Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide analysis of Cushion willow provides insights into alpine plant divergence in a biodiversity hotspot
Genome-wide analysis of Cushion willow provides insights into alpine plant divergence in a biodiversity hotspot
Exceptional alpine plant diversity exists in the Hengduan Mountains. Here, through genome assembly and population genomics studies, the authors find notable intraspecific divergence among Cushion willow populations isolated by the sky island-like habitats and consider it contributes to speciation and biodiversity.
- Jia-hui Chen
- , Yuan Huang
- & Hang Sun
-
Article
| Open Access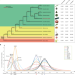 The wax gourd genomes offer insights into the genetic diversity and ancestral cucurbit karyotype
The wax gourd genomes offer insights into the genetic diversity and ancestral cucurbit karyotype
Cucurbits fruits have diverse shapes and sizes, but their genomes evolution and genetic basis of diversity are unclear. Here, the authors show that the wax gourd genome has the most ancestral karyotype among cucurbits and identify candidate genes which contribute to large fruit size by comparative and population genomics analyses.
- Dasen Xie
- , Yuanchao Xu
- & Zhonghua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Improved polygenic prediction by Bayesian multiple regression on summary statistics
Improved polygenic prediction by Bayesian multiple regression on summary statistics
Various approaches are being used for polygenic prediction including Bayesian multiple regression methods that require access to individual-level genotype data. Here, the authors extend BayesR to utilise GWAS summary statistics (SBayesR) and show that it outperforms other summary statistic-based methods.
- Luke R. Lloyd-Jones
- , Jian Zeng
- & Peter M. Visscher
-
Article
| Open Access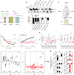 Quantitating the epigenetic transformation contributing to cholesterol homeostasis using Gaussian process
Quantitating the epigenetic transformation contributing to cholesterol homeostasis using Gaussian process
How epigenetics coordinate with genetics to impact protein fitness is unknown. Here, using a Variation Spatial Profiling strategy and machine learning, the authors map HDAC impact on a full set of Niemann pick C1 disease variants to quantitate an unanticipated plasticity in central dogma.
- Chao Wang
- , Samantha M. Scott
- & William E. Balch
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying the polygenic contribution to variable expressivity in eleven rare genetic disorders
Quantifying the polygenic contribution to variable expressivity in eleven rare genetic disorders
Rare genetic disorders (RGDs) often exhibit significant clinical variability among affected individuals. Here, Oetjens et al. systematically study the contribution of common genetic variation to variable expressivity of RGDs and find it is frequently influenced by polygenic factors identified in genome-wide association studies of relevant traits.
- M. T. Oetjens
- , M. A. Kelly
- & D. H. Ledbetter
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association mapping of date palm fruit traits
Genome-wide association mapping of date palm fruit traits
Date palm is an important fruit crop in the Middle East and North Africa. Here, the authors report an improved genome assembly of this species and perform GWAS mapping of sex determining region and 21 fruit traits using high density SNP data generated from re-sequencing of the mapping population.
- Khaled M. Hazzouri
- , Muriel Gros-Balthazard
- & Michael D. Purugganan
-
Article
| Open Access Contribution of retrotransposition to developmental disorders
Contribution of retrotransposition to developmental disorders
Retrotransposition events have been linked to some human disorders. Here, Gardner et al. systematically search for mobile genetic elements (ME) in trio whole exome-sequencing datasets and ascertain 9 de novo MEs and further estimate genome-wide germline ME burden and constraint.
- Eugene J. Gardner
- , Elena Prigmore
- & Matthew E. Hurles
-
Article
| Open Access Longshot enables accurate variant calling in diploid genomes from single-molecule long read sequencing
Longshot enables accurate variant calling in diploid genomes from single-molecule long read sequencing
Single-molecule sequencing (SMS) such as Pacific Biosciences and Oxford Nanopore generate long reads with high error rate. Here, the authors develop Longshot, a computational method that detects and phases single nucleotide variants (SNV) in diploid genomes using SMS data.
- Peter Edge
- & Vikas Bansal
-
Article
| Open Access Rare mutations in the complement regulatory gene CSMD1 are associated with male and female infertility
Rare mutations in the complement regulatory gene CSMD1 are associated with male and female infertility
Many molecular and physiological mechanisms in the regulation of fertility are shared between female and male mammals. Here, Lee et al. report an association of CNVs in CSMD1 with early idiopathic menopause in women and show that loss of Csmd1 leads to gonadal dysfunction in both male and female mice.
- Arthur S. Lee
- , Jannette Rusch
- & Donald F. Conrad
-
Article
| Open Access Characterizing rare and low-frequency height-associated variants in the Japanese population
Characterizing rare and low-frequency height-associated variants in the Japanese population
Thousands of genetic loci are known to associate with human height, but these are mainly based on studies in European ancestry populations. Here, Akiyama et al. construct a genotype reference panel for the Japanese population followed by GWAS and report 573 height associated variants in 191,787 Japanese.
- Masato Akiyama
- , Kazuyoshi Ishigaki
- & Yoichiro Kamatani
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary and functional impact of common polymorphic inversions in the human genome
Evolutionary and functional impact of common polymorphic inversions in the human genome
Inversions are a little-studied type of genomic variation that could contribute to phenotypic traits. Here the authors characterize 45 common polymorphic inversions in human populations and investigate their evolutionary and functional impact.
- Carla Giner-Delgado
- , Sergi Villatoro
- & Mario Cáceres
-
Article
| Open Access Resequencing 545 ginkgo genomes across the world reveals the evolutionary history of the living fossil
Resequencing 545 ginkgo genomes across the world reveals the evolutionary history of the living fossil
Ginkgo is one of the living fossils from the plant kingdom. Here, authors conduct population genomics analyses to reveal its refugia and demographic history, and provide evidence of multiple anthropogenic introductions of ginkgo from eastern China into different continents.
- Yun-Peng Zhao
- , Guangyi Fan
- & Song Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Extensive disruption of protein interactions by genetic variants across the allele frequency spectrum in human populations
Extensive disruption of protein interactions by genetic variants across the allele frequency spectrum in human populations
Low frequency coding single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) are predicted to disproportionately affect protein function. Here, the authors evaluate 2,009 missense SNVs across 2,185 protein-protein interactions using yeast two-hybrid and protein complementation assays and find that disruptive SNVs often occur in disease-associated genes.
- Robert Fragoza
- , Jishnu Das
- & Haiyuan Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Similarities and differences in patterns of germline mutation between mice and humans
Similarities and differences in patterns of germline mutation between mice and humans
Estimates of mutation rates differ between species. Here, Lindsay et al. perform side-by-side analyses of germline mutation rates using multi-sibling mouse and human pedigrees and find different mutation rates between species, also stratified by sex and temporal stage of mutation acquisition.
- Sarah J. Lindsay
- , Raheleh Rahbari
- & Matthew E. Hurles
-
Article
| Open Access Components of genetic associations across 2,138 phenotypes in the UK Biobank highlight adipocyte biology
Components of genetic associations across 2,138 phenotypes in the UK Biobank highlight adipocyte biology
While many pleiotropic genetic loci have been identified, how they contribute to phenotypes across traits and diseases is unclear. Here, the authors propose decomposition of genetic associations (DeGAs), which uses singular value decomposition, to characterize the underlying latent structure of genetic associations of 2,138 phenotypes.
- Yosuke Tanigawa
- , Jiehan Li
- & Manuel A. Rivas
-
Article
| Open Access A high-resolution map of non-crossover events reveals impacts of genetic diversity on mammalian meiotic recombination
A high-resolution map of non-crossover events reveals impacts of genetic diversity on mammalian meiotic recombination
During meiotic recombination, genetic information is transferred or exchanged between parental chromosome copies. Using a large hybrid mouse pedigree, the authors generated high-resolution maps of these transfer/exchange events and discovered new properties governing their processing and resolution.
- Ran Li
- , Emmanuelle Bitoun
- & Simon R. Myers
-
Article
| Open Access Ancient DNA from the skeletons of Roopkund Lake reveals Mediterranean migrants in India
Ancient DNA from the skeletons of Roopkund Lake reveals Mediterranean migrants in India
Remains of several hundred humans are scattered around Roopkund Lake, situated over 5,000 meters above sea level in the Himalayan Mountains. Here the authors analyze genome-wide data from 38 skeletons and find 3 clusters with different ancestries and dates, showing the people were desposited in multiple catastrophic events.
- Éadaoin Harney
- , Ayushi Nayak
- & Niraj Rai
-
Article
| Open Access The determinants of genetic diversity in butterflies
The determinants of genetic diversity in butterflies
Theory suggests that neutral genetic diversity is determined by census population size, but this is not observed empirically. Here, the authors show that in butterflies, neutral genetic diversity correlates with both body size and chromosome number, suggesting that linked selection is also an important factor.
- Alexander Mackintosh
- , Dominik R. Laetsch
- & Konrad Lohse
-
Article
| Open Access Transposition favors the generation of large effect mutations that may facilitate rapid adaption
Transposition favors the generation of large effect mutations that may facilitate rapid adaption
The contribution of transposable elements (TEs) to the creation of heritable mutations is unknown. Here the authors show in Arabidopsis that TEs accumulate exponentially once mobilized and that COPIA retrotransposons preferentially integrate in environmental response genes in a H2A.Z-dependent manner.
- Leandro Quadrana
- , Mathilde Etcheverry
- & Vincent Colot
-
Article
| Open Access Sequencing of Chinese castor lines reveals genetic signatures of selection and yield-associated loci
Sequencing of Chinese castor lines reveals genetic signatures of selection and yield-associated loci
Castor is an important industrial oil crop, but knowledge on its genetic diversity is limited. Here, Fan et al. show geographic pattern of Chinese castors that have developed during domestication by population genetic analyses, and reveal candidate genes associated with agronomically important traits.
- Wei Fan
- , Jianjun Lu
- & Peng Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Lack of long-term acclimation in Antarctic encrusting species suggests vulnerability to warming
Lack of long-term acclimation in Antarctic encrusting species suggests vulnerability to warming
Genetic adaptation and physiological acclimation can potentially buffer species against climate change. Here, the authors perform a long-term warming experiment of Antarctic encrusting communities and show that focal animal species failed to acclimate and lacked genetic variation in tolerance to warming.
- Melody S. Clark
- , Leyre Villota Nieva
- & Lloyd S. Peck
-
Article
| Open Access Analysis of polygenic risk score usage and performance in diverse human populations
Analysis of polygenic risk score usage and performance in diverse human populations
Predominant participation of European-ancestry individuals in genetic studies has hindered the better understanding of genetic risk in non-European ancestry individuals. Here, Duncan et al. quantify polygenic risk score use and performance in worldwide populations.
- L. Duncan
- , H. Shen
- & B. Domingue
-
Article
| Open Access Extensive intraspecific gene order and gene structural variations in upland cotton cultivars
Extensive intraspecific gene order and gene structural variations in upland cotton cultivars
While multiple cotton genomes are available, genome wide variation comparison between allotetraploid upland cotton cultivars remain unexplored. Here, the authors assemble two upland cotton cultivars and reveal large scale structural variations on chromosome A08.
- Zhaoen Yang
- , Xiaoyang Ge
- & Fuguang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-platform discovery of haplotype-resolved structural variation in human genomes
Multi-platform discovery of haplotype-resolved structural variation in human genomes
Structural variants (SVs) in human genomes contribute diversity and diseases. Here, the authors use a multi-platform strategy to generate haplotype-resolved SVs for three human parent–child trios.
- Mark J. P. Chaisson
- , Ashley D. Sanders
- & Charles Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Whole genome sequencing of canids reveals genomic regions under selection and variants influencing morphology
Whole genome sequencing of canids reveals genomic regions under selection and variants influencing morphology
Being man’s best friend, dogs have been bred and selected for certain morphologic traits and breed-associated behaviours. Here, Plassais et al. analyse 722 canine whole genome sequences including modern breeds, wild canids and village dogs by GWAS and search for signatures of selection.
- Jocelyn Plassais
- , Jaemin Kim
- & Elaine A. Ostrander
-
Article
| Open Access A high-quality apple genome assembly reveals the association of a retrotransposon and red fruit colour
A high-quality apple genome assembly reveals the association of a retrotransposon and red fruit colour
Existing apple genome assemblies all derive from Golden Delicious. Here, the authors combine different sequencing technologies to assemble a high quality genome of an anther-derived homozygous genotype HFTH1 and find the association of a retrotransposon and red fruit colour.
- Liyi Zhang
- , Jiang Hu
- & Peihua Cong
-
Article
| Open Access Low genetic variation is associated with low mutation rate in the giant duckweed
Low genetic variation is associated with low mutation rate in the giant duckweed
While the role of effective population size (Ne) in explaining variation in genetic diversity has received much attention, the role of spontaneous mutation rate is largely ignored. Here, Xu et al. show that giant duckweed has a high Ne yet low genetic diversity, likely due to its low mutation rate.
- Shuqing Xu
- , Jessica Stapley
- & Meret Huber
-
Article
| Open Access Whole-genome resequencing of 472 Vitis accessions for grapevine diversity and demographic history analyses
Whole-genome resequencing of 472 Vitis accessions for grapevine diversity and demographic history analyses
Despite the importance of grapevine cultivation in human history and the economic values of cultivar improvement, large-scale genomic variation data are lacking. Here the authors resequence 472 Vitis accessions and use the identified genetic variations for domestication history, demography, and GWAS analyses.
- Zhenchang Liang
- , Shengchang Duan
- & Yang Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Genome maps across 26 human populations reveal population-specific patterns of structural variation
Genome maps across 26 human populations reveal population-specific patterns of structural variation
Large structural variants (SV) are understudied in human genetics research because of the difficulty to detect them in the routinely generated short-read sequencing data. Here, the authors generate optical genome maps of 154 individuals from 26 populations that allow comprehensive examination of large SVs.
- Michal Levy-Sakin
- , Steven Pastor
- & Pui-Yan Kwok
-
Article
| Open Access Association study in African-admixed populations across the Americas recapitulates asthma risk loci in non-African populations
Association study in African-admixed populations across the Americas recapitulates asthma risk loci in non-African populations
The burden of asthma varies between ancestries, but GWAS have so far focused on mainly European ancestry populations. Here, Daya et al. perform GWAS for asthma in 14,654 individuals of African ancestry and, besides confirming previously known loci, identify two potentially African ancestry-specific loci.
- Michelle Daya
- , Nicholas Rafaels
- & Maria Yazdanbakhsh
-
Article
| Open Access Biological relevance of computationally predicted pathogenicity of noncoding variants
Biological relevance of computationally predicted pathogenicity of noncoding variants
Researchers can make use of a variety of computational tools to prioritize genetic variants and predict their pathogenicity. Here, the authors evaluate the performance of six of these tools in three typical biological tasks and find generally low concordance of predictions and experimental confirmation.
- Li Liu
- , Maxwell D. Sanderford
- & Sudhir Kumar
-
Article
| Open Access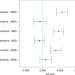 Approximate Bayesian computation with deep learning supports a third archaic introgression in Asia and Oceania
Approximate Bayesian computation with deep learning supports a third archaic introgression in Asia and Oceania
Introgression of Neanderthals and Denisovans left genomic signals in anatomically modern human after Out-of-Africa event. Here, the authors identify a third archaic introgression common to all Asian and Oceanian human populations by applying an approximate Bayesian computation with a Deep Learning framework.
- Mayukh Mondal
- , Jaume Bertranpetit
- & Oscar Lao
-
Article
| Open Access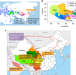 Origin and evolution of qingke barley in Tibet
Origin and evolution of qingke barley in Tibet
The origin of Tibetan barley (qingke) has been a controversial issue for many years. Here, the authors conduct population genomics study to support that qingke is derived from eastern domesticated barley instead of Tibetan wild barley and suggest southern Tibetan Plateau as its introduction route.
- Xingquan Zeng
- , Yu Guo
- & Nyima Tashi
-
Article
| Open Access Dissection of genetic variation and evidence for pleiotropy in male pattern baldness
Dissection of genetic variation and evidence for pleiotropy in male pattern baldness
Male pattern baldness (MPB) is a polygenic trait that affects the majority of European men. Here, Yap et al. estimate heritability, partitioned by autosomes and the X-chromosome, of MPB in the UK Biobank cohort, perform GWAS for MPB and find genetic correlation with other sex-specific traits.
- Chloe X. Yap
- , Julia Sidorenko
- & Peter M. Visscher
-
Article
| Open Access Latin Americans show wide-spread Converso ancestry and imprint of local Native ancestry on physical appearance
Latin Americans show wide-spread Converso ancestry and imprint of local Native ancestry on physical appearance
Latin Americans trace their ancestry to the admixture of Native Americans, Europeans and Sub-Saharan Africans. Here, the authors develop a novel haplotype-based approach and analyse over 6,500 Latin Americans to infer the geographically-detailed genetic structure of this population.
- Juan-Camilo Chacón-Duque
- , Kaustubh Adhikari
- & Andrés Ruiz-Linares
-
Article
| Open Access A semi-supervised approach for predicting cell-type specific functional consequences of non-coding variation using MPRAs
A semi-supervised approach for predicting cell-type specific functional consequences of non-coding variation using MPRAs
Predicting the functional consequences of non-coding genetic variants is a challenge. Here, He et al. present GenoNet, a semi-supervised method that combines information from experimentally confirmed regulatory variants with cell type- and tissue specific annotation for function prediction.
- Zihuai He
- , Linxi Liu
- & Iuliana Ionita-Laza
-
Article
| Open Access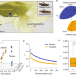 Genetic variation in PTPN1 contributes to metabolic adaptation to high-altitude hypoxia in Tibetan migratory locusts
Genetic variation in PTPN1 contributes to metabolic adaptation to high-altitude hypoxia in Tibetan migratory locusts
Vertebrate adaptation to high-altitude life has been extensively investigated, while invertebrates are less well-studied. Here, the authors find signals of adaptive evolution in genomes of migratory locusts from the Tibetan Plateau, and implicate a PTPN1 coding mutation in their hypoxia response.
- Ding Ding
- , Guangjian Liu
- & Le Kang
-
Article
| Open Access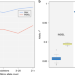 Cohort-wide deep whole genome sequencing and the allelic architecture of complex traits
Cohort-wide deep whole genome sequencing and the allelic architecture of complex traits
Rare genetic variants can contribute to complex traits but this contribution is not well understood. Here, the authors analyse deep whole genome sequencing data across 1457 individuals from an isolated Greek population and find association of rare variant burdens with cardiometabolic traits.
- Arthur Gilly
- , Daniel Suveges
- & Eleftheria Zeggini
-
Article
| Open Access A homozygous loss-of-function mutation leading to CYBC1 deficiency causes chronic granulomatous disease
A homozygous loss-of-function mutation leading to CYBC1 deficiency causes chronic granulomatous disease
Mutations in genes encoding NAPDH oxidase subunits are known to be causative for the primary immunodeficiency chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). Here, the authors identify CYBC1 mutations in patients with CGD and show that CYBC1 is important for formation of the NADPH complex and respiratory burst.
- Gudny A. Arnadottir
- , Gudmundur L. Norddahl
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access A reference haplotype panel for genome-wide imputation of short tandem repeats
A reference haplotype panel for genome-wide imputation of short tandem repeats
Short-tandem repeats (STR), similar to single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), contribute to complex traits, but their ascertainment by next-generation sequencing is costly. Here, Saini et al. provide a SNP+STR haplotype reference panel that allows imputation of STRs from SNP array data.
- Shubham Saini
- , Ileena Mitra
- & Melissa Gymrek
-
Article
| Open Access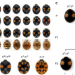 Repeated inversions within a pannier intron drive diversification of intraspecific colour patterns of ladybird beetles
Repeated inversions within a pannier intron drive diversification of intraspecific colour patterns of ladybird beetles
The harlequin ladybird beetle, Harmonia axyridis, has remarkable phenotypic diversity, with over 200 colour patterns. Here, Ando et al. show that this patterning is regulated by the transcription factor gene pannier and has diversified by repeated inversions and cis-regulatory modifications of pannier.
- Toshiya Ando
- , Takeshi Matsuda
- & Teruyuki Niimi
-
Article
| Open Access Deep-coverage whole genome sequences and blood lipids among 16,324 individuals
Deep-coverage whole genome sequences and blood lipids among 16,324 individuals
Common genetic variants associated with plasma lipids have been extensively studied for a better understanding of common diseases. Here, the authors use whole-genome sequencing of 16,324 individuals to analyze rare variant associations and to determine their monogenic and polygenic contribution to lipid traits.
- Pradeep Natarajan
- , Gina M. Peloso
- & Sebastian Zoellner
-
Article
| Open Access Early selection of bZIP73 facilitated adaptation of japonica rice to cold climates
Early selection of bZIP73 facilitated adaptation of japonica rice to cold climates
Japonica rice can grow further north than wild or indica rice and is more tolerant of cold climates. Here, the authors show that bZIP73 likely underwent selection in the early phase of rice domestication to facilitate cold tolerance in japonica by modulating ABA and ROS homeostasis.
- Citao Liu
- , Shujun Ou
- & Chengcai Chu
-
Article
| Open Access Genome‐wide mapping of plasma protein QTLs identifies putatively causal genes and pathways for cardiovascular disease
Genome‐wide mapping of plasma protein QTLs identifies putatively causal genes and pathways for cardiovascular disease
Genetic variation can influence levels of disease-related plasma proteins and, thus, contribute to the pathogenesis of complex diseases. Here, the authors perform genome-wide QTL analysis for 71 plasma proteins to identify causal proteins for coronary heart disease and provide a molecular QTL browser.
- Chen Yao
- , George Chen
- & Daniel Levy
-
Article
| Open Access A tutorial on how not to over-interpret STRUCTURE and ADMIXTURE bar plots
A tutorial on how not to over-interpret STRUCTURE and ADMIXTURE bar plots
Clustering methods such as STRUCTURE and ADMIXTURE are widely used in population genetic studies to investigate ancestry. Here, the authors provide a tutorial on how to interpret results of these analyses and a tool to test the goodness of fit of the model.
- Daniel J. Lawson
- , Lucy van Dorp
- & Daniel Falush
-
Article
| Open Access De novo human genome assemblies reveal spectrum of alternative haplotypes in diverse populations
De novo human genome assemblies reveal spectrum of alternative haplotypes in diverse populations
The majority of the human reference genome assembly is represented as a single consensus haplotype. Here, Wong et al. analyze de novo assemblies of 17 diverse, haplotype-resolved genomes to gain insights into the structure of genetic diversity and compile a list of alternative haplotypes across populations.
- Karen H. Y. Wong
- , Michal Levy-Sakin
- & Pui-Yan Kwok
-
Article
| Open Access Gene expression drives the evolution of dominance
Gene expression drives the evolution of dominance
Dominance is difficult to measure in natural populations as it is confounded with fitness. Here, Huber et al. developed a new approach to co-estimate dominance and selection coefficients, and found that the observed relationship is best fit by a new model of dominance based on gene expression level.
- Christian D. Huber
- , Arun Durvasula
- & Kirk E. Lohmueller
-
Article
| Open Access Population genomics of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal-group 23 reveals early emergence and rapid global dissemination
Population genomics of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal-group 23 reveals early emergence and rapid global dissemination
Since the 1980s, hypervirulent clonal-group CG23 serotype K1 Klebsiella pneumoniae has been recognised as a prominent cause of community-acquired liver abscess and other severe infections. Here, the authors investigate the genomic evolutionary history of CG23 and suggest a new reference strain for CG23.
- Margaret M. C. Lam
- , Kelly L. Wyres
- & Kathryn E. Holt
-
Article
| Open Access Promoter interactome of human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes connects GWAS regions to cardiac gene networks
Promoter interactome of human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes connects GWAS regions to cardiac gene networks
Human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hESC-CM) are a widely used model to study cardiac genomics. Here, Choy et al. perform promoter capture Hi-C to map long-range chromosomal interactions of hESC-CMs and to study overlap of such regions with genetic loci associated with cardiac phenotypes.
- Mun-Kit Choy
- , Biola M. Javierre
- & Bernard D. Keavney

 Ranking of non-coding pathogenic variants and putative essential regions of the human genome
Ranking of non-coding pathogenic variants and putative essential regions of the human genome