Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Delayed gut microbiota development in high-risk for asthma infants is temporarily modifiable by Lactobacillus supplementation
Delayed gut microbiota development in high-risk for asthma infants is temporarily modifiable by Lactobacillus supplementation
Gut microbial dysbiosis in infancy is associated with childhood atopy and the development of asthma. Here, the authors show that gut microbiota perturbation is evident in the very earliest stages of postnatal life, continues throughout infancy, and can be partially rescued by Lactobacillus supplementation in high-risk for asthma infants.
- Juliana Durack
- , Nikole E. Kimes
- & Susan V. Lynch
-
Article
| Open Access Loss of microRNA-128 promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart regeneration
Loss of microRNA-128 promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart regeneration
During early postnatal development in mammals, cardiomyocytes exit the cell cycle, losing their regenerative capacity. Here the authors show that, following myocardial infarction, loss of microRNA-128 promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac regeneration in adult mice partly via enhancing the expression of the chromatin modifier SUZ12.
- Wei Huang
- , Yuliang Feng
- & Yigang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A community approach to mortality prediction in sepsis via gene expression analysis
A community approach to mortality prediction in sepsis via gene expression analysis
Sepsis is characterized by deregulated host response to infection. Efficient therapies are still needed but a limitation for sepsis treatment is the heterogeneity in patients. Here Sweeney et al. generate prognostic models based on gene expression to improve risk stratification classification and prediction for 30-day mortality of patients.
- Timothy E. Sweeney
- , Thanneer M. Perumal
- & Raymond J. Langley
-
Article
| Open Access Actionable perturbations of damage responses by TCL1/ATM and epigenetic lesions form the basis of T-PLL
Actionable perturbations of damage responses by TCL1/ATM and epigenetic lesions form the basis of T-PLL
T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia (T-PLL) is a rare malignancy with a poor prognosis. Here, the authors investigate the genomic landscape, gene expression profiles and functional mechanisms in 111 patients, highlighting TCL1 overexpression and ATM aberrations as core lesions which co-operate to impair DNA damage processing.
- A. Schrader
- , G. Crispatzu
- & M. Herling
-
Article
| Open Access Mutations in CFAP43 and CFAP44 cause male infertility and flagellum defects in Trypanosoma and human
Mutations in CFAP43 and CFAP44 cause male infertility and flagellum defects in Trypanosoma and human
Asthenozoospermia is a major cause of male infertility, and multiple morphological abnormalities of the flagella (MMAF) is a particularly severe form. Here, using whole-exome sequencing of 78 MMAF patients, the authors identify mutations in two WDR proteins, CFAP43 and CFAP44, and confirm that these proteins are required for flagellogenesis in mouse and Trypanosoma brucei.
- Charles Coutton
- , Alexandra S. Vargas
- & Pierre F. Ray
-
Article
| Open Access Myeloid-derived interleukin-1β drives oncogenic KRAS-NF-κΒ addiction in malignant pleural effusion
Myeloid-derived interleukin-1β drives oncogenic KRAS-NF-κΒ addiction in malignant pleural effusion
Malignant pleural effusion (MPE) is a life-threatening cancer-related disorder. Here, the authors show that KRAS-mutant tumor cells require IKKα, activated via host-provided IL-1β, to promote MPE development and that co-inhibition of both KRAS and IKKα ameliorates the development of MPE in mouse models.
- Antonia Marazioti
- , Ioannis Lilis
- & Georgios T. Stathopoulos
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic network biomarker indicates pulmonary metastasis at the tipping point of hepatocellular carcinoma
Dynamic network biomarker indicates pulmonary metastasis at the tipping point of hepatocellular carcinoma
Biomarkers of the tipping point before metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) could help stratify patient treatment. Here, the authors study dynamic network biomarkers to identify CALM3 as a potential suppressor of metastasis, the level of which can predict overall survival and relapse-free survival in postoperative HCC.
- Biwei Yang
- , Meiyi Li
- & Jinglin Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Impaired β-arrestin recruitment and reduced desensitization by non-catechol agonists of the D1 dopamine receptor
Impaired β-arrestin recruitment and reduced desensitization by non-catechol agonists of the D1 dopamine receptor
Dopamine receptor agonists are used for the treatment of various psychiatric diseases. Here, the authors screen approximately three million compounds and identify a novel class of D1R agonists that do not have a catechol scaffold and possess promising pharmacokinetic properties.
- David L. Gray
- , John A. Allen
- & Michael D. Ehlers
-
Article
| Open Access Development of a chimeric Zika vaccine using a licensed live-attenuated flavivirus vaccine as backbone
Development of a chimeric Zika vaccine using a licensed live-attenuated flavivirus vaccine as backbone
Given the recent Zika virus (ZIKV) epidemic, development of an effective vaccine is of high importance. Here, the authors use a licensed live-attenuated flavivirus vaccine backbone to develop a ZIKV vaccine and determine immunogenicity, safety and protection profiles in different animal models.
- Xiao-Feng Li
- , Hao-Long Dong
- & Cheng-Feng Qin
-
Article
| Open Access Neuropathic MORC2 mutations perturb GHKL ATPase dimerization dynamics and epigenetic silencing by multiple structural mechanisms
Neuropathic MORC2 mutations perturb GHKL ATPase dimerization dynamics and epigenetic silencing by multiple structural mechanisms
Microrchidia CW-type zinc finger protein 2 (MORC2) is an effector of epigenetic silencing by the human silencing hub (HUSH). Here the authors present the crystal structures of MORC2 and disease-causing MORC2 mutants and give mechanistic insights into how MORC2 mediates HUSH-dependent silencing.
- Christopher H. Douse
- , Stuart Bloor
- & Yorgo Modis
-
Article
| Open Access Dissection and function of autoimmunity-associated TNFAIP3 (A20) gene enhancers in humanized mouse models
Dissection and function of autoimmunity-associated TNFAIP3 (A20) gene enhancers in humanized mouse models
The human TNFAIP3 gene, which encodes for A20, is associated with autoimmune diseases. Here, the authors use BAC transgenics combined with CRISPR- and recombineering-mediated genome editing to dissect in vivo and in primary immune cells, the role of enhancers regulating TNFAIP3.
- Upneet K. Sokhi
- , Mark P. Liber
- & Shiaoching Gong
-
Article
| Open Access A secondary RET mutation in the activation loop conferring resistance to vandetanib
A secondary RET mutation in the activation loop conferring resistance to vandetanib
Mechanisms of acquired resistance to RET tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancers are largely unknown. Here, the authors report in a lung adenocarcinoma patient harboring a CCDC6-RET mutation in the RET kinase (S904F) that results in resistance to the kinase inhibitor vandetanib by increasing the ATP affinity and autophosphorylation activity of RET kinase.
- Takashi Nakaoku
- , Takashi Kohno
- & Koichi Goto
-
Article
| Open Access Epigenetic modulation of Fgf21 in the perinatal mouse liver ameliorates diet-induced obesity in adulthood
Epigenetic modulation of Fgf21 in the perinatal mouse liver ameliorates diet-induced obesity in adulthood
FGF21 exerts beneficial metabolic effects on multiple tissues. Here the authors show that the Fgf21 gene is demethylated during the postnatal suckling period, creating an epigenetic memory that determines the responsiveness of the Fgf21 gene to inducers such as PPARα activators or fasting in adulthood.
- Xunmei Yuan
- , Kazutaka Tsujimoto
- & Yoshihiro Ogawa
-
Article
| Open Access The p55TNFR-IKK2-Ripk3 axis orchestrates arthritis by regulating death and inflammatory pathways in synovial fibroblasts
The p55TNFR-IKK2-Ripk3 axis orchestrates arthritis by regulating death and inflammatory pathways in synovial fibroblasts
TNF is a major therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and synovial fibroblasts are central to the pathogenesis of RA. Here the authors dissect TNF-induced death and activation signalling in RA synovial fibroblasts and TNF-driven arthritis and indicate that a successful therapeutic strategy might be to target both IKK2 and RIPK3 at the same time.
- Marietta Armaka
- , Caroline Ospelt
- & George Kollias
-
Article
| Open Access Ultraconserved element uc.372 drives hepatic lipid accumulation by suppressing miR-195/miR4668 maturation
Ultraconserved element uc.372 drives hepatic lipid accumulation by suppressing miR-195/miR4668 maturation
Ultraconserved RNAs are a class of long non-coding RNAs whose functions are yet to be identified. Here Guo and colleagues show that an ultraconserved RNA uc.372 promotes lipogenesis and lipid accumulation within the hepatocytes by suppressing the maturation of miR-195/miR-4668 that inhibits lipogenic gene expression.
- Jun Guo
- , Weiwei Fang
- & Jian Li
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic alterations driving metastatic colony formation are acquired outside of the primary tumour in melanoma
Genetic alterations driving metastatic colony formation are acquired outside of the primary tumour in melanoma
For several cancer types, mouse models indicate that metastasis occurs early. Here, the authors show that human melanoma cells disseminate early and illustrate a genetic colonisation signature that evolves in parallel at different sites.
- Melanie Werner-Klein
- , Sebastian Scheitler
- & Christoph A. Klein
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of mutant TERT by BRAF V600E/MAP kinase pathway through FOS/GABP in human cancer
Regulation of mutant TERT by BRAF V600E/MAP kinase pathway through FOS/GABP in human cancer
The mechanism of tumor progression robustly promoted by co-existing BRAF V600E and TERT promoter mutations is not known. Here, the authors show a mechanism of mutant TERT activation by BRAF V600E and MAPK pathways in which FOS, as a transcription factor of the GABPB promoter, functionally links the two oncogenes.
- Rengyun Liu
- , Tao Zhang
- & Mingzhao Xing
-
Article
| Open Access Unravelling the immune signature of Plasmodium falciparum transmission-reducing immunity
Unravelling the immune signature of Plasmodium falciparum transmission-reducing immunity
Naturally acquired antibodies may inhibit Plasmodium survival in mosquitoes, alter malaria transmission dynamics, and form the basis for transmission-blocking vaccines. Here, using sera from malaria-exposed individuals, Stone et al. reveal novel antibody correlates of transmission-reducing activity.
- Will J. R. Stone
- , Joseph J. Campo
- & Matthijs M. Jore
-
Article
| Open Access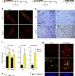 SOD3 improves the tumor response to chemotherapy by stabilizing endothelial HIF-2α
SOD3 improves the tumor response to chemotherapy by stabilizing endothelial HIF-2α
Tumour vasculature influences drug delivery. Here, the authors show that SOD3 re-expression enhances doxorubicin delivery and effects through normalization of tumour vasculature via the HIF-2a/VE-cadherin pathway.
- Emilia Mira
- , Lorena Carmona-Rodríguez
- & Santos Mañes
-
Article
| Open Access IL-6/STAT3 pathway induced deficiency of RFX1 contributes to Th17-dependent autoimmune diseases via epigenetic regulation
IL-6/STAT3 pathway induced deficiency of RFX1 contributes to Th17-dependent autoimmune diseases via epigenetic regulation
Th17 cells are a common pathogenic effector cell in autoimmune inflammatory diseases. Here the authors show that the transcription factor RFX1 limits Th17 differentiation and is protective against the pathogenesis of Th17-driven autoimmune diseases.
- Ming Zhao
- , Yixin Tan
- & Qianjin Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of overactive TGF-β attenuates progression of heterotopic ossification in mice
Inhibition of overactive TGF-β attenuates progression of heterotopic ossification in mice
Heterotopic ossification (HO) is a painful disease of unknown etiology characterized by extraskeletal bone formation after injury. Here the authors show that TGF-β is increased in HO lesions, where it promotes the early stages of HO pathology, and demonstrate that TGF-β inhibition ameliorates HO in mice.
- Xiao Wang
- , Fengfeng Li
- & Xu Cao
-
Article
| Open Access α-cell glucokinase suppresses glucose-regulated glucagon secretion
α-cell glucokinase suppresses glucose-regulated glucagon secretion
Glucagon secretion is promoted during hypoglycemia and inhibited by increased glucose levels. Here, Basco et al. show that glucokinase suppresses glucose-regulated glucagon secretion by modulating the intracellular ATP/ADP ratio and the closure of KATP channels in α-cells.
- Davide Basco
- , Quan Zhang
- & Bernard Thorens
-
Article
| Open Access AhR and SHP regulate phosphatidylcholine and S-adenosylmethionine levels in the one-carbon cycle
AhR and SHP regulate phosphatidylcholine and S-adenosylmethionine levels in the one-carbon cycle
Methyl metabolites in the one-carbon cycle, such as phosphatidylcholines and S-adenosylmethionine, play a role in hepatic triglyceride regulation. Here Kim et al. show that AhR and SHP are both involved in the expression of several key enzymes of one-carbon metabolism, with the former regulating them early after feeding and the latter inhibiting AhR at later stages.
- Young-Chae Kim
- , Sunmi Seok
- & Jongsook Kim Kemper
-
Article
| Open Access A ligand-specific blockade of the integrin Mac-1 selectively targets pathologic inflammation while maintaining protective host-defense
A ligand-specific blockade of the integrin Mac-1 selectively targets pathologic inflammation while maintaining protective host-defense
Integrin-based therapeutics could block inflammatory processes but they also impair host defence, limiting their usefulness. Here the authors report an anti-Mac1 antibody that blocks its interaction with pro-inflammatory ligand CD40L but not other ligands, and show that it can protect against sepsis in mice.
- Dennis Wolf
- , Nathaly Anto-Michel
- & Andreas Zirlik
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure reveals vaccine elicited bactericidal human antibody targeting a conserved epitope on meningococcal fHbp
Crystal structure reveals vaccine elicited bactericidal human antibody targeting a conserved epitope on meningococcal fHbp
Factor H binding protein (fHbp) is a meningococcal virulence factor and a component of vaccines against serogroup B Neisseria meningitidis. Here, the authors characterize the vaccine-elicited human antibody Fab 1A12 and present both the free and the fHbp-bound Fab 1A12 crystal structures.
- Jacinto López-Sagaseta
- , Peter T. Beernink
- & Matthew J. Bottomley
-
Article
| Open Access A microengineered vascularized bleeding model that integrates the principal components of hemostasis
A microengineered vascularized bleeding model that integrates the principal components of hemostasis
Hemostasis is a complex ensemble of events, but current bleeding assays only analyze single components like coagulation or platelet function. Here the authors present a comprehensive vascularized microfluidic mechanical injury bleeding model that addresses different aspects of the hemostatic process.
- Yumiko Sakurai
- , Elaissa T. Hardy
- & Wilbur A. Lam
-
Article
| Open Access Activin-dependent signaling in fibro/adipogenic progenitors causes fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva
Activin-dependent signaling in fibro/adipogenic progenitors causes fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva is a severe disorder characterized by heterotopic ossification, and is caused by mutations in ACVR1. Here, the authors show that expression of mutant ACVR1 in fibro/adipogenic progenitors recapitulates disease progression, and that this can be halted by systemic inhibition of activin A in mice.
- John B. Lees-Shepard
- , Masakazu Yamamoto
- & David J. Goldhamer
-
Article
| Open Access Characterizing steroid hormone receptor chromatin binding landscapes in male and female breast cancer
Characterizing steroid hormone receptor chromatin binding landscapes in male and female breast cancer
Male breast cancer (MBC) is rare and largely hormonally driven. Here, the authors examine the action of steroid hormone receptors in male and female breast cancers and find gender selective hormone receptor action that associates with the survival of MBC patients.
- Tesa M. Severson
- , Yongsoo Kim
- & Wilbert Zwart
-
Article
| Open Access Replication confers β cell immaturity
Replication confers β cell immaturity
Adult beta cells, which are highly specialised insulin-secreting cells, rarely replicate. Puri et al. demonstrate that beta cell proliferative capacity is inversely correlated with their functionality and differentiation state, by inducing proliferation of adult cells with ectopic overexpression of the cell cycle regulator c-Myc.
- Sapna Puri
- , Nilotpal Roy
- & Matthias Hebrok
-
Article
| Open Access Direct effects of transcranial electric stimulation on brain circuits in rats and humans
Direct effects of transcranial electric stimulation on brain circuits in rats and humans
Though transcranial electric stimulation has been used to influence brain activity, it is debated whether neuronal spiking activity is directly affected by commonly-used protocols. Here, the authors quantify the voltage gradients necessary to instantaneously affect neuronal spiking and show that they are higher than commonly-used protocols.
- Mihály Vöröslakos
- , Yuichi Takeuchi
- & Antal Berényi
-
Article
| Open Access Cellular stressors contribute to the expansion of hematopoietic clones of varying leukemic potential
Cellular stressors contribute to the expansion of hematopoietic clones of varying leukemic potential
Cellular stressors can impact clonal hematopoiesis. Here, the authors explore the impact of cytotoxic therapy and hematopoietic transplantation on clonal expansion, suggesting different stressors can promote expansion of distinct long-lived clones.
- Terrence N. Wong
- , Christopher A. Miller
- & Daniel C. Link
-
Article
| Open Access IL-6 receptor blockade corrects defects of XIAP-deficient regulatory T cells
IL-6 receptor blockade corrects defects of XIAP-deficient regulatory T cells
XLP-2 syndrome is caused by XIAP mutation. Here the authors show that mouse and human XIAP-deficient regulatory T cells have defective suppressive function as a result of conversion to proinflammatory cytokine producing cells, an effect that can be prevented by blocking the IL-6 receptor.
- Wan-Chen Hsieh
- , Tzu-Sheng Hsu
- & Ming-Zong Lai
-
Article
| Open Access Tbx5a lineage tracing shows cardiomyocyte plasticity during zebrafish heart regeneration
Tbx5a lineage tracing shows cardiomyocyte plasticity during zebrafish heart regeneration
It is not clear if it is the embryonic origin or anatomical location of cardiomyocytes that restrict their contribution to zebrafish heart regeneration. Here, the authors show a plasticity of embryonic precursors following tbx5a fate mapping and that trabecular cardiomyocytes help to rebuild the cortical myocardium.
- Héctor Sánchez-Iranzo
- , María Galardi-Castilla
- & Nadia Mercader
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-guided design of an Hsp90β N-terminal isoform-selective inhibitor
Structure-guided design of an Hsp90β N-terminal isoform-selective inhibitor
The molecular chaperone Hsp90 oversees the folding of many proteins associated with cancer progression but existing small-molecule inhibitors of this pathway are not isoform-selective. Here, the authors rationally design an Hsp90 inhibitor that displays high selectivity for the Hsp90β isoform.
- Anuj Khandelwal
- , Caitlin N. Kent
- & Brian S. J. Blagg
-
Article
| Open Access Transcriptomic alterations during ageing reflect the shift from cancer to degenerative diseases in the elderly
Transcriptomic alterations during ageing reflect the shift from cancer to degenerative diseases in the elderly
Ageing is associated with a pronounced shift in mortality from cancer to degenerative diseases. Here, the authors show that in concordance with this shift, conserved transcriptional alterations during ageing across four vertebrates align with degenerative diseases but are opposite to those in cancer.
- Peer Aramillo Irizar
- , Sascha Schäuble
- & Christoph Kaleta
-
Article
| Open Access GWAS of epigenetic aging rates in blood reveals a critical role for TERT
GWAS of epigenetic aging rates in blood reveals a critical role for TERT
Epigenetic clocks based on DNA methylation levels are estimators of chronological age. Here, the authors perform a GWAS of epigenetic aging rates in blood and find SNP variants in the TERT locus associated with increased intrinsic epigenetic age are also associated with longer telomeres.
- Ake T. Lu
- , Luting Xue
- & Steve Horvath
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct epigenetic programs regulate cardiac myocyte development and disease in the human heart in vivo
Distinct epigenetic programs regulate cardiac myocyte development and disease in the human heart in vivo
How the cardiac myocyte epigenome is rearranged during development, postnatal maturation and disease is not well understood. Here, the authors investigate the human cardiac myocyte epigenome during development and chronic heart failure and identify distinct epigenetic programs regulating these processes.
- Ralf Gilsbach
- , Martin Schwaderer
- & Lutz Hein
-
Article
| Open Access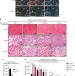 Lsd1 regulates skeletal muscle regeneration and directs the fate of satellite cells
Lsd1 regulates skeletal muscle regeneration and directs the fate of satellite cells
Satellite cells can differentiate both into myocytes and brown adipocytes. Here, the authors show that the histone demethylase Lsd1 prevents adipogenic differentiation of satellite cells by repressing expression of Glis1, and that its ablation changes satellite cell fate towards brown adipocytes and delays muscle regeneration in mice.
- Milica Tosic
- , Anita Allen
- & Roland Schüle
-
Article
| Open Access Endothelial deletion of Ino80 disrupts coronary angiogenesis and causes congenital heart disease
Endothelial deletion of Ino80 disrupts coronary angiogenesis and causes congenital heart disease
Heart development requires compaction of the ventricular wall into a dense myocardium at mid-gestation. Here, Rhee and colleagues show that the chromatin remodeller Ino80 is critical for the formation of the coronary vasculature, and show that coronary vessels are needed for successful cardiac compaction during embryonic development.
- Siyeon Rhee
- , Jae I. Chung
- & Kristy Red-Horse
-
Article
| Open Access AMPK activation counteracts cardiac hypertrophy by reducing O-GlcNAcylation
AMPK activation counteracts cardiac hypertrophy by reducing O-GlcNAcylation
AMPK activation inhibits cardiac hypertrophy. Here the authors show that this occurs independently of previously proposed mechanisms and that AMPK controls the phosphorylation of the aminotransferase GFAT, thereby preventing cardiac hypertrophy through the reduction of protein O-GlcNAcylation.
- Roselle Gélinas
- , Florence Mailleux
- & Luc Bertrand
-
Article
| Open Access Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factor-1α are required for normal endometrial repair during menstruation
Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factor-1α are required for normal endometrial repair during menstruation
About a quarter of pre-menopausal women will suffer from heavy menstrual bleeding in their lives. Here, Maybin and colleagues show hypoxia and subsequent activation of HIF-1α during menses are required for normal endometrial repair, and identify pharmacological stabilisation of HIF-1α as a potential therapeutic strategy for this debilitating condition.
- Jacqueline A. Maybin
- , Alison A. Murray
- & Hilary O. D. Critchley
-
Article
| Open Access Long-acting injectable atovaquone nanomedicines for malaria prophylaxis
Long-acting injectable atovaquone nanomedicines for malaria prophylaxis
Long-acting antimalarials could provide improved prophylaxis and treatment options in the field. Here, Bakshi et al. develop a long-acting injectable atovaquone nanomedicine that prevents malaria infection prophylactically for up to 4 weeks in mice with no evidence for generation of resistant parasites.
- Rahul P. Bakshi
- , Lee M. Tatham
- & Theresa A. Shapiro
-
Article
| Open Access Re-analysis of public genetic data reveals a rare X-chromosomal variant associated with type 2 diabetes
Re-analysis of public genetic data reveals a rare X-chromosomal variant associated with type 2 diabetes
Genome-wide association studies have uncovered several loci associated with diabetes risk. Here, the authors reanalyse public type 2 diabetes GWAS data to fine map 50 known loci and identify seven new ones, including one near ATGR2 on the X-chromosome that doubles the risk of diabetes in men.
- Sílvia Bonàs-Guarch
- , Marta Guindo-Martínez
- & David Torrents
-
Article
| Open Access Direct cell–cell contact between mature osteoblasts and osteoclasts dynamically controls their functions in vivo
Direct cell–cell contact between mature osteoblasts and osteoclasts dynamically controls their functions in vivo
Communication between osteoblasts and osteoclasts is essential for bone homeostasis, but the mode of interaction is unclear. The authors use intravital two-photon microscopy in mice to show that these cells directly interact, regulating activity of osteoclasts, and that the interaction is modulated by parathyroid hormone administration.
- Masayuki Furuya
- , Junichi Kikuta
- & Masaru Ishii
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing insulin- and leptin-induced oxidation of PTP1B for therapeutic development
Harnessing insulin- and leptin-induced oxidation of PTP1B for therapeutic development
The activity of protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B, a major metabolic regulator, depends on its oxidation state. Here the authors identify and characterize a small molecule that targets the oxidized, inactive form of PTP1B, suggesting a new therapeutic approach to diabetes and obesity.
- Navasona Krishnan
- , Christopher A. Bonham
- & Nicholas K. Tonks
-
Article
| Open Access GWAS in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia reveals novel genetic associations at chromosomes 17q12 and 8q24.21
GWAS in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia reveals novel genetic associations at chromosomes 17q12 and 8q24.21
Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia is common in Latino Americans. Here, the authors conduct a genome-wide association study in a Californian cohort containing children of Latino heritage, and identify loci on 17q12 and 8q24 which may affect hematopoietic and growth-regulation pathways.
- Joseph L. Wiemels
- , Kyle M. Walsh
- & Xiaomei Ma
-
Article
| Open Access BLM helicase suppresses recombination at G-quadruplex motifs in transcribed genes
BLM helicase suppresses recombination at G-quadruplex motifs in transcribed genes
Bloom syndrome is characterized by high levels of sister chromatid exchanges (SCEs). Here, the authors use single-cell DNA template strand-sequencing to map SCEs in patient cells, and propose that the BLM helicase protects the genome against unwanted recombination at sites of G-quadruplex structures.
- Niek van Wietmarschen
- , Sarra Merzouk
- & Peter M. Lansdorp
-
Article
| Open Access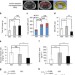 Fibroblast growth factor 21 increases insulin sensitivity through specific expansion of subcutaneous fat
Fibroblast growth factor 21 increases insulin sensitivity through specific expansion of subcutaneous fat
FGF21 has a number of beneficial metabolic effects. Here, Li et al. show that FGF21 promotes the healthy expansion of subcutaneous white adipose tissue, promoting the healthy expansion of fat tissue as a regulatory mechanism to maintain systemic insulin sensitivity during nutrient excess.
- Huating Li
- , Guangyu Wu
- & Weiping Jia
-
Article
| Open Access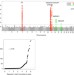 Genome-wide association study in 79,366 European-ancestry individuals informs the genetic architecture of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels
Genome-wide association study in 79,366 European-ancestry individuals informs the genetic architecture of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with multiple human pathologic conditions. In a genome-wide association study of 79,366 individuals, Jiang et al. replicate four and identify two new genetic loci for serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and find evidence for a shared genetic basis with autoimmune diseases.
- Xia Jiang
- , Paul F. O’Reilly
- & Douglas P. Kiel

 Selection of GalNAc-conjugated siRNAs with limited off-target-driven rat hepatotoxicity
Selection of GalNAc-conjugated siRNAs with limited off-target-driven rat hepatotoxicity