Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Endothelium-specific depletion of LRP1 improves glucose homeostasis through inducing osteocalcin
Endothelium-specific depletion of LRP1 improves glucose homeostasis through inducing osteocalcin
The vascular endothelium contributes to metabolic regulation, however, the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. Here the authors show that endothelial low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 regulates glucose homeostasis via osteocalcin expression.
- Hua Mao
- , Luge Li
- & Xinchun Pi
-
Article
| Open Access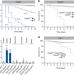 A nutrient-responsive hormonal circuit mediates an inter-tissue program regulating metabolic homeostasis in adult Drosophila
A nutrient-responsive hormonal circuit mediates an inter-tissue program regulating metabolic homeostasis in adult Drosophila
Maintaining metabolic homeostasis during feeding and fasting states is critical to animal survival. Here the authors show that Capa hormone signaling, homologs to mammalian Neuromedin U, helps control homeostasis via regulation of nutrient uptake and energy storage in Drosophila.
- Takashi Koyama
- , Selim Terhzaz
- & Kenneth V. Halberg
-
Article
| Open Access Intravital imaging of islet Ca2+ dynamics reveals enhanced β cell connectivity after bariatric surgery in mice
Intravital imaging of islet Ca2+ dynamics reveals enhanced β cell connectivity after bariatric surgery in mice
Bariatric surgery procedures reduce weight and improve metabolic diseases. Here the authors investigate the effects of Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy (VSG) on beta-cell function in mice using in vivo Ca2 + imaging and show that VSG increases beta-cell function and intra-islet connectivity.
- Elina Akalestou
- , Kinga Suba
- & Guy A. Rutter
-
Article
| Open Access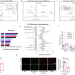 The pesticide chlorpyrifos promotes obesity by inhibiting diet-induced thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue
The pesticide chlorpyrifos promotes obesity by inhibiting diet-induced thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue
Chlorpyrifos is a widely-used pesticide and a common residue on vegetables and fruits. Here the authors show that at non-neurotoxic doses, chlorpyrifos reduces energy expenditure, by inhibiting diet induced thermogenesis, and promotes obesity and insulin resistance.
- Bo Wang
- , Evangelia E. Tsakiridis
- & Gregory R. Steinberg
-
Article
| Open Access O-GlcNAcylated p53 in the liver modulates hepatic glucose production
O-GlcNAcylated p53 in the liver modulates hepatic glucose production
p53 regulates signalling pathways involved in metabolic homeostasis. Here the authors show that O-GlcNAcylation of p53 in the liver plays a key role in the physiological regulation of glucose homeostasis, potentially via controlling the expression of the gluconeogenic enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase.
- Maria J. Gonzalez-Rellan
- , Marcos F. Fondevila
- & Ruben Nogueiras
-
Article
| Open Access The Hippo kinase LATS2 impairs pancreatic β-cell survival in diabetes through the mTORC1-autophagy axis
The Hippo kinase LATS2 impairs pancreatic β-cell survival in diabetes through the mTORC1-autophagy axis
Diabetes is characterized by dysfunction and loss of beta-cells, and promoting beta-cell survival is of therapeutic interest. Here the authors show that Large-tumor suppressor 2 (LATS2), a core component of the Hippo signaling pathway, induces beta-cell failure through mTORC1 hyperactivation and autophagic flux suppression.
- Ting Yuan
- , Karthika Annamalai
- & Amin Ardestani
-
Article
| Open Access Intestinal-derived FGF15 protects against deleterious effects of vertical sleeve gastrectomy in mice
Intestinal-derived FGF15 protects against deleterious effects of vertical sleeve gastrectomy in mice
The mechanisms that mediate the effects of weight loss surgeries such as vertical sleeve gastrectomy (VSG) are incompletely understood. Here the authors show that intestinal FGF15 is necessary to improve glucose tolerance and to prevent the loss of muscle and bone mass after VSG, potentially via protection against bile acid toxicity.
- Nadejda Bozadjieva-Kramer
- , Jae Hoon Shin
- & Randy J. Seeley
-
Article
| Open Access Brown adipose tissue is the key depot for glucose clearance in microbiota depleted mice
Brown adipose tissue is the key depot for glucose clearance in microbiota depleted mice
Gut microbiota deficient mice demonstrate enhanced glucose clearance, but which tissues are responsible for this improvement are still unclear. Here the authors report that brown adipose tissue contributes to the enhanced glucose clearance in gut microbiota depleted mice and that this response is dissociated from adaptive thermogenesis.
- Min Li
- , Li Li
- & John R. Speakman
-
Article
| Open Access Pancreatic Ppy-expressing γ-cells display mixed phenotypic traits and the adaptive plasticity to engage insulin production
Pancreatic Ppy-expressing γ-cells display mixed phenotypic traits and the adaptive plasticity to engage insulin production
The cellular identity and function of the pancreatic polypeptide (Ppy)-producing γ-cells are incompletely understood. Here the authors show that these cells are heterogeneous and display adaptive plasticity to engage in insulin production following β-cell injury, but loss of the Ppy gene or γ-cells in mice does not affect weight or glycemia under basal conditions.
- Marta Perez-Frances
- , Léon van Gurp
- & Pedro L. Herrera
-
Article
| Open Access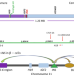 Large parental differences in chromatin organization in pancreatic beta cell line explaining diabetes susceptibility effects
Large parental differences in chromatin organization in pancreatic beta cell line explaining diabetes susceptibility effects
A SNP distant from the human insulin (INS) gene near the KRTAP5-6 gene confers increased susceptibility to type 2 diabetes when present on the paternal allele while decreased susceptibility when on the maternal allele. Here the authors show that long-range contacts between the INS locus and the KRTAP5-6 gene locus distinguish paternal and maternal alleles.
- Xing Jian
- & Gary Felsenfeld
-
Article
| Open Access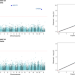 GIGYF1 loss of function is associated with clonal mosaicism and adverse metabolic health
GIGYF1 loss of function is associated with clonal mosaicism and adverse metabolic health
Mosaic loss of chromosome Y (LOY) is a common form of clonal mosaicism in leukocytes. Here, the authors extend genetic association analyses to rare variation using exome-sequence data from 82,277 males, finding that loss-of-function alleles in GIGYF1 are associated with six-fold higher susceptibility to both LOY and Type 2 Diabetes.
- Yajie Zhao
- , Stasa Stankovic
- & John R. B. Perry
-
Article
| Open Access Limited survival and impaired hepatic fasting metabolism in mice with constitutive Rag GTPase signaling
Limited survival and impaired hepatic fasting metabolism in mice with constitutive Rag GTPase signaling
The mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) integrates nutrient and hormonal signals to control metabolism. Here the authors investigate the effects of constitutive nutrient signaling through genetic activation of RagA in adult mice and show that constitutive nutrient signaling regulates the response to feeding-fasting cycles and does not drive liver cancer.
- Celia de la Calle Arregui
- , Ana Belén Plata-Gómez
- & Alejo Efeyan
-
Article
| Open Access Viral infiltration of pancreatic islets in patients with COVID-19
Viral infiltration of pancreatic islets in patients with COVID-19
New-onset hyperglycemia and complications of preexisting diabetes have been observed in COVID-19 patients, however, the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. Here, the authors show that SARS-CoV-2 is detectable in both endocrine and exocrine cells of the pancreata of patients with COVID-19.
- Charlotte Steenblock
- , Stefanie Richter
- & Stefan R. Bornstein
-
Article
| Open Access Determinants of penetrance and variable expressivity in monogenic metabolic conditions across 77,184 exomes
Determinants of penetrance and variable expressivity in monogenic metabolic conditions across 77,184 exomes
Penetrance of variants in monogenic disease and clinical utility of common polygenic variation has not been well explored on a large-scale. Here, the authors use exome sequencing data from 77,184 individuals to generate penetrance estimates and assess the utility of polygenic variation in risk prediction of monogenic variants.
- Julia K. Goodrich
- , Moriel Singer-Berk
- & Miriam S. Udler
-
Article
| Open Access Smart-watch-programmed green-light-operated percutaneous control of therapeutic transgenes
Smart-watch-programmed green-light-operated percutaneous control of therapeutic transgenes
Wearable smart devices often have green light diodes to monitor health. Here the authors use this to control a light-activated genetic switch for GLP1 production in diabetic mice.
- Maysam Mansouri
- , Marie-Didiée Hussherr
- & Martin Fussenegger
-
Article
| Open Access Visceral obesity and insulin resistance associate with CD36 deletion in lymphatic endothelial cells
Visceral obesity and insulin resistance associate with CD36 deletion in lymphatic endothelial cells
Genetic variants in CD36 have been associated with metabolic syndrome. Here, the authors found that lymphatic vessel integrity and lipid transport are influenced by CD36 expression, and lymphatic endothelial cell CD36 deficiency causes visceral obesity and insulin resistance, which are risk factors for metabolic syndrome and diabetes.
- Vincenza Cifarelli
- , Sila Appak-Baskoy
- & Nada A. Abumrad
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical combinations potentiate human pluripotent stem cell-derived 3D pancreatic progenitor clusters toward functional β cells
Chemical combinations potentiate human pluripotent stem cell-derived 3D pancreatic progenitor clusters toward functional β cells
Human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC) derived pancreatic beta cells are a promising and potentially limitless source for cell replacement therapy. Here the authors perform stage-wise chemical screening to develop an improved protocol for hPSC differentiation to functional pancreatic beta cells at high efficiency.
- Haisong Liu
- , Ronghui Li
- & Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte
-
Article
| Open Access Sam68 promotes hepatic gluconeogenesis via CRTC2
Sam68 promotes hepatic gluconeogenesis via CRTC2
Hepatic gluconeogenesis is important for glucose homeostasis and a therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes. Here, the authors show that the RNA-binding adaptor protein Sam68 promotes the expression level of gluconeogenic genes and increases blood glucose levels by stabilizing the transcriptional coactivator CRTC2, while hepatic Sam68 deletion alleviates hyperglycemia in mice.
- Aijun Qiao
- , Junlan Zhou
- & Gangjian Qin
-
Article
| Open Access A small molecule HIF-1α stabilizer that accelerates diabetic wound healing
A small molecule HIF-1α stabilizer that accelerates diabetic wound healing
Impaired wound healing is a serious complication in diabetic patients, and is associated with reduced HIF1α stability. Here, the authors design a small molecule that stabilizes HIF1α by blocking its interaction with VHL and show that it promotes wound healing in mouse models of diabetes.
- Guodong Li
- , Chung-Nga Ko
- & Chung-Hang Leung
-
Article
| Open Access β-Arrestin-1 is required for adaptive β-cell mass expansion during obesity
β-Arrestin-1 is required for adaptive β-cell mass expansion during obesity
During insulin-resistance, the compensatory expansion of beta-cell mass is able to delay or the onset of overt type 2 diabetes. Here, the authors report that beta-arrestin-1, an intracellular protein known to regulate signalling through G protein-coupled receptors, is essential for beta-cell replication and function in insulin-resistant mice.
- Luiz F. Barella
- , Mario Rossi
- & Jürgen Wess
-
Article
| Open Access Reinforcing one-carbon metabolism via folic acid/Folr1 promotes β-cell differentiation
Reinforcing one-carbon metabolism via folic acid/Folr1 promotes β-cell differentiation
Regeneration of insulin-producing beta-cells may become a future alternative treatment of diabetes. Here the authors report a genetic screen in a zebrafish model that mimics the loss of beta-cells in diabetes, and identified that the folate receptor Folr1 or folinic acid treatment can stimulate beta-cell regeneration.
- Christos Karampelias
- , Habib Rezanejad
- & Olov Andersson
-
Article
| Open Access A functional motif of long noncoding RNA Nron against osteoporosis
A functional motif of long noncoding RNA Nron against osteoporosis
LncRNAs are implicated in the pathogenesis of a number of diseases. Here, the authors show that the lncRNA Nron suppresses bone resorption, and show that delivery of a functional motif of Nron increases bone mass in mouse models of osteoporosis.
- Fujun Jin
- , Junhui Li
- & Xiaogang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A deep learning system for detecting diabetic retinopathy across the disease spectrum
A deep learning system for detecting diabetic retinopathy across the disease spectrum
As the leading cause of vision loss in working-age adults, diabetic retinopathy requires routinely retinal screening. Here the authors develop a deep learning system that can facilitate the screening by providing real-time image quality assessment, lesions detection, and grades across the disease spectrum.
- Ling Dai
- , Liang Wu
- & Weiping Jia
-
Article
| Open Access Decreased GLUT2 and glucose uptake contribute to insulin secretion defects in MODY3/HNF1A hiPSC-derived mutant β cells
Decreased GLUT2 and glucose uptake contribute to insulin secretion defects in MODY3/HNF1A hiPSC-derived mutant β cells
Heterozygous HNF1A mutations can give rise to maturity onset diabetes of the young 3 (MODY3), characterized by insulin secretion defects. Here the authors show that MODY3-related HNF1A mutation in patient hiPSCderived pancreatic cells decreases glucose transporter GLUT2 expression due to compromised DNA binding.
- Blaise Su Jun Low
- , Chang Siang Lim
- & Adrian Kee Keong Teo
-
Article
| Open Access mRNA therapy restores euglycemia and prevents liver tumors in murine model of glycogen storage disease
mRNA therapy restores euglycemia and prevents liver tumors in murine model of glycogen storage disease
Glycogen Storage Disease 1a (Gsd1a) is an inherited disorder caused by glucose 6-phosphatase (G6Pase-α) deficiency and characterized by hypoglycaemia and high risk of liver cancer. Here the authors develop a mRNA-based G6Pase-α delivery therapy that is efficacious and safe in a mouse model of GSD1a.
- Jingsong Cao
- , Minjung Choi
- & Paloma H. Giangrande
-
Article
| Open Access Orphan GPR116 mediates the insulin sensitizing effects of the hepatokine FNDC4 in adipose tissue
Orphan GPR116 mediates the insulin sensitizing effects of the hepatokine FNDC4 in adipose tissue
The soluble bioactive form of the transmembrane protein fibronectin type III domain containing 4 (sFNDC4) has anti-inflammatory effects and improves insulin sensitivity. Here the authors show that liver derived sFNDC4 signals through adipose tissue GPCR GPR116 to promote insulin-mediated glucose uptake.
- Anastasia Georgiadi
- , Valeria Lopez-Salazar
- & Stephan Herzig
-
Article
| Open Access A BAFF/APRIL axis regulates obesogenic diet-driven weight gain
A BAFF/APRIL axis regulates obesogenic diet-driven weight gain
Interactions between the immune system and adipose tissue contribute to the regulation of body weight, however, the underlying mechanisms remain incompletely understood. Here the authors dissect the role of two structurally and functionally similar immune mediators, BAFF and APRIL, in modifying diet-induced weight gain and adipocyte lipid handling.
- Calvin C. Chan
- , Isaac T. W. Harley
- & Senad Divanovic
-
Article
| Open Access Peripheral-specific Y1 receptor antagonism increases thermogenesis and protects against diet-induced obesity
Peripheral-specific Y1 receptor antagonism increases thermogenesis and protects against diet-induced obesity
Neuropeptide Y signalling in the periphery contributes to the regulation of metabolic and energy homeostasis. Here the authors show that blocking Y1R signalling in peripheral tissues using the selective antagonist BIBO3304 ameliorates diet-induced obesity and improves whole-body glucose metabolism.
- Chenxu Yan
- , Tianshu Zeng
- & Yan-Chuan Shi
-
Review Article
| Open Access Emerging concepts in intestinal immune control of obesity-related metabolic disease
Emerging concepts in intestinal immune control of obesity-related metabolic disease
At the centre of intestinal health and the fight against obesity and metabolic syndrome is the intestinal microbiota and its interaction with our immune systems. Here the authors Review the current understanding of how these systems interact and how we can capitalize on recent advances to provide better therapeutic options.
- Saad Khan
- , Helen Luck
- & Daniel A. Winer
-
Article
| Open Access RANKL regulates male reproductive function
RANKL regulates male reproductive function
There are few treatments for male infertility. Here, the authors show that the receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL) signalling pathway has important functions in sperm production and maturation, improves fertility in male mice and shows potential as a male infertility target.
- Martin Blomberg Jensen
- , Christine Hjorth Andreassen
- & Anders Juul
-
Article
| Open Access COVID-19 pathophysiology may be driven by an imbalance in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
COVID-19 pathophysiology may be driven by an imbalance in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
The SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 is involved in the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS). Over-activation of RAAS in swine results in a disease state similar to that of COVID-19 in human patients, suggesting that COVID-19 pathophysiology may be driven, at least in part, by an imbalance of this hormonal system.
- Susanne Rysz
- , Jonathan Al-Saadi
- & Johan Lundberg
-
Article
| Open Access VPS39-deficiency observed in type 2 diabetes impairs muscle stem cell differentiation via altered autophagy and epigenetics
VPS39-deficiency observed in type 2 diabetes impairs muscle stem cell differentiation via altered autophagy and epigenetics
Insulin resistance and lower muscle strength in relation to mass are hallmarks of type 2 diabetes. Here, the authors report alterations in muscle stem cells from individuals with type 2 diabetes that may contribute to these phenotypes through VPS39 mediated effects on autophagy and epigenetics.
- Cajsa Davegårdh
- , Johanna Säll
- & Charlotte Ling
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR-based genome editing in primary human pancreatic islet cells
CRISPR-based genome editing in primary human pancreatic islet cells
The editing of primary human islets could provide insight into diabetes pathogenesis. Here the authors use CRISPR-Cas9 to target regulatory elements associated with T2D susceptibility.
- Romina J. Bevacqua
- , Xiaoqing Dai
- & Seung K. Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Loss of endothelial glucocorticoid receptor accelerates diabetic nephropathy
Loss of endothelial glucocorticoid receptor accelerates diabetic nephropathy
The endothelial glucocorticoid receptor plays a key role in the regulation of many diseases, including diabetes. Loss of this receptor results in accelerated renal fibrosis, a heightened inflammatory milieu, augmented Wnt signaling and suppression of fatty acid oxidation in diabetic kidneys.
- Swayam Prakash Srivastava
- , Han Zhou
- & Julie Goodwin
-
Article
| Open Access Deficiency of TMEM53 causes a previously unknown sclerosing bone disorder by dysregulation of BMP-SMAD signaling
Deficiency of TMEM53 causes a previously unknown sclerosing bone disorder by dysregulation of BMP-SMAD signaling
Sclerosing bone disorder (SBD) includes a broad spectrum of monogenic diseases characterised by increased bone density. Here, the authors describe a previously unknown SBD in four families caused by mutations in TMEM53 and demonstrate the role this protein plays in BMP signalling during bone formation.
- Long Guo
- , Aritoshi Iida
- & Shiro Ikegawa
-
Article
| Open Access Activating mutations in BRAF disrupt the hypothalamo-pituitary axis leading to hypopituitarism in mice and humans
Activating mutations in BRAF disrupt the hypothalamo-pituitary axis leading to hypopituitarism in mice and humans
Mutations in components of the MAP kinase pathway are associated with a group of syndromes known as RASopathies. Here, the authors identify gain-of-function mutations in BRAF in patients with RASopathies and congenital hypopituitarisms. This article demonstrates a central role for BRAF in the development of the hypothalamo-pituitary axis leading to endocrine deficiencies in patients with RASopathies.
- Angelica Gualtieri
- , Nikolina Kyprianou
- & Carles Gaston-Massuet
-
Article
| Open Access Loss of bone morphogenetic protein-binding endothelial regulator causes insulin resistance
Loss of bone morphogenetic protein-binding endothelial regulator causes insulin resistance
Type 2 diabetes is associated with chronic inflammation and is characterized by insulin resistance. Here, the authors identify a crucial role for endothelial BMPER function in glucose homeostasis, and BMPER overexpression was shown to alleviate insulin resistance and hyperglycemia in diabetic mice.
- Hua Mao
- , Luge Li
- & Xinchun Pi
-
Perspective
| Open Access Epigenetic mechanisms in breast cancer therapy and resistance
Epigenetic mechanisms in breast cancer therapy and resistance
Endocrine therapy has been the mainstay for hormone responsive breast cancer treatment. Here, Garcia-Martinez and colleagues discuss epigenetic mechanisms regulating ER + breast cancer and endocrine therapy resistance, and highlight approaches to rewire the cancer epigenome to improve targeted therapies for this cancer.
- Liliana Garcia-Martinez
- , Yusheng Zhang
- & Lluis Morey
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolic responses to mild cold acclimation in type 2 diabetes patients
Metabolic responses to mild cold acclimation in type 2 diabetes patients
Cold acclimation has been shown to have beneficial metabolic effects, including improved insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes. Here the authors show that a mild cold acclimation regiment during which overt shivering was prevented did not result in improved insulin sensitivity in a small group of patients with type 2 diabetes.
- Carlijn M. E. Remie
- , Michiel P. B. Moonen
- & Patrick Schrauwen
-
Article
| Open Access Hyocholic acid species as novel biomarkers for metabolic disorders
Hyocholic acid species as novel biomarkers for metabolic disorders
The early identification of metabolic disorders could improve or prevent overt disease. Here the authors show that the circulating concentration of hyocholic acid (HCA) species is decreased in the context of obesity and diabetes and increased after gastric bypass surgery in humans, and further that serum HCA species are predictive of metabolic outcomes in healthy individuals.
- Xiaojiao Zheng
- , Tianlu Chen
- & Wei Jia
-
Article
| Open Access Lysates of Methylococcus capsulatus Bath induce a lean-like microbiota, intestinal FoxP3+RORγt+IL-17+ Tregs and improve metabolism
Lysates of Methylococcus capsulatus Bath induce a lean-like microbiota, intestinal FoxP3+RORγt+IL-17+ Tregs and improve metabolism
Dietary changes can impact the microbial constitution of the gastrointestinal tract and modulate the local immune response. Here, the authors show supplementation using lysates of Methylococcus capsulatus Bath result in changes to the microbiota, modulate Treg populations and metabolic read outs in a dietary control murine model.
- Benjamin A. H. Jensen
- , Jacob B. Holm
- & Tor E. Lea
-
Article
| Open Access GWAS for autoimmune Addison’s disease identifies multiple risk loci and highlights AIRE in disease susceptibility
GWAS for autoimmune Addison’s disease identifies multiple risk loci and highlights AIRE in disease susceptibility
Autoimmune Addison’s disease is a rare complex disease, which has not yet been characterized by non-biased genetic studies. Here, the authors perform the first GWAS for the disease, identifying nine loci including two coding variants in the gene Autoimmune Regulator (AIRE).
- Daniel Eriksson
- , Ellen Christine Røyrvik
- & Eystein Sverre Husebye
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic determinants of daytime napping and effects on cardiometabolic health
Genetic determinants of daytime napping and effects on cardiometabolic health
The genetic basis of daytime napping and the directional effect of daytime napping on cardiometabolic health are unknown. Here, the authors perform a genome-wide association study on self-reported daytime napping in the UK Biobank and Mendelian randomization to explore causal associations.
- Hassan S. Dashti
- , Iyas Daghlas
- & Richa Saxena
-
Article
| Open Access Time-restricted feeding normalizes hyperinsulinemia to inhibit breast cancer in obese postmenopausal mouse models
Time-restricted feeding normalizes hyperinsulinemia to inhibit breast cancer in obese postmenopausal mouse models
Obesity and its associated metabolic changes, including hyperinsulinemia and aberrant circadian rhythms, increases the risk for a variety of cancers including postmenopausal breast cancer. Here, the authors show that restricting when mice eat, but not what or how much they eat, delays breast cancer initiation and reduces tumor growth in obese mice in addition to improving insulin sensitivity and restoring circadian rhythms.
- Manasi Das
- , Lesley G. Ellies
- & Nicholas J. G. Webster
-
Article
| Open Access DsbA-L deficiency in T cells promotes diet-induced thermogenesis through suppressing IFN-γ production
DsbA-L deficiency in T cells promotes diet-induced thermogenesis through suppressing IFN-γ production
Adipose tissue-resident T cells are known to regulate thermogenesis and energy expenditure. Here the authors report that deletion of mitochondria-localized protein DsbA-L in T cells promotes diet-induced thermogenesis via suppressing IFN-γ production.
- Haiyan Zhou
- , Xinyi Peng
- & Feng Liu
-
Article
| Open Access High-fat diet-induced upregulation of exosomal phosphatidylcholine contributes to insulin resistance
High-fat diet-induced upregulation of exosomal phosphatidylcholine contributes to insulin resistance
High-fat diet plays a role in development of insulin resistance. Here, the authors report a mechanism that underlies the development of diet induced insulin resistance through the activation of an aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediated signalling pathway in the liver by faecal exosomes derived from intestinal cells.
- Anil Kumar
- , Kumaran Sundaram
- & Huang-Ge Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access An autophagy enhancer ameliorates diabetes of human IAPP-transgenic mice through clearance of amyloidogenic oligomer
An autophagy enhancer ameliorates diabetes of human IAPP-transgenic mice through clearance of amyloidogenic oligomer
Islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) deposition is associated with islet cell loss in diabetes. Here the authors show that a small molecule autophagy enhancer reduces IAPP accumulation in vitro, and also improves glucose tolerance in hIAPP+ mice fed high-fat diet, accompanied by reduced hIAPP accumulation, in vivo.
- Jinyoung Kim
- , Kihyoun Park
- & Myung-Shik Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Sex-dimorphic genetic effects and novel loci for fasting glucose and insulin variability
Sex-dimorphic genetic effects and novel loci for fasting glucose and insulin variability
Sex differences in fasting glucose and insulin have been identified, but the genetic loci underlying these differences have not. Here, the authors perform a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies to detect sex-specific and sex-dimorphic loci associated with fasting glucose and insulin.
- Vasiliki Lagou
- , Reedik Mägi
- & Inga Prokopenko
-
Article
| Open Access Improvement of obesity-associated disorders by a small-molecule drug targeting mitochondria of adipose tissue macrophages
Improvement of obesity-associated disorders by a small-molecule drug targeting mitochondria of adipose tissue macrophages
Adipose tissue macrophages are central to controlling inflammation in the context of obesity. Here the authors present a new infrared dye (IR-61) that accumulates in the mitochondria of these cells resulting in anti-inflammatory effects that counter obesity-associated pathology in mice.
- Yawei Wang
- , Binlin Tang
- & Chunmeng Shi

 A functional genomics pipeline identifies pleiotropy and cross-tissue effects within obesity-associated GWAS loci
A functional genomics pipeline identifies pleiotropy and cross-tissue effects within obesity-associated GWAS loci