Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Label-free imaging for quality control of cardiomyocyte differentiation
Label-free imaging for quality control of cardiomyocyte differentiation
Differentiation of hPSCs to cardiomyocytes suffers from high variability. Here the authors report a label-free live cell imaging platform based on autofluorescence imaging to enable the prediction of cardiomyocyte differentiation efficiency from hPSCs.
- Tongcheng Qian
- , Tiffany M. Heaster
- & Melissa C. Skala
-
Article
| Open Access Post-capillary venules are the key locus for transcytosis-mediated brain delivery of therapeutic nanoparticles
Post-capillary venules are the key locus for transcytosis-mediated brain delivery of therapeutic nanoparticles
Limited understanding of the interactions between nanoparticle drug carriers and the blood-brain barrier underlies many translational failures in treatments of brain disorders. Here the authors use two-photon microscopy in mice to characterize the receptor-mediated transcytosis of nanoparticles at all steps of delivery from the blood to the brain in vivo.
- Krzysztof Kucharz
- , Kasper Kristensen
- & Martin Johannes Lauritzen
-
Article
| Open Access Detecting structural heterogeneity in single-molecule localization microscopy data
Detecting structural heterogeneity in single-molecule localization microscopy data
Particle fusion can improve signal-to-noise ratio in single molecule localization microscopy, but is limited by structural heterogeneity. Here, the authors demonstrate an unsupervised classification method that differentiates structurally different DNA origami structures without prior knowledge.
- Teun A.P.M. Huijben
- , Hamidreza Heydarian
- & Bernd Rieger
-
Article
| Open Access In silico voltage-sensitive dye imaging reveals the emergent dynamics of cortical populations
In silico voltage-sensitive dye imaging reveals the emergent dynamics of cortical populations
Voltage-sensitive dye imaging (VSDI) is a powerful technique for measuring membrane potential dynamics of neurons but the effective resolution is limited. Here, the authors developed an in silico model of VSDI to probe activity in a biologically detailed reconstruction of rodent neocortical microcircuits.
- Taylor H. Newton
- , Michael W. Reimann
- & Henry Markram
-
Article
| Open Access Robust adaptive optics for localization microscopy deep in complex tissue
Robust adaptive optics for localization microscopy deep in complex tissue
It is difficult to apply SMLM to complex biological tissues. Here the authors report REALM, Robust and Effective Adaptive Optics in Localisation Microscopy, to improve SMLM in tissue and use this to resolve the organisation of spectrin in the axon initial segment in brain tissue.
- Marijn E. Siemons
- , Naomi A. K. Hanemaaijer
- & Lukas C. Kapitein
-
Article
| Open Access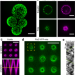 FtsZ induces membrane deformations via torsional stress upon GTP hydrolysis
FtsZ induces membrane deformations via torsional stress upon GTP hydrolysis
During bacterial cell division, the protein FtsZ is the main component of the contractile ring, though how precisely FtsZ treadmilling and its ability to deform membranes cooperate are unclear. Here, the authors show that dynamic FtsZ may deform lipid membranes via torsional stress that may provide sufficient force to constrict membranes in vivo and in vitro.
- Diego A. Ramirez-Diaz
- , Adrián Merino-Salomón
- & Petra Schwille
-
Article
| Open Access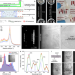 Cellular lensing and near infrared fluorescent nanosensor arrays to enable chemical efflux cytometry
Cellular lensing and near infrared fluorescent nanosensor arrays to enable chemical efflux cytometry
The authors present nanosensor chemical cytometry, based on an array of nIR fluorescent single walled carbon nanotube integrated along a microfluidic channel. The lensing effect of the flowing cells allows for extracting information, and correlating biomolecular information with physical properties.
- Soo-Yeon Cho
- , Xun Gong
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Article
| Open Access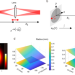 Wide field light-sheet microscopy with lens-axicon controlled two-photon Bessel beam illumination
Wide field light-sheet microscopy with lens-axicon controlled two-photon Bessel beam illumination
Here, the authors present a two-photon light-sheet microscopy with an extended Bessel beam for a tunable field of view and reduced photodamage. They demonstrate long-term imaging of cellular dynamics over the whole body of medaka fish.
- Sota Takanezawa
- , Takashi Saitou
- & Takeshi Imamura
-
Article
| Open Access N-aryl pyrido cyanine derivatives are nuclear and organelle DNA markers for two-photon and super-resolution imaging
N-aryl pyrido cyanine derivatives are nuclear and organelle DNA markers for two-photon and super-resolution imaging
It is challenging to develop DNA probes that allow staining of both organelle and nuclear DNA, are compatible with super resolution imaging and avoid UV-light photo-excitation. The authors overcome these issues with N-aryl pyrido cyanine derivatives showing high DNA specificity and membrane permeability.
- Kakishi Uno
- , Nagisa Sugimoto
- & Yoshikatsu Sato
-
Article
| Open Access Quantification of FRET-induced angular displacement by monitoring sensitized acceptor anisotropy using a dim fluorescent donor
Quantification of FRET-induced angular displacement by monitoring sensitized acceptor anisotropy using a dim fluorescent donor
The FRET efficiency usually predominantly depends on the proximity of donor and acceptor. Here the authors report an anisotropy-based mode of FRET detection, FRET-induced Angular Displacement Evaluation via Dim donor (FADED), to allow quantification of the relative angle between donor and acceptor.
- Danai Laskaratou
- , Guillermo Solís Fernández
- & Hideaki Mizuno
-
Article
| Open Access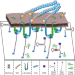 Super-resolved visualization of single DNA-based tension sensors in cell adhesion
Super-resolved visualization of single DNA-based tension sensors in cell adhesion
Relatively little is known about cell-matrix interactions and the intracellular transduction of an initial ligand-receptor binding event on the single-molecule level. Here authors combine ligand-decorated DNA tension sensors with DNA-PAINT super-resolution microscopy to study the mechanical engagement of single integrin receptors and the downstream influence on actin bundling.
- Thomas Schlichthaerle
- , Caroline Lindner
- & Ralf Jungmann
-
Article
| Open Access J-aggregates of meso-[2.2]paracyclophanyl-BODIPY dye for NIR-II imaging
J-aggregates of meso-[2.2]paracyclophanyl-BODIPY dye for NIR-II imaging
J-aggregation has been proved to be an efficient strategy for the development of fluorescent imaging agents in the NIR-II spectral region but the design of appropriate J-aggregates is challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate J-aggregation of a BODIPY dye with NIR-II emission and demonstrate lymph node imaging for fluorescence guided surgery.
- Kang Li
- , Xingchen Duan
- & Zhipeng Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional TIRF-SIM–traction force microscopy (2D TIRF-SIM-TFM)
Two-dimensional TIRF-SIM–traction force microscopy (2D TIRF-SIM-TFM)
Quantifying rapid and small cellular forces is a major challenge in mechanobiology. Here, the authors show a >2-fold spatially and >10-fold temporally force sampling improvement combining traction force microscopy with total internal reflection fluorescence super-resolution structured illumination microscopy.
- Liliana Barbieri
- , Huw Colin-York
- & Marco Fritzsche
-
Article
| Open Access Astigmatic traction force microscopy (aTFM)
Astigmatic traction force microscopy (aTFM)
Quantifying rapidly progressing three-dimensional forces generated by cells remains a major challenge in mechanobiology. Here, the authors show that combining traction force microscopy with astigmatic imaging permits sensitive out-of-plane force estimation on the second timescale.
- Di Li
- , Huw Colin-York
- & Marco Fritzsche
-
Article
| Open Access SLPI is a critical mediator that controls PTH-induced bone formation
SLPI is a critical mediator that controls PTH-induced bone formation
The mechanism by which parathyroid hormone mediates the switch from bone resorption to bone formation is unclear. Here, the authors show that SLPI regulates the communication between osteoblasts and osteoclasts to promote the anabolic effect of parathyroid hormone.
- Akito Morimoto
- , Junichi Kikuta
- & Masaru Ishii
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous readout of multiple FRET pairs using photochromism
Simultaneous readout of multiple FRET pairs using photochromism
Performing multiple FRET measurements at once can be challenging. Here the authors report a method to discriminate between overlapping FRET pairs, even if the fluorophores display almost identical absorption and emission spectra, based on the photochromism of the donor fluorophores.
- Thijs Roebroek
- , Wim Vandenberg
- & Peter Dedecker
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing 3D structure of gluten in wheat dough by optical clearing imaging
Revealing 3D structure of gluten in wheat dough by optical clearing imaging
Gluten is a crucial quality determinant of wheat-based food products, however, its structure remains unknown due to the lack of imaging techniques. Here, the authors report the 3D structure of gluten in millimeter scale and at submicron resolution by combining an optical clearing reagent with two-photon microscopy.
- Takenobu Ogawa
- & Yasuki Matsumura
-
Article
| Open Access Whole-brain tissue mapping toolkit using large-scale highly multiplexed immunofluorescence imaging and deep neural networks
Whole-brain tissue mapping toolkit using large-scale highly multiplexed immunofluorescence imaging and deep neural networks
It is challenging to map complex processes in brain tissue. Here the authors report a toolkit enabling large-scale multiplexed IHC and automated cell classification whereby they use a conventional epifluorescence microscope and deep neural networks to phenotype all major cell classes of the brain.
- Dragan Maric
- , Jahandar Jahanipour
- & Badrinath Roysam
-
Article
| Open Access Metamaterial assisted illumination nanoscopy via random super-resolution speckles
Metamaterial assisted illumination nanoscopy via random super-resolution speckles
Structured illumination microscopy is usually limited to 2 times spatial resolution improvement over the diffraction limit. Here, the authors introduce a metamaterial structure to generate speckle-like sub-diffraction limit illumination patterns in the near field, and achieve a 7-fold resolution improvement down to 40 nm.
- Yeon Ui Lee
- , Junxiang Zhao
- & Zhaowei Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Kinesin-1 activity recorded in living cells with a precipitating dye
Kinesin-1 activity recorded in living cells with a precipitating dye
Monitoring the activity of the processive motor protein kinesin-1 in live cells is currently difficult. Here the authors report the fluorogenic small molecule QPD-OTf, a kinesin-1 substrate that causes activity-dependent dye precipitation.
- Simona Angerani
- , Eric Lindberg
- & Nicolas Winssinger
-
Article
| Open Access MINFLUX nanometer-scale 3D imaging and microsecond-range tracking on a common fluorescence microscope
MINFLUX nanometer-scale 3D imaging and microsecond-range tracking on a common fluorescence microscope
Minimal photon fluxes (MINFLUX) has enabled molecule-scale resolution in fluorescence microscopy but this had not been shown in standard, broadly applicable microscopy platforms. Here the authors report a solution to allow normal fluorescence microscopy while also providing 1-3 nm 3D resolution.
- Roman Schmidt
- , Tobias Weihs
- & Stefan W. Hell
-
Article
| Open Access pHmScarlet is a pH-sensitive red fluorescent protein to monitor exocytosis docking and fusion steps
pHmScarlet is a pH-sensitive red fluorescent protein to monitor exocytosis docking and fusion steps
A number of pH-sensitive fluorescent proteins exist which enable monitoring of some but not all steps of exocytosis. Here the authors engineer a bright, photostable red pH-sensitive fluorescent protein, pHmScarlet, to allow visualisation of the docking and fusion events of exocytosis.
- Anyuan Liu
- , Xiaoshuai Huang
- & Pingyong Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional total-internal reflection fluorescence nanoscopy with nanometric axial resolution by photometric localization of single molecules
Three-dimensional total-internal reflection fluorescence nanoscopy with nanometric axial resolution by photometric localization of single molecules
Achieving high axial resolution is challenging in single-molecule localization microscopy. Here, the authors present a photometric method to decode the axial position of single molecules in a total internal reflection fluorescence microscope without hardware modification, and show nearly isotropic nanometric resolution.
- Alan M. Szalai
- , Bruno Siarry
- & Fernando D. Stefani
-
Article
| Open Access Repeat DNA-PAINT suppresses background and non-specific signals in optical nanoscopy
Repeat DNA-PAINT suppresses background and non-specific signals in optical nanoscopy
DNA-PAINT is a super-resolution imaging technique which suffers from high background signals and non-specific binding. Here the authors report Repeat DNA-PAINT which is capable of supressing background noise and preventing photoinduced site loss, as well as decreasing the time taken for the sampling process.
- Alexander H. Clowsley
- , William T. Kaufhold
- & Christian Soeller
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging dynamic mTORC1 pathway activity in vivo reveals marked shifts that support time-specific inhibitor therapy in AML
Imaging dynamic mTORC1 pathway activity in vivo reveals marked shifts that support time-specific inhibitor therapy in AML
The role of mTORC1 in AML has not yet been proven due to the mixed results of its inhibitors in clinical trials. Here the authors show the real-time dynamics of the mTORC1 pathway in association with AML growth and response to chemotherapy with fluorescent markers, providing guidance for timed intervention with pathway-specific inhibitors.
- Toshihiko Oki
- , Francois Mercier
- & David T. Scadden
-
Article
| Open Access Minutes-timescale 3D isotropic imaging of entire organs at subcellular resolution by content-aware compressed-sensing light-sheet microscopy
Minutes-timescale 3D isotropic imaging of entire organs at subcellular resolution by content-aware compressed-sensing light-sheet microscopy
High resolution imaging of large biological volumes typically takes a long time from hours to days. Here the authors use a Bessel light-sheet approach combined with a content-aware compressed sensing computational pipeline to image whole mouse organs at subcellular resolution in a few minutes.
- Chunyu Fang
- , Tingting Yu
- & Peng Fei
-
Article
| Open Access A dual-labeling probe to track functional mitochondria–lysosome interactions in live cells
A dual-labeling probe to track functional mitochondria–lysosome interactions in live cells
Dynamic labeling and tracking of organelle–organelle contacts is essential to understand the formation and function of these interactions. Here the authors present a small molecule probe, Coupa, that labels mitochondria and lysosomes with blue and red fluorescence, respectively.
- Qixin Chen
- , Hongbao Fang
- & Jiajie Diao
-
Article
| Open Access Non-invasive single-cell morphometry in living bacterial biofilms
Non-invasive single-cell morphometry in living bacterial biofilms
Accurate cell detection in dense bacterial biofilms is challenging. Here, the authors report an image analysis pipeline that is able to accurately segment and classify single bacterial cells in 3D fluorescence images: Bacterial Cell Morphometry 3D (BCM3D).
- Mingxing Zhang
- , Ji Zhang
- & Andreas Gahlmann
-
Article
| Open Access High-dimensional super-resolution imaging reveals heterogeneity and dynamics of subcellular lipid membranes
High-dimensional super-resolution imaging reveals heterogeneity and dynamics of subcellular lipid membranes
Lipid membranes are heterogeneous and dynamically regulated in cells. Here the authors report a Spectrum and Polarisation Optical Tomography (SPOT) method where they use Nile Red dye to resolve membrane morphology, polarity and phase in cells.
- Karl Zhanghao
- , Wenhui Liu
- & Dayong Jin
-
Article
| Open Access BrainPhys neuronal medium optimized for imaging and optogenetics in vitro
BrainPhys neuronal medium optimized for imaging and optogenetics in vitro
Current media for neuronal cell and organoid cultures are suboptimal for functional imaging and optogenetics experiments, owing to phototoxicity and unphysiological performance. Here the authors formulate an optimised neuronal medium to support live cell imaging and electrophysiological activity.
- Michael Zabolocki
- , Kasandra McCormack
- & Cedric Bardy
-
Article
| Open Access Unscrambling fluorophore blinking for comprehensive cluster detection via photoactivated localization microscopy
Unscrambling fluorophore blinking for comprehensive cluster detection via photoactivated localization microscopy
Determining molecular clustering in Photoactivated Localization Microscopy (PALM) experiments requires knowledge of the blinking properties of the fluorophore to prevent overcounting artefacts. Here the authors develop an experimental and analytical framework to determine the blinking parameters of fluorophores and incorporate this information into cluster analysis.
- René Platzer
- , Benedikt K. Rossboth
- & Mario Brameshuber
-
Article
| Open Access Concerted localization-resets precede YAP-dependent transcription
Concerted localization-resets precede YAP-dependent transcription
The transcriptional regulator YAP shuttles rapidly between the cytoplasm and nucleus, but whether and how dynamics such as amplitude and frequency affect target gene transcription is unclear. Here, using live imaging of endogenous YAP and target-gene transcription, the authors show that YAP-dependent signalling is encoded through rapid and concerted changes in the nucleo-cytoplasmic distribution of YAP.
- J. Matthew Franklin
- , Rajarshi P. Ghosh
- & Jan T. Liphardt
-
Article
| Open Access NIR-II bioluminescence for in vivo high contrast imaging and in situ ATP-mediated metastases tracing
NIR-II bioluminescence for in vivo high contrast imaging and in situ ATP-mediated metastases tracing
Conventional bioluminescence imaging usually operates in the visible region and its performance is limited by strong tissue absorption and scattering. Here, the authors present bioluminescence probes (BPs) with emission in the second near infrared (NIR-II) region, and show the NIR-II-BPs could sensitively recognize tumor metastasis with a high tumor-to-normal tissue ratio.
- Lingfei Lu
- , Benhao Li
- & Fan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Turn-on chemiluminescence probes and dual-amplification of signal for detection of amyloid beta species in vivo
Turn-on chemiluminescence probes and dual-amplification of signal for detection of amyloid beta species in vivo
Detection of amyloid beta deposits is often performed with fluorescent compounds that bind plaques. Here the authors develop turn-on chemiluminescent probes that bind amyloid beta plaques in vivo, and amplify the signal via chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer to the plaque-binding fluorescent molecule CRANAD-3.
- Jing Yang
- , Wei Yin
- & Chongzhao Ran
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed Optical Sensors in Arrayed Islands of Cells for multimodal recordings of cellular physiology
Multiplexed Optical Sensors in Arrayed Islands of Cells for multimodal recordings of cellular physiology
Existing fluorescent protein-based sensor measurements are limited to 4 or fewer simultaneously recorded modalities due to spectral overlap. Here the authors introduce Multiplexed Optical Sensors in Arrayed Islands of Cells (MOSAIC), which enables parallel recording of tens of physiological parameters using dense arrays of cell islands, each expressing a different fluorescent sensor.
- Christopher A. Werley
- , Stefano Boccardo
- & Adam E. Cohen
-
Article
| Open Access Light microscopy of proteins in their ultrastructural context
Light microscopy of proteins in their ultrastructural context
Imaging specific proteins in the ultrastructural context largely relies on correlative light/electron microscopy, but fluorophore incompatibility and registration issues limit its use. Here the authors develop an expansion microscopy method with pan-labeling of the proteome to obtain EM-equivalent light microscopy images.
- Ons M’Saad
- & Joerg Bewersdorf
-
Article
| Open Access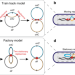 Direct observation of independently moving replisomes in Escherichia coli
Direct observation of independently moving replisomes in Escherichia coli
How chromosome replication and segregation is organised in E. coli is a matter of debate. Here the authors visualise the bacterial chromosome and the replisomes during DNA replication, providing support for a previously suggested train track model.
- Aleksandre Japaridze
- , Christos Gogou
- & Cees Dekker
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral cross-cumulants for multicolor super-resolved SOFI imaging
Spectral cross-cumulants for multicolor super-resolved SOFI imaging
Here, the authors generalize cumulant analysis by extending it into the spectral domain to allow multicolour super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging. The simultaneous acquisition of two spectral channels followed by spectral cross-cumulant analysis and unmixing allows denser spectral and spatial sampling of the super-resolved image.
- K. S. Grußmayer
- , S. Geissbuehler
- & T. Lasser
-
Article
| Open Access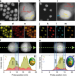 Ultrafast photochemistry produces superbright short-wave infrared dots for low-dose in vivo imaging
Ultrafast photochemistry produces superbright short-wave infrared dots for low-dose in vivo imaging
Deep tissue imaging has been limited by the low brightness of probes emitting in the second near-infrared window. Here, the authors use femtosecond laser irradiation to grow a protective shell on Ag2S nanoparticles, achieving 80-fold quantum yield enhancement and imaging with low excitation intensities.
- Harrisson D. A. Santos
- , Irene Zabala Gutiérrez
- & Daniel Jaque
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed imaging of nucleome architectures in single cells of mammalian tissue
Multiplexed imaging of nucleome architectures in single cells of mammalian tissue
The three-dimensional architecture of the genome affects genomic functions. Here, the authors developed Multiplexed Imaging of Nucleome Architectures to measure multiscale chromatin folding, RNA profiles, and associations of numerous genomic regions with nuclear lamina and nucleoli in the same, single cells in heterogeneous tissue.
- Miao Liu
- , Yanfang Lu
- & Siyuan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Plasma-derived extracellular vesicles from Plasmodium vivax patients signal spleen fibroblasts via NF-kB facilitating parasite cytoadherence
Plasma-derived extracellular vesicles from Plasmodium vivax patients signal spleen fibroblasts via NF-kB facilitating parasite cytoadherence
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) in plasma can affect pathogenesis of parasites, but details remain unclear. Here, Toda et al. characterize plasma-derived EVs from Plasmodium vivax patients and show that PvEVs are preferentially taken up by human spleen fibroblasts, facilitating parasite cytoadherence.
- Haruka Toda
- , Miriam Diaz-Varela
- & Hernando A. del Portillo
-
Article
| Open Access Encoding quantized fluorescence states with fractal DNA frameworks
Encoding quantized fluorescence states with fractal DNA frameworks
Though DNA framework-based scaffolds for biomolecular assembly are attractive for bioimaging applications, realizing super-multiplex fluorescent amplifiers remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a topological engineering approach to designing fractal DNA frameworks for multiplexed amplifiers.
- Jiang Li
- , Jiangbing Dai
- & Chunhai Fan
-
Article
| Open Access A live cell reporter of exosome secretion and uptake reveals pathfinding behavior of migrating cells
A live cell reporter of exosome secretion and uptake reveals pathfinding behavior of migrating cells
A prior live-cell exosome reporter showed dim fluorescence and could not be expressed stably, limiting its usefulness. Here the authors stabilise the reporter to allow long-term tracking of exosomes, and incorporate a second fluorophore to visualise the entire exosome lifecycle.
- Bong Hwan Sung
- , Ariana von Lersner
- & Alissa M. Weaver
-
Article
| Open Access Versatile whole-organ/body staining and imaging based on electrolyte-gel properties of biological tissues
Versatile whole-organ/body staining and imaging based on electrolyte-gel properties of biological tissues
Tissue clearing has revolutionised histology, but limited penetration of antibodies and stains into thick tissue segments is still a bottleneck. Here, the authors characterise optically cleared tissue as an electrolyte gel and apply this knowledge to stain the entirety of thick tissue samples.
- Etsuo A. Susaki
- , Chika Shimizu
- & Hiroki R. Ueda
-
Article
| Open Access Paracrine control of α-cell glucagon exocytosis is compromised in human type-2 diabetes
Paracrine control of α-cell glucagon exocytosis is compromised in human type-2 diabetes
Glucagon is elevated Type-2 diabetes, which contributes to poor glucose control in patients with the disease. Here the authors report that secretion of the hormone is controlled by paracrine inhibition, and that resistance of α-cells to somatostatin can explain hyperglucagonemia in type-2 diabetes.
- Muhmmad Omar-Hmeadi
- , Per-Eric Lund
- & Sebastian Barg
-
Article
| Open Access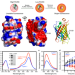 A rationally enhanced red fluorescent protein expands the utility of FRET biosensors
A rationally enhanced red fluorescent protein expands the utility of FRET biosensors
TagRFP is a bright red fluorescent protein, but undergoes photoconversion to a dark state, making it undesirable for conventional fluorescence microscopy. Here, the authors introduce stabilising mutations to create super-TagRFP (stagRFP) and demonstrate its application as both a FRET acceptor and FRET donor.
- Gary C. H. Mo
- , Clara Posner
- & Jin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access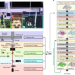 Automated highly multiplexed super-resolution imaging of protein nano-architecture in cells and tissues
Automated highly multiplexed super-resolution imaging of protein nano-architecture in cells and tissues
Super-resolution imaging of multiple target proteins in the same sample can provide important information of cellular nanostructure, but has not been routinely achieved. Here, the authors present a fully automated 3D STORM approach using a re-staining protocol to image 15 targets in single cells and 16 targets in neuronal tissue.
- Maja Klevanski
- , Frank Herrmannsdoerfer
- & Thomas Kuner
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning for cluster analysis of localization microscopy data
Machine learning for cluster analysis of localization microscopy data
The characterization of clusters in single-molecule microscopy data is vital to reconstruct emerging spatial patterns. Here, the authors present a fast and accurate machine-learning approach to clustering, to address the issues related to the size of the data and to sample heterogeneity.
- David J. Williamson
- , Garth L. Burn
- & Dylan M. Owen
-
Article
| Open Access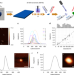 Exfoliated near infrared fluorescent silicate nanosheets for (bio)photonics
Exfoliated near infrared fluorescent silicate nanosheets for (bio)photonics
Near-infrared (NIR) fluorophores have attracted interest for bioimaging; yet availability, biocompatibility and application can be an issue. Here, the authors report on the development of Egyptian Blue nanosheets with high NIR fluorescence and photostability demonstrating bioimaging applications in vivo.
- Gabriele Selvaggio
- , Alexey Chizhik
- & Sebastian Kruss

 Quantifying nanodiamonds biodistribution in whole cells with correlative iono-nanoscopy
Quantifying nanodiamonds biodistribution in whole cells with correlative iono-nanoscopy