News & Views |
Featured
-
-
-
Article |
 An improved high-performance lithium–air battery
An improved high-performance lithium–air battery
Lithium–air batteries have the possibility of having a very high energy density, but their use has been hampered by a limited number of charge–discharge cycles and a low current-rate capability. Now, exploiting a suitable, stable electrolyte allows an advanced lithium–air battery to operate with many cycles at various capacity and rate values.
- Hun-Gi Jung
- , Jusef Hassoun
- & Bruno Scrosati
-
Article |
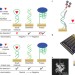 An ultrasensitive universal detector based on neutralizer displacement
An ultrasensitive universal detector based on neutralizer displacement
A universal detector of small molecules, proteins and nucleic acids is described that relies on the displacement of a neutralizer molecule from a sensor surface. When the neutralizer is displaced by an analyte, an electrochemical signal is generated. Ultrasensitive limits of detection are achieved, and a new record for the electrochemical detection of bacteria (0.15 colony-forming units per microlitre) is reported.
- Jagotamoy Das
- , Kristin B. Cederquist
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
Article |
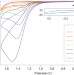 A soluble copper–bipyridine water-oxidation electrocatalyst
A soluble copper–bipyridine water-oxidation electrocatalyst
Copper and bipyridine (bpy) self-assemble in aqueous solutions at high pH into an active electrocatalyst for the oxidation of water to O2, one of the great challenges in energy catalysis. These solutions contain primarily (bpy)Cu(OH)2, and are robust and active catalysts, albeit at high overpotentials.
- Shoshanna M. Barnett
- , Karen I. Goldberg
- & James M. Mayer
-
Review Article |
 Electron-transfer processes in dendrimers and their implication in biology, catalysis, sensing and nanotechnology
Electron-transfer processes in dendrimers and their implication in biology, catalysis, sensing and nanotechnology
Redox sites can be incorporated within dendrimers — highly branched, well-defined macromolecules — at specific locations, such as their core, branching points, periphery or inner cavities. These dendrimers can serve to functionalize surfaces, and electron-transfer processes at their redox sites show promise for various applications ranging from metallo-protein modelling to sensing to catalysis.
- Didier Astruc
-
Article |
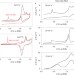 The promoting effect of adsorbed carbon monoxide on the oxidation of alcohols on a gold catalyst
The promoting effect of adsorbed carbon monoxide on the oxidation of alcohols on a gold catalyst
Adsorbed carbon monoxide typically acts to poison the oxidation of alcohols on heterogeneous catalysts and electrocatalysts. Here, it is shown that carbon monoxide that has been adsorbed irreversibly on a Au(111) surface can act as a promoter for this process by enhancing the scission of C–H bonds in the alcohol to yield the corresponding aldehyde.
- Paramaconi Rodriguez
- , Youngkook Kwon
- & Marc T. M. Koper
-
News & Views |
 Oxidizing water two ways
Oxidizing water two ways
Iridium complexes can show impressive homogeneous water-oxidation activity, but they can also act as precursors to heterogeneous catalysts. Understanding exactly what the catalytically active species is can be difficult, but now a technique has been applied that reveals the true nature of a catalyst, helping to remove this ambiguity.
- Thomas J. Meyer
-
News & Views |
 Feeling the strain
Feeling the strain
Characterizing electrochemical behaviour on the nanometre scale is fundamental to gaining complete insight into the working mechanisms of fuel cells. The application of a new scanning probe microscopy technique can now relate local surface structure to electrochemical activity at a resolution below 10 nm.
- Johannes A. A. W. Elemans
-
News & Views |
 Picking perovskites
Picking perovskites
The search for efficient oxygen reduction catalysts made from perovskite oxides rather than expensive precious metals is hindered by the sheer range of these oxides — where should the search begin? Developing design rules that can identify the best candidates is the first step towards a more targeted strategy.
- Robert F. Savinell
-
Article |
 Design principles for oxygen-reduction activity on perovskite oxide catalysts for fuel cells and metal–air batteries
Design principles for oxygen-reduction activity on perovskite oxide catalysts for fuel cells and metal–air batteries
With the cost of noble metal oxygen-reduction catalysts rendering some fuel cells and batteries prohibitively expensive, the search for effective and cheaper catalysts is underway and would be speeded up by ‘design principles’. Now, the catalytic activity of oxide materials has been correlated to σ*-orbital occupation and the extent of metal–oxygen covalency.
- Jin Suntivich
- , Hubert A. Gasteiger
- & Yang Shao-Horn
-
News & Views |
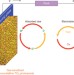 Out with both baby and bathwater
Out with both baby and bathwater
After two decades of research, the efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells seems to have reached a plateau. Now, changing both electrolyte and dye opens up new opportunities that offer the hope that the efficiency ceiling can be broken.
- C. Michael Elliott
-
Article |
 High-efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells with ferrocene-based electrolytes
High-efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells with ferrocene-based electrolytes
Dye-sensitized solar cells combining electrolytes based on the ferrocene/ferrocenium redox couple with a metal-free organic donor–acceptor sensitizer are reported to achieve a record 7.5% energy conversion efficiency, revealing the great potential of ferrocene-based electrolytes for future dye-sensitized solar cell applications.
- Torben Daeneke
- , Tae-Hyuk Kwon
- & Leone Spiccia
-
Article |
 DNA charge transport over 34 nm
DNA charge transport over 34 nm
The potential for using molecules as wires in nanoscale electronics is somewhat tempered by the challenges in making long and uniform structures. Now, it has been shown that DNA — which is easily synthesized to precise lengths — can conduct charge over 34 nm on multiplexed gold electrodes, a distance that surpasses most reports of molecular wires.
- Jason D. Slinker
- , Natalie B. Muren
- & Jacqueline K. Barton
-
News & Views |
 Waves in microscopy
Waves in microscopy
Advances in transduction of electrochemical activity through surface plasmon resonance afford new opportunities for spatially and temporally resolved studies of interfaces.
- Lane A. Baker
- & Chiao-Chen Chen
-
Article |
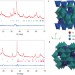 Rapid room-temperature synthesis of nanocrystalline spinels as oxygen reduction and evolution electrocatalysts
Rapid room-temperature synthesis of nanocrystalline spinels as oxygen reduction and evolution electrocatalysts
Ceramic preparation of spinels — materials useful for a wide range of applications — requires complicated procedures and heat treatment over long periods. Now, it is shown that rapid synthesis of nanocrystalline Co–Mn–O spinels can be achieved under ambient conditions, and the resulting nanoparticles exhibit considerable catalytic activity towards the electrochemical oxygen reduction/evolution reactions.
- Fangyi Cheng
- , Jian Shen
- & Jun Chen
-
Research Highlights |
 Catalysis in a drought
Catalysis in a drought
A ruthenium complex has been shown to catalyse the oxidation of water in a non-aqueous solvent with a rate greater than in the aqueous system.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
Article |
 Enhanced electrocatalysis of the oxygen reduction reaction based on patterning of platinum surfaces with cyanide
Enhanced electrocatalysis of the oxygen reduction reaction based on patterning of platinum surfaces with cyanide
The phosphoric acid fuel cell is limited by its slow rate of oxygen reduction at the cathode, but now an approach to the rational design of improved catalysts for this process has been developed. Molecular patterning of platinum surfaces with cyanide adsorbates is used to block the adsorption of spectator anions without hindering oxygen reduction, thus improving catalytic activity.
- Dusan Strmcnik
- , María Escudero-Escribano
- & Nenad M. Marković
-
Article |
 Raising the cycling stability of aqueous lithium-ion batteries by eliminating oxygen in the electrolyte
Raising the cycling stability of aqueous lithium-ion batteries by eliminating oxygen in the electrolyte
Aqueous lithium-ion batteries have great potential as stationary power sources, but they have had problems with poor stability. A significant improvement in their cycling stability has been achieved by eliminating oxygen, adjusting the electrolyte pH values, and using a carbon-coated electrode material.
- Jia-Yan Luo
- , Wang-Jun Cui
- & Yong-Yao Xia
-
Article |
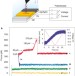 Electrically induced bonding of DNA to gold
Electrically induced bonding of DNA to gold
The assembly and evaluation of molecular structures on surfaces has been boosted by advances in single-molecule techniques. The development of such methods are continued here, showing that double-stranded DNA, bound to the tip of an atomic force microscope, can be deposited on the surface of a gold electrode using an electrical trigger.
- Matthias Erdmann
- , Ralf David
- & Hermann E. Gaub
-
Article |
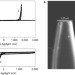 Electrochemistry through glass
Electrochemistry through glass
Glass is widely used as an electrical insulator in electrodes, but in spite of its high resistance, 100-nm-thick layers of glass have now been shown to be sufficiently conductive for electrochemical measurements. Obtaining redox couples through glass-covered nanoelectrodes suggests that the pH response of the glass is due to the formation of a hydrogel layer in acidic solution.
- Jeyavel Velmurugan
- , Dongping Zhan
- & Michael V. Mirkin
-
Article |
 Lattice-strain control of the activity in dealloyed core–shell fuel cell catalysts
Lattice-strain control of the activity in dealloyed core–shell fuel cell catalysts
The rational design of catalytic materials requires synthetic control over their reactive properties. Now, the activity of dealloyed Pt–Cu bimetallic nanoparticles, which catalyse the oxygen reduction reaction, can be tuned through control of the geometric strain at their surface.
- Peter Strasser
- , Shirlaine Koh
- & Anders Nilsson
-
Article |
 An organic redox electrolyte to rival triiodide/iodide in dye-sensitized solar cells
An organic redox electrolyte to rival triiodide/iodide in dye-sensitized solar cells
Although the triiodide/iodide redox couple works efficiently in dye-sensitized solar cells it restricts functionality by absorbing visible light. Now, a disulfide/thiolate redox couple that has negligible absorption in the visible spectral range is presented, which in conjunction with a sensitized heterojunction, displays an efficiency of 6.4% under standard illumination test conditions.
- Mingkui Wang
- , Nathalie Chamberland
- & Michael Grätzel
-
News & Views |
 Protons on tap
Protons on tap
Electrochemistry has so far been mostly centred around measuring factors and coefficients. Through the reversible reduction and oxidation of an electrode coating formed from three-dimensional hybrid aniline–gold nanoparticles, it has now moved on to controlling the pH of a solution, thus triggering specific reactions.
- Reginald M. Penner
-
Article |
 High-spin ground states via electron delocalization in mixed-valence imidazolate-bridged divanadium complexes
High-spin ground states via electron delocalization in mixed-valence imidazolate-bridged divanadium complexes
Single-molecule magnets are clusters of metal ions linked together by organic bridges, with properties typically arising from exchange coupling of unpaired metal electrons. In mixed-valence systems, another magnetic mechanism involving itinerant electrons can also occur and induce a high-spin ground state. Now, such electron delocalization has been observed through an imidazolate bridge — a common linker in metal-organic architectures — which may enable the construction of higher spin clusters or three-dimensional magnets.
- Bettina Bechlars
- , Deanna M. D'Alessandro
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Article |
 Nanocrystalline intermetallics on mesoporous carbon for direct formic acid fuel cell anodes
Nanocrystalline intermetallics on mesoporous carbon for direct formic acid fuel cell anodes
Formic acid fuel cells require nanosized intermetallic nanoparticles as anode catalysts, but current techniques are poor at producing the small size required. Now, surface-modified ordered mesoporous carbons have been used to produce nanocrystallites as small as 1.5 nm that are extremely active catalysts.
- Xiulei Ji
- , Kyu Tae Lee
- & Linda F. Nazar
-
News & Views |
 Radical attraction of like charges
Radical attraction of like charges
Although it may seem counter-intuitive, the attraction between positively charged radical ions offers a new approach to driving controlled motion in molecular machines.
- Harry L. Anderson

 Taking charge of detection
Taking charge of detection