Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A uniform survey of allele-specific binding and expression over 1000-Genomes-Project individuals
A uniform survey of allele-specific binding and expression over 1000-Genomes-Project individuals
Using variants from the 1000 Genomes Project, RNA-seq and ChIP-seq data from related projects, this study describes a resource and survey of allele-specific binding and gene expression. A catalogue of allelic SNPs and annotation elements is available as an online resource at alleledb.gersteinlab.org.
- Jieming Chen
- , Joel Rozowsky
- & Mark Gerstein
-
Article
| Open Access Meta-analysis of gene–environment-wide association scans accounting for education level identifies additional loci for refractive error
Meta-analysis of gene–environment-wide association scans accounting for education level identifies additional loci for refractive error
This report by the Consortium for Refractive Error and Myopia uses gene-environment-wide interaction study (GEWIS) to identify genetic loci that affect environmental influence in myopia development, and identifies ethnic specific genetic loci that attribute to eye refractive errors.
- Qiao Fan
- , Virginie J. M. Verhoeven
- & Kari Matti Mäkelä
-
Article
| Open Access Variants near CHRNA3/5 and APOE have age- and sex-related effects on human lifespan
Variants near CHRNA3/5 and APOE have age- and sex-related effects on human lifespan
Understanding the genetic influences on human aging requires a large number of subjects for a study of sufficient power. Here, Jim Wilson and colleagues use information on parental ages at death to show that common variants near the genes for apolipoprotein E and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha 5 are associated with longer lifespan.
- Peter K. Joshi
- , Krista Fischer
- & James F. Wilson
-
Correspondence
| Open AccessCorrespondence: Reply to ‘SEMA4A variation and risk of colorectal cancer’
- Heinz Sill
- , Eduard Schulz
- & C. Richard Boland
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: SEMA4A variation and risk of colorectal cancer
Correspondence: SEMA4A variation and risk of colorectal cancer
- Ben Kinnersley
- , Daniel Chubb
- & Richard S. Houlston
-
Article
| Open Access A variant at 9p21.3 functionally implicates CDKN2B in paediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia aetiology
A variant at 9p21.3 functionally implicates CDKN2B in paediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia aetiology
A risk variant located at 9p21.3 is associated with cancer risk in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Here, the authors show that this variant affects the gene expression of the tumour suppressor gene Cdkn2b.
- Eric A. Hungate
- , Sapana R. Vora
- & Kenan Onel
-
Article
| Open Access Common and rare variants associating with serum levels of creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase
Common and rare variants associating with serum levels of creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase
Creatine kinase (CK) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) are biomarkers of tissue damages including myopathy and myocardial infarction. Here, Patrick Sulem and colleagues perform a genome-wide association study to identify common and rare genetic variants that associates with serum CK or LDH levels.
- Ragnar P. Kristjansson
- , Asmundur Oddsson
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access GWAS of 89,283 individuals identifies genetic variants associated with self-reporting of being a morning person
GWAS of 89,283 individuals identifies genetic variants associated with self-reporting of being a morning person
Circadian rhythms and related behaviours vary across individuals. Here, a large genome-wide association study reveals common single nucleotide variants influencing whether an individual reports as being a ‘morning person’ by identifying 15 significant loci, including 7 near known circadian genes.
- Youna Hu
- , Alena Shmygelska
- & David A. Hinds
-
Article
| Open Access Joint mouse–human phenome-wide association to test gene function and disease risk
Joint mouse–human phenome-wide association to test gene function and disease risk
Phenome-wide association is a novel method that links sequence variants to a spectrum of phenotypes and diseases. Here the authors generate detailed mouse genetic and phenome data which links their phenome-wide association study (PheWAS) of mouse to corresponding PheWAS in human.
- Xusheng Wang
- , Ashutosh K. Pandey
- & Robert W. Williams
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide screening identifies a KCNIP1 copy number variant as a genetic predictor for atrial fibrillation
Genome-wide screening identifies a KCNIP1 copy number variant as a genetic predictor for atrial fibrillation
Tsai et al. here utilize a multi-stage genome-wide association study in Taiwanese population to show a copy number variation in the intron of potassium interacting channel 1 gene (KCNIP1) to be strongly associated with atrial fibrillation. The study also examines the functionality of KCNIP1 in heart electrophysiological function using cultured myocytes and zebrafish.
- Chia-Ti Tsai
- , Chia-Shan Hsieh
- & Jiunn-Lee Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic associations at 53 loci highlight cell types and biological pathways relevant for kidney function
Genetic associations at 53 loci highlight cell types and biological pathways relevant for kidney function
Reduced glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) is a hallmark of chronic kidney disease. Here, Pattaro et al. conduct a meta-analysis to discover several new loci associated with variation in eGFR and find that genes associated with eGFR loci often encode proteins potentially related to kidney development.
- Cristian Pattaro
- , Alexander Teumer
- & Caroline S. Fox
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association study identifies variation at 6q25.1 associated with survival in multiple myeloma
Genome-wide association study identifies variation at 6q25.1 associated with survival in multiple myeloma
The prognosis of multiple myeloma patients varies widely. Here, to identify genetic factors associated with differing prognoses, the authors carried out a meta-analysis of four genome-wide association studies and identified a risk variant associated with survival interval.
- David C. Johnson
- , Niels Weinhold
- & Gareth J. Morgan
-
Article
| Open Access Sequence variants in the PTCH1 gene associate with spine bone mineral density and osteoporotic fractures
Sequence variants in the PTCH1 gene associate with spine bone mineral density and osteoporotic fractures
Bone mineral density (BMD) is the best predictor of osteoporotic fracture risk. Here, the authors perform a genome wide association study in Icelanders and people of European and East-Asian descent, and identify a new allele in intron 15 of the PTCH1gene that associates with reduced BMD.
- Unnur Styrkarsdottir
- , Gudmar Thorleifsson
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Yak whole-genome resequencing reveals domestication signatures and prehistoric population expansions
Yak whole-genome resequencing reveals domestication signatures and prehistoric population expansions
Based on whole genome resequencing of more than 80 wild and domestic yaks from high-altitude Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, this study recovers demographic and genetic processes underlying the domestication of this animal. Qiu et al.also identify genes and associated pathways as candidates for selection during the domestication process.
- Qiang Qiu
- , Lizhong Wang
- & Jianquan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Patterns and functional implications of rare germline variants across 12 cancer types
Patterns and functional implications of rare germline variants across 12 cancer types
Published sequencing data sets of cancer samples could be used to identify genetic variants associated with the risk of developing cancer. Here, Luet al. analyse over 4,000 tumour-normal pairs to reveal variable frequencies of inherited susceptibilities across 12 cancer types and find enrichment of functionally validated missense variants of unknown significance.
- Charles Lu
- , Mingchao Xie
- & Li Ding
-
Article
| Open Access The genetic basis of natural variation in mushroom body size in Drosophila melanogaster
The genetic basis of natural variation in mushroom body size in Drosophila melanogaster
The mushroom bodies (MBs) in an insect brain integrate and process sensory information. Using fully sequenced/inbred lines of the Drosophila Genetic Reference Panel, this study performs genome wide association analyses and identifies candidate genes affecting MB size, and uses RNAi to functionally validate the identified loci.
- Liesbeth Zwarts
- , Lies Vanden Broeck
- & Patrick Callaerts
-
Article
| Open Access DICER1 and microRNA regulation in post-traumatic stress disorder with comorbid depression
DICER1 and microRNA regulation in post-traumatic stress disorder with comorbid depression
DICER1 is required for the maturation of miRNAs which regulate expression of thousands of genes. Here the authors show significantly reduced levels of DICER1in individuals having post-traumatic stress disorder and comorbid depression suggestive of a role in the molecular mechanism of the condition.
- Aliza P. Wingo
- , Lynn M. Almli
- & Kerry J. Ressler
-
Article
| Open Access Allelic variation contributes to bacterial host specificity
Allelic variation contributes to bacterial host specificity
One of the key aspects for controlling infectious diseases is understanding how pathogens cross host species. Here the authors conduct a genome-wide analysis of Salmonella and show a high degree of variation, enabling host-adapted colonization among Salmonellaintestinal and systemic serovars.
- Min Yue
- , Xiangan Han
- & Dieter M. Schifferli
-
Article
| Open Access MHC variation sculpts individualized microbial communities that control susceptibility to enteric infection
MHC variation sculpts individualized microbial communities that control susceptibility to enteric infection
Composition of the gut microbiota is regulated by IgA antibodies which are produced under the control of MHCII-restricted B cells. Here the authors show that MHCII polymorphisms sculpt bacterial composition of the gut, which influences a host’s susceptibility to enteric Salmonellainfection.
- Jason L. Kubinak
- , W. Zac Stephens
- & June L. Round
-
Article
| Open Access Improved imputation of low-frequency and rare variants using the UK10K haplotype reference panel
Improved imputation of low-frequency and rare variants using the UK10K haplotype reference panel
Imputation uses genotype information from SNP arrays to infer the genotypes of missing markers. Here, the authors show that an imputation reference panel derived from whole-genome sequencing of 3,781 samples from the UK10K project improves the imputation accuracy and coverage of low frequency variants compared to existing methods.
- Jie Huang
- , Bryan Howie
- & Nicole Soranzo
-
Article
| Open Access Rare variant discovery by deep whole-genome sequencing of 1,070 Japanese individuals
Rare variant discovery by deep whole-genome sequencing of 1,070 Japanese individuals
The Tohoku Medical Megabank Organization establishes a biobank with detailed patient health care and genome information. Here the authors analyse whole-genome sequences of 1,070 Japanese individuals, allowing them to catalogue 21 million single-nucleotide variants including 12 million novel ones.
- Masao Nagasaki
- , Jun Yasuda
- & Masayuki Yamamoto
-
Article
| Open Access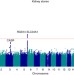 Common and rare variants associated with kidney stones and biochemical traits
Common and rare variants associated with kidney stones and biochemical traits
Kidney stone formation is influenced by genetic factors and recurrent stone formation places a significant burden on health care systems. Here Oddsson et al.perform a large-scale genome-wide association study and uncover new genetic variants associated with kidney stone susceptibility and associated biochemical traits.
- Asmundur Oddsson
- , Patrick Sulem
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Rare coding variants and X-linked loci associated with age at menarche
Rare coding variants and X-linked loci associated with age at menarche
Previous studies have linked over 100 genomic loci to age-at-menarche but that work was restricted to common autosomal variation. Here, Lunetta et al. identify associations with rare protein-coding and X-linked variants, implicating new mechanisms that regulate puberty timing.
- Kathryn L. Lunetta
- , Felix R. Day
- & John R. B. Perry
-
Article
| Open Access Clinically relevant copy number variations detected in cerebral palsy
Clinically relevant copy number variations detected in cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a heterogeneous disorder that has been historically attributed to environmental factors with genetic contributions being discovered more recently. Here the authors perform microarray-based analysis of copy number variations in a cohort of children with CP and their parents and find chromosomal abnormalities linked to the disease.
- Maryam Oskoui
- , Matthew J. Gazzellone
- & Stephen W. Scherer
-
Article
| Open Access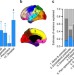 Large-scale genomics unveil polygenic architecture of human cortical surface area
Large-scale genomics unveil polygenic architecture of human cortical surface area
How genetic variation contributes to brain morphology is still poorly understood. Here Chenet al. combine brain imaging with single-nucleotide polymorphism data to discover that a substantial degree of cortical variation is derived from underlying genetic differences.
- Chi-Hua Chen
- , Qian Peng
- & Anders M. Dale
-
Article
| Open Access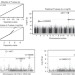 Three missense variants of metabolic syndrome-related genes are associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin levels
Three missense variants of metabolic syndrome-related genes are associated with alpha-1 antitrypsin levels
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is a common genetic disorder in Europeans. Here Setohet al. perform a genome-wide association study of AAT serum levels in a Japanese population and find three missense variants in the metabolism genes ALDH2, HNF1A and GCKR.
- Kazuya Setoh
- , Chikashi Terao
- & Fumihiko Matsuda
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide burden of deleterious coding variants increased in schizophrenia
Genome-wide burden of deleterious coding variants increased in schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a complex disorder with high heritability but poorly understood genetics. Here Olde Loohuis et al.compare schizophrenia patients to unaffected individuals and identify an increased individual burden of rare deleterious mutations in patients.
- Loes M. Olde Loohuis
- , Jacob A. S. Vorstman
- & Roel A. Ophoff
-
Article |
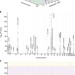 Genome-wide association study identifies novel genetic variants contributing to variation in blood metabolite levels
Genome-wide association study identifies novel genetic variants contributing to variation in blood metabolite levels
Metabolites are important indicators of the physiological state of the body and potential biomarkers for disease. Here, Draisma et al. use a genome-wide association study to identify novel single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with blood metabolite levels in genes of pharmaceutical importance.
- Harmen H. M. Draisma
- , René Pool
- & Dorret I. Boomsma
-
Article |
 Analysis of deletion breakpoints from 1,092 humans reveals details of mutation mechanisms
Analysis of deletion breakpoints from 1,092 humans reveals details of mutation mechanisms
Structural variation is a major source of complexity in the human genome. Here Abyzov et al.present the identification, classification and analysis of a large database of variants giving an insight into mechanisms generating them.
- Alexej Abyzov
- , Shantao Li
- & Mark B. Gerstein
-
Article
| Open Access Temporal regulation of kin recognition maintains recognition-cue diversity and suppresses cheating
Temporal regulation of kin recognition maintains recognition-cue diversity and suppresses cheating
It is unclear how variation in cues that enable recognition of kin and facilitate cooperation is maintained. Here, the authors show that rare variants of Dictyostelium discoideumare excluded from aggregates when the potential for social cheating is high, but subsequently rejoin the aggregate and produce spores.
- Hsing-I Ho
- & Gad Shaulsky
-
Article
| Open Access A Mendelian randomization study of the effect of type-2 diabetes on coronary heart disease
A Mendelian randomization study of the effect of type-2 diabetes on coronary heart disease
In order to effectively design interventions, it is useful to understand the complex interplay between multiple syndromes. Here, Ahmad et al. use genome-wide association study data and Mendelian randomisation to examine the influence of Type 2 diabetes and fasting glucose levels on coronary heart disease.
- Omar S. Ahmad
- , John A. Morris
- & J. Brent Richards
-
Article
| Open Access Comprehensive survey of condition-specific reproductive isolation reveals genetic incompatibility in yeast
Comprehensive survey of condition-specific reproductive isolation reveals genetic incompatibility in yeast
Chromosomal rearrangements may hamper intraspecific hybrid fertility. Here the authors show that environment-specific genetic incompatibility segregates readily within intermating populations and leads to intrinsic reproductive isolation within a yeast species.
- Jing Hou
- , Anne Friedrich
- & Joseph Schacherer
-
Article |
 Calibrating genomic and allelic coverage bias in single-cell sequencing
Calibrating genomic and allelic coverage bias in single-cell sequencing
Artifacts caused by whole-genome amplification bias are a recurrent challenge in single-cell sequencing analysis. Here, the authors develop statistical models and demonstrate an efficient strategy for controlling amplification errors by a joint analysis of single cell genomes.
- Cheng-Zhong Zhang
- , Viktor A. Adalsteinsson
- & J. Christopher Love
-
Article
| Open Access Increased prevalence of EPAS1 variant in cattle with high-altitude pulmonary hypertension
Increased prevalence of EPAS1 variant in cattle with high-altitude pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension and congestive right heart failure afflict some cattle living at high altitude in an autosomal dominant pattern, yet no responsible genes have been identified. Here Newman et al.use whole-exome sequencing to identify variants in the hypoxia inducible factor gene, EPAS1.
- John H. Newman
- , Timothy N. Holt
- & Rizwan Hamid
-
Article
| Open Access New basal cell carcinoma susceptibility loci
New basal cell carcinoma susceptibility loci
Basal cell carcinoma is a common cancer among people of European ancestry, with associated high economic costs to monitor and treat. Here Stacey et al.conduct a genome-wide association study on Icelandic and other European populations, identifying four novel loci associated with cancer susceptibility.
- Simon N. Stacey
- , Hannes Helgason
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Mammalian adaptation of influenza A(H7N9) virus is limited by a narrow genetic bottleneck
Mammalian adaptation of influenza A(H7N9) virus is limited by a narrow genetic bottleneck
H7N9 bird flu viruses cause mild disease in poultry but can occasionally infect humans with fatal consequences. Here, the authors show that viral genetic diversification is low in ferrets and high in chickens, suggesting that a genetic bottleneck limits H7N9 adaptation to mammals
- Hassan Zaraket
- , Tatiana Baranovich
- & Richard J. Webby
-
Article
| Open Access The genome-wide effects of ionizing radiation on mutation induction in the mammalian germline
The genome-wide effects of ionizing radiation on mutation induction in the mammalian germline
Ionizing radiation (IR) is an extensively studied mutagenic agent that can lead to the accumulation of extra mutations in the offspring of irradiated parents. Here the authors provide a comprehensive genome-wide survey of the consequences of IR on the mammalian germline.
- Adeolu B. Adewoye
- , Sarah J. Lindsay
- & Matthew E. Hurles
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic structure characterization of Chileans reflects historical immigration patterns
Genetic structure characterization of Chileans reflects historical immigration patterns
Chileans are genetically admixed. Here, the authors find that the average admixing time is around 10 generations ago and show the contribution of European men and Native-American women to the Chilean population.
- Susana Eyheramendy
- , Felipe I. Martinez
- & Gabriela M. Repetto
-
Article |
 Epigenetic variation in the Egfr gene generates quantitative variation in a complex trait in ants
Epigenetic variation in the Egfr gene generates quantitative variation in a complex trait in ants
Variation in complex traits is generated by the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. Here, the authors show that genome-wide DNA methylation indirectly regulates quantitative methylation of the Egfrgene to generate continuous size variation of larvae workers in the carpenter ant.
- Sebastian Alvarado
- , Rajendhran Rajakumar
- & Moshe Szyf
-
Article
| Open Access Genome of the Netherlands population-specific imputations identify an ABCA6 variant associated with cholesterol levels
Genome of the Netherlands population-specific imputations identify an ABCA6 variant associated with cholesterol levels
Frequencies of rare variants fluctuate over populations, hampering gene discovery. Here the authors use a population-specific reference panel, the Genome of the Netherlands, to discover four novel loci involved in lipid metabolism, including an exonic variant in ABCA6.
- Elisabeth M. van Leeuwen
- , Lennart C. Karssen
- & Cornelia M. van Duijn
-
Article |
 Genomic landscape of paediatric adrenocortical tumours
Genomic landscape of paediatric adrenocortical tumours
Pediatric adrenocortical carcinoma is a rare malignancy with poor prognosis. Here the authors analyse the genomes, exomes and transcriptomes of 37 such tumours and identify genetic alterations whose nature, timing and potential interactions are key events with prognostic significance in pediatric adrenocortical tumorigenesis.
- Emilia M. Pinto
- , Xiang Chen
- & Gerard P. Zambetti
-
Article
| Open Access Whole-genome sequence-based analysis of thyroid function
Whole-genome sequence-based analysis of thyroid function
Levels of circulating thyrotropin and free thyroxine reflect thyroid function, however, their genetic underpinnings remain poorly understood. Taylor et al. take advantage of whole-genome sequence data from cohorts within the UK10K project to identify novel variants associated with these traits.
- Peter N. Taylor
- , Eleonora Porcu
- & Pingbo Zhang
-
Article |
 FAAH genetic variation enhances fronto-amygdala function in mouse and human
FAAH genetic variation enhances fronto-amygdala function in mouse and human
Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) is a key regulator of endocannabinoid signalling. Here, the authors develop a knock-in mouse that recapitulates a common human mutation in the FAAH gene and demonstrate parallel neural and behavioural alterations across species, suggesting a gain-of-function in fear regulation.
- Iva Dincheva
- , Andrew T. Drysdale
- & Francis S. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Long-range epigenetic regulation is conferred by genetic variation located at thousands of independent loci
Long-range epigenetic regulation is conferred by genetic variation located at thousands of independent loci
There is a functional link between SNPs and epigenetic variations when they are in close range, but the long-range effect is unclear. Here, by analysing methylation quantitative trait loci, the authors demonstrate that methylation levels at CpG sites in lymphocytes are correlated with distal SNPs.
- Mathieu Lemire
- , Syed H.E. Zaidi
- & Thomas J. Hudson
-
Article |
 Host genetic determinants of microbiota-dependent nutrition revealed by genome-wide analysis of Drosophila melanogaster
Host genetic determinants of microbiota-dependent nutrition revealed by genome-wide analysis of Drosophila melanogaster
The gut microbiota affects animal nutrition, but it is unclear whether this effect depends on host genetic makeup. This study shows that host genotype modifies the gut microbiota’s impact on host nutrition, and identifies genetic determinants of this variation in the fruit fly.
- Adam J. Dobson
- , John M. Chaston
- & Angela E. Douglas
-
Article |
 Coordinated regulatory variation associated with gestational hyperglycaemia regulates expression of the novel hexokinase HKDC1
Coordinated regulatory variation associated with gestational hyperglycaemia regulates expression of the novel hexokinase HKDC1
Maternal glucose levels during pregnancy can affect the metabolic health of a developing fetus, both early on and later in life. Here, the authors reveal that genetic variants in several regulatory elements alter glucose homeostasis during pregnancy by reducing the expression of a novel hexokinase gene, HKDC1.
- Cong Guo
- , Anton E. Ludvik
- & Timothy E. Reddy
-
Article
| Open Access Low-frequency and rare exome chip variants associate with fasting glucose and type 2 diabetes susceptibility
Low-frequency and rare exome chip variants associate with fasting glucose and type 2 diabetes susceptibility
Both rare and common variants contribute to the aetiology of complex traits such as type 2 diabetes (T2D). Here, the authors examine the effect of coding variation on glycaemic traits and T2D, and identify low-frequency variation in GLP1Rsignificantly associated with these traits.
- Jennifer Wessel
- , Audrey Y Chu
- & Mark O Goodarzi
-
Article |
 Intratumoral genome diversity parallels progression and predicts outcome in pediatric cancer
Intratumoral genome diversity parallels progression and predicts outcome in pediatric cancer
Phenotypic and genetic heterogeneity of cells within a tumour is thought to mediate treatment resistance and contribute to cancer progression. Here the authors show that genetic diversity in pediatric cancers is common after chemotherapy and can be quantified to predict survival.
- Linda Holmquist Mengelbier
- , Jenny Karlsson
- & David Gisselsson
-
Article
| Open Access Novel variation and de novo mutation rates in population-wide de novo assembled Danish trios
Novel variation and de novo mutation rates in population-wide de novo assembled Danish trios
The generation of a national pan-genome, a population-specific catalogue of genetic variation, may advance the impact of clinical genetics studies. Here the Besenbacher et al. carry out deep sequencing and de novo assembly of 10 parent–child trios to generate a Danish pan-genome that provides insight into structural variation, de novomutation rates and variant calling.
- Søren Besenbacher
- , Siyang Liu
- & Simon Rasmussen

 Identifying genetically driven clinical phenotypes using linear mixed models
Identifying genetically driven clinical phenotypes using linear mixed models