Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access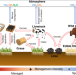 Climate warming from managed grasslands cancels the cooling effect of carbon sinks in sparsely grazed and natural grasslands
Climate warming from managed grasslands cancels the cooling effect of carbon sinks in sparsely grazed and natural grasslands
Grasslands, and the livestock that live there, are dynamic sources and sinks of greenhouse gases, but what controls these fluxes remains poorly characterized. Here the authors show that on the global level, grasslands are climate neutral owing to the cancelling effects of managed vs. natural systems.
- Jinfeng Chang
- , Philippe Ciais
- & Dan Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access The origin of the Moon’s Earth-like tungsten isotopic composition from dynamical and geochemical modeling
The origin of the Moon’s Earth-like tungsten isotopic composition from dynamical and geochemical modeling
Tungsten isotopes between the Earth and Moon are compared in this new study. The authors find that traditional models of Moon formation are very unlikely to reproduce the Moon's Earth-like isotopic composition.
- Rebecca A. Fischer
- , Nicholas G. Zube
- & Francis Nimmo
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous collapses of Nares Strait ice arches leads to enhanced export of Arctic sea ice
Anomalous collapses of Nares Strait ice arches leads to enhanced export of Arctic sea ice
Ice arches that form along Nares Strait, which separates Greenland and Ellesmere Island, act to reduce the export of thick multi-year ice out of the Arctic. Here, we show that there has been a recent trend towards shorter duration arch formation that has resulted in enhanced transport of ice along the strait.
- G. W. K. Moore
- , S. E. L. Howell
- & K. McNeil
-
Article
| Open Access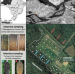 A new hypothesis for the origin of Amazonian Dark Earths
A new hypothesis for the origin of Amazonian Dark Earths
Amazonian Dark Earth is soil that has had mysteriously high fertility since ancient times, despite the fact that surrounding soils have very low nutrients. Here the authors’ use of isotope reconstructions indicate that these soils predate human settlement and could have alluvial and burning origins.
- Lucas C. R. Silva
- , Rodrigo Studart Corrêa
- & Roberto Ventura Santos
-
Article
| Open Access Group 2i Isochrysidales produce characteristic alkenones reflecting sea ice distribution
Group 2i Isochrysidales produce characteristic alkenones reflecting sea ice distribution
Some algae produce compounds called alkenones that can reconstruct sea surface temperature through geological time, but in high latitudes unknown species complicate use of this proxy. Here the authors find a lineage of sea ice algae that produces alkenones and can be used as a paleo-sensor for sea ice abundance.
- Karen Jiaxi Wang
- , Yongsong Huang
- & Patricia Cabedo-Sanz
-
Article
| Open Access A framework to predict the price of energy for the end-users with applications to monetary and energy policies
A framework to predict the price of energy for the end-users with applications to monetary and energy policies
Global energy transformation requires quantifying the "price of energy" and studying its evolution. Here the authors present a predictive framework that calculates the average US price of energy, estimating future energy demands for up to four years with excellent accuracy, designing and optimizing energy and monetary policies.
- Stefanos G. Baratsas
- , Alexander M. Niziolek
- & Efstratios N. Pistikopoulos
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessVariables in the effect of land use on soil extrapore enzymatic activity and carbon stabilization
- Melanie M. Glenn
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reply to: “Variables in the effect of land use on soil extrapore enzymatic activity and carbon stabilization” by Glenn (2020)
Reply to: “Variables in the effect of land use on soil extrapore enzymatic activity and carbon stabilization” by Glenn (2020)
- A. N. Kravchenko
- , A. K. Guber
- & Y. Kuzyakov
-
Article
| Open Access Lunar impact crater identification and age estimation with Chang’E data by deep and transfer learning
Lunar impact crater identification and age estimation with Chang’E data by deep and transfer learning
Using Chang’E data, the authors here identify more than 109,000 previously unrecognized lunar craters and date almost 19,000 craters based on transfer learning with deep neural networks. A new lunar crater database is derived and distributed to the planetary community.
- Chen Yang
- , Haishi Zhao
- & Ziyuan Ouyang
-
Article
| Open Access Organism body size structures the soil microbial and nematode community assembly at a continental and global scale
Organism body size structures the soil microbial and nematode community assembly at a continental and global scale
It is unclear whether body size affects community assembly mechanisms of soil biota. Here, the authors analyse soil microbial and nematode communities sampled along a 4000-km transect in China and global soil microbiome data to show that bacterial assembly is governed by high dispersal, whereas larger taxa are more influenced by deterministic processes.
- Lu Luan
- , Yuji Jiang
- & Bo Sun
-
Article
| Open Access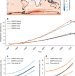 Greater Greenland Ice Sheet contribution to global sea level rise in CMIP6
Greater Greenland Ice Sheet contribution to global sea level rise in CMIP6
The potential contribution of Greenland Ice Sheet to sea level rise in the future is known to be substantial. Here, the authors undertake new modelling showing that the Greenland Ice Sheet sea level rise contribution is 7.9 cm more using the CMIP6 SSP585 scenario compared to CMIP5 using multiple RCP8.5 simulations.
- Stefan Hofer
- , Charlotte Lang
- & Xavier Fettweis
-
Article
| Open Access Calculation of external climate costs for food highlights inadequate pricing of animal products
Calculation of external climate costs for food highlights inadequate pricing of animal products
Agricultural greenhouse gas emissions not only amplify the global climate crisis, but cause damage currently unaccounted for by food prices. Here the authors show the calculation of prices with internalized climate costs for food categories and production systems, revealing strong market distortions.
- Maximilian Pieper
- , Amelie Michalke
- & Tobias Gaugler
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming gender inequality for climate resilient development
Overcoming gender inequality for climate resilient development
Gender inequality increases vulnerability to climate change impacts and reduces societies’ adaptive capacity. Here the authors show how gender inequality may evolve in the future in five scenarios of socioeconomic development and highlight the importance of incorporating gender inequality in climate change research and policy.
- Marina Andrijevic
- , Jesus Crespo Cuaresma
- & Carl-Friedrich Schleussner
-
Article
| Open Access Using metacommunity ecology to understand environmental metabolomes
Using metacommunity ecology to understand environmental metabolomes
Despite growing interest in environmental metabolomics, we lack conceptual frameworks for considering how metabolites vary across space and time in ecological systems. Here, the authors apply (species) community assembly concepts to metabolomics data, offering a way forward in understanding the assembly of metabolite assemblages.
- Robert E. Danczak
- , Rosalie K. Chu
- & James C. Stegen
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying and addressing the prevalence and bias of study designs in the environmental and social sciences
Quantifying and addressing the prevalence and bias of study designs in the environmental and social sciences
Randomised controlled experiments are the gold standard for scientific inference, but environmental and social scientists often rely on different study designs. Here the authors analyse the use of six common study designs in the fields of biodiversity conservation and social intervention, and quantify the biases in their estimates.
- Alec P. Christie
- , David Abecasis
- & William J. Sutherland
-
Article
| Open Access A social engineering model for poverty alleviation
A social engineering model for poverty alleviation
Current inequality and market consumption modelling appears to be subjective. Here the authors combined all three axes of poverty modelling - Engel-Krishnakumar’s microeconomics, Aoki-Chattopadhyay’s mathematical precept and found that multivariate construction is a key component of economic data analysis, implying all modes of income and expenditure need to be considered to arrive at a proper weighted prediction of poverty.
- Amit K. Chattopadhyay
- , T. Krishna Kumar
- & Iain Rice
-
Article
| Open Access Iron mineral dissolution releases iron and associated organic carbon during permafrost thaw
Iron mineral dissolution releases iron and associated organic carbon during permafrost thaw
Iron minerals trap carbon in permafrost, preventing microbial degradation and release to the atmosphere as CO2, but the stability of this carbon as permafrost thaws is unclear. Here the authors use nanoscale analyses to show that thaw conditions stimulate Fe-reducing bacteria that trigger carbon release.
- Monique S. Patzner
- , Carsten W. Mueller
- & Casey Bryce
-
Article
| Open Access Consistent effects of pesticides on community structure and ecosystem function in freshwater systems
Consistent effects of pesticides on community structure and ecosystem function in freshwater systems
The effects of pesticides on individual species could propagate into additional community-wide and ecosystem-level effects. Here the authors use a mesocosm experiment to test how a diverse array of herbicides and insecticides disrupt aquatic community structure and ecosystem function.
- Samantha L. Rumschlag
- , Michael B. Mahon
- & Jason R. Rohr
-
Article
| Open Access Strong hydroclimatic controls on vulnerability to subsurface nitrate contamination across Europe
Strong hydroclimatic controls on vulnerability to subsurface nitrate contamination across Europe
Excess fertilizer use causes subsurface contamination. Here, the authors conduct an assessment of water quality vulnerability across Europe, finding that 75% of agricultural regions are susceptible to nitrate contamination for least one-third of the year, two times more than using standard estimation procedure.
- R. Kumar
- , F. Heße
- & S. Attinger
-
Comment
| Open Access Building resilient Arctic science amid the COVID-19 pandemic
Building resilient Arctic science amid the COVID-19 pandemic
Arctic research faces unprecedented disruptions due to COVID-19. This ‘pause’ gives an opportunity to reflect on the current state and the future of Arctic science and move towards a more resilient, thus equitable, coordinated, safe and locally-embedded Arctic research enterprise. Arctic science has been greatly affected by COVID-19. This comment looks forward to how Arctic science could be conducted in the future.
- Andrey N. Petrov
- , Larry D. Hinzman
- & Alona Yefimenko
-
Review Article
| Open Access Plant-based and cell-based approaches to meat production
Plant-based and cell-based approaches to meat production
Large-scale meat production can have negative impacts on public health, the environment and animal welfare. In this Review, the authors consider plant-based and cell-based approaches to meat production and the challenges they face.
- Natalie R. Rubio
- , Ning Xiang
- & David L. Kaplan
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic symbioses reveal pathways to coral survival through prolonged heatwaves
Dynamic symbioses reveal pathways to coral survival through prolonged heatwaves
Climate change and local anthropogenic stressors threaten the persistence of coral reefs. Here the authors track coral bleaching over the course of a heatwave and find that some colonies recovered from bleaching while high temperatures persisted, but only at sites lacking in other strong anthropogenic stressors.
- Danielle C. Claar
- , Samuel Starko
- & Julia K. Baum
-
Article
| Open Access Extraterrestrial hexamethylenetetramine in meteorites—a precursor of prebiotic chemistry in the inner solar system
Extraterrestrial hexamethylenetetramine in meteorites—a precursor of prebiotic chemistry in the inner solar system
This manuscript tackles the origin of organic molecules in carbonaceous meteorites. Identifying hexamethylenetetramine in three carbonaceous meteorites, the authors propose formation from ammonia and formaldehyde by photochemical and thermal reactions in the interstellar medium, followed by the incorporation into planetary systems.
- Yasuhiro Oba
- , Yoshinori Takano
- & Shogo Tachibana
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic interactions among growing stressors increase risk to an Arctic ecosystem
Synergistic interactions among growing stressors increase risk to an Arctic ecosystem
Multiple co-occurring stressors may affect food webs in ways that are not predictable by studying individual stressors. Here the authors apply a network interaction model to a marine food web in the Arctic, finding that nonlinear interactions between stressors can more than double the risk of population collapse compared to simpler simulations.
- K. R. Arrigo
- , Gert L. van Dijken
- & R. M. Bailey
-
Article
| Open Access Domestication via the commensal pathway in a fish-invertebrate mutualism
Domestication via the commensal pathway in a fish-invertebrate mutualism
It has been hypothesized that domestication can occur through the ‘commensal pathway’ in which the domesticate takes advantage of a niche created as a byproduct by the domesticator. Here, Brooker et al. provide evidence for a commensal domestication process between longfin damselfish and mysid shrimps.
- Rohan M. Brooker
- , Jordan M. Casey
- & William E. Feeney
-
Article
| Open Access Pervasive subduction zone devolatilization recycles CO2 into the forearc
Pervasive subduction zone devolatilization recycles CO2 into the forearc
The fate of subducted CO2 remains debated, with estimates mainly from numerical predictions varying from wholesale decarbonation of the shallow subducting slab to massive deep subduction of CO2. Here, the authors present field-based data and show that ~40% to ~65% of the CO2 in subducting crust is released via metamorphic decarbonation reactions at forearc depths.
- E. M. Stewart
- & Jay J. Ague
-
Article
| Open Access Weak tides during Cryogenian glaciations
Weak tides during Cryogenian glaciations
How and why the ‘Snowball Earth’ occurred during the Cryogenian period is debated. Here, the authors show that the cryogenian ocean hosted diminished tidal amplitudes and associated energy dissipation rates, reaching 10-50% of today’s rates thus perhaps contributing to prolonged glaciations.
- J. A. Mattias Green
- , Hannah S. Davies
- & Christopher Scotese
-
Article
| Open Access Janus electrocatalytic flow-through membrane enables highly selective singlet oxygen production
Janus electrocatalytic flow-through membrane enables highly selective singlet oxygen production
Electrocatalytic processes are promising for automated and scalable synthesis of singlet oxygen, but they are energy- and chemical-intensive. Here the authors present a Janus electrocatalytic membrane that selectively produces singlet oxygen with low energy consumption and free of chemical precursors.
- Yumeng Zhao
- , Meng Sun
- & Menachem Elimelech
-
Article
| Open Access Glacial heterogeneity in Southern Ocean carbon storage abated by fast South Indian deglacial carbon release
Glacial heterogeneity in Southern Ocean carbon storage abated by fast South Indian deglacial carbon release
A Southern Ocean influences on the carbon cycle is considered a key component of deglacial changes. Here, the authors show spatial differences in glacial Southern Ocean carbon storage that dissipated rapidly 14.6 kyr ago, revealing a South Indian Ocean contribution to rapid deglacial atmospheric CO2 increases.
- Julia Gottschalk
- , Elisabeth Michel
- & Samuel L. Jaccard
-
Article
| Open Access Excess forest mortality is consistently linked to drought across Europe
Excess forest mortality is consistently linked to drought across Europe
Droughts pose an increasingly important threat to forests. Here the authors analyse a high-resolution Landsat-based dataset of forest canopy mortality in Europe over 1987–2016 to show that drought is already a major driver of tree mortality.
- Cornelius Senf
- , Allan Buras
- & Rupert Seidl
-
Article
| Open Access The economic costs of planting, preserving, and managing the world’s forests to mitigate climate change
The economic costs of planting, preserving, and managing the world’s forests to mitigate climate change
Forests are critical for stabilizing our climate, but costs of mitigation remain uncertain. Here the authors show the global forest sector could reduce emissions by 6.0 GtCO2 yr−1 in 2055, or roughly 10% of the mitigation needed to limit warming to 1.5 °C by mid-century, at a cost of 393 billion USD yr−1, or $281/tCO2.
- K. G. Austin
- , J. S. Baker
- & A. Bean
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative estimates of average geomagnetic axial dipole dominance in deep geological time
Quantitative estimates of average geomagnetic axial dipole dominance in deep geological time
This study describes how the geomagnetic axial dipole dominance of Earth’s magnetic field remained stable through large parts of the geological time. Since other characteristics of the geomagnetic field have changed substantially on the same timescales, this new observation provides a challenge for future core modeling studies.
- Andrew J. Biggin
- , Richard K. Bono
- & Pavel V. Doubrovine
-
Article
| Open Access Organo–organic and organo–mineral interfaces in soil at the nanometer scale
Organo–organic and organo–mineral interfaces in soil at the nanometer scale
Historically it has been maintained that soil organic carbon (SOC) is stabilized through interactions with mineral interfaces. Here the authors use cryo-electron microscopy and spectroscopy to show that SOC interactions can also occur between organic forms in patchy, disordered structure.
- Angela R. Possinger
- , Michael J. Zachman
- & Johannes Lehmann
-
Article
| Open Access Light-driven formation of manganese oxide by today’s photosystem II supports evolutionarily ancient manganese-oxidizing photosynthesis
Light-driven formation of manganese oxide by today’s photosystem II supports evolutionarily ancient manganese-oxidizing photosynthesis
Photosynthetic formation of manganese (Mn) oxides from dissolved Mn ions was proposed to occur in ancestral photosystems before oxygenic photosynthesis evolved. Here, the authors provide evidence for this hypothesis by showing that photosystem II devoid of the Mn cluster oxidises Mn ions leading to formation of Mn-oxide nanoparticles.
- Petko Chernev
- , Sophie Fischer
- & Holger Dau
-
Comment
| Open Access Simplicity lacks robustness when projecting heat-health outcomes in a changing climate
Simplicity lacks robustness when projecting heat-health outcomes in a changing climate
Extreme heat adversely affects human health, productivity, and well-being, with more frequent and intense heatwaves projected to increase exposures. However, current risk projections oversimplify critical inter-individual factors of human thermoregulation, resulting in unreliable and unrealistic estimates of future adverse health outcomes.
- Jennifer K. Vanos
- , Jane W. Baldwin
- & Kristie L. Ebi
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous moulting by Antarctic krill drives major pulses of carbon export in the north Scotia Sea, Southern Ocean
Continuous moulting by Antarctic krill drives major pulses of carbon export in the north Scotia Sea, Southern Ocean
Antarctic krill are known to be important to the carbon cycle, but the exact contribution is not known. Here the authors show that krill moulting is a major vector of carbon export in the Southern Ocean, together with krill faecal pellets accounting for almost 90% of annual particulate organic carbon flux.
- C. Manno
- , S. Fielding
- & G. A. Tarling
-
Article
| Open Access Large deep-sea zooplankton biomass mirrors primary production in the global ocean
Large deep-sea zooplankton biomass mirrors primary production in the global ocean
Zooplankton biomass in the dark ocean is thought to be low and weakly coupled to epipelagic primary production, but recent evidence suggests otherwise. Here the authors analyse data from the Malaspina Circumnavigation Expedition and published data to estimate bathypelagic zooplankton biomass and assess its relationship to primary production, currently not well accounted for in oceanic C budget.
- S. Hernández-León
- , R. Koppelmann
- & C. M. Duarte
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring the trade-offs between electric heating policy and carbon mitigation in China
Exploring the trade-offs between electric heating policy and carbon mitigation in China
China has enacted Electric Heating Policy to substitute electricity for in-home combustion for rural residential heating. Here the authors show that this shift would greatly increase national carbon emissions by 101.69–162.89 megatons in 2015 while impeding China’s carbon mitigation process in the future.
- Jianxiao Wang
- , Haiwang Zhong
- & Chongqing Kang
-
Article
| Open Access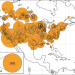 The human impact on North American erosion, sediment transfer, and storage in a geologic context
The human impact on North American erosion, sediment transfer, and storage in a geologic context
Human activities have accelerated soil erosion and landscape change in many areas. Here the authors show how rates of erosion, sediment transfer and alluvial sedimentation have increased by an order of magnitude across North America since European colonization, far exceeding the rates expected of natural processes.
- David B. Kemp
- , Peter M. Sadler
- & Veerle Vanacker
-
Article
| Open Access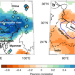 Seven centuries of reconstructed Brahmaputra River discharge demonstrate underestimated high discharge and flood hazard frequency
Seven centuries of reconstructed Brahmaputra River discharge demonstrate underestimated high discharge and flood hazard frequency
This study investigates flood hazards of the Brahmaputra River, Bangladesh. Based on a tree ring reconstruction of seasonal river discharge, climate modelling, and historic documentation of flood events, the authors suggest flood hazard risk is underestimated by ~24–38% in the present day compared to the past 700 years.
- Mukund P. Rao
- , Edward R. Cook
- & Peter J. Webster
-
Article
| Open Access Iceberg melting substantially modifies oceanic heat flux towards a major Greenlandic tidewater glacier
Iceberg melting substantially modifies oceanic heat flux towards a major Greenlandic tidewater glacier
Iceberg melting releases large volumes of freshwater in fjords, yet the impact on oceanic heat delivery to tidewater glaciers is unknown. Here the authors show that iceberg melting invigorates fjord circulation in a large, iceberg-congested fjord, thereby increasing oceanic heat delivery to its tidewater glaciers.
- B. J. Davison
- , T. R. Cowton
- & A. J. Sole
-
Article
| Open Access Global hotspots for the occurrence of compound events
Global hotspots for the occurrence of compound events
Compound climate events such as floods and droughts together can cause severe socio-economic impacts. Here, the authors analyse global hazard pairs from 1980–2014 and find global hotspots for the occurrence of compound events.
- Nina N. Ridder
- , Andy J. Pitman
- & Jakob Zscheischler
-
Article
| Open Access Biomineral armor in leaf-cutter ants
Biomineral armor in leaf-cutter ants
Biomineral armour is known in a number of diverse creatures but has not previously been observed in insects. Here, the authors report on the discovery and characterization of high-magnesium calcite armour which overlays the exoskeletons of leaf-cutter ants.
- Hongjie Li
- , Chang-Yu Sun
- & Cameron R. Currie
-
Article
| Open Access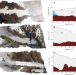 Centennial response of Greenland’s three largest outlet glaciers
Centennial response of Greenland’s three largest outlet glaciers
The Greenland Ice Sheet is the largest land ice contributor to sea level rise and understanding the long-term glacier response to external forcing is key to improved projections. Here the authors show Greenland’s three largest outlet glaciers will likely exceed current worst-case scenario
- Shfaqat A. Khan
- , Anders A. Bjørk
- & Toni Schenk
-
Article
| Open Access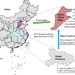 Impacts of irrigated agriculture on food–energy–water–CO2 nexus across metacoupled systems
Impacts of irrigated agriculture on food–energy–water–CO2 nexus across metacoupled systems
Local human activities can lead to cross-border environmental impacts through the food–energy–water–CO2 nexus. Here, the authors report wide variations in environmental impacts of irrigated agriculture across counties within the North China Plain under different environmental and socioeconomic scenarios.
- Zhenci Xu
- , Xiuzhi Chen
- & Yunkai Li
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-year incubation experiments boost confidence in model projections of long-term soil carbon dynamics
Multi-year incubation experiments boost confidence in model projections of long-term soil carbon dynamics
As the climate warms, soil carbon stores will likely be degraded by microbes and released as CO2, but these predictions are based on laboratory incubations that might not reflect real rates. Here the authors optimize model projections using dozens of short- and long-term incubations in forest and grasslands.
- Siyang Jian
- , Jianwei Li
- & Melanie A. Mayes
-
Article
| Open Access Consistent population declines but idiosyncratic range shifts in Alpine orchids under global change
Consistent population declines but idiosyncratic range shifts in Alpine orchids under global change
Many mountain species are threatened by climate change and habitat loss. Here, the authors investigate population declines and range shifts of orchids in an alpine region in NE Italy over 28 years. For most species, population size decreased, while range shifts were idiosyncratic with over half of the species lagging behind climate change.
- Costanza Geppert
- , Giorgio Perazza
- & Lorenzo Marini
-
Comment
| Open Access Using alt text to make science Twitter more accessible for people with visual impairments
Using alt text to make science Twitter more accessible for people with visual impairments
Scientists increasingly post images and photos on social media to share their research activities. However, posting images and photos could potentially exclude people with visual impairments. Here, we outline actions that should be taken to foster accessibility and inclusion in posting scientific images on social media.
- Domenico Chiarella
- , Justin Yarbrough
- & Christopher A.-L. Jackson
-
Article
| Open Access Alaskan carbon-climate feedbacks will be weaker than inferred from short-term experiments
Alaskan carbon-climate feedbacks will be weaker than inferred from short-term experiments
Warming in the high latitudes is expected to stimulate soil organic matter decomposition which leads to enhanced carbon emissions. Here, the authors show that short-term experiments do not capture the complexity of vegetation dynamics in the Arctic and might thus not provide a full picture of long term processes.
- Nicholas J. Bouskill
- , William J. Riley
- & Robert F. Grant

 Exposure to pesticides in utero impacts the fetal immune system and response to vaccination in infancy
Exposure to pesticides in utero impacts the fetal immune system and response to vaccination in infancy