Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Population genomics of apricots unravels domestication history and adaptive events
Population genomics of apricots unravels domestication history and adaptive events
The evolutionary and domestication history of apricots is poorly understood. Here, the authors provide four apricot high-quality genome assemblies, the genomes of 578 accessions from natural and cultivated populations, and show that Chinese and European apricots constitute two different gene pools, resulting from independent domestication events.
- Alexis Groppi
- , Shuo Liu
- & Véronique Decroocq
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of the interplay of genetics and culture in Ethiopia
Evidence of the interplay of genetics and culture in Ethiopia
Ethiopia is one of the most ethnically and culturally diverse countries. Here, the authors look at genetic and cultural variation in 1,214 Ethiopians to unravel the relationship between genetic admixture and cultural factors.
- Saioa López
- , Ayele Tarekegn
- & Garrett Hellenthal
-
Article
| Open Access Leveraging supervised learning for functionally informed fine-mapping of cis-eQTLs identifies an additional 20,913 putative causal eQTLs
Leveraging supervised learning for functionally informed fine-mapping of cis-eQTLs identifies an additional 20,913 putative causal eQTLs
Finding causal variants and genes from GWAS loci results remains a challenge. Here, the authors train a model to predict if a variant affects nearby gene expression, and apply the method to identify new possible causal eQTLs and mechanisms of GWAS loci.
- Qingbo S. Wang
- , David R. Kelley
- & Hilary K. Finucane
-
Article
| Open Access Distinctive genetic structure and selection patterns in Plasmodium vivax from South Asia and East Africa
Distinctive genetic structure and selection patterns in Plasmodium vivax from South Asia and East Africa
The genetic diversity of Plasmodium vivax strains in South Asia isn’t well described. Here, the authors sequence P. vivax from returning UK travelers and establish South Asian isolates as subpopulation distinct from East African and South East Asian isolates.
- Ernest Diez Benavente
- , Emilia Manko
- & Taane G. Clark
-
Article
| Open Access Integrative reconstruction of cancer genome karyotypes using InfoGenomeR
Integrative reconstruction of cancer genome karyotypes using InfoGenomeR
Karyotyping of cancer genomes at the base-level is technically challenging. Here, the authors introduce InfoGenomeR, an algorithm that can infer cancer genome karyotypes from whole-genome sequencing data, and test their model on breast, ovarian and brain cancer samples; and identify private and shared mutations between primary and metastatic cancer samples.
- Yeonghun Lee
- & Hyunju Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying therapeutic drug targets using bidirectional effect genes
Identifying therapeutic drug targets using bidirectional effect genes
Prioritising genes as potential drug targets is challenging and often unsuccessful once testing efficacy in humans. Here, the authors propose an approach to identifying drug targets that uses evidence from gain- or loss-of-function mutations associated with bidirectional effects on phenotypes.
- Karol Estrada
- , Steven Froelich
- & Lon R. Cardon
-
Article
| Open Access Human-lineage-specific genomic elements are associated with neurodegenerative disease and APOE transcript usage
Human-lineage-specific genomic elements are associated with neurodegenerative disease and APOE transcript usage
Knowledge of genomic features specific to humans may be important for understanding disease. Here the authors demonstrate a potential role for these human-lineage-specific sequences in brain development and neurological disease.
- Zhongbo Chen
- , David Zhang
- & Mina Ryten
-
Article
| Open Access Widespread signatures of natural selection across human complex traits and functional genomic categories
Widespread signatures of natural selection across human complex traits and functional genomic categories
Methods to study how natural selection shapes genetic architecture of complex traits rely on individual level genome-wide association study (GWAS) data. Here, the authors present a Bayesian method using GWAS summary statistics to study genetic architecture and apply this to 155 complex traits.
- Jian Zeng
- , Angli Xue
- & Jian Yang
-
Article
| Open Access PopDel identifies medium-size deletions simultaneously in tens of thousands of genomes
PopDel identifies medium-size deletions simultaneously in tens of thousands of genomes
Identifying structural variants (SVs) from whole genome sequence data has been a significant bioinformatic challenge. Here, the authors describe PopDel, which uses a joint SV detection approach to reliably and efficiently identify 500-10,000 bp deletions across large population cohorts.
- Sebastian Niehus
- , Hákon Jónsson
- & Birte Kehr
-
Article
| Open Access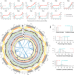 Comprehensive genomic resources related to domestication and crop improvement traits in Lima bean
Comprehensive genomic resources related to domestication and crop improvement traits in Lima bean
Lima bean is an important crop for improving food security in Latin America and elsewhere. Here, the authors assemble its genome, conduct population genomics analysis using genotyping-by-sequencing data, and identify differentially expressed genes between two pod developmental stages.
- Tatiana Garcia
- , Jorge Duitama
- & Maria Isabel Chacón-Sánchez
-
Article
| Open Access Complete sequences of Schizosaccharomyces pombe subtelomeres reveal multiple patterns of genome variation
Complete sequences of Schizosaccharomyces pombe subtelomeres reveal multiple patterns of genome variation
Sequencing and mapping of long repetitive regions can be challenging due to technical difficulties in sequencing and assembly of the sequence data. Here authors report the complete sequences of subtelomeric homologous (SH) regions of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe to reveal highly polymorphic and hot spots for genome variation features.
- Yusuke Oizumi
- , Takuto Kaji
- & Junko Kanoh
-
Article
| Open Access The patterns of deleterious mutations during the domestication of soybean
The patterns of deleterious mutations during the domestication of soybean
The accumulation of recombination events in selfing species may lead to a rapid fixation of both beneficial and deleterious mutations. Here, the authors resequence 781 soybean accessions, show purging of deleterious mutation during domestication, and report genome-wide associations for seed protein and oil traits.
- Myung-Shin Kim
- , Roberto Lozano
- & Soon-Chun Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid parallel adaptation despite gene flow in silent crickets
Rapid parallel adaptation despite gene flow in silent crickets
Gene flow is classically thought to impede local adaptation via parallel evolution. However, a genomic study on Hawaiian crickets from different island populations finds evidence of parallel adaptation to the same lethal parasitoid in spite of strong ongoing gene flow.
- Xiao Zhang
- , Jack G. Rayner
- & Nathan W. Bailey
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic signatures of recombination in a natural population of the bdelloid rotifer Adineta vaga
Genomic signatures of recombination in a natural population of the bdelloid rotifer Adineta vaga
Ancient, asexual lineages are rare as a lack of recombination is usually an evolutionary dead end. Here, authors compare complete genomes of 11 individual bdelloid rotifers that suggest evidence of regular genetic exchange between individuals in a species that was previously thought to be asexual.
- Olga A. Vakhrusheva
- , Elena A. Mnatsakanova
- & Alexey S. Kondrashov
-
Article
| Open Access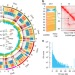 Genome of Solanum pimpinellifolium provides insights into structural variants during tomato breeding
Genome of Solanum pimpinellifolium provides insights into structural variants during tomato breeding
Solanum pimpinellifolium (SP) is the progenitor of cultivated tomato and an important germplasm. Here, the authors assemble SP genome, identify structural variants (SVs) by comparing with modern cultivar, reveal SVs associated with important breeding traits, and detect SVs harboring master regulators of fruit quality traits.
- Xin Wang
- , Lei Gao
- & Zhangjun Fei
-
Article
| Open Access Towards a reference genome that captures global genetic diversity
Towards a reference genome that captures global genetic diversity
The human reference genome does not fully reflect human genetic diversity. Here, the authors analyse 338 human genome assemblies from diverse populations to identify missing sequences, define non-reference unique insertions and construct a Human Diversity Reference.
- Karen H. Y. Wong
- , Walfred Ma
- & Pui-Yan Kwok
-
Article
| Open Access Genome biology of the paleotetraploid perennial biomass crop Miscanthus
Genome biology of the paleotetraploid perennial biomass crop Miscanthus
The perennial grass Miscanthus is a promising biomass crop. Here, via genomics and transcriptomics, the authors reveal its allotetraploid origin, characterize gene expression associated with rhizome development and nutrient recycling, and describe the hybrid origin of the triploid M. x giganteus.
- Therese Mitros
- , Adam M. Session
- & Daniel S. Rokhsar
-
Article
| Open Access The structural variation landscape in 492 Atlantic salmon genomes
The structural variation landscape in 492 Atlantic salmon genomes
This study presents and validates a novel approach to reliably identify structural variations (SVs) in non-model genomes using whole genome sequencing, which was used to detect 15,483 SVs in 492 Atlantic salmon, shedding light on their roles in genome evolution and the genetic architecture of domestication.
- Alicia C. Bertolotti
- , Ryan M. Layer
- & Daniel J. Macqueen
-
Article
| Open Access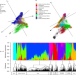 Diversity analysis of 80,000 wheat accessions reveals consequences and opportunities of selection footprints
Diversity analysis of 80,000 wheat accessions reveals consequences and opportunities of selection footprints
Genebanks hold comprehensive collections of wild species, wild relatives, and landraces that are useful for genetic improvement. Here, the authors report the genotype of nearly 80,000 wheat accessions using DArTseq technology to show the less explored genetic diversity.
- Carolina Sansaloni
- , Jorge Franco
- & Kevin Pixley
-
Article
| Open Access Fonio millet genome unlocks African orphan crop diversity for agriculture in a changing climate
Fonio millet genome unlocks African orphan crop diversity for agriculture in a changing climate
Fonio millet is a fast growing orphan cereal crop with a great potential for dryland agriculture. Here, the authors report chromosome-scale reference genome assembly and population genomic resources to shed light on genetic diversity, population structure and domestication of fonio millet.
- Michael Abrouk
- , Hanin Ibrahim Ahmed
- & Simon G. Krattinger
-
Article
| Open Access American mastodon mitochondrial genomes suggest multiple dispersal events in response to Pleistocene climate oscillations
American mastodon mitochondrial genomes suggest multiple dispersal events in response to Pleistocene climate oscillations
Pleistocene population dynamics can inform the consequences of current climate change. This phylogeography of 35 complete American mastodon mitochondrial genomes suggests distinct lineages in this species repeatedly expanded northwards and then went locally extinct in response to glacial cycles.
- Emil Karpinski
- , Dirk Hackenberger
- & Hendrik N. Poinar
-
Article
| Open Access Theoretical and empirical quantification of the accuracy of polygenic scores in ancestry divergent populations
Theoretical and empirical quantification of the accuracy of polygenic scores in ancestry divergent populations
Polygenic scores (PGS) are often based on GWAS data from individuals of European ancestry, thus limiting their use in populations of non-European ancestry. Here, the authors predict the relative accuracy of PGS across ancestries and suggest that causal variants are mostly shared across continents.
- Ying Wang
- , Jing Guo
- & Loic Yengo
-
Article
| Open Access Genome assembly of wild tea tree DASZ reveals pedigree and selection history of tea varieties
Genome assembly of wild tea tree DASZ reveals pedigree and selection history of tea varieties
Wild teas are considered as valuable resource for studying domestication and breeding. Here, Zhang et al. report genome of wild tea DASZ and transcriptome of 217 accessions, which clarify pedigree of Chinese tea cultivars and show tea may not have undergone long-term artificial directional selection on flavor-related metabolites.
- Weiyi Zhang
- , Youjun Zhang
- & Weiwei Wen
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and population genomics of structural variation in a songbird genus
Discovery and population genomics of structural variation in a songbird genus
Structural genomic variation can fuel evolution. Here, authors present genome data from seven Corvus species and unearth structural variants that vary between incipient crow species in Europe, with implications for premating isolation involving plumage patterning.
- Matthias H. Weissensteiner
- , Ignas Bunikis
- & Jochen B. W. Wolf
-
Article
| Open Access The Seminavis robusta genome provides insights into the evolutionary adaptations of benthic diatoms
The Seminavis robusta genome provides insights into the evolutionary adaptations of benthic diatoms
Available genomics studies have mostly focused on planktonic centric diatom. Here, the authors report the genome assembly of the marine biofilm-forming diatom Seminavis robusta and the resequencing data of a panel of accessions to reveal their evolutionary adaptations.
- Cristina Maria Osuna-Cruz
- , Gust Bilcke
- & Klaas Vandepoele
-
Article
| Open Access Germline de novo mutation rates on exons versus introns in humans
Germline de novo mutation rates on exons versus introns in humans
Evidence that somatic mutation rates in introns exceed those in exons challenges the molecular evolution tenet that mutation rate and sequence function are independent. Here, authors analyze germline de novo mutations and reveal no evidence for mutation rate differences between exons and introns.
- Miguel Rodriguez-Galindo
- , Sònia Casillas
- & Antonio Barbadilla
-
Article
| Open Access Functional annotation of rare structural variation in the human brain
Functional annotation of rare structural variation in the human brain
Structural variants (SVs) contribute to the genetic architecture of many brain-related disorders. Here, the authors integrate SV calls from genome sequencing (n = 755) with RNA-seq data (n = 629) from post-mortem dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex to annotate the gene regulatory effects of SVs in the human brain and their potential to contribute to disease.
- Lide Han
- , Xuefang Zhao
- & Douglas M. Ruderfer
-
Article
| Open Access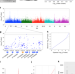 Adaptive reduction of male gamete number in the selfing plant Arabidopsis thaliana
Adaptive reduction of male gamete number in the selfing plant Arabidopsis thaliana
Reduction of pollen grain number is widespread in selfing plants, but the determining gene is unknown. Here, the authors show that a ribosome-biogenesis factor encoding gene RDP1 is responsible for adaptive reduction of male gamete number in Arabidopsis thaliana.
- Takashi Tsuchimatsu
- , Hiroyuki Kakui
- & Kentaro K. Shimizu
-
Article
| Open Access Landscape of multi-nucleotide variants in 125,748 human exomes and 15,708 genomes
Landscape of multi-nucleotide variants in 125,748 human exomes and 15,708 genomes
Multi-nucleotide variants (MNV) are genetic variants in close proximity of each other on the same haplotype whose functional impact is difficult to predict if they reside in the same codon. Here, Wang et al. use the gnomAD dataset to assemble a catalogue of MNVs and estimate their global mutation rate.
- Qingbo Wang
- , Emma Pierce-Hoffman
- & Daniel G. MacArthur
-
Article
| Open Access Chromosome-level assembly of the horseshoe crab genome provides insights into its genome evolution
Chromosome-level assembly of the horseshoe crab genome provides insights into its genome evolution
Horseshoe crabs have been morphologically stable across evolutionary time. Here, the authors generate a chromosome-level assembly for the mangrove horseshoe crab, with implications for innate immunity, and challenging assumptions about the role of genome duplication in adaptive radiation.
- Prashant Shingate
- , Vydianathan Ravi
- & Byrappa Venkatesh
-
Article
| Open Access The impact of antimalarial resistance on the genetic structure of Plasmodium falciparum in the DRC
The impact of antimalarial resistance on the genetic structure of Plasmodium falciparum in the DRC
The genome of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum contains a record of past evolutionary forces. Here, using 2537 parasite sequences from the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the authors demonstrate how drug pressure and human movement have shaped the present-day parasite population.
- Robert Verity
- , Ozkan Aydemir
- & Jonathan J. Juliano
-
Article
| Open Access Haplotype-resolved genomes provide insights into structural variation and gene content in Angus and Brahman cattle
Haplotype-resolved genomes provide insights into structural variation and gene content in Angus and Brahman cattle
Taurine and indicine cattle have different desirable traits making them better adapted to different climates across the world. Here, Low et al. describe a pipeline to produce haplotype-resolved, chromosome-level genomes of Angus and Brahman cattle breeds from a crossbred individual and report on comparisons of the two genomes.
- Wai Yee Low
- , Rick Tearle
- & John L. Williams
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-model functionalization of disease-associated PTEN missense mutations identifies multiple molecular mechanisms underlying protein dysfunction
Multi-model functionalization of disease-associated PTEN missense mutations identifies multiple molecular mechanisms underlying protein dysfunction
Mutations in PTEN have been associated with various human disease, including autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and cancer. Here, the authors assess the function of 106 PTEN variants in yeast, invertebrate models and cell culture and report that PTEN variants generally decrease protein stability.
- Kathryn L. Post
- , Manuel Belmadani
- & Kurt Haas
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear-mitochondrial DNA segments resemble paternally inherited mitochondrial DNA in humans
Nuclear-mitochondrial DNA segments resemble paternally inherited mitochondrial DNA in humans
Recent evidence has questioned the dogma of strict maternal transmission of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) in humans. Wei et al. saw no evidence of paternal transmission of mtDNA in 11,035 human trios, and show that nuclear-mitochondrial segments (NUMTs) can give the impression of paternal mtDNA transmission, but are actually inherited through the nuclear genome.
- Wei Wei
- , Alistair T. Pagnamenta
- & Patrick F. Chinnery
-
Article
| Open Access Ancestry deconvolution and partial polygenic score can improve susceptibility predictions in recently admixed individuals
Ancestry deconvolution and partial polygenic score can improve susceptibility predictions in recently admixed individuals
Polygenic scores are believed to hold future promise for trait prediction and personalized medicine, but are sensitive to demographic history. Here, Marnetto et al. develop partial polygenic scores supplemented with local ancestry deconvolution which improves prediction accuracy into recently admixed European populations.
- Davide Marnetto
- , Katri Pärna
- & Luca Pagani
-
Article
| Open Access Dimensionality reduction reveals fine-scale structure in the Japanese population with consequences for polygenic risk prediction
Dimensionality reduction reveals fine-scale structure in the Japanese population with consequences for polygenic risk prediction
Population structure, even subtle differences within seemingly homogenous populations, can have an impact on the accuracy of polygenic prediction. Here, Sakaue et al. use dimensionality reduction methods to reveal fine-scale structure in the Biobank Japan cohort and explore the performance of polygenic risk scores.
- Saori Sakaue
- , Jun Hirata
- & Yukinori Okada
-
Article
| Open Access Low rates of mutation in clinical grade human pluripotent stem cells under different culture conditions
Low rates of mutation in clinical grade human pluripotent stem cells under different culture conditions
Mutations in human pluripotent stem cells (PSC) and whether any form during culture prior to use in a human clinical context are a concern. Here, the authors use hPSCs derived to cGMP standards and show they have low mutation rates after culture, noting this decreases on culturing in low (5%) oxygen conditions.
- Oliver Thompson
- , Ferdinand von Meyenn
- & Peter W. Andrews
-
Article
| Open Access Gene clustering and copy number variation in alkaloid metabolic pathways of opium poppy
Gene clustering and copy number variation in alkaloid metabolic pathways of opium poppy
The opium poppy has been a source of painkilling drugs synthesized by the benzylisoquinoline alkaloid pathway. Here, the authors report an improved genome assembly and reveal gene clustering and copy number variation in alkaloid metabolic pathways.
- Qiushi Li
- , Sukanya Ramasamy
- & Sam Yeaman
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-resolution localization of causal variants across the genome
Multi-resolution localization of causal variants across the genome
GWAS analysis currently relies mostly on linear mixed models, which do not account for linkage disequilibrium (LD) between tested variants. Here, Sesia et al. propose KnockoffZoom, a non-parametric statistical method for the simultaneous discovery and fine-mapping of causal variants, assuming only that LD is described by hidden Markov models (HMMs).
- Matteo Sesia
- , Eugene Katsevich
- & Chiara Sabatti
-
Article
| Open Access Chromosome-level assemblies of multiple Arabidopsis genomes reveal hotspots of rearrangements with altered evolutionary dynamics
Chromosome-level assemblies of multiple Arabidopsis genomes reveal hotspots of rearrangements with altered evolutionary dynamics
Despite tremendous genomic resources in the Arabidopsis community, only a few whole genome de novo assemblies are available. Here, the authors report chromosome-level reference-quality assemblies of seven A. thaliana accessions and reveal hotspots of rearrangements with altered evolutionary dynamics.
- Wen-Biao Jiao
- & Korbinian Schneeberger
-
Article
| Open Access Balancing selection via life-history trade-offs maintains an inversion polymorphism in a seaweed fly
Balancing selection via life-history trade-offs maintains an inversion polymorphism in a seaweed fly
Few studies empirically pinpoint how balanced polymorphisms are maintained. “Mérot et al”. identify an inversion polymorphism that is maintained in seaweed fly populations because of antagonistic pleiotropy that mediates a classic life history tradeoff between larval survival and adult reproduction.
- Claire Mérot
- , Violaine Llaurens
- & Maren Wellenreuther
-
Article
| Open Access Human and mouse essentiality screens as a resource for disease gene discovery
Human and mouse essentiality screens as a resource for disease gene discovery
Discovery of causal variants for monogenic disorders has been facilitated by whole exome and genome sequencing, but does not provide a diagnosis for all patients. Here, the authors propose a Full Spectrum of Intolerance to Loss-of-Function (FUSIL) categorization that integrates gene essentiality information to aid disease gene discovery.
- Pilar Cacheiro
- , Violeta Muñoz-Fuentes
- & Coleen Kane
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide rare variant analysis for thousands of phenotypes in over 70,000 exomes from two cohorts
Genome-wide rare variant analysis for thousands of phenotypes in over 70,000 exomes from two cohorts
Population-based association analyses of rare genetic variants with complex traits are limited by the availability of data from sufficiently large cohorts. Here, Cirulli et al. report gene-based collapsing analysis of exomes from 49,960 participants of the UK Biobank and 21,866 participants of the Healthy Nevada Project over a total of 4377 traits.
- Elizabeth T. Cirulli
- , Simon White
- & Nicole L. Washington
-
Article
| Open Access Integrative analysis reveals RNA G-quadruplexes in UTRs are selectively constrained and enriched for functional associations
Integrative analysis reveals RNA G-quadruplexes in UTRs are selectively constrained and enriched for functional associations
G-quadruplexes (G4s) are secondary structures that can form in both DNA and RNA from guanine-rich sequences which are enriched in untranslated regions (UTRs). Here, Lee et al. find that putative G4-forming sequences are evolutionarily constrained, enriched for RNA-binding protein interactions and enriched for disease genetic associations.
- David S. M. Lee
- , Louis R. Ghanem
- & Yoseph Barash
-
Article
| Open Access The Medical Genome Reference Bank contains whole genome and phenotype data of 2570 healthy elderly
The Medical Genome Reference Bank contains whole genome and phenotype data of 2570 healthy elderly
Healthspan and healthy aging are areas of research with potential socioeconomic impact. Here, the authors present the Medical Genome Reference Bank (MGRB) which consist of over 4,000 individuals aged 70 years and older without a history of the major age-related diseases and report on results from whole-genome sequencing and association analyses.
- Mark Pinese
- , Paul Lacaze
- & David M. Thomas
-
Article
| Open Access Rare copy number variants in over 100,000 European ancestry subjects reveal multiple disease associations
Rare copy number variants in over 100,000 European ancestry subjects reveal multiple disease associations
Associations of copy number variations (CNVs) with complex traits are challenging to study because of their low frequency. Here, the authors analyse SNP array and array comparative genomic hybridization data of 100,028 individuals and report their associations with immune-related, cardiometabolic and neuropsychiatric diseases as well as cancer.
- Yun Rose Li
- , Joseph T. Glessner
- & Hakon Hakonarson
-
Article
| Open Access CaSpER identifies and visualizes CNV events by integrative analysis of single-cell or bulk RNA-sequencing data
CaSpER identifies and visualizes CNV events by integrative analysis of single-cell or bulk RNA-sequencing data
RNA-sequencing is mostly used to assess gene expression; however, it can also give information about genetic variants. Here, the authors present CaSpER, a statistical framework that utilises RNA-sequencing reads to identify and visualise CNV events by integrating transcriptome-wide expression and allelic shift profiles.
- Akdes Serin Harmanci
- , Arif O. Harmanci
- & Xiaobo Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Predictive impact of rare genomic copy number variations in siblings of individuals with autism spectrum disorders
Predictive impact of rare genomic copy number variations in siblings of individuals with autism spectrum disorders
Siblings of those with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) have increased likelihood of ASD or related subclinical traits. Here, studying 253 ASD families, D’Abate et al. test the predictive value of genomic copy number variation involving ASD-associated loci, with confirmation in a second cohort.
- L. D’Abate
- , S. Walker
- & S. W. Scherer
-
Article
| Open Access GraphTyper2 enables population-scale genotyping of structural variation using pangenome graphs
GraphTyper2 enables population-scale genotyping of structural variation using pangenome graphs
Structural variants may be omitted in sequence analysis despite their importance in genome variation and phenotypic impact. Here the authors present GraphTyper2, which uses pangenome graphs to genotype structural variants using short-reads and can be applied in large-scale sequencing studies.
- Hannes P. Eggertsson
- , Snaedis Kristmundsdottir
- & Pall Melsted

 Four chromosome scale genomes and a pan-genome annotation to accelerate pecan tree breeding
Four chromosome scale genomes and a pan-genome annotation to accelerate pecan tree breeding