron-impact induced ionization and subsequent dissociation of tetrahydrofuran, model for biochemically relevant systems, in a micro-solvated environment.
- Enliang Wang
- , Xueguang Ren
- & Alexander Dorn
-
Article
| Open Access Origins of fast diffusion of water dimers on surfaces
Origins of fast diffusion of water dimers on surfaces
The experimental observation that water dimers diffuse more rapidly than monomers across materials’ surfaces is yet to be clarified. Here the authors show by ab initio calculations classical and quantum mechanical mechanisms for faster water dimer diffusion on a broad range of metal and non-metal surfaces.
- Wei Fang
- , Ji Chen
- & Angelos Michaelides
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidating the mechanism of heterogeneous Wacker oxidation over Pd-Cu/zeolite Y by transient XAS
Elucidating the mechanism of heterogeneous Wacker oxidation over Pd-Cu/zeolite Y by transient XAS
Unlike the homogeneous Wacker process, understanding of the mechanism of the heterogeneous system remains superficial. Here, the authors investigate the mechanism of heterogeneous Wacker oxidation over Pd-Cu/zeolite Y through the synergistic combination of kinetic, spectroscopic and chemometric studies.
- Jerick Imbao
- , Jeroen A. van Bokhoven
- & Maarten Nachtegaal
-
Article
| Open Access Confined water-mediated high proton conduction in hydrophobic channel of a synthetic nanotube
Confined water-mediated high proton conduction in hydrophobic channel of a synthetic nanotube
Water confined in natural or synthetic hydrophobic nano-spaces behaves differently than in the bulk. Here the authors investigate water in hydrophobic synthetic 1D nanochannels revealing water clustering in tetramers and octamers and high proton conductivity, along with a continuous liquid to solid transition.
- Ken-ichi Otake
- , Kazuya Otsubo
- & Hiroshi Kitagawa
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanistic insight into carbon-carbon bond formation on cobalt under simulated Fischer-Tropsch synthesis conditions
Mechanistic insight into carbon-carbon bond formation on cobalt under simulated Fischer-Tropsch synthesis conditions
The mechanism by which C-C bonds form during Fischer-Tropsch synthesis remains debated while spectroscopic identification of reaction intermediates remains scarce. Here, the authors identify alkylidynes as reactive intermediates for C-C bond formation on cobalt terrace sites and moreover show that these intermediates are stabilized by the high surface coverage typical for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis.
- C. J. (Kees-Jan) Weststrate
- , Devyani Sharma
- & J. W. (Hans) Niemantsverdriet
-
Article
| Open Access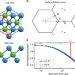 Nanoscopic diffusion of water on a topological insulator
Nanoscopic diffusion of water on a topological insulator
Water molecular motion on surfaces underpins a range of phenomena in nature. The authors resolve the nanoscale-nanosecond motion of water at a topological insulator’s surface by helium spin-echo spectroscopy and computations, reporting hopping among sites and repulsion between water molecules.
- Anton Tamtögl
- , Marco Sacchi
- & William Allison
-
Article
| Open Access Feshbach resonances in the F + H2O → HF + OH reaction
Feshbach resonances in the F + H2O → HF + OH reaction
Feshbach resonances are transiently trapped states along a reaction coordinate, providing a probe to the reaction’s potential energy surface (PES) but difficult to analyze in polyatomic systems. Here the authors identify Feshbach resonances in a reacting 4-atom system by state-to-state quantum dynamics using a full-dimensional PES.
- Xiaoren Zhang
- , Lulu Li
- & Dong H. Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Strong inverse kinetic isotope effect observed in ammonia charge exchange reactions
Strong inverse kinetic isotope effect observed in ammonia charge exchange reactions
Inverse kinetic isotope effects (KIEs) are rarely observed. Here, the authors report an inverse KIE in the charge transfer reaction of \({{\rm{Xe}}}^{+}\) with ammonia. \({{\rm{ND}}}_{3}\) reacts more than 3 times faster than \({{\rm{NH}}}_{3}\), despite no N-H or N-D bonds being broken, with implications for our understanding of interstellar chemistry.
- L. S. Petralia
- , A. Tsikritea
- & B. R. Heazlewood
-
Article
| Open Access In situ mapping of activity distribution and oxygen evolution reaction in vanadium flow batteries
In situ mapping of activity distribution and oxygen evolution reaction in vanadium flow batteries
Redox flow batteries are attractive for large-scale energy storage, but electrode activity should be better understood to improve electrochemical performance. Here the authors map the surface activity distribution of a vanadium redox flow battery electrode with spatial resolution of a single fiber.
- Kaijie Ma
- , Yunong Zhang
- & Yonghong He
-
Article
| Open Access Picosecond to millisecond tracking of a photocatalytic decarboxylation reaction provides direct mechanistic insights
Picosecond to millisecond tracking of a photocatalytic decarboxylation reaction provides direct mechanistic insights
The spectroscopic tracking of complex, multi-step chemical reactions is challenging due to the dynamic timescales of the elementary steps. Here, the authors track a four-step, light-induced decarboxylation reaction in real time to provide new mechanistic insights.
- Aditi Bhattacherjee
- , Mahima Sneha
- & Andrew J. Orr-Ewing
-
Article
| Open Access Two-electron transfer stabilized by excited-state aromatization
Two-electron transfer stabilized by excited-state aromatization
Excited state aromaticity gives rise to unique photophysical properties which may aid the design of functional photoactive materials. Here, the authors spectroscopically characterize an acceptor-donor-acceptor system featuring a two-electron transfer process stabilized by aromatization in the lower energy excited state.
- Jinseok Kim
- , Juwon Oh
- & Dongho Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Deciphering nanoconfinement effects on molecular orientation and reaction intermediate by single molecule imaging
Deciphering nanoconfinement effects on molecular orientation and reaction intermediate by single molecule imaging
Nanoconfinement effects on changing molecular transport and reaction kinetics in heterogeneous catalysis have been widely recognized. Here, the authors design a core-shell nanocatalyst with aligned linear nanopores to uncover nanoconfinement effects on catalytic activity and adsorption strength by single molecule imaging.
- Bin Dong
- , Yuchen Pei
- & Ning Fang

 Uptake of N2O5 by aqueous aerosol unveiled using chemically accurate many-body potentials
Uptake of N2O5 by aqueous aerosol unveiled using chemically accurate many-body potentials