Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
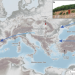 East-to-west human dispersal into Europe 1.4 million years ago
East-to-west human dispersal into Europe 1.4 million years ago
Burial-dating methods using cosmogenic nuclides indicate that the oldest stone tools at Korolevo archaeological site in western Ukraine date to around 1.4 million years ago, providing evidence of early human dispersal into Europe from the east.
- R. Garba
- , V. Usyk
- & J. D. Jansen
-
Article
| Open Access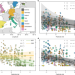 Pesticide use negatively affects bumble bees across European landscapes
Pesticide use negatively affects bumble bees across European landscapes
Results from 316 Bombus terrestris colonies at 106 agricultural sites across eight European countries find pesticides in bumble bee pollen to be associated with reduced colony performance, especially in areas of intensive agriculture.
- Charlie C. Nicholson
- , Jessica Knapp
- & Maj Rundlöf
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term organic carbon preservation enhanced by iron and manganese
Long-term organic carbon preservation enhanced by iron and manganese
Catalysis of simple organic carbon molecules into complex macromolecules by Fe and Mn may play a fundamental role in organic carbon preservation, to a degree that could substantially affect the Earth’s carbon and oxygen cycles.
- Oliver W. Moore
- , Lisa Curti
- & Caroline L. Peacock
-
Perspective |
 Lead immobilization for environmentally sustainable perovskite solar cells
Lead immobilization for environmentally sustainable perovskite solar cells
An analysis of chemical processes to immobilize lead from perovskite solar cells is presented, highlighting the need for a standard lead-leakage test and mathematical model to reliably evaluate the potential environmental risk of perovskite optoelectronics.
- Hui Zhang
- , Jin-Wook Lee
- & Nam-Gyu Park
-
Article |
 Chlorine activation and enhanced ozone depletion induced by wildfire aerosol
Chlorine activation and enhanced ozone depletion induced by wildfire aerosol
Comparison of model simulations with atmospheric observations from the Southern Hemisphere mid-latitudes following the 2020 Australian wildfires shows that the wildfire aerosol composition promotes stratospheric chlorine and ozone depletion chemistry.
- Susan Solomon
- , Kane Stone
- & Peidong Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Arctic Ocean annual high in \({{\boldsymbol{p}}}_{{{\bf{CO}}}_{{\bf{2}}}}\) could shift from winter to summer
Arctic Ocean annual high in \({{\boldsymbol{p}}}_{{{\bf{CO}}}_{{\bf{2}}}}\) could shift from winter to summer
Simulations suggest that the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the Arctic Ocean will shift from a winter to a summer maximum owing to enhanced summer sea surface warming from earlier sea-ice retreat.
- James C. Orr
- , Lester Kwiatkowski
- & Hans-Otto Pörtner
-
Article |
 Continuous air purification by aqueous interface filtration and absorption
Continuous air purification by aqueous interface filtration and absorption
An air purification strategy is presented that moves air in the form of bubbles through an ion-doped conjugated polymer-coated matrix, which captures larger particulate matter, infiltrated with a selected functional liquid, which captures smaller particulate matter.
- Yunmao Zhang
- , Yuhang Han
- & Xu Hou
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral monoterpenes reveal forest emission mechanisms and drought responses
Chiral monoterpenes reveal forest emission mechanisms and drought responses
Analysis of atmospheric data on two enantiomerically separated forms of monoterpene from a controlled drought and rewetting experiment in an enclosed tropical rainforest ecosystem showed distinct diel emission peaks, regulated by different production pathways.
- Joseph Byron
- , Juergen Kreuzwieser
- & Jonathan Williams
-
Article |
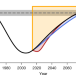 Integrated ozone depletion as a metric for ozone recovery
Integrated ozone depletion as a metric for ozone recovery
An integrated ozone depletion metric indicates the impact of any new emission and provides a useful complementary metric of the impact of specific emissions of an ozone depleting substance for both the scientific and policy communities.
- John A. Pyle
- , James Keeble
- & Paul T. Griffiths
-
Article |
 Pulsed hydraulic-pressure-responsive self-cleaning membrane
Pulsed hydraulic-pressure-responsive self-cleaning membrane
The PiezoMem membrane responsive to hydraulic pressure is introduced, showing the ability to convert pressure pulses into electroactive responses for in situ self-cleaning and enabling broad-spectrum antifouling action towards a range of membrane foulants.
- Yang Zhao
- , Yuna Gu
- & Guandao Gao
-
Article
| Open Access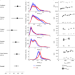 Enhanced silica export in a future ocean triggers global diatom decline
Enhanced silica export in a future ocean triggers global diatom decline
Mesocosm experiments in different biomes show that future ocean acidification will slow down the dissolution of biogenic silica, decreasing silicic acid availability in the surface ocean and triggering a global decline of diatoms as revealed by Earth system model simulations.
- Jan Taucher
- , Lennart T. Bach
- & Ulf Riebesell
-
Article
| Open Access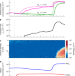 Synergistic HNO3–H2SO4–NH3 upper tropospheric particle formation
Synergistic HNO3–H2SO4–NH3 upper tropospheric particle formation
By performing experiments under upper tropospheric conditions, nitric acid, sulfuric acid and ammonia can form particles synergistically, at rates orders of magnitude faster than any two of the three components.
- Mingyi Wang
- , Mao Xiao
- & Neil M. Donahue
-
Article |
 A solid-state electrolysis process for upcycling aluminium scrap
A solid-state electrolysis process for upcycling aluminium scrap
A solid-state electrochemical scheme is demonstrated that shows promise for upcycling aluminium scrap metal.
- Xin Lu
- , Zhengyang Zhang
- & Tetsuya Nagasaka
-
Article
| Open Access Global fine-scale changes in ambient NO2 during COVID-19 lockdowns
Global fine-scale changes in ambient NO2 during COVID-19 lockdowns
The satellite instrument TROPOMI is used to assess ambient NO2 levels at approximately one-kilometre resolution across 215 cities worldwide during COVID-19 lockdowns, finding about 30% lower NO2 concentrations in countries with strict lockdowns.
- Matthew J. Cooper
- , Randall V. Martin
- & Chris A. McLinden
-
Article |
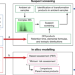 Uncovering global-scale risks from commercial chemicals in air
Uncovering global-scale risks from commercial chemicals in air
A new framework is proposed for assessing the risks of the atmospheric transformation products of commercial chemicals, combining laboratory and field experiments, advanced techniques for screening suspect chemicals, and in silico modelling.
- Qifan Liu
- , Li Li
- & John Liggio
-
Article |
 Direct radiative effects of airborne microplastics
Direct radiative effects of airborne microplastics
Preliminary modelling of airborne microplastics suggests that they may be exerting a minor cooling influence on the present-day atmosphere, and continued production could have increasing effects on the climate system in future.
- Laura E. Revell
- , Peter Kuma
- & Sally Gaw
-
Article |
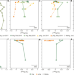 Mercury stable isotopes constrain atmospheric sources to the ocean
Mercury stable isotopes constrain atmospheric sources to the ocean
Mercury deposition pathways from the atmosphere to the ocean remain uncertain, but mercury stable isotope measurements from the Atlantic and Mediterranean show that ocean uptake of gaseous elemental mercury is more important than previously thought.
- Martin Jiskra
- , Lars-Eric Heimbürger-Boavida
- & Jeroen E. Sonke
-
Article
| Open Access The nutritional quality of cereals varies geospatially in Ethiopia and Malawi
The nutritional quality of cereals varies geospatially in Ethiopia and Malawi
Geospatial variation in the micronutrient composition (calcium, iron, selenium and zinc) of staple cereal grains is nutritionally important at subnational scales in Ethiopia and Malawi; these data could be used to improve surveillance of micronutrient deficiencies in the region.
- D. Gashu
- , P. C. Nalivata
- & M. R. Broadley
-
Article
| Open Access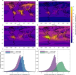 Ubiquitous atmospheric production of organic acids mediated by cloud droplets
Ubiquitous atmospheric production of organic acids mediated by cloud droplets
The oxidation of hydrated formaldehyde from cloud droplets is the dominant source of atmospheric formic acid, increasing atmospheric acidity by reducing cloud and rainwater pH.
- B. Franco
- , T. Blumenstock
- & D. Taraborrelli
-
Article |
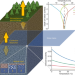 Widespread six degrees Celsius cooling on land during the Last Glacial Maximum
Widespread six degrees Celsius cooling on land during the Last Glacial Maximum
Analyses and modelling of noble gases in groundwater show that the mean annual surface temperatures of low-altitude, low-to-mid-latitude land masses were about 6 °C cooler during the Last Glacial Maximum than during the Late Holocene.
- Alan M. Seltzer
- , Jessica Ng
- & Martin Stute
-
Article |
 Sources of particulate-matter air pollution and its oxidative potential in Europe
Sources of particulate-matter air pollution and its oxidative potential in Europe
Observations and air-quality modelling reveal that the sources of particulate matter and oxidative potential in Europe are different, implying that reducing mass concentrations of particulate matter alone may not reduce oxidative potential.
- Kaspar R. Daellenbach
- , Gaëlle Uzu
- & André S. H. Prévôt
-
Article |
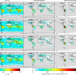 Satellite isoprene retrievals constrain emissions and atmospheric oxidation
Satellite isoprene retrievals constrain emissions and atmospheric oxidation
Direct satellite measurements of atmospheric isoprene are compared with model predictions, showing broad agreement but highlighting spatial and temporal biases in modelled isoprene and nitrogen oxide emissions.
- Kelley C. Wells
- , Dylan B. Millet
- & Jose D. Fuentes
-
Article |
 Preindustrial 14CH4 indicates greater anthropogenic fossil CH4 emissions
Preindustrial 14CH4 indicates greater anthropogenic fossil CH4 emissions
Isotopic evidence from ice cores indicates that preindustrial-era geological methane emissions were lower than previously thought, suggesting that present-day emissions of methane from fossil fuels are underestimated.
- Benjamin Hmiel
- , V. V. Petrenko
- & E. Dlugokencky
-
Article |
 Premature mortality related to United States cross-state air pollution
Premature mortality related to United States cross-state air pollution
This analysis of the exchange of air pollution amongst the contiguous United States finds that, on average, around half of the early deaths caused by a state’s air pollution occurs outside that state, with different contributions by different emission sectors and chemical species.
- Irene C. Dedoussi
- , Sebastian D. Eastham
- & Steven R. H. Barrett
-
Article |
 Light-driven anaerobic microbial oxidation of manganese
Light-driven anaerobic microbial oxidation of manganese
Anoxygenic photosynthetic microorganisms can biomineralize manganese oxides without molecular oxygen being present and without high-potential photosynthetic reaction centres, which sheds doubt on proposed dates for the origins of oxygenic photosynthetic metabolism.
- Mirna Daye
- , Vanja Klepac-Ceraj
- & Tanja Bosak
-
Letter |
 A large source of cloud condensation nuclei from new particle formation in the tropics
A large source of cloud condensation nuclei from new particle formation in the tropics
Widespread formation of new particles from condensable vapours observed in the tropical upper troposphere is an important source of cloud condensation nuclei in the lower troposphere, affecting cloud properties.
- Christina J. Williamson
- , Agnieszka Kupc
- & Charles A. Brock
-
Letter |
 Isotopic constraint on the twentieth-century increase in tropospheric ozone
Isotopic constraint on the twentieth-century increase in tropospheric ozone
Isotope data from polar firn and ice are used to constrain the increase in tropospheric ozone between 1850 and 2005 ad.
- Laurence Y. Yeung
- , Lee. T. Murray
- & Jérôme Chappellaz
-
Letter |
 Increase in CFC-11 emissions from eastern China based on atmospheric observations
Increase in CFC-11 emissions from eastern China based on atmospheric observations
Emissions from eastern China account for approximately 40 to 60 per cent of the global rise in emissions of trichlorofluoromethane (CFC-11), which may be a result of new production and use.
- M. Rigby
- , S. Park
- & D. Young
-
Article |
 Secondary organic aerosol reduced by mixture of atmospheric vapours
Secondary organic aerosol reduced by mixture of atmospheric vapours
Adding reactive gases such as isoprene to mixtures lowers the production of secondary organic aerosol in the atmosphere, thus reducing the atmospheric particulate burden, with implications for human health and climate.
- Gordon McFiggans
- , Thomas F. Mentel
- & Astrid Kiendler-Scharr
-
Letter |
 Industrial and agricultural ammonia point sources exposed
Industrial and agricultural ammonia point sources exposed
Satellite observations reveal over 200 ammonia hotspots associated with agricultural and industrial point sources, which emit much larger quantities of ammonia to the atmosphere than previously thought.
- Martin Van Damme
- , Lieven Clarisse
- & Pierre-François Coheur
-
Letter |
 An unexpected and persistent increase in global emissions of ozone-depleting CFC-11
An unexpected and persistent increase in global emissions of ozone-depleting CFC-11
Atmospheric CFC-11 concentrations have been declining less rapidly since 2012; evidence suggests that this finding is explained by an increase in the emission of CFC-11during these years.
- Stephen A. Montzka
- , Geoff S. Dutton
- & James W. Elkins
-
Letter |
 A compositional tipping point governing the mobilization and eruption style of rhyolitic magma
A compositional tipping point governing the mobilization and eruption style of rhyolitic magma
Measurements of the composition-dependent viscosity of rhyolitic magma reveal a tipping point that changes the physical properties of the melt and controls the transition between effusive and explosive eruptions.
- D. Di Genova
- , S. Kolzenburg
- & D. B. Dingwell
-
Letter |
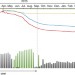 Tundra uptake of atmospheric elemental mercury drives Arctic mercury pollution
Tundra uptake of atmospheric elemental mercury drives Arctic mercury pollution
A two-year study of mercury deposition in the Arctic finds that the main source of mercury is gaseous elemental mercury, which is deposited throughout the year and leads to very high soil mercury levels.
- Daniel Obrist
- , Yannick Agnan
- & Detlev Helmig
-
Letter |
 Biofuel blending reduces particle emissions from aircraft engines at cruise conditions
Biofuel blending reduces particle emissions from aircraft engines at cruise conditions
Compared to using conventional jet fuel, the use of a biofuel blend reduces aircraft engine particle emissions at cruising altitude by about 50–70 per cent.
- Richard H. Moore
- , Kenneth L. Thornhill
- & Bruce E. Anderson
-
Letter |
 Water balance creates a threshold in soil pH at the global scale
Water balance creates a threshold in soil pH at the global scale
There is an abrupt transition from alkaline to acid soil pH when mean annual precipitation exceeds mean annual potential evapotranspiration, demonstrating that climate creates a nonlinear pattern in soil solution chemistry at the global scale.
- E. W. Slessarev
- , Y. Lin
- & O. A. Chadwick
-
Letter |
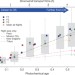 Oil sands operations as a large source of secondary organic aerosols
Oil sands operations as a large source of secondary organic aerosols
The evaporation and atmospheric oxidation of low-volatility organic vapours from mined oil sands material is shown to be responsible for a large amount of secondary organic aerosol mass—which affects air quality and climate change—observed during airborne measurements in Canada.
- John Liggio
- , Shao-Meng Li
- & Drew R. Gentner
-
Letter
| Open Access The role of low-volatility organic compounds in initial particle growth in the atmosphere
The role of low-volatility organic compounds in initial particle growth in the atmosphere
The growth of nucleated organic particles has been investigated in controlled laboratory experiments under atmospheric conditions; initial growth is driven by organic vapours of extremely low volatility, and accelerated by more abundant vapours of slightly higher volatility, leading to markedly different modelled concentrations of atmospheric cloud condensation nuclei when this growth mechanism is taken into account.
- Jasmin Tröstl
- , Wayne K. Chuang
- & Urs Baltensperger
-
Letter |
 Rapid cycling of reactive nitrogen in the marine boundary layer
Rapid cycling of reactive nitrogen in the marine boundary layer
Aircraft measurements, laboratory photolysis experiments and modelling calculations reveal a mechanism for the recycling of nitric acid into nitrogen oxides; this enables observations to be reconciled with model studies, and suggests that particulate nitrate photolysis could be a substantial tropospheric nitrogen oxide source.
- Chunxiang Ye
- , Xianliang Zhou
- & Christoph Knote
-
Letter |
 The terrestrial biosphere as a net source of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere
The terrestrial biosphere as a net source of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere
The net balance of terrestrial biogenic greenhouse gases produced as a result of human activities and the climatic impact of this balance are uncertain; here the net cumulative impact of the three greenhouse gases, methane, nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide, on the planetary energy budget from 2001 to 2010 is a warming of the planet.
- Hanqin Tian
- , Chaoqun Lu
- & Steven C. Wofsy
-
Letter |
 Future ocean hypercapnia driven by anthropogenic amplification of the natural CO2 cycle
Future ocean hypercapnia driven by anthropogenic amplification of the natural CO2 cycle
Data-based projections suggest that the natural CO2 cycle could be amplified by up to ten times by 2100 in some oceanic regions if atmospheric CO2 concentrations continue to increase, which could detrimentally affect major fisheries.
- Ben I. McNeil
- & Tristan P. Sasse
-
Letter |
 Rapid removal of organic micropollutants from water by a porous β-cyclodextrin polymer
Rapid removal of organic micropollutants from water by a porous β-cyclodextrin polymer
An alternative material to activated carbon for water remediation is reported: a porous material based on crosslinked cyclodextrins that is better than activated carbons at adsorbing a range of pharmaceuticals, pesticides and other anthropogenic pollutants.
- Alaaeddin Alsbaiee
- , Brian J. Smith
- & William R. Dichtel
-
Letter |
 Grassland biodiversity bounces back from long-term nitrogen addition
Grassland biodiversity bounces back from long-term nitrogen addition
Data from the long-running Park Grass Experiment is used to show that grassland biodiversity is recovering since UK atmospheric nitrogen levels started to decline 25 years ago in all but the most acidic soils.
- J. Storkey
- , A. J. Macdonald
- & M. J. Crawley
-
Perspective |
 The contentious nature of soil organic matter
The contentious nature of soil organic matter
Instead of containing stable and chemically unique ‘humic substances’, as has been widely accepted, soil organic matter is a mixture of progressively decomposing organic compounds; this has broad implications for soil science and its applications.
- Johannes Lehmann
- & Markus Kleber
-
Letter |
 The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale
The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale
Investigation of premature mortality by seven emission sources of atmospheric pollutants shows that outdoor air pollution, mostly by fine particulate matter, leads to more than three million premature deaths per year worldwide, which could double by 2050.
- J. Lelieveld
- , J. S. Evans
- & A. Pozzer
-
Letter |
 Erosion of organic carbon in the Arctic as a geological carbon dioxide sink
Erosion of organic carbon in the Arctic as a geological carbon dioxide sink
Measurements of sediments eroded by the Mackenzie River reveal the widespread export of permafrost-derived biospheric carbon that is several thousand years old, and demonstrate its burial in the Arctic Ocean, suggesting that high-latitude rivers can act as important carbon dioxide sinks.
- Robert G. Hilton
- , Valier Galy
- & Damien Calmels
-
Letter |
 Statistical analysis of iron geochemical data suggests limited late Proterozoic oxygenation
Statistical analysis of iron geochemical data suggests limited late Proterozoic oxygenation
Iron-based proxies are used to track the redox chemistry of ancient oceans, but do not reveal the sharp oxygenation event in the late Proterozoic eon that is expected from previous evaluations of proxy records.
- Erik A. Sperling
- , Charles J. Wolock
- & David T. Johnston
-
Letter |
 Basin-scale transport of hydrothermal dissolved metals across the South Pacific Ocean
Basin-scale transport of hydrothermal dissolved metals across the South Pacific Ocean
Hydrothermal dissolved iron, manganese, and aluminium from the southern East Pacific Rise is transported several thousand kilometres westward across the South Pacific Ocean; global hydrothermal dissolved iron input is estimated to be more than four times what was previously thought and modelling suggests it must be physically or chemically stabilized in solution.
- Joseph A. Resing
- , Peter N. Sedwick
- & Alessandro Tagliabue
-
Letter |
 Seed coating with a neonicotinoid insecticide negatively affects wild bees
Seed coating with a neonicotinoid insecticide negatively affects wild bees
Neonicotinoid seed coating is associated with reduced density of wild bees, as well as reduced nesting of solitary bees and reduced colony growth and reproduction of bumblebees, but appears not to affect honeybees.
- Maj Rundlöf
- , Georg K. S. Andersson
- & Henrik G. Smith
-
Letter |
 Multi-omics of permafrost, active layer and thermokarst bog soil microbiomes
Multi-omics of permafrost, active layer and thermokarst bog soil microbiomes
A multi-omics approach, integrating metagenomics, metatranscriptomics and metaproteomics, determines the phylogenetic composition of the microbial community and assesses its functional potential and activity along a thaw transition from intact permafrost to thermokast bog.
- Jenni Hultman
- , Mark P. Waldrop
- & Janet K. Jansson

 Dearomatization drives complexity generation in freshwater organic matter
Dearomatization drives complexity generation in freshwater organic matter